本文主要是介绍yolov8训练初体验,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
最近在爬一些数据,有些网址的验证码比较难搞,于是使用yolov8来解决。
一、数据打标签并转为txt
使用的软件为X-AnyLabeling。内置各种模型,方便打标。
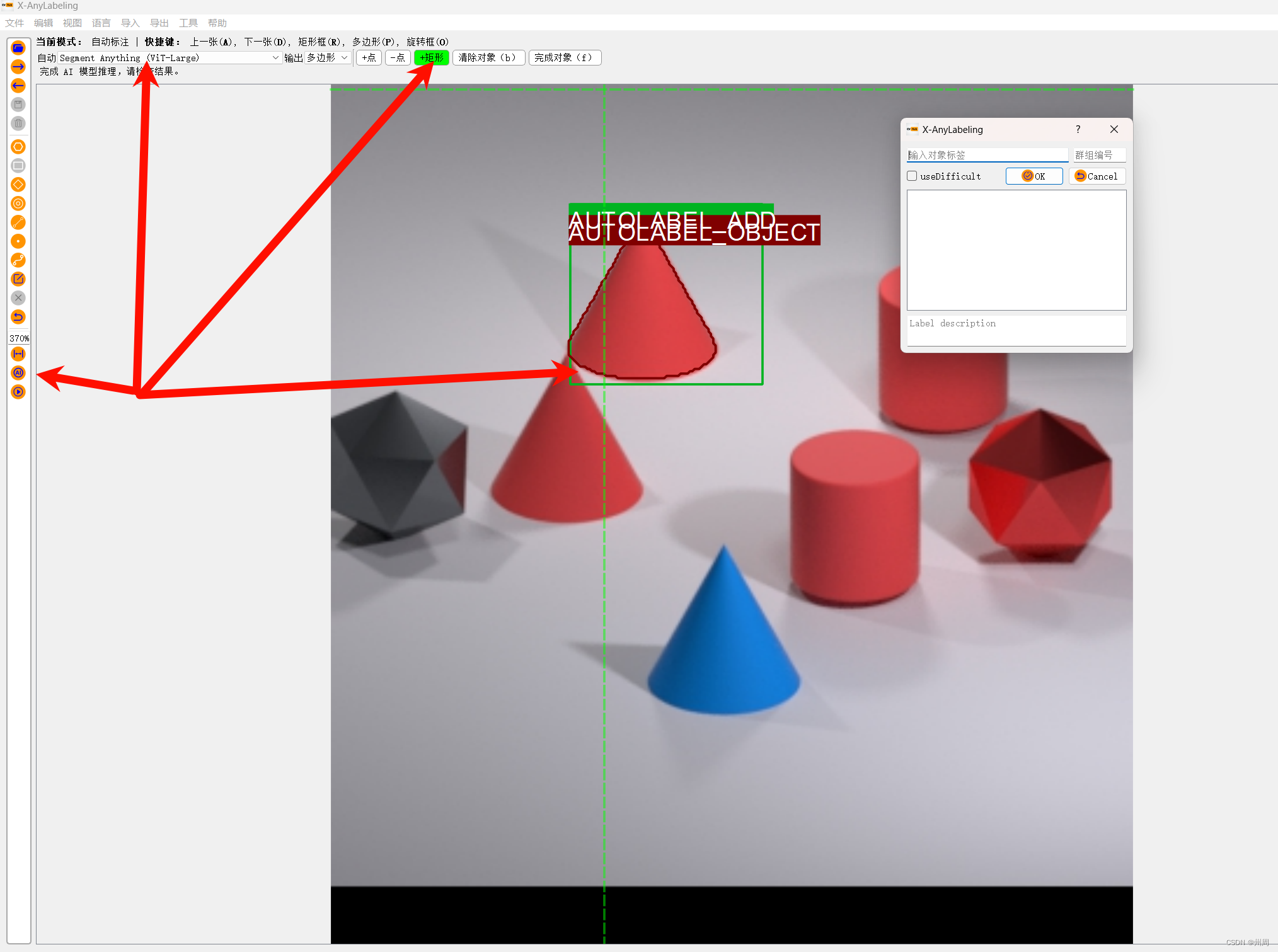
打标完成后由于是json格式,所以我们使用python转换即可
import json
import os#矩形框时def labelme_to_yolo(label_me_json_file, cls2id_dict):label_me_json = json.load(open(label_me_json_file, mode='r', encoding='UTF-8'))shapes = label_me_json['shapes']img_width, img_height = label_me_json['imageWidth'], label_me_json['imageHeight']img_path = label_me_json['imagePath']img_data = label_me_json['imageData'] if 'imageData' in label_me_json else ''labels = []for s in shapes:s_type = s['shape_type']s_type = s_type.lower()if s_type == 'rectangle':pts = s['points']x1, y1 = pts[0] # left cornerx2, y2 = pts[1] # right cornerx = (x1 + x2) / 2 / img_widthy = (y1 + y2) / 2 / img_heightw = abs(x2 - x1) / img_widthh = abs(y2 - y1) / img_heightcid = cls2id_dict[s['label']]labels.append(f'{cid} {x} {y} {w} {h}')return labelsdef write_label2txt(save_txt_path, label_list):f = open(save_txt_path, "w", encoding="UTF-8")for label in label_list:temp_list = label.split(" ")f.write(temp_list[0])f.write(" ")f.write(temp_list[1])f.write(" ")f.write(temp_list[2])f.write(" ")f.write(temp_list[3])f.write(" ")f.write(temp_list[4])f.write("\n")if __name__ == '__main__':# 原始图片文件夹路径img_dir = r"D:\pic\pic"# 原始JSON标签文件夹路径json_dir = r"D:\pic\label_json"# 生成保存TXT文件夹路径save_dir = r"D:\pic\label_txt"# 类别和序号的映射字典cls2id_dict = {"building1": "0"}if not os.path.exists(save_dir):os.makedirs(save_dir)for json_name in os.listdir(json_dir):json_path = os.path.join(json_dir, json_name)txt_name = json_name.split(".")[0] + ".txt"save_txt_path = os.path.join(save_dir, txt_name)labels = labelme_to_yolo(json_path, cls2id_dict)write_label2txt(save_txt_path, labels)# 处理 X-Anylabeling 多边形矩阵的标注 json 转化 txt,提取点
import json
