本文主要是介绍Mysql使用中的性能优化——批量插入的规模对比,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在《Mysql使用中的性能优化——单次插入和批量插入的性能差异》中,我们观察到单次批量插入的数量和耗时呈指数型关系。
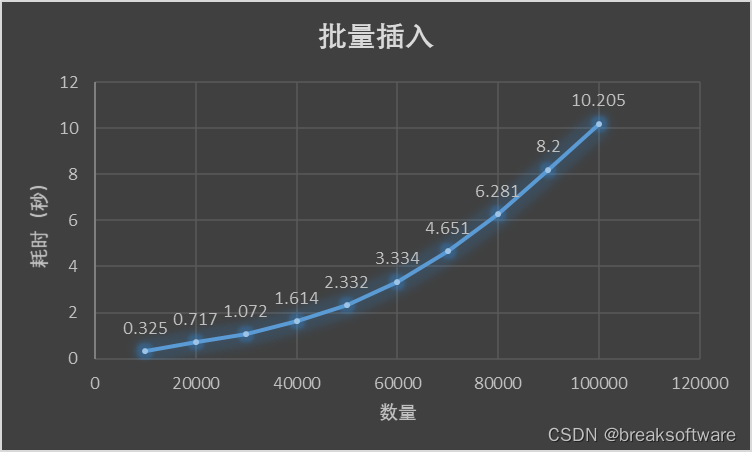
这个说明,不是单次批量插入的数量越多越好。本文我们将通过实验测试出本测试案例中最佳的单次批量插入数量。
结论
本案例中约每次插入2000~5000条数据时耗时最少。
实验数据
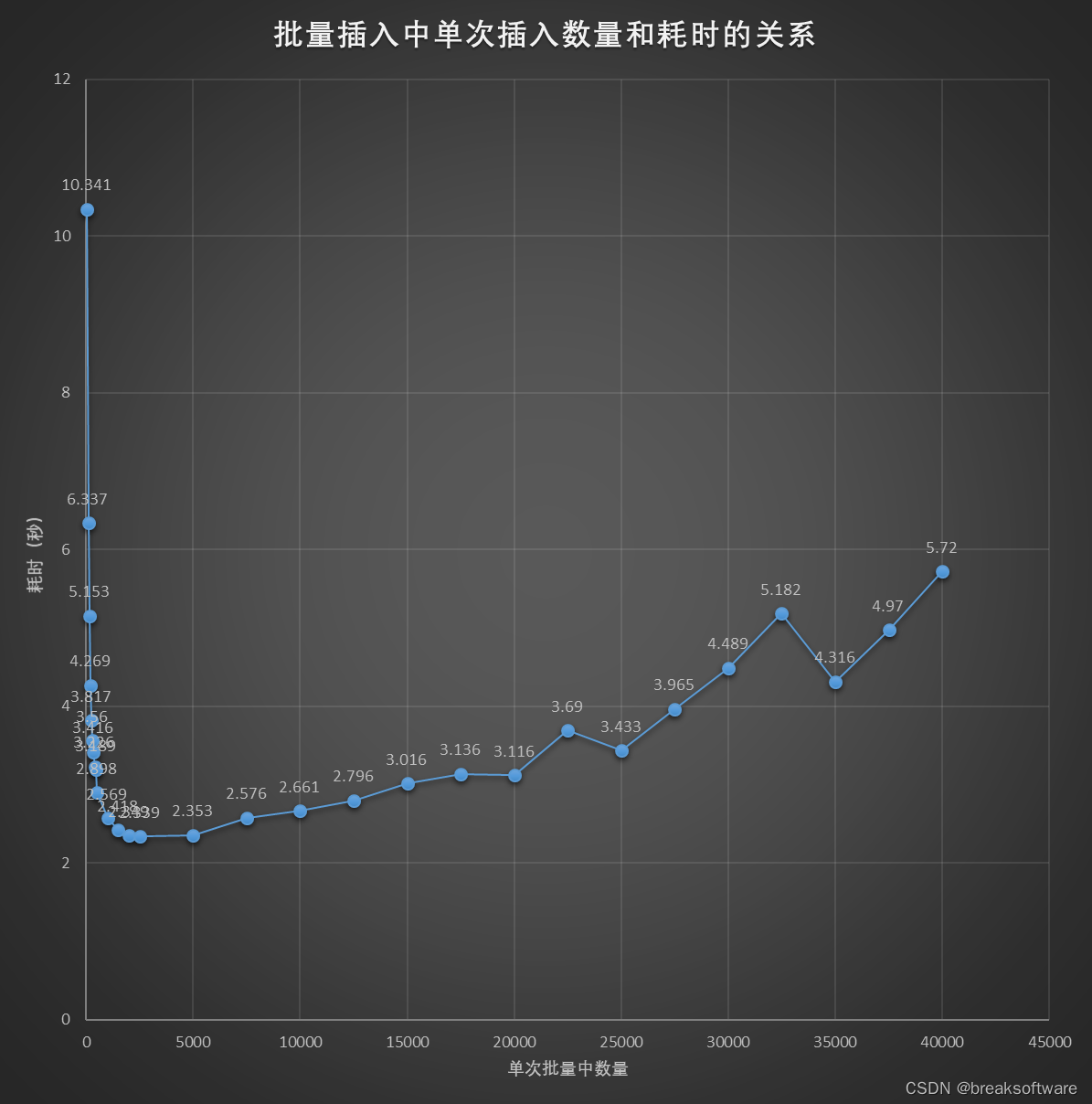
可以看到“单次批量中数量”和耗时呈U型曲线关系。
如果单次批量中数量过少,效率会接近于单次插入,效率会收到很大影响。
如果单次批量中数量过多,效率也会快速增加。
测试环境
见《Mysql使用中的性能优化——搭建Mysql的监测服务》
测试脚本
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS testdb;
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS testdb;
USE testdb;DROP TABLE IF EXISTS test_insert;
CREATE TABLE test_insert (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,name TEXT
) engine=InnoDB;DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS test_insert_proc_batch_bulk;
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE test_insert_proc_batch_bulk(IN name TEXT, IN fromNum INT, IN toNum INT)
BEGINDECLARE i INT DEFAULT fromNum;DECLARE new_names TEXT DEFAULT '';SET @sql = 'INSERT INTO test_insert (name) VALUES ';WHILE i < toNum DOSET new_names = CONCAT(name, i);SET i = i + 1;SET @sql = CONCAT(@sql, '("', new_names, '"),');END WHILE;SET @sql = LEFT(@sql, LENGTH(@sql) - 1);PREPARE stmt FROM @sql;EXECUTE stmt;DEALLOCATE PREPARE stmt;COMMIT;
END //
DELIMITER ;DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS test_insert_proc_batch;
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE test_insert_proc_batch(IN name TEXT, IN count INT, IN step INT)
BEGINDECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0;DECLARE new_name TEXT DEFAULT '';WHILE i < count DOSET new_name = CONCAT(name, i);CALL test_insert_proc_batch_bulk(new_name, i, i + step);SET i = i + step;END WHILE;COMMIT;
END //
