本文主要是介绍0基础学习PyFlink——Map和Reduce函数处理单词统计,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在很多讲解大数据的案例中,往往都会以一个单词统计例子来抛砖引玉。本文也不免俗,例子来源于PyFlink的《Table API Tutorial》,我们会通过几种方式统计不同的单词出现的个数,从而达到循序渐进的学习效果。
常规方法
# input.py
word_count_data = ["To be, or not to be,--that is the question:--","Whether 'tis nobler in the mind to suffer","The slings and arrows of outrageous fortune","Or to take arms against a sea of troubles,","And by opposing end them?--To die,--to sleep,--","No more; and by a sleep to say we end","The heartache, and the thousand natural shocks","That flesh is heir to,--'tis a consummation","Devoutly to be wish'd. To die,--to sleep;--","To sleep! perchance to dream:--ay, there's the rub;","For in that sleep of death what dreams may come,","When we have shuffled off this mortal coil,","Must give us pause: there's the respect","That makes calamity of so long life;","For who would bear the whips and scorns of time,","The oppressor's wrong, the proud man's contumely,","The pangs of despis'd love, the law's delay,","The insolence of office, and the spurns","That patient merit of the unworthy takes,","When he himself might his quietus make","With a bare bodkin? who would these fardels bear,","To grunt and sweat under a weary life,","But that the dread of something after death,--","The undiscover'd country, from whose bourn","No traveller returns,--puzzles the will,","And makes us rather bear those ills we have","Than fly to others that we know not of?","Thus conscience does make cowards of us all;","And thus the native hue of resolution","Is sicklied o'er with the pale cast of thought;","And enterprises of great pith and moment,","With this regard, their currents turn awry,","And lose the name of action.--Soft you now!","The fair Ophelia!--Nymph, in thy orisons","Be all my sins remember'd."]
一般的思路我们是:
- 遍历这个list将每行用空格切割成独立单词,存储到一个新的list中
- 遍历步骤1产生的新的list,使用map记录统计结果,key是单词,value是次数
# common.py
from input import word_count_datawordCount = dict()
for line in word_count_data:wordsOneline = line.split()for word in wordsOneline:wordCount.update({word:wordCount.get(word,0)+1})print(wordCount)
{‘To’: 4, ‘be,’: 1, ‘or’: 1, ‘not’: 2, ‘to’: 7, ‘be,–that’: 1, ‘is’: 2, ‘the’: 15, ‘question:–’: 1, ‘Whether’: 1, “'tis”: 1, ‘nobler’: 1, ‘in’: 3, ‘mind’: 1, ‘suffer’: 1, ‘The’: 7, ‘slings’: 1, ‘and’: 7, ‘arrows’: 1, ‘of’: 14, ‘outrageous’: 1, ‘fortune’: 1, ‘Or’: 1, ‘take’: 1, ‘arms’: 1, ‘against’: 1, ‘a’: 5, ‘sea’: 1, ‘troubles,’: 1, ‘And’: 5, ‘by’: 2, ‘opposing’: 1, ‘end’: 2, ‘them?–To’: 1, ‘die,–to’: 2, ‘sleep,–’: 1, ‘No’: 2, ‘more;’: 1, ‘sleep’: 2, ‘say’: 1, ‘we’: 4, ‘heartache,’: 1, ‘thousand’: 1, ‘natural’: 1, ‘shocks’: 1, ‘That’: 3, ‘flesh’: 1, ‘heir’: 1, “to,–'tis”: 1, ‘consummation’: 1, ‘Devoutly’: 1, ‘be’: 1, “wish’d.”: 1, ‘sleep;–’: 1, ‘sleep!’: 1, ‘perchance’: 1, ‘dream:–ay,’: 1, “there’s”: 2, ‘rub;’: 1, ‘For’: 2, ‘that’: 3, ‘death’: 1, ‘what’: 1, ‘dreams’: 1, ‘may’: 1, ‘come,’: 1, ‘When’: 2, ‘have’: 2, ‘shuffled’: 1, ‘off’: 1, ‘this’: 2, ‘mortal’: 1, ‘coil,’: 1, ‘Must’: 1, ‘give’: 1, ‘us’: 3, ‘pause:’: 1, ‘respect’: 1, ‘makes’: 2, ‘calamity’: 1, ‘so’: 