本文主要是介绍保研机试之【动态规划】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本文为博客:动态规划解题套路框架 | labuladong 的算法笔记 的笔记
前言
动态规划问题的一般形式就是求最值,求解动态规划的核心问题是穷举。动态规划三要素为:最优子结构、重叠子问题、状态转移方程。首先要判断,该问题是否具有重复子问题,如果有则可以用动态规划求解。动态规划问题存在「重叠子问题」,如果暴力穷举的话效率会很低,所以需要你使用「备忘录」或者「DP table」来优化穷举过程;动态规划只有列出正确的「状态转移方程」,才能正确地穷举。
理解重复子问题:https://leetcode.cn/problems/fibonacci-number/description/
递归算法的时间复杂度怎么计算?就是用子问题个数乘以解决一个子问题需要的时间。
暴力求解(注意树的形状)
会存在很多计算重复的情况,这也是为什么不采用备忘录会导致效率低下,时间复杂度为O(
),因为子问题个数为
,解决一个子问题需要的时间(加法)为1。
带备忘录的递归解法(注意树的剪枝)
最后就剩类似红色方框的形状:
时间复杂度为O(n),因为子问题个数为n,解决一个子问题需要的时间(加法)为1。
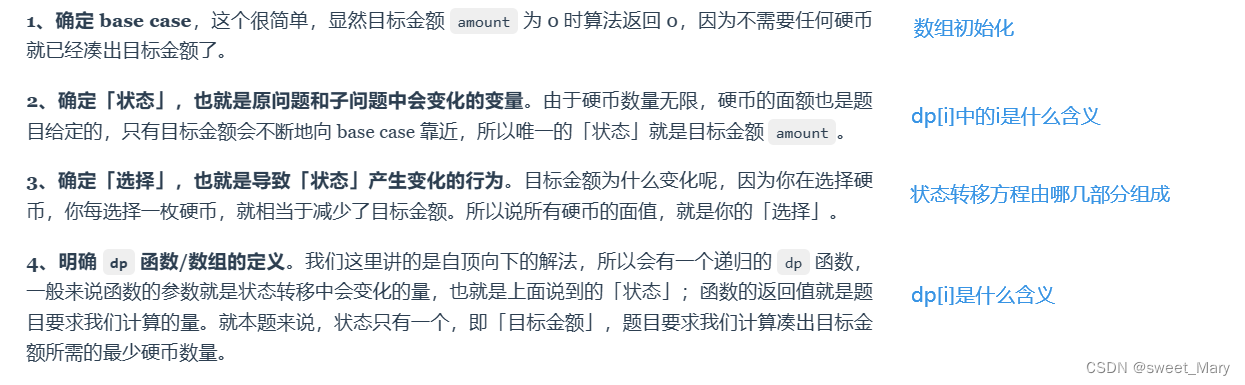
dp 数组的迭代(递推)解法
理解状态转移方程:动态规划解题套路框架 | labuladong 的算法笔记
暴力求解
class Solution { public:int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {if(amount==0){return 0;}if(amount<0){return -1;}int ans=INT_MAX;for(int i:coins){int temp=coinChange(coins,amount-i);if(temp==-1){continue;}ans=min(ans,temp+1);}if(ans==INT_MAX){return -1;}else{return ans;}} };直接超时:
带备忘录的递归
class Solution { public:unordered_map<int,int> hmap;int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {if(amount==0){return 0;}if(amount<0){return -1;}if(hmap.find(amount)!=hmap.end()){return hmap[amount];}int ans=INT_MAX;for(int i:coins){int temp;if(hmap.find(amount-i)!=hmap.end()){temp=hmap[amount-i];}else{temp=coinChange(coins,amount-i);if(temp==-1){continue;}else{hmap[amount-i]=temp;}}ans=min(ans,temp+1);}if(ans==INT_MAX){return -1;}else{return ans;}} };但是!
dp 数组的迭代解法
class Solution { public:int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {vector<int> g(10010,amount+1);g[0]=0;for(int i=1;i<=amount;i++){for(auto j:coins){if(i-j>=0){g[i]=min(g[i],g[i-j]+1);}}}if(g[amount]>amount){return -1;}return g[amount];} };
这篇关于保研机试之【动态规划】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!