本文主要是介绍管道铺设系统-最小生成树(Prim、Kruskal算法实现),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
管道铺设系统-最小生成树(Prim、Kruskal算法实现)
问题
开发一个管线铺设辅助系统,以我校东校区为例,在东校区大学生活动中心、学生公寓、学生食堂、21层主楼、第一、二、三、四教学楼、原图书馆、机械馆、原信息馆、人文馆、体育馆之间铺设输水管道,设计算法并实现使铺设的输水管道距离最短。系统要求具备从文本读取数据、显示最佳铺设方案,以及绘制最佳方案的简单示意图等功能。
功能需求
1)将管线经过的建筑物以及建筑物之间的距离,抽象成无向图,并以矩阵的形式表示,并保存在文本中,系统通过读取文本的方式,获取该矩阵;
2)从Prim算法和Kruskal算法中至少选择一种实现管线铺设的最优方案,系统可以最优方案的生成过程,并且可以文本的形式输出;
3)在系统上可以生成最优方案的简易图。
功能实现
Prim算法
(1)基本思想:
设N=(V,E)是最小连通网,TE是N上最小生成树中边的集合,初始令U={u0}(u0∈V),TE={}。
在所有u∈U,v∈V-U的边(u,v)∈E中,找一条代价最小的边(u0,v0),将边(u0,v0)并入集合TE,同时v0并入U。
重复上述操作,直到U=V为止,则T=(V,TE)为N的最小生成树。
(2)代码展示:
①定义顶点数据类型。由于我们需要绘制出最小生成树的动态过程,所以需要记录顶点的坐标。顶点数据类型为我们定义的结构体类型,它包括三个信息,即x坐标,y坐标和顶点名称。
//点
typedef struct
{char data;int x;int y;
}VerTex;
②定义图的信息。图的信息包括点集、邻接矩阵、点的个数和边的个数。
typedef struct
{VerTex vexs[MVNum];int arcs[MVNum][MVNum];int vexnum, arcnum;
}AMGraph;
③定义候选最短边集数组closeEdge[n],数组元素包括 adjvex 和 lowcost两个域,分别表示候选最短边的邻接点和权值。
// 定义记录从顶点集U到V-U代价最小的边的数组
typedef struct {char adjvex; // 候选最短边邻接点 int lowcost; // 候选最短边权值
}arr;
arr closedge[MVNum];
(3)运行结果
①选择Prim起点,生成最小生成树
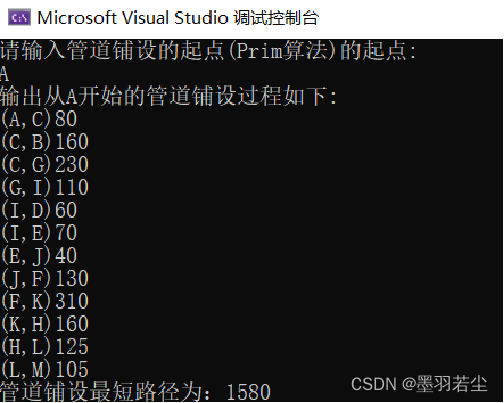
②动态过程展示
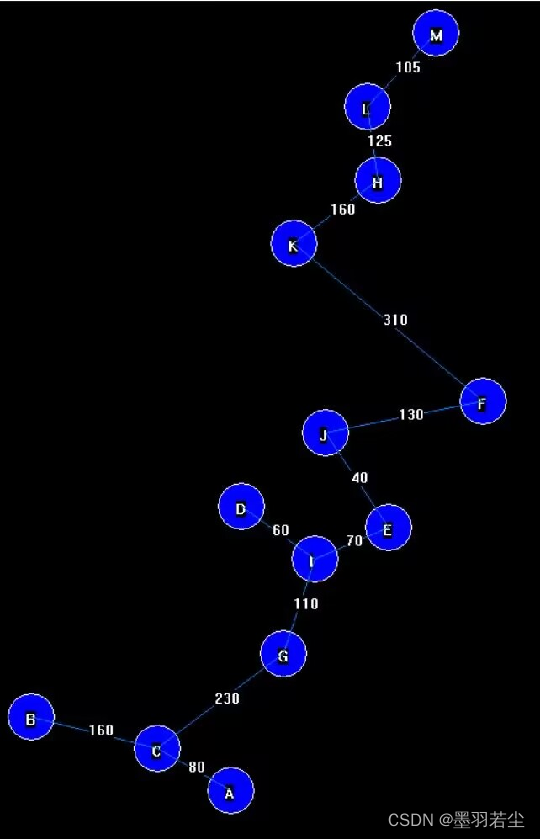
③保存在文本文档中

Kruska算法
(1)运行结果
①依次按下回车键,构建最小生成树
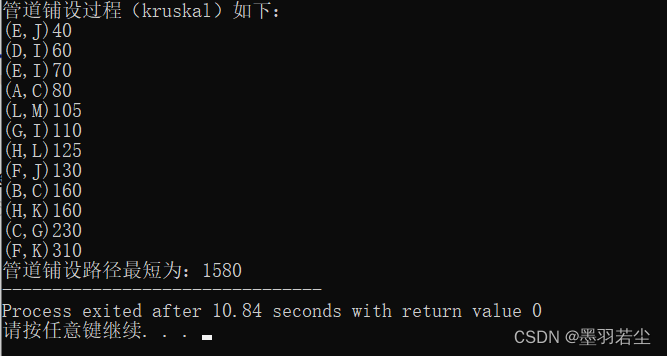
②动态过程展示
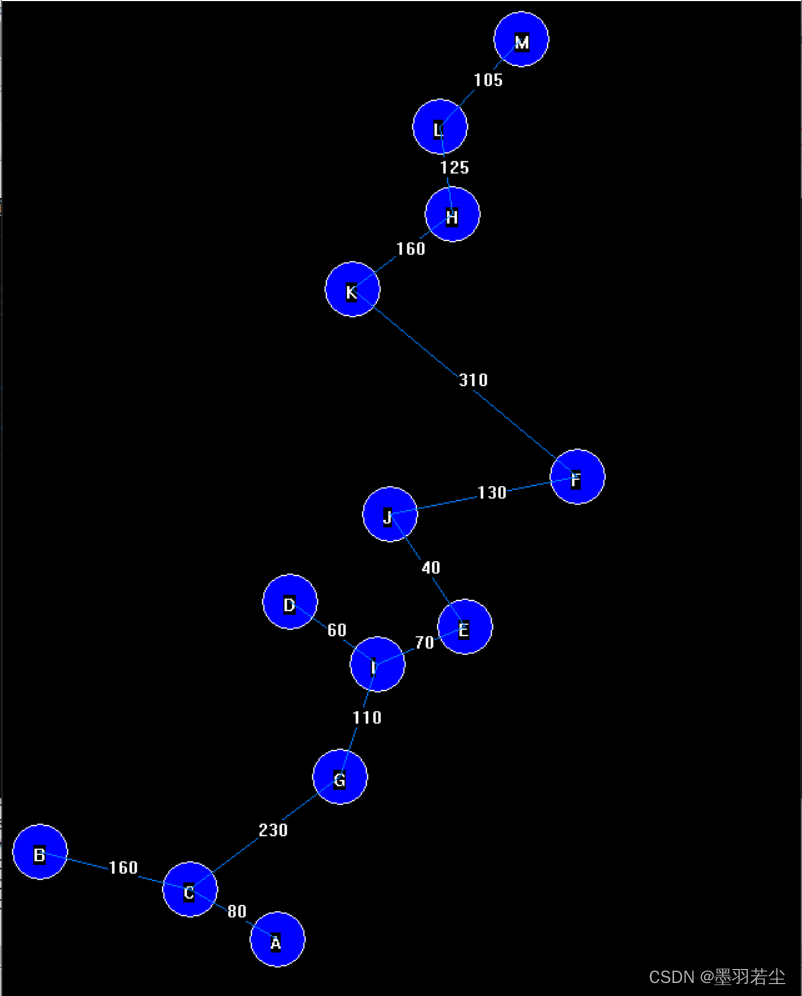
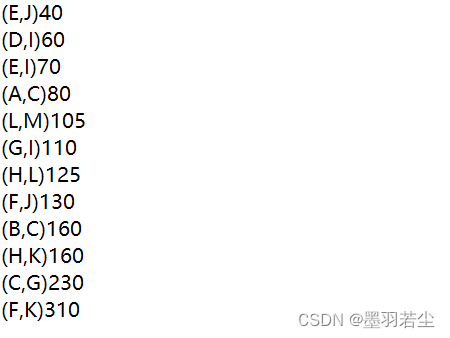
③保存在文本文档中
参考资料
[1] https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1yp4y1Q74o?share_source=copy_web
[2] http://t.csdn.cn/4jtnv
[3] http://t.csdn.cn/qXRBx
[4]https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/b2c186c8c86d7c856ef6fffd.html
附:
读取的文本:
13 78
A 220 750
B 30 680
C 150 710
D 230 480
E 370 500
F 460 380
G 270 620
H 360 170
I 300 530
J 310 410
K 280 230
L 350 100
M 415 30
0 255 80 380 410 550 260 865 350 440 775 980 1100
255 0 160 370 450 590 310 840 380 470 730 930 1000
80 160 0 330 380 530 230 820 320 410 720 920 1000
380 370 330 0 100 230 130 490 60 110 390 580 680
410 450 380 100 0 150 150 470 70 40 380 560 650
550 590 530 230 150 0 300 350 220 130 310 450 530
260 310 230 130 150 300 0 610 110 185 550 715 810
865 840 820 490 470 350 610 0 500 420 160 125 210
350 380 320 60 70 220 110 500 0 80 440 600 705
