本文主要是介绍MPI并行化实现K-means算法,使用zoo数据集,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 详细算法设计
- 算法流程
- 主要函数及其功能说明
- 输入及输出文件格式
- 程序运行实验结果
- 算法源代码
该算法的并行化中使用了zoo数据集,数据集地址:(http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Zoo)
详细算法设计
采用主从方式,由一个进程充当主节点负责数据的划分与分发,其他进程完成本地数据的计算,并将结果返回给主节点做聚合。
1、选定进程0为主节点,首先调用loadDate函数从数据集文件zoo.data中读取数据集,每次读取一行数据,并把数据按animal结构体指定的结构保存到内存中,结构体如下所示:
struct animal{int name;int type;int characters[D];
};
zoo.data每一行是个18维的数据。其中第一维表示动物的名字,是个字符串,为了方便MPI中数据的传递,将动物名映射成一个int型索引保存到属性name中,而索引到字符串名称的映射通过另一个变量idx2name,它是一个哈希表。中间的16维代表了该动物的特征,全为整数,因此保存到一个长度维D=16的数组characters中。最后一维代表了该动物所属的类型,也为整数,保存到属性type中。
2、完成了数据的读取后,主节点0向其他从节点分发数据,首先告知各个节点需要处理的数据量,假设进程数为size,数据总量为N,那么除主节点不处理数据外,其他从节点处理的数据量为dataNum = N/(size-1),节点i处理数据的范围为(i-1)*dataNum~i*dataNum。确定好每个从节点处理的数据量和数据范围后,进程0将对应的数据分发给这个节点。
3、进程0随机选择每个聚类的中心点,并发送给其他进程。
4、其他从节点进程根据自己分配得到的数据,计算数据块中每个点到各个聚类中心点的距离,取距离最小的那个类为该点所属的聚类,并计算每个聚类包含的数据量local_cnt,同时将每个数据的属性值叠加到对应聚类i的属性和local_cluster_center[i]上,最后将这些结果返回给进程0方便计算新的聚类中心。这些结果的传递采用MPI_Reduce函数进行规约,规约操作op为求和MPI_SUM。该步骤要调用两个函数cluster和distance,其中cluster计算每个数据点所属的新的类型,它会调用distance计算数据点到聚类中心点的距离。
5、进程0根据local_cnt和local_cluster_center计算新的聚类中心,新的聚类中心i为sum(local_cluster_center[i])/sum(local_cnt[i]),然后发送给其他进程。
6、返回步骤进行新的一轮迭代,直到达到指定的迭代轮数epoch。
7、将聚类结果保存到文件中,将属于同一类的动物保存在一个cluster中。
算法流程

主要函数及其功能说明
1、int loadData(string filename,animal* &data):从文件filename中读取数据保存到data中
2、double distance(int charc[],double center_charc[]):求数据点charc和聚类中心center_charc之间的欧式距离 d i s = ∑ i = 1 D ( c h a r c [ i ] − c e n t e r _ c h a r c [ i ] ) 2 dis=\sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^{D}(charc[i]-center\_charc[i])^2} dis=∑i=1D(charc[i]−center_charc[i])2
double distance(int charc[],double center_charc[]){double dis=0.0;for(int i=0;i<D;i++){dis+=(charc[i]*1.0-center_charc[i])*(charc[i]*1.0-center_charc[i]);}return sqrt(dis);
}
3、void cluster(animal* &data,int dataSize,double data_center[][D],double new_data_center[][D],int cnt[]):判断data中每个数据点所属的类型,data_center为当前的聚类中心,new_data_center为每个聚类包含的所有数据点的属性之和,cnt每个聚类包含的数据个数
void cluster(animal* &data,int dataSize,double data_center[][D],double new_data_center[][D],int cnt[]){for(int i=0;i<dataSize;i++){double min_dis=10000.0;int clusterId=-1;for(int j=0;j<K;j++){double cur_dis=distance(data[i].characters,data_center[j]);if(cur_dis<min_dis){min_dis=cur_dis;clusterId=j;}}//便于后续计算新的聚类中心for(int j=0;j<D;j++){new_data_center[clusterId][j]+=data[i].characters[j];}cnt[clusterId]++;//每一类包含的个数data[i].type=clusterId;//保存新的所属的类别}
