本文主要是介绍YOLOv8改进:添加EMA注意力机制,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1、EMA介绍

论文:[2305.13563v1] Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module with Cross-Spatial Learning (arxiv.org)
录用:ICASSP2023
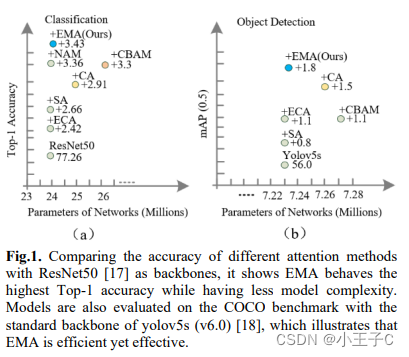
本文提出了一种新的跨空间学习方法,并设计了一个多尺度并行子网络来建立短和长依赖关系。
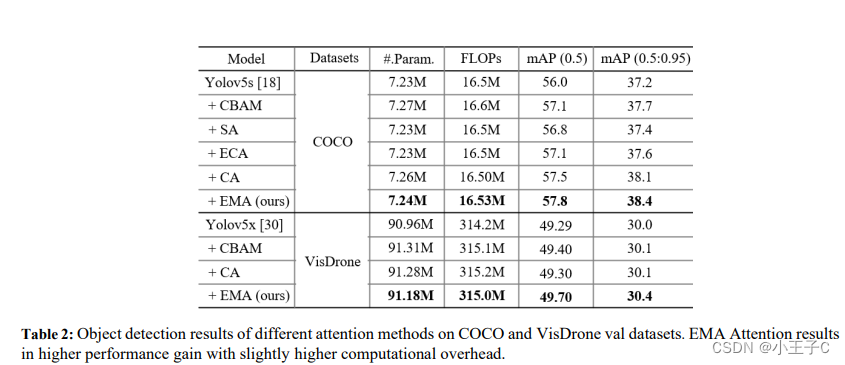
用YOLOv5x作为骨干CNN在VisDrone数据集上进行目标检测,其中CA, CBAM和EMA注意力分别集成到检测器中。从表2的结果可以看出,CA, CBAM和EMA都可以提高目标检测的基线性能。
2.EMA加入yolov8
2.1 添加EMA.py文件
在yolov8的ultralytics/nn/EMA.py文件中新建一个名为EMA.py文件,将下述代码复制到EMA.py文件中并保存。
import torch
from torch import nnclass EMA(nn.Module):def __init__(self, channels, factor=8):super(EMA, self).__init__()self.groups = factorassert channels // self.groups > 0self.softmax = nn.Softmax(-1)self.agp = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))self.pool_h = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 1))self.pool_w = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, None))self.gn = nn.GroupNorm(channels // self.groups, channels // self.groups)self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(channels // self.groups, channels // self.groups, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)self.conv3x3 = nn.Conv2d(channels // self.groups, channels // self.groups, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)def forward(self, x):b, c, h, w = x.size()group_x = x.reshape(b * self.groups, -1, h, w) # b*g,c//g,h,wx_h = self.pool_h(group_x)x_w = self.pool_w(group_x).permute(0, 1, 3, 2)hw = self.conv1x1(torch.cat([x_h, x_w], dim=2))x_h, x_w = torch.split(hw, [h, w], dim=2)x1 = self.gn(group_x * x_h.sigmoid() * x_w.permute(0, 1, 3, 2).sigmoid())x2 = self.conv3x3(group_x)x11 = self.softmax(self.agp(x1).reshape(b * self.groups, -1, 