本文主要是介绍使用Aspect来对访问方法进行预处理和后处理,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
例子摘自李刚老师的《JavaEE企业应用实战(第四版)》661页
使用aspect中的@Around、@Before、@After、@AfterReturning,例子如下
切面类
package com.aspect;import java.util.Arrays;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect
public class FourAdviceTest {/*** 可以在执行方法之前和之后改变参数和返回值* @param joinPoint用于获取目标方法相关信息的参数* @return 最终的返回值* @throws Throwable*/@Around("execution(* com.service.*.*(..))")public Object processTx(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {System.out.println("Around增强:执行方法之前,模拟开始事物");Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();if(args != null && args.length > 0 && args[0].getClass() == String.class) {args[0] = "增加的前缀" + args[0];}Object rvt = joinPoint.proceed();System.out.println("Around增强:执行方法之后,模拟结束事物");if(rvt != null && rvt instanceof Integer) {rvt = (Integer)rvt * (Integer)rvt;}return rvt;}/*** 可以在执行方法之前对目标方法的参数进行判断* 通过抛出一个异常来阻断目标方法的访问* @param joinPoint*/@Before("execution(* com.service.*.*(..))")public void authority(JoinPoint joinPoint) {System.out.println("Before增强:模拟权限检查");System.out.println("Before增强:被织入增强处理的目标目标方法为:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());System.out.println("Before增强:目标方法的参数为:" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));joinPoint.getArgs()[0] = "除了Around其他的都是是不可以修改目标方法的参数的";System.out.println("joinPoint.getArgs()[0]:"+joinPoint.getArgs()[0]);System.out.println("Before增强:目标方法的参数为:" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));System.out.println("Before增强:被织入增强处理的目标对象为:" + joinPoint.getTarget());}/*** 可以在执行方法之后对目标方法的参数进行判断* @param joinPoint*/@After("execution(* com.service.*.*(..))")public void release(JoinPoint joinPoint) {System.out.println("After增强:模拟方法结束后的释放资源");System.out.println("After增强:被织入增强处理的目标方法为:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());System.out.println("After增强:目标方法的参数为:" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));System.out.println("After增强:被织入增强处理的目标对象为" + joinPoint.getTarget());}/*** 与After的区别在于AfterReturning只有在方法执行成功的之后才会被织入,如果After和* AfterReturning同时存在于一个文件中,谁写在前面谁先运行* @param joinPoint* @param rvt方法的返回值*/@AfterReturning(pointcut="execution(* com.service.*.*(..))", returning="rvt")public void log(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object rvt) {System.out.println("AfterReturning增强:获取目标方法的返回值:" + rvt);System.out.println("AfterReturning增强:模拟日志功能");System.out.println("AfterReturning增强:获织入增强的目标方法为:" + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());System.out.println("AfterReturning增强:目标方法的参数为:" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));System.out.println("AfterReturning增强:被织入增强处理的目标对象为:" + joinPoint.getTarget());}
}
Bean类
package com.service.impl;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import com.service.Hello;
@Component
public class HelloImpl implements Hello {@Overridepublic void hello() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("HelloImpl中的hello方法");}@Overridepublic int addUser(String name, String pass) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("执行Hello组件的addUser添加用户:" + name);if(name.length() < 3 || name.length() > 40) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("name的参数长度必须大于3小于10");}return 92;}
}测试代码
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");HelloImpl helloImpl = applicationContext.getBean("helloImpl", HelloImpl.class);helloImpl.addUser("Slience", "12");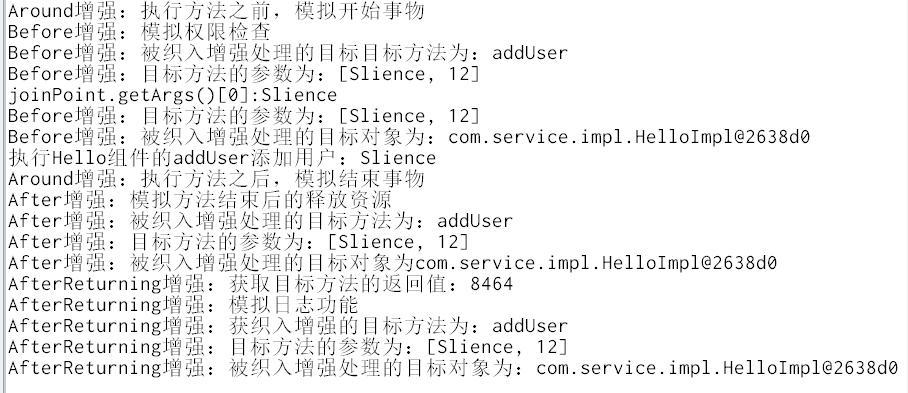
值得注意的是@After和@AfterReturning或者有多个@After和@AfterReturning如果同时存在于一个文件里,他们的执行顺序是从上到下依次执行的;还有就是这里面只有@Around可以修改目标方法的接收参数和返回值,其他的都不可以修改;还有就是可以使用@AfterThrowing来对目标方法抛出的异常进行捕获和操作。
这篇关于使用Aspect来对访问方法进行预处理和后处理的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




