本文主要是介绍数据分析:基于sparcc的co-occurrence网络,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
介绍
Sparcc是基于16s或metagenomics数据等计算组成数据之间关联关系的算法。通常使用count matrix数据。
安装Sparcc软件
git clone git@github.com:JCSzamosi/SparCC3.git
export PATH=/path/SparCC3:$PATHwhich SparCC.py
导入数据
注:使用rarefy抽平的count matrix数据
library(dplyr)
library(tibble)dat <- read.table("dat_rarefy10000_v2.tsv", header = T)
过滤数据
filter_fun <- function(prof=dat , tag="dat ", cutoff=0.005){# prof=dat # tag="dat " # cutoff=0.005dat <- cbind(prof[, 1, drop=F], prof[, -1] %>% summarise(across(everything(), function(x){x/sum(x)}))) %>%column_to_rownames("OTUID")#dat.cln <- dat[rowSums(dat) > cutoff, ]remain <- apply(dat, 1, function(x){length(x[x>cutoff])}) %>% data.frame() %>%setNames("Counts") %>%rownames_to_column("OTUID") %>%mutate(State=ifelse(Counts>1, "Remain", "Discard")) %>%filter(State == "Remain")# countcount <- prof %>% filter(OTUID%in%remain$OTUID)filename <- paste0("../dataset/Sparcc/", tag, "_rarefy10000_v2_", cutoff, ".tsv")write.table(count, file = filename, quote = F, sep = "\t", row.names = F)# relative abundancerelative <- dat %>% rownames_to_column("OTUID") %>%filter(OTUID%in%remain$OTUID)filename <- paste0("../dataset/Sparcc/", tag, "_rarefy10000_v2_", cutoff, "_rb.tsv")write.table(relative, file = filename, quote = F, sep = "\t", row.names = F)
}filter_fun(prof=dat, tag="dat", cutoff=0.005)
filter_fun(prof=dat, tag="dat", cutoff=0.001)
Result: 保留过滤后的count matrix和relative abundance matrix两类型矩阵
sparcc analysis
该过程分成两步:1.计算相关系数;2.permutation test计算p值.
-
iteration 参数使用default -i 20
-
permutation 参数: 1000次
# Step 1 - Compute correlations
python /data/share/toolkits/SparCC3/SparCC.py sxtr_rarefy10000_v2_0.001.tsv -i 20 --cor_file=sxtr_sparcc.tsv > sxtr_sparcc.log
echo "Step 1 - Compute correlations Ended successfully!"# Step 2 - Compute bootstraps
python /data/share/toolkits/SparCC3/MakeBootstraps.py sxtr_rarefy10000_v2_0.001.tsv -n 1000 -t bootstrap_#.txt -p pvals/ >> sxtr_sparcc.log
echo "Step 2 - Compute bootstraps Ended successfully!"# Step 3 - Compute p-values
for n in {0..999}; do /data/share/toolkits/SparCC3/SparCC.py pvals/bootstrap_${n}.txt -i 20 --cor_file=pvals/bootstrap_cor_${n}.txt >> sxtr_sparcc.log; done
python /data/share/toolkits/SparCC3/PseudoPvals.py sxtr_sparcc.tsv pvals/bootstrap_cor_#.txt 1000 -o pvals/pvals.two_sided.txt -t two_sided >> sxtr_sparcc.log
echo "Step 3 - Compute p-values Ended successfully!"# step 4 - Rename file
mv pvals/pvals.two_sided.txt sxtr_pvals.two_sided.tsv
mv cov_mat_SparCC.out sxtr_cov_mat_SparCC.tsv
echo "step 4 - Rename file Ended successfully!"
co-occurrence network
网络图要符合以下要求:
-
保留相互之间显著差异(p < 0.05)OTU;
-
genus分类学水平表示OTU来源;
-
OTU间相关性用颜色区分,且线条粗细代表相关系数大小;
-
OTU点大小表示其丰度大小;
-
统计网络中正负相关数目;
导入画图数据
library(igraph)
library(psych)dat_cor <- read.table("dat_cov_mat_SparCC.tsv", header = T, row.names = 1)
dat_pval <- read.table("dat_pvals.two_sided.tsv", header = T, row.names = 1)
dat_rb5 <- read.table("dat_rarefy10000_v2_0.005_rb.tsv", header = T, row.names = 1)
dat_tax <- read.csv("dat_taxonomy.csv")
画图
-
数据处理
-
数据可视化
-
数据存储
cornet_plot <- function(mcor=dat_cor, mpval=dat_pval, mrb=dat_rb5, tax=dat_tax, type="dat_5"){# mcor <- dat_cor# mpval <- dat_pval# mrb <- dat_rb5# tax <- dat_tax# type="dat_05"# trim all NA in pvalue < 0.05mpval[mpval > 0.05] <- NAremain <- apply(mpval, 1, function(x){length(x[!is.na(x)])}) %>% data.frame() %>%setNames("counts") %>%rownames_to_column("OTUID") %>%filter(counts > 0)remain_pval <- mpval[as.character(remain$OTUID), as.character(remain$OTUID)]# remove non significant edges remain_cor <- mcor[as.character(remain$OTUID), as.character(remain$OTUID)]for(i in 1:nrow(remain_pval)){for(j in 1:ncol(remain_pval)){if(is.na(remain_pval[i, j])){remain_cor[i, j] <- 0}}}# OTU