本文主要是介绍转录组上游分析,Count计算,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本期教程原文链接:转录组定量,最简单的操作,你会吗?
本期教程

第六章 转录本定量分析
定量软件有RSEM,eXpress,salmoe,kallisto,featureCounts。在网络中吗,都有比较详细的教程,大家可以自己去学习。
本教程中推荐使用两种方式获得转录本的表达量,stringtie -eB,featureCounts,stringtie自带的脚本程序prepDE.py。
6.1 Stringtie -eB
Stringtie -eB是通过stringtie组装后的merge.gtf注释信息二次与.bam文件进行转录本表达量的比对,获得转录本的FPKM,此后使用Ballgown 包结合使用,进行后续的分析。详情可看Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown, 2016, Nat Protoc一文。
此步骤操作后,每个样本会获得新的gtf文件。
stringtie –e –B -p 8 -G stringtie_merged.gtf -o ballgown/ERR188245/ERR188245_chrX.gtf ERR188245_chrX.bam
使用R语言中的ballgown进行分析

pheno_data = read.csv("geuvadis_phenodata.csv")
bg_chrX = ballgown(dataDir = "ballgown", samplePattern = "ERR", pData=pheno_data)
bg_chrX_filt = subset(bg_chrX,"rowVars(texpr(bg_chrX)) >1",genomesubset=TRUE)
results_transcripts = stattest(bg_chrX_filt, feature="transcript",covariate="sex",adjustvars = c("population"), getFC=TRUE, meas="FPKM")
##
# Identify genes that show statistically significant differences between groups. For this we can run the same function that we used to identify differentially expressed transcripts, but here we set feature="gene" in the stattest command:
results_genes = stattest(bg_chrX_filt, feature="gene", covariate="sex", adjustvars = c("population"), getFC=TRUE, meas="FPKM")# Add gene names and gene IDs to the results_transcripts data frame:
results_transcripts = data.frame(geneNames=ballgown::geneNames(bg_chrX_filt), geneIDs=ballgown::geneIDs(bg_chrX_filt), results_transcripts)#Sort the results from the smallest P value to the largest:
results_transcripts = arrange(results_transcripts,pval)
results_genes = arrange(results_genes,pval)
# Write the results to a csv file that can be shared and distributed:
write.csv(results_transcripts, "chrX_transcript_results.csv", row.names=FALSE)
write.csv(results_genes, "chrX_gene_results.csv", row.names=FALSE)
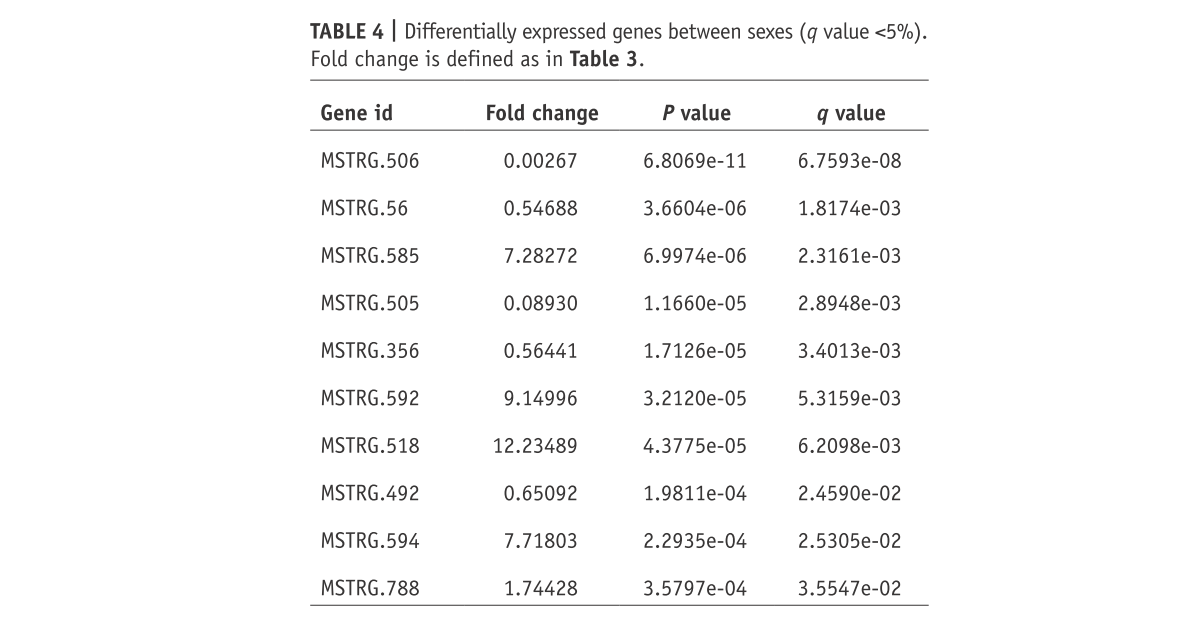
