本文主要是介绍Android自定义View之如期相遇的百分比进度条RatioProgress,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
- 需求
- 简述
- 实际应用效果图
- Demo效果图
- 分析
- 自定义View的基本步骤
- 自定义View属性
- RatioProgress分析
- 布局以及代码中的使用
- 布局文件
- 实际java代码中的控制
- 其它
- Demo下载
- 参考链接
需求
简述:
当进入比赛详情页面时,根据点赞数按比例分割整个屏幕宽度,这个过程以动态进度条的形式显示
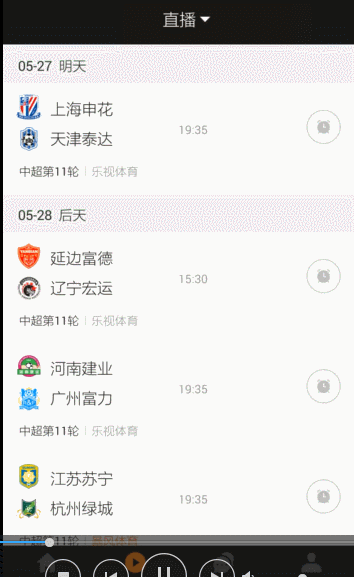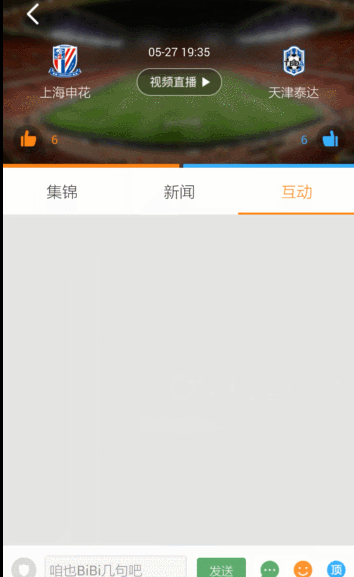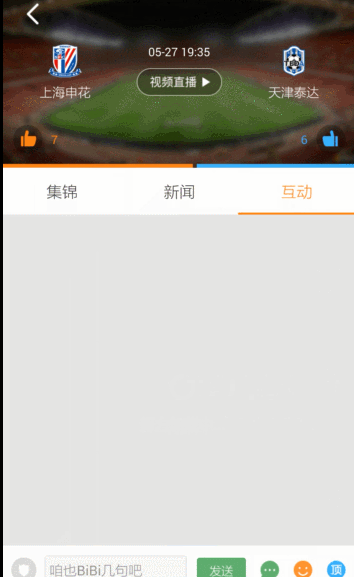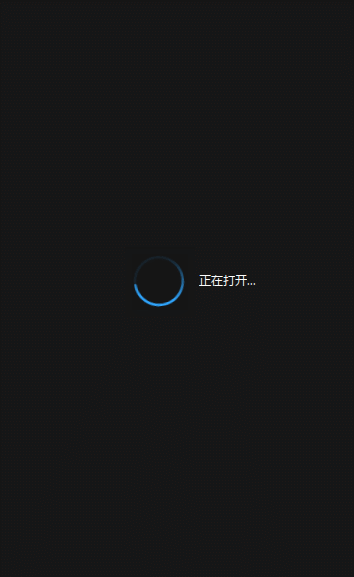
实际应用效果图:
Demo效果图:
分析
自定义View的基本步骤:
- 自定义View的属性
- 在View的构造方法中获得我们自定义的属性
- 重写onMesure(非必须,大部分情况下需要)
- 重写onDraw
自定义View属性:
在res/values/ 下建立一个attrs.xml ,在里面定义我们的属性和声明我们的整个样式,format是指该属性的取值类型
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources><declare-styleable name="RatioProgress"><attr name="direction" format="string" /><attr name="progressColor" format="color" /></declare-styleable></resources>这里,我根据需求定义了两个属性,分别为direction和progressColor
- direction表示进度条的绘制方向,有两个值,分别为“left”和“right”
“left”表示从左到右进行显示,“right”表示从右向左进行显示
- progressColor表示进度条的显示背景颜色
RatioProgress分析:
- 通过rectBgBounds 绘制背景矩形,进行占位,背景设置为透明的
通过rectProgressBounds来绘制进度条,背景颜色就是通过如下自定义属性进行设置
sus:progressColor="@color/CommonTextSelect"- bgPaint和progressPaint分别为绘制背景和进度条的画笔
关键步骤之重写onDraw方法
@Overrideprotected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {super.onDraw(canvas);canvas.drawRect(rectBgBounds, bgPaint);if (TextUtils.equals(direction, "left")) {rectProgressBounds = new RectF(0, 0, progress, layout_height);} else if (TextUtils.equals(direction, "right")) {rectProgressBounds = new RectF(getWidth() - progress, 0, getWidth(), layout_height);}else{rectProgressBounds = new RectF(0, 0, progress, layout_height);}canvas.drawRect(rectProgressBounds, progressPaint);}
这里根据direction属性来设置rectProgressBounds 的坐标位置
我在 setupBounds()中通过start方法开启一个线程
final Runnable r = new Runnable() {public void run() {running = true;Log.e("thread", "progress="+progress);Log.e("thread", "getWidth()="+getWidth());while (progress < getWidth()) {incrementProgress();//progress++;try {Thread.sleep(sleepDelay);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}running = false;}};public void start(){if (!running) {progress = 0;Thread s = new Thread(r);s.start();}}
- 并通过incrementProgress方法递增progress,然后再通过handler发消息不断进行绘制
/*** Increment the progress by 1 (of 100)*/public void incrementProgress() {isProgress = true;progress++;/** if (progress > 200) progress = 100;*/spinHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);}RatioProgress 完整代码:
public class RatioProgress extends View {// Sizes (with defaults)private int layout_height = 0;private int layout_width = 0;// Colors (with defaults)private int bgColor = Color.TRANSPARENT;//private int progressColor = 0xFF339933;// Paintsprivate Paint progressPaint = new Paint();private Paint bgPaint = new Paint();// Rectanglesprivate RectF rectBgBounds = new RectF();private RectF rectProgressBounds = new RectF();int progress = 0;boolean isProgress;private String direction;/*** progress的颜色*/private int progressColor;boolean running;int sleepDelay;public int getSleepDelay() {return sleepDelay;}public void setSleepDelay(int sleepDelay) {this.sleepDelay = sleepDelay;}private Handler spinHandler = new Handler() {/*** This is the code that will increment the progress