1, ‘long’: 1, ‘life;’: 1, ‘who’: 2, ‘would’: 2, ‘bear’: 2, ‘whips’: 1, ‘scorns’: 1, ‘time,’: 1, “oppressor’s”: 1, ‘wrong,’: 1, ‘proud’: 1, “man’s”: 1, ‘contumely,’: 1, ‘pangs’: 1, “despis’d”: 1, ‘love,’: 1, “law’s”: 1, ‘delay,’: 1, ‘insolence’: 1, ‘office,’: 1, ‘spurns’: 1, ‘patient’: 1, ‘merit’: 1, ‘unworthy’: 1, ‘takes,’: 1, ‘he’: 1, ‘himself’: 1, ‘might’: 1, ‘his’: 1, ‘quietus’: 1, ‘make’: 2, ‘With’: 2, ‘bare’: 1, ‘bodkin?’: 1, ‘these’: 1, ‘fardels’: 1, ‘bear,’: 1, ‘grunt’: 1, ‘sweat’: 1, ‘under’: 1, ‘weary’: 1, ‘life,’: 1, ‘But’: 1, ‘dread’: 1, ‘something’: 1, ‘after’: 1, ‘death,–’: 1, “undiscover’d”: 1, ‘country,’: 1, ‘from’: 1, ‘whose’: 1, ‘bourn’: 1, ‘traveller’: 1, ‘returns,–puzzles’: 1, ‘will,’: 1, ‘rather’: 1, ‘those’: 1, ‘ills’: 1, ‘Than’: 1, ‘fly’: 1, ‘others’: 1, ‘know’: 1, ‘of?’: 1, ‘Thus’: 1, ‘conscience’: 1, ‘does’: 1, ‘cowards’: 1, ‘all;’: 1, ‘thus’: 1, ‘native’: 1, ‘hue’: 1, ‘resolution’: 1, ‘Is’: 1, ‘sicklied’: 1, “o’er”: 1, ‘with’: 1, ‘pale’: 1, ‘cast’: 1, ‘thought;’: 1, ‘enterprises’: 1, ‘great’: 1, ‘pith’: 1, ‘moment,’: 1, ‘regard,’: 1, ‘their’: 1, ‘currents’: 1, ‘turn’: 1, ‘awry,’: 1, ‘lose’: 1, ‘name’: 1, ‘action.–Soft’: 1, ‘you’: 1, ‘now!’: 1, ‘fair’: 1, ‘Ophelia!–Nymph,’: 1, ‘thy’: 1, ‘orisons’: 1, ‘Be’: 1, ‘all’: 1, ‘my’: 1, ‘sins’: 1, “remember’d.”: 1}
上述的代码在一个双层for循环中简单粗暴的解决了问题。如果不给用双层for循环,则需要将其改成两个单层for循环
# common_1.py
from input import word_count_datawords = []
for line in word_count_data:words.extend(line.split())wordCount = {}
for word in words:wordCount.update({word:wordCount.get(word,0)+1})print(wordCount)
如果不给显示的使用for循环,有什么办法呢?这儿我们就引入map和reduce。
Map
map(func, *iterables) --> map object
Make an iterator that computes the function using arguments from each of the iterables. Stops when the shortest iterable is exhausted.
简单来说,map会对传入的迭代器(第二个参数)执行处理方法(第一个参数),并将该方法的返回结果放入一个结构中,最后我们可以使用map返回的迭代器逐个访问计算结果。
举个例子:
import sys
source=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
iter=map(lambda x: x+1, source)
while True:try:print(next(iter))except StopIteration:sys.exit()
2
3
4
5
6
7
上例中我们给map的处理函数设置为一个匿名函数,它会返回每个遍历数字的自增1的值。
对应到我们单词统计的例子,我们可以使用下面代码,遍历word_count_data每行,然后将其用空格切分出list并返回。这样wordsLists就是“一个元素是一行单词list”的list的迭代器。
from input import word_count_data
wordsLists=map(lambda line: line.split(), word_count_data)
[
[‘To’, ‘be,’, ‘or’, ‘not’, ‘to’, ‘be,–that’, ‘is’, ‘the’, ‘question:–’],
[‘Whether’, “'tis”, ‘nobler’, ‘in’, ‘the’, ‘mind’, ‘to’, ‘suffer’],
……
]
Reduce
functools.reduce(function, iterable[, initializer])
Apply function of two arguments cumulatively to the items of iterable, from left to right, so as to reduce the iterable to a single value. For example, reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) calculates ((((1+2)+3)+4)+5). The left argument, x, is the accumulated value and the right argument, y, is the update value from the iterable. If the optional initializer is present, it is placed before the items of the iterable in the calculation, and serves as a default when the iterable is empty. If initializer is not given and iterable contains only one item, the first item is returned.