# Identify transcripts and genes with a q value <0.05:
subset(results_transcripts,results_transcripts$qval<0.05)
subset(results_genes,results_genes$qval<0.05)
# Make the plots pretty. This step is optional, but if you do run it you will get the plots in the nice colors that we used to generate our figures:tropical= c('darkorange', 'dodgerblue', 'hotpink', 'limegreen', 'yellow')
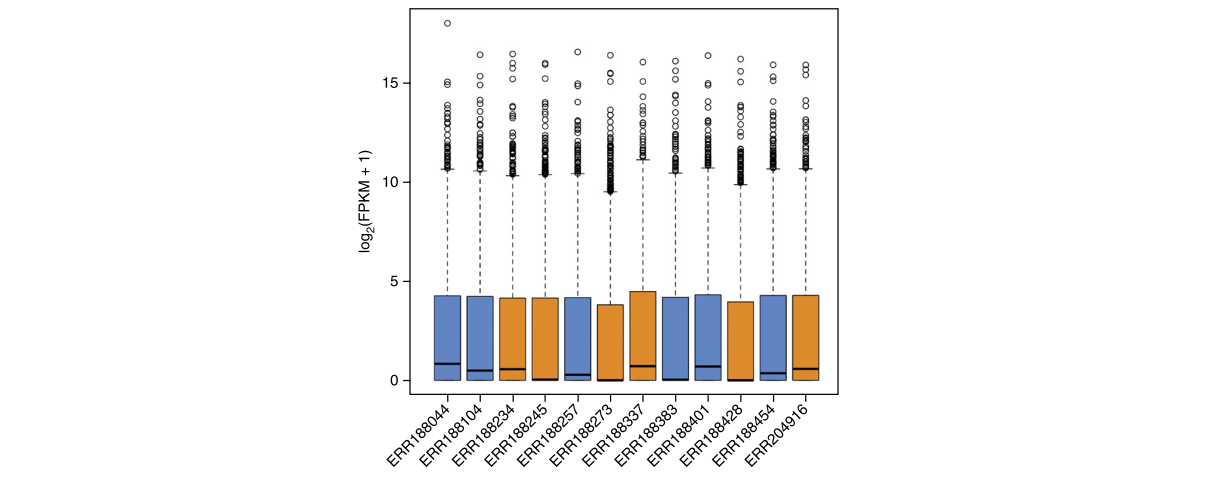
palette(tropical)## Show the distribution of gene abundances (measured as FPKM values) across samples, colored by sex (Fig. 3).
fpkm = texpr(bg_chrX,meas="FPKM")
fpkm = log2(fpkm+1)
boxplot(fpkm,col=as.numeric(pheno_data$sex),las=2,ylab='log2(FPKM+1)')
# Make plots of individual transcripts across samples. For example, here we show how to create a plot for the 12th transcript in the data set (Fig. 4). The first two commands below show the name of the transcript (NM_012227) and the name of the gene that contains it (GTP binding protein 6, GTPBP6):
ballgown::transcriptNames(bg_chrX)[12]
## 12
## "NM_012227"
ballgown::geneNames(bg_chrX)[12]
## 12
## "GTPBP6"
plot(fpkm[12,] ~ pheno_data$sex, border=c(1,2), main=paste(ballgown::geneNames(bg_chrX)[12],' :', ballgown::transcriptNames(bg_chrX)[12]),pch=19, xlab="Sex", ylab='log2(FPKM+1)')
points(fpkm[12,] ~ jitter(as.numeric(pheno_data$sex)), col=as.numeric(pheno_data$sex))

6.2 Stringtie中的prepDE.py程序
prepDE.py是stringtie软件中自带的获得转录本丰度的脚本,6.1中的HISAT2+Stringtie+Ballgown是一组黄金组合,但是还有很多的局限性。因此,个人建议仍是获得count值,后再进一步的分析,这样的方法更利于下游分析。
具体详情可查看官方文档:http://ccb.jhu.edu/software/stringtie/index.shtml?t=manual
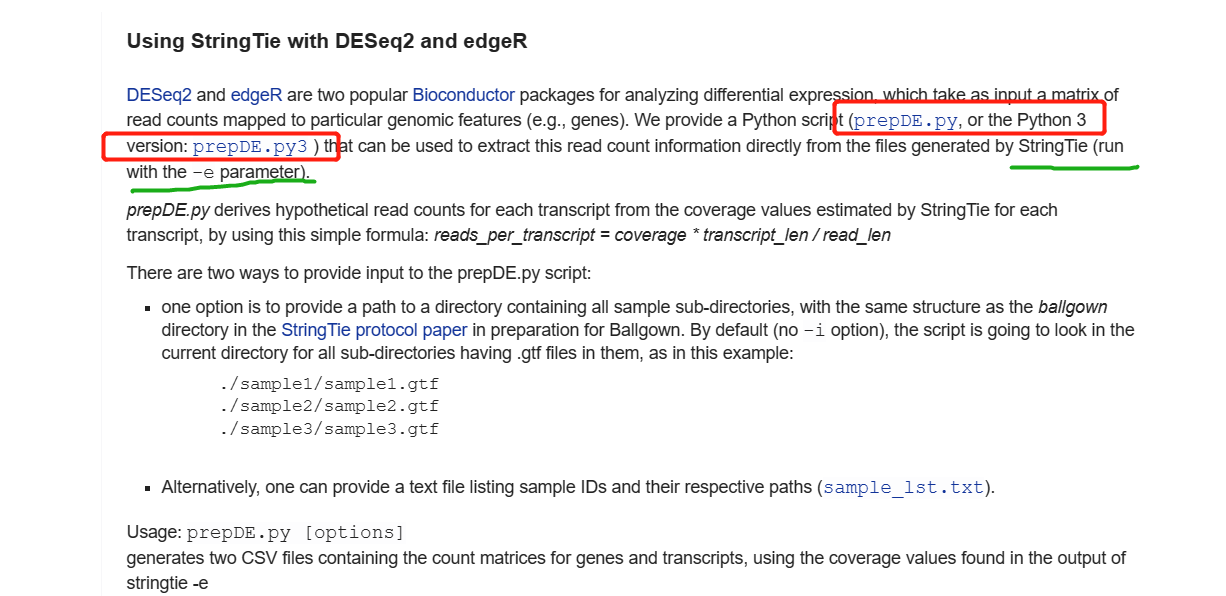
注意:
prepDE.py脚本需要输入strintie -e输出的gtf文件- 此外,需要获得gtf文件的路径,sample_lst.txt
本期教程原文链接:转录组定量,最简单的操作,你会吗?
prepDE.py -h
Usage: prepDE.py [options]Generates two CSV files containing the count matrices for genes and