import osname2id = { '球体' : 0,'立方体': 1,'圆锥体': 2,'圆柱体': 3,'多面体': 4} # 修改你的类别并且赋与 indexdef decode_json(json_floder_path, txt_outer_path, json_name):txt_name = os.path.join(txt_outer_path,json_name[:-5]) + '.txt'with open(txt_name, 'a') as f:json_path = os.path.join(json_floder_path, json_name)data = json.load(open(json_path, 'r', encoding='utf8', errors='ignore'))img_w = data['imageWidth']img_h = data['imageHeight']isshape_type = data['shapes'][0]['shape_type']print(isshape_type)dw = 1. / (img_w)dh = 1. / (img_h)for i in data['shapes']:label_name = i['label']if (i['shape_type'] == 'polygon'):point = []for lk in range(len(i['points'])):x = float(i['points'][lk][0])y = float(i['points'][lk][1])point_x = x * dwpoint_y = y * dhpoint.append(point_x)point.append(point_y)try:formatted_line = f"{name2id[label_name]} {' '.join(str(a) for a in point)}\n"f.write(formatted_line)except KeyError:print(f"Warning: Label name '{label_name}' not found in name2id mapping.")f.close()if __name__ == "__main__":json_floder_path = r'D:\pic\label_json' # 存放 json 的文件夹的绝对路径txt_outer_path = r'D:\pic\label_txt' # 存放 txt 的文件夹绝对路径json_names = os.listdir(json_floder_path)flagcount = 0for json_name in json_names:decode_json(json_floder_path, txt_outer_path, json_name)flagcount += 1print('-----------转化完毕------------')
二、使用yolov8训练
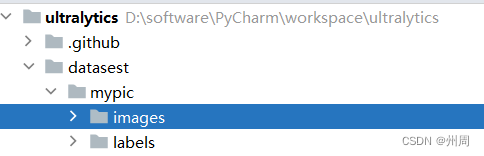
2.1 将图片和标签分别放在datasets目录下
2.2创建yaml文件
trian为训练的图片
val为预测的图片
train: D:\\software\\PyCharm\\workspace\\ultralytics\\datasest\\mypic\\images
val: D:\\software\\PyCharm\\workspace\\SomeTry\\yanzhengma\\val names:0: '球体'1: '立方体'2: '圆锥体'3: '圆柱体'4: '多面体'2.3 创建训练代码
YOLOv8文档
from ultralytics import YOLOmodel = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
model.train(data='mypic.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, batch=8)#用训练后的模型进行预测
yolo predict model=runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt source=D:\\software\\PyCharm\\workspace\\SomeTry\\yanzhengma\\val\\1719060455810geetest_image.jpg训练结果
这篇关于yolov8训练初体验的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