DELIMITER ;TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 50);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 100);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 150);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 200);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 250);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 300);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 350);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 400);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 450);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 1000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 1500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 2000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 2500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 5000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 7500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 10000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 12500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 15000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 17500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 20000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 22500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 25000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 27500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 30000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 32500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 35000);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 37500);
TRUNCATE TABLE test_insert;
CALL test_insert_proc_batch('test', 100000, 40000);
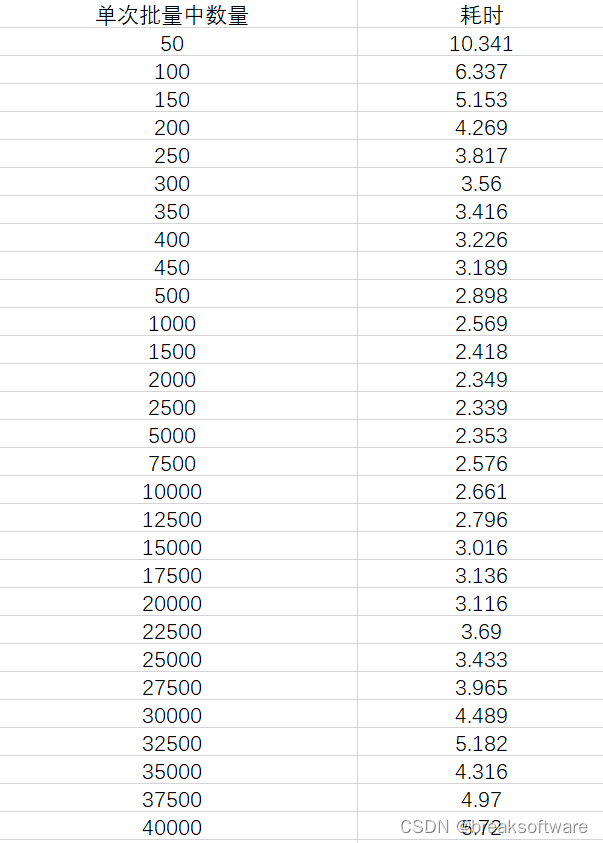
测试结果原始数据
这篇关于Mysql使用中的性能优化——批量插入的规模对比的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




