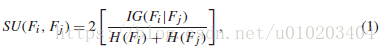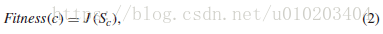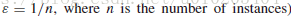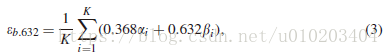本文主要是介绍马尔可夫毯式遗传算法在基因选择中的应用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
#引用
##LaTex
@article{ZHU20073236,
title = “Markov blanket-embedded genetic algorithm for gene selection”,
journal = “Pattern Recognition”,
volume = “40”,
number = “11”,
pages = “3236 - 3248”,
year = “2007”,
issn = “0031-3203”,
doi = “https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2007.02.007”,
url = “http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320307000945”,
author = “Zexuan Zhu and Yew-Soon Ong and Manoranjan Dash”,
keywords = “Microarray, Feature selection, Markov blanket, Genetic algorithm (GA), Memetic algorithm (MA)”
}
##Normal
Zexuan Zhu, Yew-Soon Ong, Manoranjan Dash,
Markov blanket-embedded genetic algorithm for gene selection,
Pattern Recognition,
Volume 40, Issue 11,
2007,
Pages 3236-3248,
ISSN 0031-3203,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2007.02.007.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320307000945)
Keywords: Microarray; Feature selection; Markov blanket; Genetic algorithm (GA); Memetic algorithm (MA)
#摘要
Microarray technologies
the smallest possible set of genes
Markov blanket-embedded genetic algorithm (MBEGA) for gene selection problem
Markov blanket and predictive power in classifier model
filter, wrapper, and standard GA
evaluation criteria:
classification accuracy, number of selected genes, computational cost, and robustness
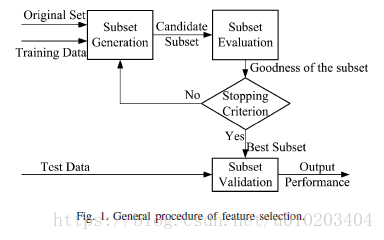
#主要内容
##Markov Blanket(Markov毯)
F F F — 所有特征的集合
C C C — 类别
一个特征 F i F_i Fi的Markov毯 定义如下:
定义(Markov毯)
M M M — 一个特征子集(不包含 F i F_i Fi)
即, M ∈ F M \in F M∈F且 F i ∉ M F_i \notin M Fi∈/M。
M M M为 F i F_i Fi的一个Markov毯,若