}
4、计算新的聚类中心,并分发给其他进程
MPI_Reduce(local_cluster_center,cluster_center,D*K,MPI_DOUBLE,MPI_SUM,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);MPI_Reduce(local_cnt,total_cnt,K,MPI_INT,MPI_SUM,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);if(rank==0){//计算新的聚类中心for(int i=0;i<K;i++){for(int j=0;j<D;j++){ if(total_cnt[i]!=0)cluster_center[i][j]/=total_cnt[i];}}
}
//广播新的中心
MPI_Bcast(cluster_center,K*D,MPI_DOUBLE,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
输入及输出文件格式
输入文件数据格式:zoo.data每一行是个18维的数据,如下图所示。其中第一维表示动物的名字,为一字符串;中间的16维代表了该动物的特征,全为整数;最后一维代表了该动物所属的类型,属于1~7之中的某个数。每一维数据之间用逗号隔开。

输出文件数据格式: 输出结果保存在文件clusters-mpi.txt中,一共聚类成为7大类,属于同一类的所有动物名保存在一起,由前导cluster-X引出,X为0~6之间的整数,如下图所示。

程序运行实验结果
程序由c++实现,迭代10000次,分别对比了串行k-means算法和不同进程数运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法的运行时间:
| k-means算法运行方式 | 运行时间 |
|---|---|
| 串行k-means算法 | 0.813s |
| 2个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.837s |
| 3个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.496s |
| 4个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.413s |
| 5个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.365s |
| 6个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.359s |
| 7个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.379s |
| 8个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.391s |
| 9个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.398s |
| 10个进程运行的MPI并行化的k-means算法 | 0.410s |
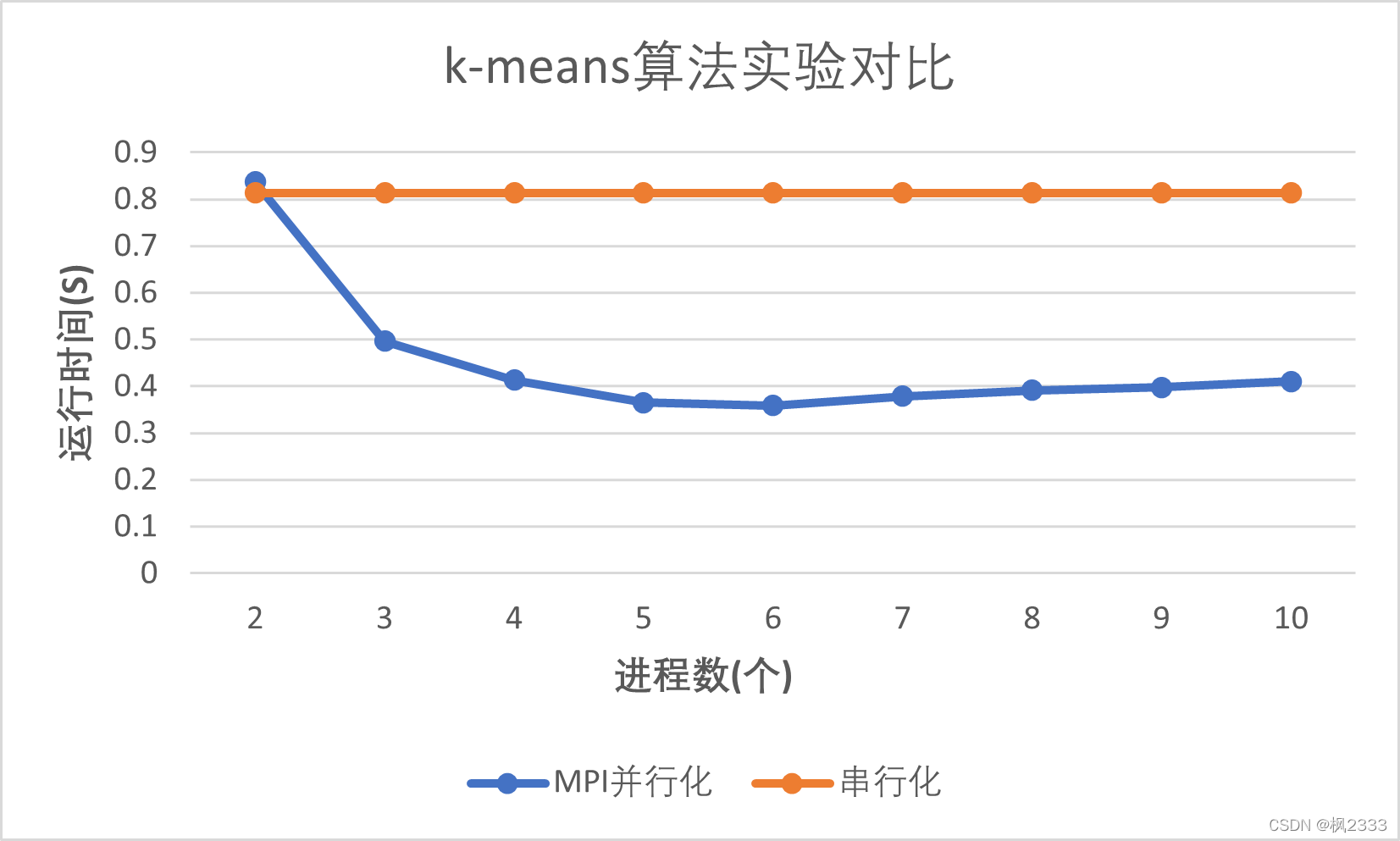
可以看到,当进程个数从2增加到6时,运行时间逐渐减少;当进程个数从6增加到10时,运行时间逐渐增大。这是因为我的笔记本电脑是6核的,当进程数小于等于核数时,运行时间会随着进程数的增加而减小;但是当进程数大于核数时,由于CPU核不能调度这些进程同时运行,所以需要在不同时间段切换不同进程运行,上下文切换需要花费时间,所以运行时间会随着进程数的增加而增大。另外,当进程数为2时,由于只有1个进程在做运算,所以运行时间和串行化的运行时间差不多。
算法源代码
//kmeans算法mpi实现
#include <mpi.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>using namespace std;const int K=7; //聚类的数目
const int D=16;//数据的维数
const int epoch=10000;//迭代轮数unordered_map<int,string> idx2name;//自定义结构体
struct animal{int name;//在idx2name中的索引int type;int characters[D];
};//从zoo.data中读取数据