440 470 410 110 40 130 185 420 80 0 370 525 625
775 730 720 390 380 310 550 160 440 370 0 190 300
980 930 920 580 560 450 715 125 600 525 190 0 105
1100 1000 1000 680 650 530 810 210 705 625 300 105 0 程序源码:
(1)Prim
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<wchar.h>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
#define MaxInt 32767
#define MVNum 100
int sum = 0;//点
typedef struct
{char data;int x;int y;
}VerTex;typedef struct
{VerTex vexs[MVNum];int arcs[MVNum][MVNum];int vexnum, arcnum;
}AMGraph;// 定义记录从顶点集U到V-U代价最小的边的数组
typedef struct {char adjvex; // 候选最短边邻接点 int lowcost; // 候选最短边权值
}arr;
arr closedge[MVNum];//确定顶点在G中的位置
int LocateVex(AMGraph G, char v)
{for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i){if (G.vexs[i].data == v){return i;}}return -1;
}
//采用邻接矩阵表示法,创建无向网G
//int CreateUDN(AMGraph& G)
//{
// int w;
// char v1, v2;
// //for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
// // for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum; ++j)
// // {
// // G.arcs[i][j] = MaxInt;
// // }
// //ReadFromTxt(G);
// //for (int k = 0; k < G.arcnum; ++k)
// //{
// // int i, j;
// // cout << "请输入第" << k + 1 << "条边依附的顶点及权值:";
// // cin >> v1 >> v2 >> w;
// // i = LocateVex(G, v1);
// // j = LocateVex(G, v2);
// // G.arcs[i][j] = w;
// // G.arcs[j][i] = G.arcs[i][j];
// //}
// return 1;
//}//从txt文件中读取邻接矩阵
void ReadFromTxt(AMGraph& G) {ifstream fin;fin.open("E:\\distance.txt", ios::in);if (!fin.is_open()) {cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;exit(1);}while (!fin.eof()) {fin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum;for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {fin >> G.vexs[i].data >> G.vexs[i].x >> G.vexs[i].y;}for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++) {fin >> G.arcs[i][j];}}fin.close();}
}void SaveToTxt(char A, int B, char p) {ofstream fout("result_prim.txt",ofstream::app);if (fout.is_open()) {fout << "(" << A << "," << p << ")" << B << endl;}fout.close();