给定 M M M, F i F_i Fi是对于 ( F ∪ C ) − M − { F i } \left( F \cup C \right) - M - \left\{ F_i \right\} (F∪C)−M−{Fi}条件独立的,
即, P ( F − M − { F i } , C ∣ F i , M ) = P ( F − M − { F i } , C ∣ M ) P \left( F - M - \left\{ F_i \right\}, C | F_i, M \right) = P \left( F - M - \left\{ F_i \right\}, C | M \right) P(F−M−{Fi},C∣Fi,M)=P(F−M−{Fi},C∣M)
给定X,两个属性A与B是条件独立的,若$P \left( A | X, B \right) = P \left( A | X \right) , 也 就 是 说 , B 并 不 能 在 X 之 外 提 供 关 于 A 的 信 息 。 若 一 个 特 征 ,也就是说,B并不能在X之外提供关于A的信息。若一个特征 ,也就是说,B并不能在X之外提供关于A的信息。若一个特征F_i 在 当 前 选 择 的 特 征 子 集 中 有 一 个 M a r k o v 毯 在当前选择的特征子集中有一个Markov毯 在当前选择的特征子集中有一个Markov毯M , 那 么 ,那么 ,那么F_i 在 在 在M 之 外 关 于 之外关于 之外关于C 不 能 提 供 其 他 选 择 的 特 征 的 信 息 , 因 此 , 不能提供其他选择的特征的信息,因此, 不能提供其他选择的特征的信息,因此,F_i 能 够 安 全 移 除 。 然 而 , 决 定 特 征 的 条 件 独 立 的 计 算 复 杂 度 通 常 非 常 高 , 因 此 , 只 使 用 一 个 特 征 来 估 计 能够安全移除。然而,决定特征的条件独立的计算复杂度通常非常高,因此,只使用一个特征来估计 能够安全移除。然而,决定特征的条件独立的计算复杂度通常非常高,因此,只使用一个特征来估计F_i$的Markov毯。
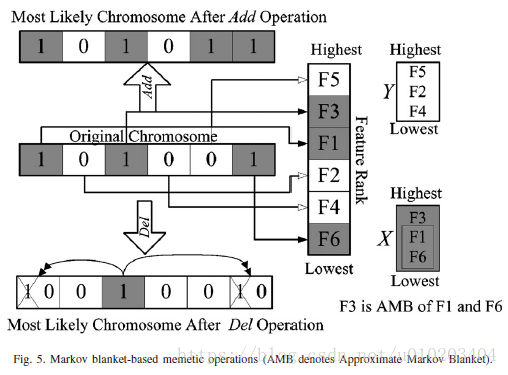
定义(近似Markov毯)
对于两个特征 F i F_i Fi与 F j F_j Fj i ≠ j i\neq j i̸=j, F j F_j Fj可看作为 F i F_i Fi的近似Markov毯,若 S U j , C ≥ S U i , C SU_{j,C} \geq SU_{i,C} SUj,C≥SUi,C 且 S U i , j ≥ S U i , C SU_{i,j} \geq SU_{i,C} SUi,j≥SUi,C,其中,
对称不确定性(symmetrical uncertainty,SU)度量特征(包括类, C C C)间的相关性,定义为:
I G ( F i ∣ F j ) IG \left( F_i | F_j \right) IG(Fi∣Fj) — 特征 F i F_i Fi与 F j F_j Fj间的信息增益
H ( F i ) H \left( F_i \right) H(Fi)与 H ( F j ) H \left( F_j \right) H(Fj) — 特征 F i F_i Fi与 F j F_j Fj的熵
S U i , C SU_{i,C} SUi,C — 特征 F i F_i Fi与类 C C C间的相关性,称为C-correlation
一个特征被认为是相关的若其C-correlation高于用户给定的阈值 γ \gamma γ,即, S i , C > γ S_{i,C} > \gamma Si,C>γ
没有任何近似Markov毯的特征为predominant feature主导特征
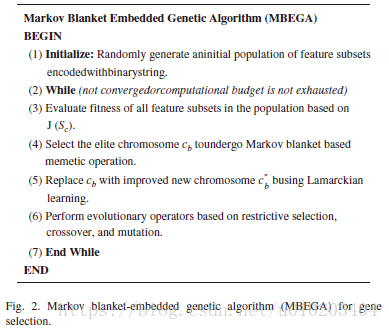
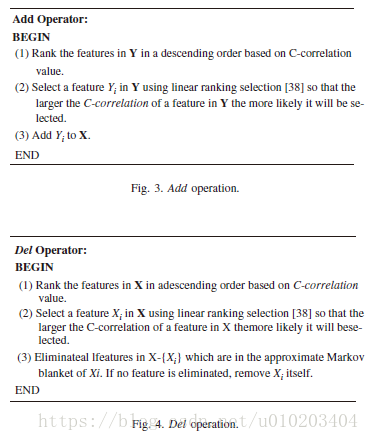
##马尔可夫毯式嵌入式遗传算法
若适应值差异小于 ε \varepsilon ε,则特征数较少的个体较好
Lamarckian learning:
通过将局部改进的个体放回种群竞争繁殖的机会,来迫使基因型反映改进的效果
X X X — 选择的特征子集
Y Y Y — 排除的特征子集
C-correlation 只计算一次