variable and so* spin the wheel*/@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {invalidate();}};/*** @param context*/public RatioProgress(Context context) {this(context, null);}/*** @param context* @param attrs*/public RatioProgress(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {this(context, attrs, 0);}/*** @param context* @param attrs* @param defStyleAttr*/public RatioProgress(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);/*** 获得我们所定义的自定义样式属性*/TypedArray a = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.RatioProgress, defStyleAttr, 0);int n = a.getIndexCount();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){int attr = a.getIndex(i);switch (attr){case R.styleable.RatioProgress_direction:direction = a.getString(attr);Log.e("direction-----------------", direction);break;case R.styleable.RatioProgress_progressColor:progressColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.TRANSPARENT);break;}}a.recycle();}@Overrideprotected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);// Share the dimensionslayout_width = w;Log.i("layout_width", layout_width + "");layout_height = h;Log.i("layout_height", layout_height + "");setupBounds();setupPaints();invalidate();}private void setupPaints() {bgPaint.setColor(bgColor);bgPaint.setAntiAlias(true);bgPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);progressPaint.setColor(progressColor);progressPaint.setAntiAlias(true);progressPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);}private void setupBounds() {int width = getWidth(); // this.getLayoutParams().width;Log.i("width", width + "");int height = getHeight(); // this.getLayoutParams().height;Log.i("height", height + "");rectBgBounds = new RectF(0, 0, width, height);start();}@Overrideprotected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {super.onDraw(canvas);canvas.drawRect(rectBgBounds, bgPaint);Log.i("progress", progress + "");if (TextUtils.equals(direction, "left")) {rectProgressBounds = new RectF(0, 0, progress, layout_height);} else if (TextUtils.equals(direction, "right")) {rectProgressBounds = new RectF(getWidth() - progress, 0, getWidth(), layout_height);}else{rectProgressBounds = new RectF(0, 0, progress, layout_height);}canvas.drawRect(rectProgressBounds, progressPaint);}/*** Increment the progress by 1 (of 100)*/public void incrementProgress() {isProgress = true;progress++;/** if (progress > 200) progress = 100;*/spinHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);}/*** Increment the progress by 1 (of 100)*/public void unIncrementProgress() {isProgress = true;progress--;/** if (progress < 1) progress = 100;*/spinHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);}/*** Set the progress to a specific value*/public void setProgress(int i) {progress = i;spinHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);}final Runnable r = new Runnable() {public void run() {running = true;Log.e("thread", "progress="+progress);Log.e("thread", "getWidth()="+getWidth());while (progress < getWidth()) {incrementProgress();//progress++;try {Thread.sleep(sleepDelay);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}running = false;}};public void start(){if (!running) {progress = 0;Thread s = new Thread(r);s.start();}}