}void MinSpanTree_PRIM(AMGraph G, char u) {// 用普里姆算法从第u个顶点出发构造网G的最小生成树T,输出T的各条边int k;k = LocateVex(G, u);//画点 setfillcolor(RGB(0, 0, 255));int radio = 22; // 圆的半径 fillcircle(G.vexs[k].x, G.vexs[k].y, radio);outtextxy(G.vexs[k].x - 5, G.vexs[k].y - 5, G.vexs[k].data);_getch();// 初始化辅助数组for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum; ++j){closedge[j].lowcost = G.arcs[k][j];closedge[j].adjvex = u;}closedge[k].lowcost = 0; //初始,U={u}int x1, x2, y1, y2;//画点线 int m;for (int i = 1; i < G.vexnum; ++i){// 寻找最短边的邻接点int min = MaxInt;for (int n = 0; n < G.vexnum; ++n){if (closedge[n].lowcost < min && closedge[n].lowcost != 0){min = closedge[n].lowcost;k = n;}}//画点 setfillcolor(RGB(0, 0, 255));int radio = 22; // 圆的半径 fillcircle(G.vexs[k].x, G.vexs[k].y, radio);outtextxy(G.vexs[k].x - 5, G.vexs[k].y - 5, G.vexs[k].data);_getch();char p;p = G.vexs[k].data;// 输出最小生成树路径cout << "(" << closedge[k].adjvex << "," << p << ")" << closedge[k].lowcost << endl;//char A = closedge[k].adjvex;//int B = closedge[k].lowcost;SaveToTxt(closedge[k].adjvex, closedge[k].lowcost, p);sum = sum + closedge[k].lowcost;m = LocateVex(G, closedge[k].adjvex);x1 = G.vexs[m].x;y1 = G.vexs[m].y;x2 = G.vexs[k].x;y2 = G.vexs[k].y;// cout << p << endl;char str[100];line(x1, y1, x2, y2);sprintf(str, "%d", closedge[k].lowcost); //转换成字符outtextxy((x1 + x2 - 10) / 2, (y1 + y2 - 20) / 2, str); //放权值 _getch();//第k顶点并入U集closedge[k].lowcost = 0;// 调整数组closedgefor (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum; ++j){if (G.arcs[k][j] < closedge[j].lowcost){closedge[j].lowcost = G.arcs[k][j];closedge[j].adjvex = p;}}}
}int main()
{initgraph(757, 881, SHOWCONSOLE);int i, j;char p;AMGraph G;ReadFromTxt(G);
// CreateUDN(G);
// for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {
// cout << G.vexs[i].data << endl;
// }
// for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i)
// {
// for (j = 0; j < G.vexnum; ++j)
// {
// if (G.arcs[i][j] != MaxInt)
// cout << G.arcs[i][j] << "\t";
// else
// cout << "0" << "\t";
// }
// cout << endl;
// }
// cout << endl;cout << "请输入管道铺设的起点(Prim算法)的起点:" << endl;cin >> p;cout << "输出从" << p << "开始的管道铺设过程如下:" << endl;MinSpanTree_PRIM(G, p);cout<<"管道铺设最短路径为:"<<sum; system("pause");closegraph();return 0;
}
(2) Kruskal
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<graphics.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<wchar.h>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