搜索范围 L L L — 定义了 A d d Add Add与 D e l Del Del操作的最大数目 — L 2 L^2 L2个操作组合
随机顺序 — 直到得到改进提升效果
Lamarckian learning process
之后是
usual evolutionary operations:
- linear ranking selection
- uniform crossover
- mutation operators with elitism
##试验
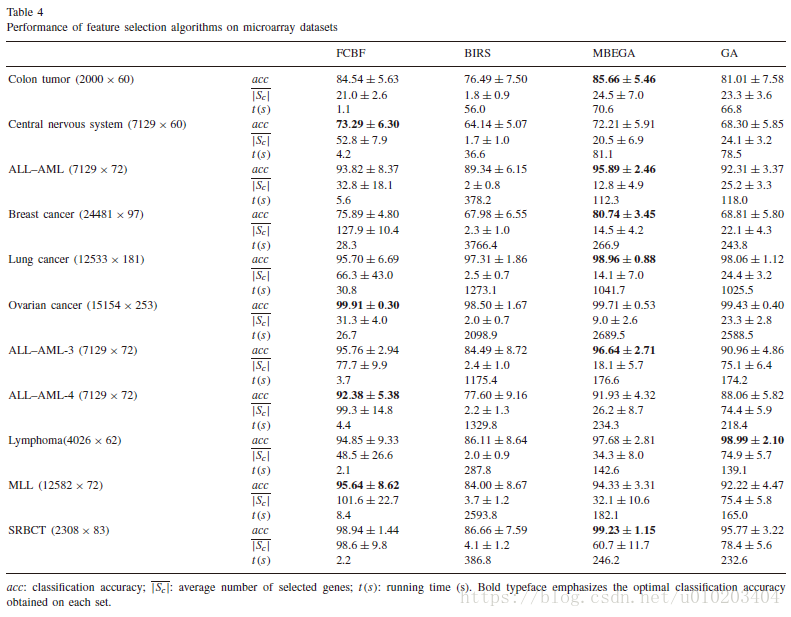
MBEGA method
考虑了:
- the FCBF (fast correlation-based filter)
- BIRS (best incremental ranked subset)
- standard GA feature selection algorithms
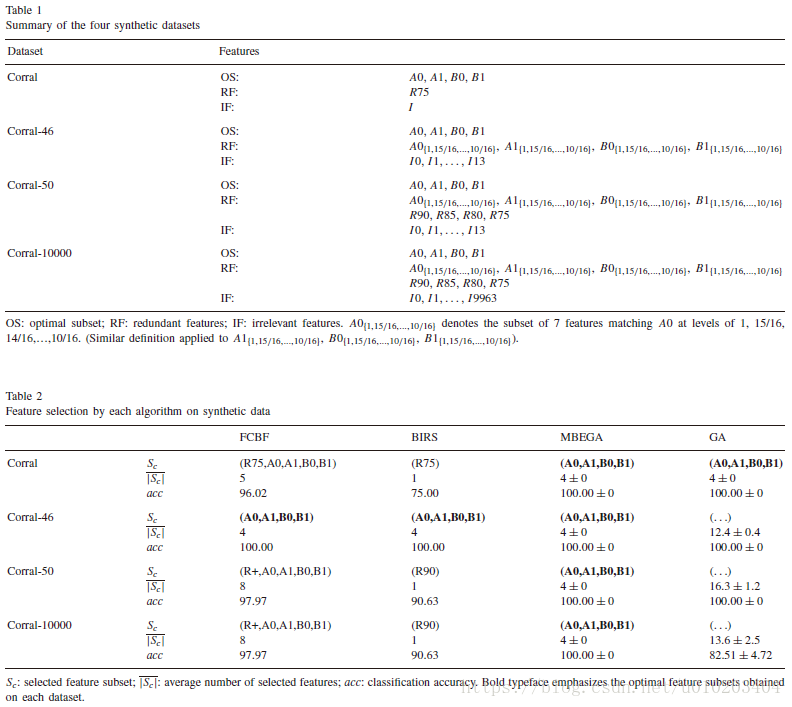
FCBF —
a fast correlation based filter method
- selecting a subset of relevant features whose C-correlation are larger than a given threshold γ \gamma γ
- sorts the relevant features in descending order in terms of C-correlation
- redundant features are eliminated one-by-one in a descending order
A feature is redundant 仅当 it has an approximate Markov blanket
predominant features with zero redundant features in terms of C-correlation
BIRS — a similar scheme as the FCBF
evaluates the goodness of features using a classifier
- ranking the genes according to some measure of interest
- sequentially selects the ranked features one-by-one based on their incremental usefulness
calls to the classifier as many times as the number of features
B I R S F BIRS_F BIRSF or B I R S W BIRS_W BIRSW — 基于 — C-correlation (i.e., symmetrical uncertainty between feature F i F_i Fi and the class C C C) or individual predictive power
B I R S F BIRS_F BIRSF 耗时更少
###synthetic data 合成数据
ten 10-fold crossvalidations
with C4.5 classifier
10 independent runs
The maximum number of selected features in each chromosome, m, is set to 50.
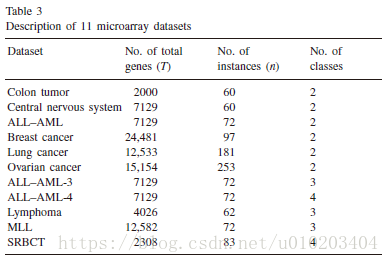
###microarray data 微阵列数据
The .632+ bootstrap
K次重采样
the support vector machine (SVM) — microarray classification problems
one-versus-rest strategy — multi-class datasets
the linear kernel SVM
这篇关于马尔可夫毯式遗传算法在基因选择中的应用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!