本文主要是介绍k近邻分类算法(kNN),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
注明:部分内容来自维基百科
In pattern recognition, the k-Nearest Neighbors algorithm (ork-NN for short) is anon-parametric method used forclassification andregression. In both cases, the input consists of the k closest training examples in thefeature space. The output depends on whether k-NN is used for classification or regression:
-
- In k-NN classification, the output is a class membership.An object is classified by a majority vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among itsk nearest neighbors (k is a positive integer, typically small). If k = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor.
-
- In k-NN regression, the output is the property value for the object. This value is the average of the values of itsk nearest neighbors.
k-NN is a type of instance-based learning, or lazy learning, where the function is only approximated locally and all computation is deferred until classification.The k-NN algorithm is among the simplest of allmachine learning algorithms.
Both for classification and regression, it can be useful to weight the contributions of the neighbors, so that the nearer neighbors contribute more to the average than the more distant ones. For example, a common weighting scheme consists in giving each neighbor a weight of 1/d, where d is the distance to the neighbor.
The neighbors are taken from a set of objects for which the class (for k-NN classification) or the object property value (for k-NN regression) is known. This can be thought of as the training set for the algorithm, though no explicit training step is required.
A shortcoming of the k-NN algorithm is that it is sensitive to the local structure of the data.
The training examples are vectors in a multidimensional feature space, each with a class label.The training phase of the algorithm consists only of storing the feature vectors and class labels of the training samples.
In the classification phase, k is a user-defined constant, and an unlabeled vector (a query or test point) is classified by assigning the label which is most frequent among thek training samples nearest to that query point.
A commonly used distance metric for continuous variables is Euclidean distance. For discrete variables, such as for text classification, another metric can be used, such as theoverlap metric (or Hamming distance). Often, the classification accuracy of k-NN can be improved significantly if the distance metric is learned with specialized algorithms such as Large Margin Nearest Neighbor or Neighbourhood components analysis.
A drawback of the basic "majority voting" classification occurs when the class distribution is skewed. That is, examples of a more frequent class tend to dominate the prediction of the new example, because they tend to be common among thek nearest neighbors due to their large number. One way to overcome this problem is to weight the classification, taking into account the distance from the test point to each of itsk nearest neighbors. The class (or value, in regression problems) of each of the k nearest points is multiplied by a weight proportional to the inverse of the distance from that point to the test point. Another way to overcome skew is by abstraction in data representation. For example in a self-organizing map (SOM), each node is a representative (a center) of a cluster of similar points, regardless of their density in the original training data. K-NN can then be applied to the SOM.
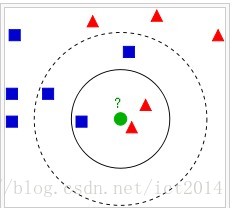
如上图所示,最中间的圆点,如果是3NN,则属于红色三角形,如果是5NN,则属于蓝色正方形。这就是kNN最基本的思想。但是,kNN对于每一个待分类的点,都需要和全部数据点进行距离计算,计算量太大。
在下面,我们将通过一段python代码来演示kNN算法。
#coding:utf-8from numpy import *
import operator
import os#创建开发用的小规模数据集
def createDataSet():group = array([[1.0,1.1],[1.0,1.0],[0,0],[0,0.1]])labels = ['A','A','B','B']return group, labels#kNN分类算法的核心函数
def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k):dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0]#dataSet的总共的行数#计算输入向量和数据集中每一个数据的欧式距离diffMat = tile(inX, (dataSetSize,1)) - dataSetsqDiffMat = diffMat**2sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1)distances = sqDistances**0.5#对距离进行排序,返回的是原来的相对位置sortedDistIndices = distances.argsort()#统计前k个最短的距离中,分类的情况classCount={}for i in range(k):voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndices[i]]classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(),key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)return sortedClassCount[0][0]#将文件中的数据转换成矩阵
def file2matrix(filename):fr = open(filename, 'r')arrayOLines = fr.readlines()numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines)returnMat = zeros((numberOfLines,3))classLabelVector = []index = 0for line in arrayOLines:line = line.strip()listFromLine = line.split('\t')returnMat[index,:] = listFromLine[0:3]classLabelVector.append(int(listFromLine[-1]))index += 1return returnMat, classLabelVector#数据的前处理步骤:归一化数值
def autoNorm(dataSet):minVals = dataSet.min(0)maxVals = dataSet.max(0)ranges = maxVals - minValsnormDataSet = zeros(shape(dataSet))m = dataSet.shape[0]normDataSet = dataSet - tile(minVals, (m,1))normDataSet = normDataSet/tile(ranges,(m,1))return normDataSet, ranges, minVals#约会网站的测试代码
def datingClassTest():hoRadio = 0.010datingDataMat, datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt')normMat,ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)m = normMat.shape[0]numTestVecs = int(m*hoRadio)errorCount = 0.0for i in range(numTestVecs):classifierResult = classify0(normMat[i,:], normMat[numTestVecs:m,:], datingLabels[numTestVecs:m],3)print "the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer is : %d" % (classifierResult, datingLabels[i])if(classifierResult != datingLabels[i]):errorCount += 1.0print "the total error rate is : %f" % (errorCount/float(numTestVecs))#约会网站预测函数
def classifyPerson():resultList = ['not at all', 'in small doses', 'in large doses']percentTats = float(raw_input("percentage of time spent playing video games?"))ffMiles = float(raw_input("frequent flier miles earned per year?"))iceCream = float(raw_input("liters of ice cream consumed per year?"))datingDataMat, datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt')normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)inArr = array([ffMiles, percentTats, iceCream])classifierResult = classify0((inArr-minVals)/ranges, normMat, datingLabels, 3)print "you will probably like this person: " , resultList[classifierResult - 1]#图像转换为向量
def img2vector(filename):returnVect = zeros((1,1024))fr = open(filename)for i in range(32):lineStr = fr.readline()for j in range(32):returnVect[0,32*i+j] = int(lineStr[j])return returnVect#手写数字识别系统的测试代码
def handwritingClassTest():hwLabels = []trainingFileList = os.listdir('trainingDigits')m = len(trainingFileList)trainingMat = zeros((m,1024))for i in range(m):fileNameStr = trainingFileList[i]fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0]classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0])hwLabels.append(classNumStr)trainingMat[i,:] = img2vector('trainingDigits/%s' % fileNameStr)testFileList = os.listdir('testDigits')errorCount = 0.0mTest = len(testFileList)for i in range(mTest):fileNameStr = testFileList[i]fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0]classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0])vectorUnderTest = img2vector('testDigits/%s' % fileNameStr)classifierResult = classify0(vectorUnderTest, trainingMat, hwLabels, 3)print "the classifier came back with: %d , the real answer is: %d" % (classifierResult, classNumStr)if(classifierResult != classNumStr):errorCount += 1.0print "\nthe total number of errors is : %d" % errorCountprint "\nthe total error rate is: %f" % (errorCount/float(mTest))#main函数
if __name__ == "__main__" :#利用小规模数据进行测试kNN分类器 group, labels = createDataSet()a = classify0([0,0], group, labels, 3)#print a #约会网站的测试代码datingClassTest()#约会网站的预测函数classifyPerson()#手写数字识别系统的测试代码handwritingClassTest()这篇关于k近邻分类算法(kNN)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







