本文主要是介绍Qt5官方demo解析集33——Qt Quick Examples - Window and Screen,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本系列所有文章可以在这里查看http://blog.csdn.net/cloud_castle/article/category/2123873
接上文Qt5官方demo解析集32——Qt Quick Examples - Threading
来到我们Qt Quick Examples的第二个例子了,之所以挑这个demo,主要是我们使用Qt开发界面(尤其是跨平台界面)时,本地屏幕信息与窗口调用是不可避免的课题。
这个例子便向我们展示了在QML中获取本地屏幕信息的方法。
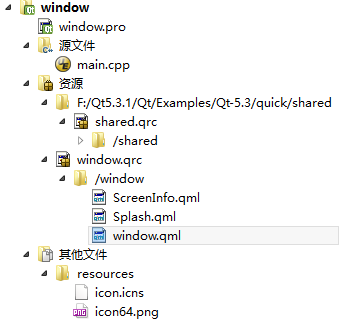
项目树如图,其中shared.qrc是很多QML示例共享的一些资源,包括按钮,滑块等。
此外,为了良好的跨平台,demo中添加了两种格式的图标文件(MAC支持的icns, 以及其他平台通用的png)。
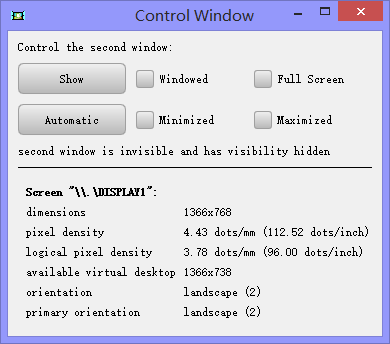
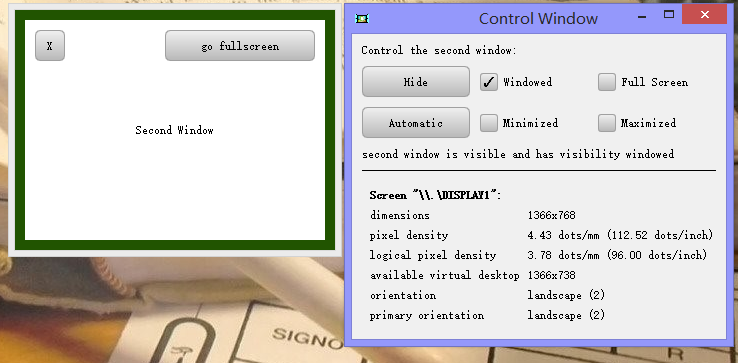
程序运行如图,我们可以调用一个子窗口,以窗口化或最大化形式显示。下方是我的笔记本屏幕的一些信息,包括分辨率,像素密度,方向等等。
由于使用到图标,我们有必要将pro文件拿出来看看:
window.pro:
TEMPLATE = appQT += quick qml
SOURCES += main.cpp
RESOURCES += \window.qrc \../shared/shared.qrc
EXAMPLE_FILES = \window.qmltarget.path = $$[QT_INSTALL_EXAMPLES]/quick/window
INSTALLS += targetICON = resources/icon64.png // 设置ICON 图标
macx: ICON = resources/icon.icns // MAC平台额外定义图标
win32: RC_FILE = resources/window.rcmain.cpp:
#include <QtGui/QGuiApplication> // 个人比较推荐的头文件包含方式
#include <QtQml/QQmlEngine>
#include <QtQml/QQmlComponent>
#include <QtQuick/QQuickWindow>
#include <QtCore/QUrl>
#include <QDebug>int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);QQmlEngine engine; // 注意到在5.3以后我们大多使用QQmlApplicationEngine来加载qml文件 // 它实际也就是封装了这里QQmlEngine + QQmlComponent,并提供了一些其他的便利函数QQmlComponent component(&engine);QQuickWindow::setDefaultAlphaBuffer(true); // 如果我们需要应用透明窗体,需要在第一个QQuickWindow出现前设置该函数为truecomponent.loadUrl(QUrl("qrc:///window/window.qml"));if ( component.isReady() )component.create();elseqWarning() << component.errorString();return app.exec();
}
我们随着加载的顺序来看第一个qml文件
window.qml:
import QtQuick 2.0
import QtQuick.Window 2.1
import "../shared" as SharedQtObject { // 非可视化的轻量顶层对象property real defaultSpacing: 10 // 各对象间隔property SystemPalette palette: SystemPalette { } // SystemPalette可以很方便地提供本地化的控件样式property var controlWindow: Window { // 主窗口width: visibilityLabel.implicitWidth * 1.2height: col.implicitHeight + defaultSpacing * 2color: palette.windowtitle: "Control Window"Column {id: colanchors.fill: parentanchors.margins: defaultSpacingspacing: defaultSpacingproperty real cellWidth: col.width / 3 - spacing // Grid 单元格宽度Text { text: "Control the second window:" }Grid {id: gridcolumns: 3spacing: defaultSpacingwidth: parent.widthShared.Button { // 来自Shared 控件包的Buttonid: showButtonwidth: col.cellWidthtext: testWindow.visible ? "Hide" : "Show"onClicked: testWindow.visible = !testWindow.visible}//! [windowedCheckbox]Shared.CheckBox { // CheckBoxtext: "Windowed"height: showButton.heightwidth: col.cellWidthBinding on checked { value: testWindow.visibility === Window.Windowed } // 注意Binding是一个QML类型,而不是关键字。