relative abundance and taxonomy rb_tax <- mrb %>% rownames_to_column("OTUID") %>%filter(OTUID%in%as.character(remain$OTUID)) %>%group_by(OTUID) %>%rowwise() %>%mutate(SumAbundance=mean(c_across(everything()))) %>%ungroup() %>%inner_join(tax, by="OTUID") %>%dplyr::select("OTUID", "SumAbundance", "Genus") %>%mutate(Genus=gsub("g__Candidatus", "Ca.", Genus),Genus=gsub("_", " ", Genus)) %>%mutate(Genus=factor(as.character(Genus)))# 构建igraph对象igraph <- graph.adjacency(as.matrix(remain_cor), mode="undirected", weighted=TRUE, diag=FALSE)# 去掉孤立点bad.vs <- V(igraph)[degree(igraph) == 0]igraph <- delete.vertices(igraph, bad.vs)# 将igraph weight属性赋值到igraph.weightigraph.weight <- E(igraph)$weight# 做图前去掉igraph的weight权重,因为做图时某些layout会受到其影响E(igraph)$weight <- NAnumber_cor <- paste0("postive correlation=", sum(igraph.weight > 0), "\n","negative correlation=", sum(igraph.weight < 0))# set edge color,postive correlation 设定为red, negative correlation设定为blueE.color <- igraph.weightE.color <- ifelse(E.color > 0, "red", ifelse(E.color < 0, "blue", "grey"))E(igraph)$color <- as.character(E.color)# 可以设定edge的宽 度set edge width,例如将相关系数与edge width关联E(igraph)$width <- abs(igraph.weight)# set vertices sizeigraph.size <- rb_tax %>% filter(OTUID%in%V(igraph)$name) igraph.size.new <- log((igraph.size$SumAbundance) * 1000000)V(igraph)$size <- igraph.size.new# set vertices colorigraph.col <- rb_tax %>% filter(OTUID%in%V(igraph)$name)pointcolor <- c("green","deeppink","deepskyblue","yellow","brown","pink","gray","cyan","peachpuff")pr <- levels(igraph.col$Genus)pr_color <- pointcolor[1:length(pr)]levels(igraph.col$Genus) <- pr_colorV(igraph)$color <- as.character(igraph.col$Genus)# 按模块着色# fc <- cluster_fast_greedy(igraph, weights=NULL)# modularity <- modularity(igraph, membership(fc))# comps <- membership(fc)# colbar <- rainbow(max(comps))# V(igraph)$color <- colbar[comps]filename <- paste0("../figure/03.Network/", type, "_Sparcc.pdf")pdf(file = filename, width = 10, height = 10)plot(igraph,main="Co-occurrence network",layout=layout_in_circle,edge.lty=1,edge.curved=TRUE,margin=c(0,0,0,0))legend(x=.8, y=-1, bty = "n",legend=pr,fill=pr_color, border=NA)text(x=.3, y=-1.2, labels=number_cor, cex = 1.5)dev.off()# calculate OTU remain_cor_sum <- apply(remain_cor, 1, function(x){res1 <- as.numeric(length(x[x>0]))res2 <- as.numeric(length(x[x<0]))res <- c(res1, res2)}) %>% t() %>% data.frame() %>%setNames(c("Negative", "Positive")) %>%rownames_to_column("OTUID")file_cor <- paste0("../figure/03.Network/", type, "_Sparcc_negpos.csv")write.csv(remain_cor_sum, file = file_cor, row.names = F)
}
运行画图函数
cornet_plot(mcor=dat_cor, mpval=dat_pval, mrb=dat_rb5, tax=dat_tax, type="dat_5")
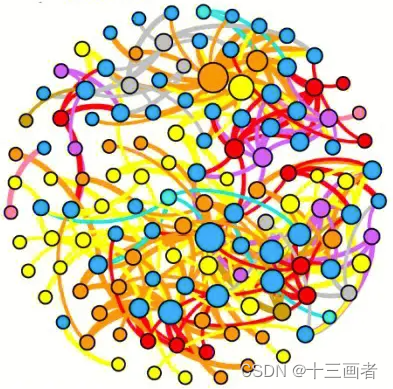
R information
sessionInfo()
R version 4.0.2 (2020-06-22)
Platform: x86_64-w64-mingw32/x64 (64-bit)
Running under: Windows 10 x64 (build 19042)Matrix products: defaultlocale:
[1] LC_COLLATE=English_United States.1252 LC_CTYPE=English_United States.1252 LC_MONETARY=English_United States.1252
[4] LC_NUMERIC=C LC_TIME=English_United States.1252
system code page: 936attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base other attached packages:
[1] psych_2.0.9 igraph_1.2.5 tibble_3.0.3 dplyr_1.0.2 loaded via a namespace (and not attached):[1] lattice_0.20-41 crayon_1.3.4 grid_4.0.2 R6_2.5.0 nlme_3.1-150 lifecycle_0.2.0 magrittr_1.5 [8] pillar_1.4.6 rlang_0.4.7 rstudioapi_0.11 vctrs_0.3.4 generics_0.1.0 ellipsis_0.3.1 tools_4.0.2
[15] glue_1.4.2 purrr_0.3.4 parallel_4.0.2 xfun_0.19 yaml_2.2.1 compiler_4.0.2 pkgconfig_2.0.3
[22] mnormt_2.0.2 tmvnsim_1.0-2 knitr_1.30 tidyselect_1.1.0
参考
-
SparCC3
-
sparcc.pdf
-
sparcc tutorial
-
Co-occurrence网络图在R中的实现
这篇关于数据分析:基于sparcc的co-occurrence网络的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