transcripts, using the coverage values found in the output of `stringtie -e`Options:-h, --help show this help message and exit-i INPUT, --input=INPUT, --in=INPUTa folder containing all sample sub-directories, or atext file with sample ID and path to its GTF file oneach line [default: ./]-g G where to output the gene count matrix [default:gene_count_matrix.csv-t T where to output the transcript count matrix [default:transcript_count_matrix.csv]-l LENGTH, --length=LENGTHthe average read length [default: 75]-p PATTERN, --pattern=PATTERNa regular expression that selects the samplesubdirectories-c, --cluster whether to cluster genes that overlap with differentgene IDs, ignoring ones with geneID pattern (seebelow)-s STRING, --string=STRINGif a different prefix is used for geneIDs assigned byStringTie [default: MSTRG]-k KEY, --key=KEY if clustering, what prefix to use for geneIDs assignedby this script [default: prepG]-v enable verbose processing--legend=LEGEND if clustering, where to output the legend file mappingtranscripts to assigned geneIDs [default: legend.csv]
- 运行:
python prepDE.py -i sample_lst.txt
## 或服务器中的Python版本是Python2或python3
prepDE.py -i sample_lst.txt
#or
prepDE.py3 -i sample_lst.txt
- sample_lst.txt ,根据自己
stringtie -e -B的输出路径进行设置
04_Result/Stringtie_eB/SRR6929571/SRR6929571.gtf
04_Result/Stringtie_eB/SRR6929572/SRR6929572.gtf
04_Result/Stringtie_eB/SRR6929573/SRR6929573.gtf
04_Result/Stringtie_eB/SRR6929574/SRR6929574.gtf
04_Result/Stringtie_eB/SRR6929577/SRR6929577.gtf
04_Result/Stringtie_eB/SRR6929578/SRR6929578.gtf
- 输出结果:
最终获得gene_count_matrix.csv转录本文件,利用此文件即可进行下有分析。
gene_count_matrix.csv
transcript_count_matrix.csv
每个基因间使用,号隔开
## gene_count_matrix.csv
gene_id,SRR6929571,SRR6929572,SRR6929573,SRR6929574,SRR6929577,SRR6929578
gene:Solyc02g160570.1,0,0,0,0,0,0
gene:Solyc02g161280.1,0,0,0,0,0,0
gene:Solyc01g017370.2,0,0,0,0,0,0
MSTRG.28366,3998,4147,4277,3955,4164,2001## transcript_count_matrix.csv
transcript_id,SRR6929571,SRR6929572,SRR6929573,SRR6929574,SRR6929577,SRR6929578
mRNA:Solyc06g071220.1.1,19,26,41,62,110,33