int loadData(string filename,animal* &data){ifstream infile;infile.open(filename);if(!infile) cout<<"failed to open file "+filename+" !\n";string str;int dataNum=0;vector<animal> tmp;while(infile>>str){animal curline;int i=0;//保存名字string name="";while(str[i]!=',')name+=str[i++];i++;//确定名字到整数索引的映射idx2name[dataNum]=name;curline.name=dataNum++;//保存特征for(int j=0;j<D;j++){curline.characters[j]=str[i]-'0';i+=2;}//保存所属类型int type=str[i]-'0';curline.type=type;tmp.push_back(curline);}data=new animal[dataNum];for(int i=0;i<dataNum;i++){data[i]=tmp[i];}return dataNum;
}//求欧式距离
double distance(int charc[],double center_charc[]){double dis=0.0;for(int i=0;i<D;i++){dis+=(charc[i]*1.0-center_charc[i])*(charc[i]*1.0-center_charc[i]);}return sqrt(dis);
}//聚类
void cluster(animal* &data,int dataSize,double data_center[][D],double new_data_center[][D],int cnt[]){for(int i=0;i<dataSize;i++){double min_dis=10000.0;int clusterId=-1;for(int j=0;j<K;j++){double cur_dis=distance(data[i].characters,data_center[j]);if(cur_dis<min_dis){min_dis=cur_dis;clusterId=j;}}//便于后续计算新的聚类中心for(int j=0;j<D;j++){new_data_center[clusterId][j]+=data[i].characters[j];}cnt[clusterId]++;//每一类包含的个数data[i].type=clusterId;//保存新的所属的类别}
}int main(int argc,char *argv[]){int rank,size;int dataNum;//每个进程处理的数据数animal* data;//保存数据double cluster_center[K][D];//数据聚类中心点memset(cluster_center,0,sizeof(cluster_center));double local_cluster_center[K][D];//每次聚类得到的新聚类中心MPI_Status status;clock_t startTime,endTime;startTime = clock();MPI_Init(&argc,&argv);MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&rank);MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&size);//进程0读取数据,同时告知每个进程它需要处理的数据量if(rank==0){dataNum=loadData("zoo.data",data);for(int i=1;i<size;i++){int nums=dataNum/(size-1);int start=(i-1)*nums;int end=i*nums;if(i==size-1)end=dataNum;int sendNum=end-start;MPI_Send(&sendNum,1,MPI_INT,i,99,MPI_COMM_WORLD);}}else{MPI_Recv(&dataNum,1,MPI_INT,0,99,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&status);}MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD); //同步一下if(rank==0){//分发数据,以字节的类型发送,一次send将所有数据发送给接收方for(int i=1;i<size;i++){int nums=dataNum/(size-1);int start=(i-1)*nums;int end=i*nums;if(i==size-1)end=dataNum;MPI_Send((void*)(data+start),sizeof(animal)*(end-start),MPI_BYTE,i,99,MPI_COMM_WORLD);}}else{data=new animal[dataNum];MPI_Recv(data,sizeof(animal)*dataNum,MPI_BYTE,0,99,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&status);}MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD); //同步一下//进程0产生随机中心点if(rank==0){srand((unsigned