#define MVNum 100
int sum = 0; //记录最小生成树总权值
//边
typedef struct edge_set {char vex1; //边的其中一个顶点char vex2; //边的另一个顶点int weight; //边的权重
}Edge;//点
typedef struct
{char data;int x;int y;
}VerTex;typedef struct
{VerTex vexs[MVNum];Edge edge[MVNum];int arcs[MVNum][MVNum];int vexnum, arcnum;
}Graph;//确定顶点在G中的位置
int locate_vex(Graph G, char v)
{for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i){if (G.vexs[i].data == v){return i;}}return -1;
}//从txt文件中读取邻接矩阵
void ReadFromTxt(Graph& G) {ifstream fin;fin.open("E:\\distance.txt", ios::in);if (!fin.is_open()) {cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;exit(1);}int k=0;while (!fin.eof()) {fin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum;for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {fin >> G.vexs[i].data >> G.vexs[i].x >> G.vexs[i].y;}//for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++) {// for (int j = i+1; j < 13; j++) {// char a = G.vexs[i].data;// char b = G.vexs[j].data;// G.edge[k].vex1 = a;// G.edge[k].vex2 = b;// fin >> G.edge[k].weight;// cout<< G.edge[k].weight<<endl;// k++;// }//}for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < G.vexnum; j++) {fin >> G.arcs[i][j];}}fin.close();}
}void SaveToTxt(char A, int B, char p) {ofstream fout("result_kruskal.txt", ofstream::app);if (fout.is_open()) {fout << "(" << A << "," << p << ")" << B << endl;}fout.close();
}//创建一个图,图的信息使用边集来存储
int create_graph(Graph& G) {//cout << "请输入图的总顶点数及边数:" << endl;//cin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum;//cout << "请依次输入各顶点的信息:" << endl;int k = 0;for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {for (int j = i+1; j < G.vexnum; j++) {char a = G.vexs[i].data;char b = G.vexs[j].data;G.edge[k].vex1 = a;G.edge[k].vex2 = b;G.edge[k].weight = G.arcs[i][j];k++;}}// 画点 setfillcolor(RGB(0, 0, 255));int radio = 22;for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; ++i){//cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "个顶点:";//cin >> G.vexs[i].data;//cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "个顶点的x坐标:";//cin >> G.vexs[i].x;//cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "个顶点的y坐标:";//cin >> G.vexs[i].y;fillcircle(G.vexs[i].x, G.vexs[i].y, radio);outtextxy(G.vexs[i].x - 5, G.vexs[i].y - 5, G.vexs[i].data);}//cout << "请输入各条边依附的顶点及权值:" << endl;//for (int k = 0; k < G.arcnum; ++k)//{// int i, j;// cout << "请输入第" << k + 1 << "条边依附的顶点及权值:";// cin >> G.edge[k].vex1 >> G.edge[k].vex2 >> G.edge[k].weight;//}return 1;
}//排序,按权重从小到大顺序排
int cmp(const void* a, const void* b) {return ((Edge*)a)->weight - ((Edge*)b)->weight;
}//找树的根
int find_root(int* parent, int t) {while (parent[t] > -1){t = parent[t]; //求顶点t上的双亲直到根结点 }return t;
}//kruskal算法实现
void kruskal(Graph G) {//将边按从小到大顺序排序qsort(G.edge, G.arcnum, sizeof(Edge), cmp);int parent[MVNum]; //判断新添加的线是否能和原来的图构成回路 // 初始化parent数组 for (int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {parent[i] = -1;}int num = 0, vex1 = -1, vex2 = -1;int p, q;int x1, y1, x2, y2;setlinecolor(RGB(0, 125, 255));for (int i = 0; i < G.arcnum; i++){// cout << G.edge[i].weight << endl;p = locate_vex(G, G.edge[i].vex1);q = locate_vex(G, G.edge[i].vex2);vex1 = find_root(parent, p);vex2 = find_root(parent, q);//cout << vex1 << endl;//cout << vex2 << endl;if (vex1 != vex2) //说明没在同一个连通分量中 {_getch();cout << "(" << G.edge[i].vex1 << "," << G.edge[i].vex2 << ")" << G.edge[i].weight << endl;SaveToTxt(G.edge[i].vex1,G.edge[i].weight,G.edge[i].vex2);sum = sum + G.edge[i].weight;parent[vex2] = vex1;//合并生成树 // 连线 x1 = G.vexs[p].x;y1 = G.vexs[p].y;x2 = G.vexs[q].x;y2 = G.vexs[q].y;char str[100];line(x1, y1, x2, y2);sprintf(str, "%d", G.edge[i].weight); //转换成字符outtextxy((x1 + x2 - 10) / 2, (y1 + y2 - 20) / 2, str); //放权值 num++;}if (num == G.vexnum - 1){Sleep(10000);return;}}
}int main() {initgraph(640, 1280, SHOWCONSOLE);Graph G;ReadFromTxt(G);create_graph(G);//for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++) {// for (int j = 0; j < 13; j++) {// cout << G.arcs[i][j];// cout << " ";// }// cout << endl;//}
// for (int i = 0; i < G.arcnum; i++) {
// cout <<G.edge[i].vex1 << G.edge[i].vex2 << G.edge[i].weight<< endl;
// }cout<<"管道铺设过程(kruskal)如下:"<<endl;kruskal(G);cout<<"管道铺设路径最短为:"<<sum;closegraph();return 0;
}这篇关于管道铺设系统-最小生成树(Prim、Kruskal算法实现)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