mRNA:Solyc07g161730.1.1,0,0,0,0,0,0
MSTRG.23978.1,3,0,0,0,0,0
mRNA:Solyc06g062940.5.1,27523,17069,18415,14892,15523,36301
MSTRG.28358.2,13,18,57,32,6,9
mRNA:Solyc05g055535.1.1,0,0,0,0,0,0
MSTRG.28358.1,123,20,410,192,52,134为方便下一步的分析,可以,号转变成\t分隔符,常说的Tab分隔符。
sed 's/,/\t/g' gene_count_matrix.csv > 01.gene_count.csv
本期教程原文链接:转录组定量,最简单的操作,你会吗?
6.3 featureCounts的使用
featureCounts是subread中脚本,可以使用subread流程进行定量,在这里直接使用前面mapped的bam文件进行转录本定量。
安装:
conda安装
conda install -y subread
源码安装:
官网:[https://sourceforge.net/projects/subread/
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/subread/files/subread-2.0.3/subread-2.0.3-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz
tar -zxvf subread-2.0.3-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz
cd subread-2.0.3-Linux-x86_64
cd bin/
#
echo 'PATH=$PATH:~/software/subread-2.0.3-Linux-x86_64/bin' >> ~/.bachrc
运行:
使用featureCounts进行定量的bam文件,我建议使用前期使用hisat2。bowtie2,bwa,或是STAR等mapped的文件。
- featureCounts可以对转录本(
trancript_id)进行定量 - featureCounts也可以对基因(
gene_id)进行定量
Usage: featureCounts [options] -a <annotation_file> -o <output_file> input_file1 [input_file2] ...
–
featureCounts -T 5 -p -t exon -g transcript_id -a annotation.gtf -o counts.txt *.bam
参数:
-T 运行线程数
-t 设置feature-type,在GTF注释中指定特征类型。如果提供多个类型,它们之间应以','隔开,中间没有空格。默认情况下是 "exon"
-g GTF注释文件需要计算的基因或转录本的表达水平。默认是:gene_id,可选择transcript_id
-a提供的注释文件,可以是参考基因组的annotation.gtf,也可以是组转后的gtf文件
-J对可变剪切进行计数
-G < string >当-J设置的时候,通过-G提供一个比对的时候使用的参考基因组文件,辅助寻找可变剪切
-o < string >输出文件的名字,输出文件的内容为read 的统计数目
-O允许多重比对,即当一个read比对到多个feature或多个metafeature的时候,这条read会被统计多次
-d < int >最短的fragment,默认是50
-D < int >最长的fragmen,默认是600-p能用在paired-end的情况中,会统计fragment而不统计read
-B在-p选择的条件下,只有两端read都比对上的fragment才会被统计
-C在-p选择的条件下,只有两端read都比对上的fragment才会被统计
运行:
featureCounts -T 20 -p -t exon -g transcript_id -a stringtie_merged.gtf -o All.transcript.count.txt *.sort.bam
获得结果:
All.transcript.count.txt
All.transcript.count.txt.summary
本期教程原文链接:转录组定量,最简单的操作,你会吗?
