本文主要是介绍poj 2007 Scrambled Polygon(凸多边形顶点输出),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=2007
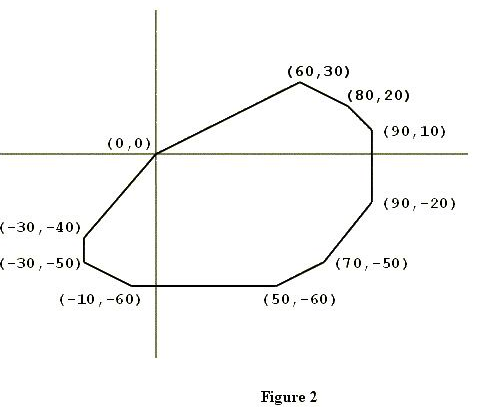
描述:从(0,0)点开始输入一个凸多边形,这个凸多边形,占有三个象限,按照逆时针的方式输出各定点。
输出例子:
Sample Input
0 0
70 -50
60 30
-30 -50
80 20
50 -60
90 -20
-30 -40
-10 -60
90 10
Sample Output
(0,0)
(-30,-40)
(-30,-50)
(-10,-60)
(50,-60)
(70,-50)
(90,-20)
(90,10)
(80,20)
(60,30)
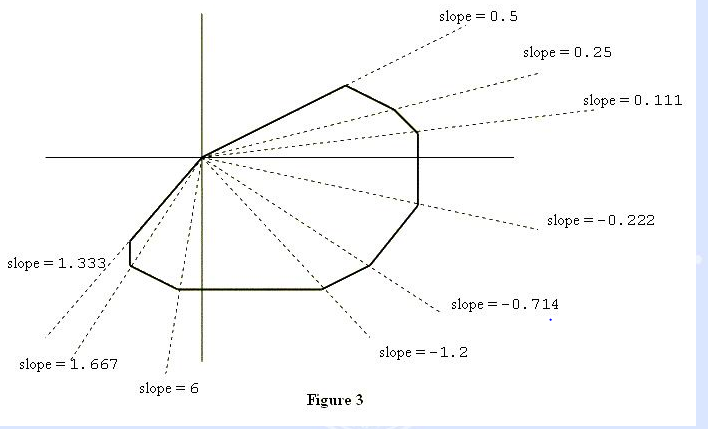
思路:从上图可以看出各象限都是斜率递增方式,建立4个vector对应四个象限,然后分别将各象限的点存储到相应的vector,最后对vector中的数据排序输出。(思路比较水)
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Vertice{
int x,y;
};
bool operator<(const Vertice &a, const Vertice &b)
{
return atan2((double)a.y, (double)a.x)<atan2((double)b.y, (double)b.x);
}
int main()
{
Vertice point;
vector<Vertice> ivec[4];
int i=0;
while(scanf("%d%d", &point.x, &point.y)!= EOF){
//while(i++<10){
//scanf("%d%d", &point.x, &point.y);
if(point.x>0&&point.y>0)
ivec[0].push_back(point);
else if(point.x<0&&point.y>0)
ivec[1].push_back(point);
else if(point.x<0&&point.y<0)
ivec[2].push_back(point);
else if(point.x>0&&point.y<0)
ivec[3].push_back(point);
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
if(ivec[i].size()!=0){
sort(ivec[i].begin(),ivec[i].end());
}
}
cout<<"(0,0)"<<endl;
int begin;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){//找出凸边形的起始点
if(ivec[i].size()==0){
begin = (i+1)%4;
break;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
int t = (begin+i)%4;
if(ivec[t].size()!=0){
vector<Vertice>::iterator it;
for(it=ivec[t].begin();it!=ivec[t].end();it++){
cout<<"("<<it->x<<","<<it->y<<")"<<endl;
}
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
网友:http://www.cnblogs.com/rainydays/archive/2011/09/02/2163310.html
View Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 55
#define pi acos(-1)
struct Point
{
int x, y;
} point[maxn];
bool operator <(const Point &a, const Point &b)
{
return atan2(a.y, a.x) < atan2(b.y, b.x);
}
double cal(double a)
{
if (a < 0)
return a + 2 * pi;
return a;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("t.txt", "r", stdin);
scanf("%d%d", &point[0].x, &point[0].y);
int n = 0;
while (scanf("%d%d", &point[n].x, &point[n].y) != EOF)
n++;
sort(point, point + n);//按照artan角度排序
double temp = 0;
point[n] = point[0];
int s;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
double a = cal(atan2(point[i + 1].y, point[i + 1].x) - atan2(point[i].y, point[i].x));//若前后两点之间的角度相差最大,这里就是凸边形的起始位置
if (a > temp)
{
temp = a;
s = (i + 1) % n;
}
}
printf("(0,0)\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("(%d,%d)\n", point[(s + i) % n].x, point[(s + i) % n].y);
return 0;
}
这篇关于poj 2007 Scrambled Polygon(凸多边形顶点输出)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!