}
布局以及代码中的使用:
布局文件
这里在LinearLayout 中定义了两个RatioProgress
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"xmlns:sus="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.soulrelay.ratioprogress"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="horizontal" ><com.soulrelay.ratioprogress.RatioProgress
android:id="@+id/left_ratio_progress"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="4dp"android:layout_marginTop="100dp"sus:direction="left"sus:progressColor="@color/CommonTextSelect" /><com.soulrelay.ratioprogress.RatioProgress
android:id="@+id/right_ratio_progress"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="4dp"android:layout_marginLeft="4dp"android:layout_marginTop="100dp"sus:direction="right" sus:progressColor="@color/CommonSelect"/></LinearLayout>实际java代码中的控制
这里主要是设置leftRatioProgress和rightRatioProgress的宽度,以及通过设置View中的线程休眠时间来控制进度条可以同时相遇
public class MainActivity extends Activity {RatioProgress leftRatioProgress;RatioProgress rightRatioProgress;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);WindowManager manager = ((WindowManager) this.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE));DisplayMetrics dm = new DisplayMetrics();manager.getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(dm);final int w = dm.widthPixels;leftRatioProgress = (RatioProgress) findViewById(R.id.left_ratio_progress);LayoutParams lp = leftRatioProgress.getLayoutParams();lp.width = w/3;leftRatioProgress.setLayoutParams(lp);rightRatioProgress = (RatioProgress) findViewById(R.id.right_ratio_progress);LayoutParams lp1 = rightRatioProgress.getLayoutParams();lp1.width = w*2/3;rightRatioProgress.setLayoutParams(lp1);leftRatioProgress.setSleepDelay(6);rightRatioProgress.setSleepDelay(3);}
}实际代码中我是根据用户的点赞数来分割屏幕宽度,设置View中的休眠时间
以下代码仅供参考:
/*** 进度条形式显示赞数的比例** @param matchInfo* @author sushuai*/private void initRatioProgress(MatchInfo matchInfo) {int width = SystemUtil.getScreenDisplayMinWidth(context);int leftWeight = matchInfo.getTeam1().getLikes();int rightWeight = matchInfo.getTeam2().getLikes();int leftWidth = 0, rightWidth = 0;if (leftWeight == 0 && rightWeight == 0) {leftWidth = rightWidth = width / 2;} else if (leftWeight == 0) {rightWidth = width;} else if (rightWeight == 0) {leftWidth = width;} else {leftWidth = width * leftWeight / (leftWeight + rightWeight);rightWidth = width * rightWeight / (leftWeight + rightWeight);}if (leftRatioProgress != null) {LayoutParams lp = leftRatioProgress.getLayoutParams();lp.width = leftWidth;leftRatioProgress.setLayoutParams(lp);if (leftWidth >= rightWidth) {leftRatioProgress.setSleepDelay(1);} else if (leftWidth != 0) {leftRatioProgress.setSleepDelay(rightWidth / leftWidth);}}if (rightRatioProgress != null) {LayoutParams lp = rightRatioProgress.getLayoutParams();lp.width = rightWidth;rightRatioProgress.setLayoutParams(lp);if (leftWidth >= rightWidth && rightWidth != 0) {rightRatioProgress.setSleepDelay(leftWidth / rightWidth);} else {rightRatioProgress.setSleepDelay(1);}}}其它
Demo下载:
传送门
参考链接:
1、http://blog.csdn.net/wangjinyu501/article/details/38298737
1、http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/24252901/
这篇关于Android自定义View之如期相遇的百分比进度条RatioProgress的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!