它等价于下面的代码
def reduce(function, iterable, initializer=None):it = iter(iterable)if initializer is None:value = next(it)else:value = initializerfor element in it:value = function(value, element)return value
它和map的相同点是:
- 都需要提供一个处理函数(第一个参数)
- 处理函数都有一个返回值
不同点是:
- 处理函数接受两个参数
- 接受第三个参数作为初始返回数据
直接看一个例子。下面这个例子中匿名函数中y参数是source的某个遍历值;x最开始是初始值100,后来是匿名函数上次执行的返回值。这样下面的结果就相当于100+1+2+3+4+5+6。
from functools import reduce
source=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
r=reduce(lambda x,y: x+y, source, 100)
print(r)
121
对应到单词统计的例子。reduce方法可以将上面list中套list的结构“简化”为一层list。
words=reduce(lambda wordsAll,wordsOneline: wordsAll+wordsOneline, wordsLists, [])
words的值是
[‘To’, ‘be,’, ‘or’, ‘not’, ‘to’, ‘be,–that’, ‘is’, ‘the’, ‘question:–’, ‘Whether’, ……]
然后对这层list做计算,统计每个单词出现的次数,也“缩小”了words说表达的单词所占的“空间”。
wordCount=reduce(lambda wordCount,word: wordCount.update({word:wordCount.get(word,0)+1}) or wordCount, words, {})
{‘To’: 4, ‘be,’: 1, ‘or’: 1, ‘not’: 2, ‘to’: 7, ‘be,–that’: 1, ‘is’: 2, ‘the’: 15,……]
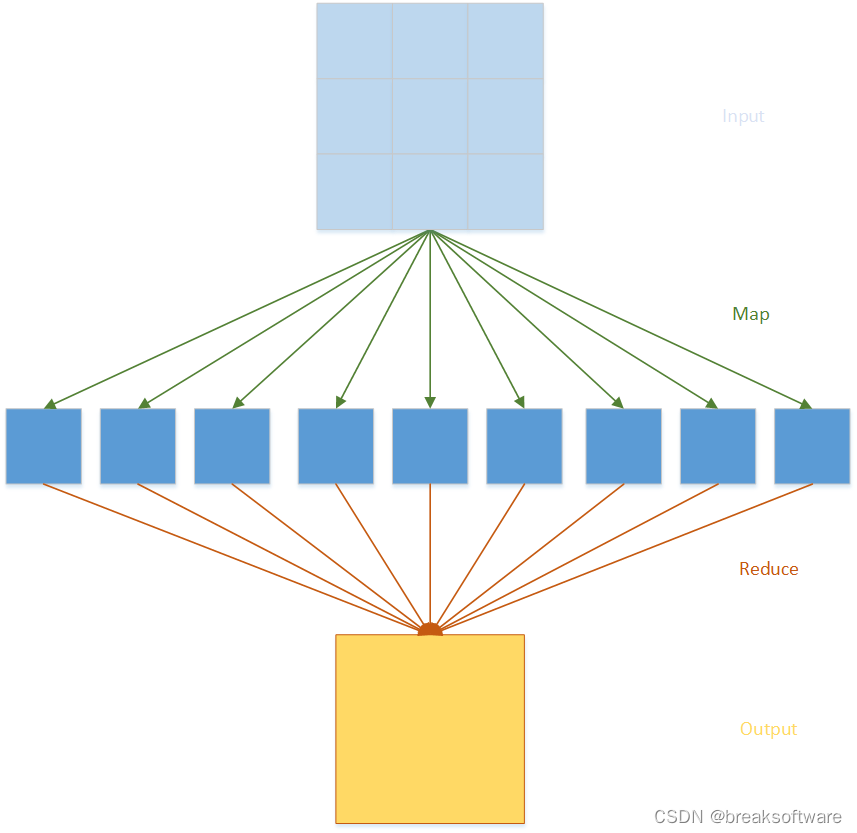
总体来说,map让输入数据被拆解(映射)到最小数据单元;reduce减少数据规模,并最终产出结果。
参考资料
- https://docs.python.org/3.10/library/functools.html?highlight=reduce
这篇关于0基础学习PyFlink——Map和Reduce函数处理单词统计的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