- count结果

6.4 Htseq定量
HTseq-count也是一个比较常用的软件,与featureCount功能一样用来计数(count)
安装:
conda install -y htseq

htseq-count -f bam -r name -s no -a 10 -t exon -i gene_id -m intersection-nonempty yourfile_name.bam ~/reference/hisat2_reference/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.86.chr_patch_hapl_scaff.gtf > counts.txt
usage: htseq-count [options] alignment_file gff_file-f {sam,bam} (default: sam)#设置输入文件的格式,该参数的值可以是sam或bam。
-r {pos,name} (default: name)#设置sam或bam文件的排序方式,该参数的值可以是name或pos。#前者表示按read名进行排序,后者表示按比对的参考基因组位置进行排序。#若测序数据是双末端测序,当输入sam/bam文件是按pos方式排序的时候,#两端reads的比对结果在sam/bam文件中一般不是紧邻的两行,#程序会将reads对的第一个比对结果放入内存,直到读取到另一端read的比对结果。#因此,选择pos可能会导致程序使用较多的内存,它也适合于未排序的sam/bam文件。#而pos排序则表示程序认为双末端测序的reads比对结果在紧邻的两行上,#也适合于单端测序的比对结果。很多其它表达量分析软件要求输入的sam/bam文件是按pos排序的,但HTSeq推荐使用name排序,且一般比对软件的默认输出结果也是按name进行排序的。
-s {yes,no,reverse} (default: yes) #数据是否来源于链特异性测序,链特异性是指在建库测序时,只测mRNA反转录出的cDNA序列,而不测该cDNA序列反向互补的另一条DNA序列;换句话说就是,链特异性能更准确反映出mRNA的序列信息
-a MINAQUAL (default: 10)#忽略比对质量低于此值的比对结果
-t FEATURETYPE #feature type (3rd column in GFF file) to be used, all features of other type are ignored (default, suitable for Ensembl GTF files: exon)#程序会对该指定的feature(gtf/gff文件第三列)进行表达量计算,而gtf/gff文件中其它的feature都会被忽略。
-i IDATTR#GFF attribute to be used as feature ID (default, suitable for Ensembl GTF files: gene_id)#设置feature ID是由gtf/gff文件第9列那个标签决定的;若gtf/gff文件多行具有相同的feature ID,则它们来自同一个feature,程序会计算这些features的表达量之和赋给相应的feature ID。
-m {union,intersection-strict,intersection-nonempty} (default: union)#设置表达量计算模式。该参数的值可以有union, intersection-strict and intersection-nonempty。这三种模式的选择请见上面对这3种模式的示意图。从图中可知,对于原核生物,推荐使用intersection-strict模式;对于真核生物,推荐使用union模式。
-o | --samout#输出一个sam文件,该sam文件的比对结果中多了一个XF标签,表示该read比对到了某个feature上。
-n #指定多线程,默认是1
运行Htseq-count:
htseq-count -f bam -r name -s no -a 10 -t exon -i transcript_id -m intersection-strict ../../03_MappedFile/Hisat2_Mapped/*.bam ../../02_Geneome_index/ITAG4.1_gene_models.gtf > htseq_counts.txt
6.5 其他流程
salmon 流程
软件官网:https://combine-lab.github.io/salmon/
6.6 Count to FPKM
- count to FPKM
使用Perl脚本进行转换
## 需要信息
1. 基因名
2. 基因长度
3. count值
使用cut提取信息:
cat All.transcript.count.txt | cut -f 1,6-13 > 01.all.count.txt
运行perl脚本:
perl CountToFPKM.pl 01.all.count.txt > 02.all.FPKM.txt
CountToFPKM.pl脚本:

本期教程原文链接:转录组定量,最简单的操作,你会吗?
往期教程部分内容





往期部分文章
1. 复现SCI文章系列专栏
2. 《生信知识库订阅须知》,同步更新,易于搜索与管理。
3. 最全WGCNA教程(替换数据即可出全部结果与图形)
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码一
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码二
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程代码分享 | 代码三
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码四
-
WGCNA分析 | 全流程分析代码 | 代码五(最新版本)
4. 精美图形绘制教程
- 精美图形绘制教程
5. 转录组分析教程
-
转录组上游分析教程[零基础]
-
一个转录组上游分析流程 | Hisat2-Stringtie
6. 转录组下游分析
-
批量做差异分析及图形绘制 | 基于DESeq2差异分析
-
GO和KEGG富集分析
-
单基因GSEA富集分析
-
全基因集GSEA富集分析
小杜的生信筆記 ,主要发表或收录生物信息学的教程,以及基于R的分析和可视化(包括数据分析,图形绘制等);分享感兴趣的文献和学习资料!!
这篇关于转录组上游分析,Count计算的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