1).permute(0, 2, 1))x12 = x2.reshape(b * self.groups, c // self.groups, -1) # b*g, c//g, hwx21 = self.softmax(self.agp(x2).reshape(b * self.groups, -1, 1).permute(0, 2, 1))x22 = x1.reshape(b * self.groups, c // self.groups, -1) # b*g, c//g, hwweights = (torch.matmul(x11, x12) + torch.matmul(x21, x22)).reshape(b * self.groups, 1, h, w)return (group_x * weights.sigmoid()).reshape(b, c, h, w)2.2 修改ultralytics/nn/task.py
首先导包
from models.EMA import EMA

接着,在task.py中找到方法 def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True) 大概在615行,添加下面代码
elif m in {EMA}:args = [ch[f],*args]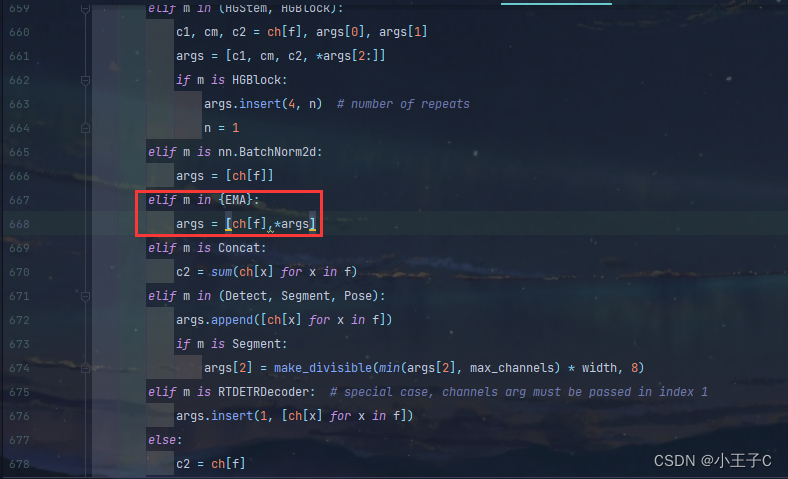
2.3 创建yolov8_a.yaml文件
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect# Parameters
nc: 7 # number of classesscales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'# [depth, width, max_channels]n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPss: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPsm: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPsl: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPsx: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:# [from, repeats, module, args]- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# - [-1, 1, EMA, [8]] # 10
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)- [-1, 1, EMA, [8]] #16- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)- [-1, 1, EMA, [8]] # 20- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 23 (P5/32-large)- [-1, 1, EMA, [8]] #24- [[16, 20, 24], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
EMA的位置可以改变,看个人的数据集效果,改注意编号的变化。
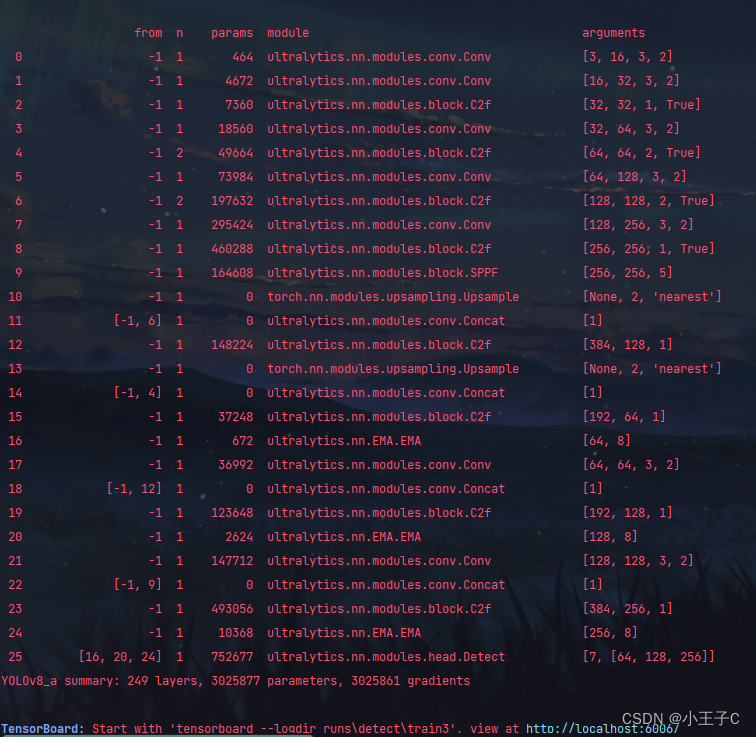
运行的时候看框架可以看到EMA说明添加成功。
这篇关于YOLOv8改进:添加EMA注意力机制的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



