本文主要是介绍FrameLayou和UI的布局优化(merge、include、ViewStub),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
FrameLayout 先来看官方文档的定义:FrameLayout是最简单的一个布局对象。它被定制为你屏幕上的一个空白备用区域,之后你可以在其中填充一个单一对象 — 比如,一张你要发布的图片。所有的子元素将会固定在屏幕的左上角;你不能为FrameLayout中的一个子元素指定一个位置。后一个子元素将会直接在前一个子元素之上进行覆盖填充,把它们部份或全部挡住(除非后一个子元素是透明的)。
我的理解是,把FrameLayout当作画布canvas,固定从屏幕的左上角开始填充图片,文字等。看看示例,原来可以利用android:layout_gravity来设置位置的:
<?xml
version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"
><ImageView
android:id="@+id/image"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"android:scaleType="center"android:src="@drawable/candle"/><TextView
android:id="@+id/text1"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_gravity="center"android:textColor="#00ff00"android:text="@string/hello"/><Button
android:id="@+id/start"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_gravity="bottom" android:text="Start"/>
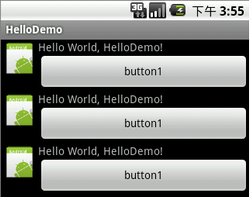
</FrameLayout>效果图

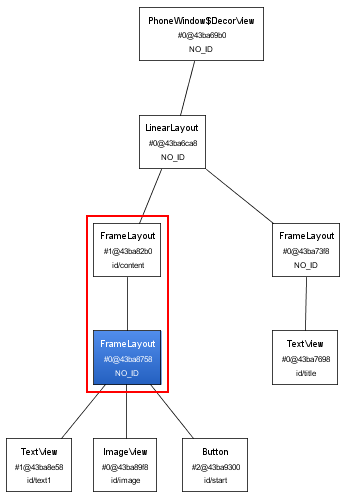
布局优化 使用tools里面的hierarchyviewer.bat来查看layout的层次。在启动模拟器启动所要分析的程序,再启动hierarchyviewer.bat,选择模拟器以及该程序,点击“Load View Hierarchy”,就会开始分析。可以save as png。
< merge> 减少视图层级结构
从上图可以看到存在两个FrameLayout,红色框住的。如果能在layout文件中把FrameLayout声明去掉就可以进一步优化布局代码了。 但是由于布局代码需要外层容器容纳,如果
直接删除FrameLayout则该文件就不是合法的布局文件。这种情况下就可以使用< merge> 标签了。
修改为如下代码就可以消除多余的FrameLayout了:
<?xml
version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"><ImageView
android:id="@+id/image"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"android:scaleType="center"android:src="@drawable/candle"/><TextView
android:id="@+id/text1"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_gravity="center"android:textColor="#00ff00"android:text="@string/hello"/><Button
android:id="@+id/start"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_gravity="bottom"android:text="Start"/>
</merge>< merge>也有一些使用限制: 只能用于xml layout文件的根元素;在代码中使用LayoutInflater.Inflater()一个以merge为根元素的
布局文件时候,需要使用View inflate (int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)指定一个ViewGroup 作为其容器,并且要设置attachToRoot 为true。
< include> 重用layout代码
如果在某个布局里面需要用到另一个相同的布局设计,可以通过< include> 标签来重用layout代码:
<?xml
version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:orientation="vertical"android:layout_width="fill_parent"android:layout_height="fill_parent"><include
android:id="@+id/layout1"
layout="@layout/relative"
/><include
android:id="@+id/layout2"
layout="@layout/relative"
/><include
android:id="@+id/layout3"
layout="@layout/relative"
/>
</LinearLayout>效果图
这里要注意的是,”@layout/relative”不是引用Layout的id,而是引用res/layout/relative.xml,其内容是前面文章介绍RelativeLayout的布局代码。
另外,通过< include>,除了可以覆写id属性值,还可以修改其他属性值,例如android:layout_width,android:height等。
< viewstub> 延迟加载
(转自http://rainhomepage.appspot.com/2010/01/use-viewstub-to-optimize-the-layout-of)
ViewStub 是一个不可见的,大小为0的View,最佳用途就是实现View的延迟加载,在需要的时候再加载View,可Java中常见的性能优化方法延迟加载一样。
当调用ViewStub的setVisibility函数设置为可见或则调用 inflate初始化该View的时候,ViewStub引用的资源开始初始化,然后引用的资源替代ViewStub自己的位置填充在ViewStub的 位置。因此在没有调用setVisibility(int) 或则 inflate()函数之前 ViewStub一种存在组件树层级结构中,但是由于ViewStub非常轻量级,这对性能影响非常小。 可以通过ViewStub的inflatedId属性来重新定义引用的layout id。 例如:
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/stub"android:inflatedId="@+id/subTree"android:layout="@layout/mySubTree"android:layout_width="120dip"android:layout_height="40dip"
/>上面定义的ViewStub,可以通过id“stub”来找到,在初始化资源“mySubTree”后,stub从父组件中删除,然后”mySubTree”替代stub的位置。初始资源”mySubTree”得到的组件可以通过inflatedId 指定的id “subTree”引用。 然后初始化后的资源被填充到一个120dip宽、40dip高的地方。
推荐使用下面的方式来初始化ViewStub:
ViewStub stub = (ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub);
View inflated = stub.inflate();
当调用inflate()函数的时候,ViewStub 被引用的资源替代,并且返回引用的view。 这样程序可以直接得到引用的view而不用再次调用函数 findViewById()来查找了。
ViewStub目前有个缺陷就是还不支持 < merge /> 标签。
layoutopt (Layout Optimization工具)
这工具可以分析所提供的Layout,并提供优化意见。在tools文件夹里面可以找到layoutopt.bat。
用法:
layoutopt < list of xml files or directories>
参数:
一个或多个的Layout xml文件,以空格间隔;或者多个Layout xml文件所在的文件夹路径
例子:
layoutopt G:/StudyAndroid/UIDemo/res/layout/main.xml
layoutopt G:/StudyAndroid/UIDemo/res/layout/main.xml G:/StudyAndroid/UIDemo/res/layout/relative.xml
layoutopt G:/StudyAndroid/UIDemo/res/layout
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/hmg25/article/details/6203130
这篇关于FrameLayou和UI的布局优化(merge、include、ViewStub)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!