这个语句等于Binding{target: checked; value: testWindow.visibility === Window.Windowed}。相对于checked: XXX 的属性绑定方式,这种方式更适用于var 类型的属性绑定。因此对于bool 型的checked 而言,checked: testWindow.visibility === Window.Windowed 也可行onClicked: testWindow.visibility = Window.Windowed}//! [windowedCheckbox]Shared.CheckBox {height: showButton.heightwidth: col.cellWidthtext: "Full Screen"Binding on checked { value: testWindow.visibility === Window.FullScreen }onClicked: testWindow.visibility = Window.FullScreen}Shared.Button { // Window.AutomaticVisibility 根据所在平台调整显示方式,比如在Windows 上为窗口,Android 则为全屏id: autoButtonwidth: col.cellWidthtext: "Automatic"onClicked: testWindow.visibility = Window.AutomaticVisibility}Shared.CheckBox {height: autoButton.heighttext: "Minimized"Binding on checked { value: testWindow.visibility === Window.Minimized }onClicked: testWindow.visibility = Window.Minimized}Shared.CheckBox {height: autoButton.heighttext: "Maximized"Binding on checked { value: testWindow.visibility === Window.Maximized }onClicked: testWindow.visibility = Window.Maximized}}function visibilityToString(v) { // 状态转换String 函数switch (v) {case Window.Windowed:return "windowed";case Window.Minimized:return "minimized";case Window.Maximized:return "maximized";case Window.FullScreen:return "fullscreen";case Window.AutomaticVisibility:return "automatic";case Window.Hidden:return "hidden";}return "unknown";}Text {id: visibilityLabeltext: "second window is " + (testWindow.visible ? "visible" : "invisible") +" and has visibility " + parent.visibilityToString(testWindow.visibility)}Rectangle {id: horizontalRulecolor: "black"width: parent.widthheight: 1}ScreenInfo { } // 屏幕信息获取,实现代码在下方}} // !controlWindowproperty var testWindow: Window { // 子窗口width: 320height: 240color: "#215400" // 窗口背景色,但我们看到的颜色只在周围一圈,是因为中间为Rectangle,那一圈为间隔defaultSpacingtitle: "Test Window with color " + colorflags: Qt.Window | Qt.WindowFullscreenButtonHintRectangle {anchors.fill: parentanchors.margins: defaultSpacing // 矩形与窗口间隔Text {anchors.centerIn: parenttext: "Second Window"}MouseArea { // 点击切换颜色anchors.fill: parentonClicked: testWindow.color = "#e0c31e"}Shared.Button {anchors.right: parent.rightanchors.top: parent.topanchors.margins: defaultSpacingtext: testWindow.visibility === Window.FullScreen ? "exit fullscreen" : "go fullscreen"width: 150onClicked: {if (testWindow.visibility === Window.FullScreen)testWindow.visibility = Window.AutomaticVisibilityelsetestWindow.visibility = Window.FullScreen}}Shared.Button {anchors.left: parent.leftanchors.top: parent.topanchors.margins: defaultSpacingtext: "X"width: 30onClicked: testWindow.visible = false // 窗口隐藏}}} // !testWindowproperty var splashWindow: Splash { // 启动窗口onTimeout: controlWindow.visible = true // 自定义信号处理函数,显示主窗口}