int)(time(NULL))); unordered_set<int> vis;int i=0;while(i<K){int idx=rand()%dataNum;//该数据没被选择过if(vis.count(idx)==0){for(int j=0;j<D;j++)cluster_center[i][j]=data[idx].characters[j];vis.insert(idx);i++;}}}//广播数据中心MPI_Bcast(cluster_center,K*D,MPI_DOUBLE,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);//开始做聚类int local_cnt[K],total_cnt[K];for(int round=0;round<epoch;round++){memset(local_cluster_center,0,sizeof(local_cluster_center));memset(local_cnt,0,sizeof(local_cnt));if(rank){cluster(data,dataNum,cluster_center,local_cluster_center,local_cnt);}memset(cluster_center,0,sizeof(cluster_center));memset(total_cnt,0,sizeof(total_cnt));//将local_cluster_center规约到进程0以便计算新的聚类中心MPI_Reduce(local_cluster_center,cluster_center,D*K,MPI_DOUBLE,MPI_SUM,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);MPI_Reduce(local_cnt,total_cnt,K,MPI_INT,MPI_SUM,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD); //同步一下if(rank==0){//计算新的聚类中心for(int i=0;i<K;i++){for(int j=0;j<D;j++){ if(total_cnt[i]!=0)cluster_center[i][j]/=total_cnt[i];}}}//广播新的中心MPI_Bcast(cluster_center,K*D,MPI_DOUBLE,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);}//收集数据,打印结果if(rank){int buf[dataNum*2];for(int i=0;i<dataNum;i++){buf[i*2]=data[i].name;buf[i*2+1]=data[i].type;}MPI_Send(buf,dataNum*2,MPI_INT,0,99,MPI_COMM_WORLD);}else{int buf[dataNum*2];for(int i=1;i<size;i++){int nums=dataNum/(size-1);int start=(i-1)*nums;int end=i*nums;if(i==size-1)end=dataNum;int sendNum=end-start;MPI_Recv(&buf[start*2],sendNum*2,MPI_INT,i,99,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&status);}vector<string> clusters[K];for(int i=0;i<dataNum;i++){clusters[buf[i*2+1]].push_back(idx2name[buf[i*2]]);}string filename="clusters-mpi.txt";ofstream out(filename);for(int i=0;i<K;i++){out<<"cluster-"<<i<<":"<<endl;int cnts=1;for(string name:clusters[i]){if(cnts%6==0)out<<name<<endl;else out<<name<<" ,";cnts++;}out<<endl<<endl;}out.close();}delete []data;MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);MPI_Finalize();endTime = clock();cout <<rank<< " : The run time is: " <<(double)(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;return 0;
}
这篇关于MPI并行化实现K-means算法,使用zoo数据集的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