}
为了在QML获取屏幕信息,Qt为我们提供了Screen类型,它可以作为其他可视的QML类型的附加对象,指向该对象所显示的设备:
ScreenInfo.qml:
import QtQuick 2.1
import QtQuick.Window 2.1Item {id: rootwidth: 400height: propertyGrid.implicitHeight + 16function orientationToString(o) { // 状态转string 函数switch (o) {case Qt.PrimaryOrientation:return "primary";case Qt.PortraitOrientation:return "portrait";case Qt.LandscapeOrientation:return "landscape";case Qt.InvertedPortraitOrientation:return "inverted portrait";case Qt.InvertedLandscapeOrientation:return "inverted landscape";}return "unknown";}Grid {id: propertyGridcolumns: 2spacing: 8x: spacingy: spacing//! [screen]Text {text: "Screen \"" + Screen.name + "\":" // 显示设备名称font.bold: true}Item { width: 1; height: 1 } // 设备名称右方的占位器Text { text: "dimensions" } // 分辨率Text { text: Screen.width + "x" + Screen.height } Text { text: "pixel density" } // 像素密度Text { text: Screen.pixelDensity.toFixed(2) + " dots/mm (" + (Screen.pixelDensity * 25.4).toFixed(2) + " dots/inch)" }Text { text: "logical pixel density" } // 逻辑像素密度Text { text: Screen.logicalPixelDensity.toFixed(2) + " dots/mm (" + (Screen.logicalPixelDensity * 25.4).toFixed(2) + " dots/inch)" }Text { text: "available virtual desktop" } // 可用虚拟桌面,比分辨率的高度少了30 是因为Windows底下的状态栏Text { text: Screen.desktopAvailableWidth + "x" + Screen.desktopAvailableHeight }Text { text: "orientation" } // 屏幕方向Text { text: orientationToString(Screen.orientation) + " (" + Screen.orientation + ")" }Text { text: "primary orientation" } // 优先方向Text { text: orientationToString(Screen.primaryOrientation) + " (" + Screen.primaryOrientation + ")" }//! [screen]}
}
最后是启动画面的实现
Splash.qml:
import QtQuick 2.0
import QtQuick.Window 2.1//! [splash-properties]
Window {id: splashcolor: "transparent"title: "Splash Window"modality: Qt.ApplicationModal // 应用窗口模式flags: Qt.SplashScreen // 启动画面property int timeoutInterval: 2000signal timeout // 自定义溢出信号
//! [splash-properties]
//! [screen-properties]x: (Screen.width - splashImage.width) / 2 // 居中y: (Screen.height - splashImage.height) / 2
//! [screen-properties]width: splashImage.width // 窗口大小与图片大小一致height: splashImage.heightImage {id: splashImagesource: "../shared/images/qt-logo.png"MouseArea {anchors.fill: parentonClicked: Qt.quit() // 点击退出}}//! [timer]Timer {interval: timeoutInterval; running: true; repeat: falseonTriggered: {visible = false // 2秒后隐藏,并发出timeout信号,以显示主窗口splash.timeout()}}//! [timer]Component.onCompleted: visible = true
}
这篇关于Qt5官方demo解析集33——Qt Quick Examples - Window and Screen的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!