本文主要是介绍5种语言实现 | 使用Dijkstra算法从起点到所有节点找到最短路径,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
编辑:东岸因为@一点人工一点智能
5种语言实现 | 使用Dijkstra算法从起点到所有节点找到最短路径C++\x5cJava\x5cPython\x5cC#\x5cJavascript,五种语言实现使用Dijkstra算法从起点到所有节点找到最短路径![]() https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6NAClr51zR_GLZGyKkr32A给定一个带权重的图和图中的一个起点,找到该点到图中所有其他节点的最短路径。
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/6NAClr51zR_GLZGyKkr32A给定一个带权重的图和图中的一个起点,找到该点到图中所有其他节点的最短路径。
注意:给定的图中不包含任何负边。
示例:
Input: src = 0, the graph is shown below.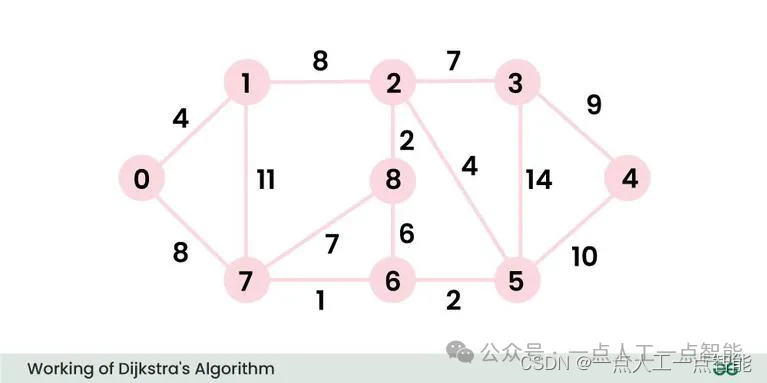
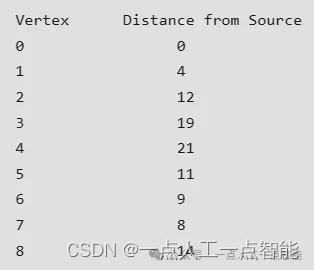
Output: 0 4 12 19 21 11 9 8 14
Explanation: The distance from 0 to 1 = 4.
The minimum distance from 0 to 2 = 12. 0->1->2
The minimum distance from 0 to 3 = 19. 0->1->2->3
The minimum distance from 0 to 4 = 21. 0->7->6->5->4
The minimum distance from 0 to 5 = 11. 0->7->6->5
The minimum distance from 0 to 6 = 9. 0->7->6
The minimum distance from 0 to 7 = 8. 0->7
The minimum distance from 0 to 8 = 14. 0->1->2->801 使用邻接矩阵的Dijkstra算法
思路是以给定起点为根节点生成一个最短路径树(SPT)。维护一个包含两个集合的邻接矩阵,
· 一个集合包含在最短路径树中的节点,
· 另一个集合包含尚未包含在最短路径树中的节点。
算法的每个步骤中,找到一个在另一个集合中(尚未包含的集合)且距离起点最小的节点。
1.1 算法
* 创建一个集合sptSet(最短路径树集合),用于跟踪包含在最短路径树中的节点,即已计算和完成的距离起点的最小距离。初始时,此集合为空。
* 为输入图中的所有节点赋予一个距离值。将所有距离值初始化为无穷大。将起点的距离值设置为0,以便首先选择它。
* 当sptSet未包含所有节点时
· 选择一个不在sptSet中且具有最小距离值的节点u。
· 将u包含到sptSet中。
· 然后更新u的所有邻接节点的距离值。
- 为了更新距离值,迭代遍历所有邻接节点。
- 对于每个邻接节点v,如果u到v的距离值(从起点开始)加上边权重小于v的距离值,则更新v的距离值。
注意:我们使用一个布尔数组sptSet[]来表示包含在SPT中的节点集合。如果值sptSet[v]为true,则表示节点v包含在SPT中,否则不包含。数组dist[]用于存储所有节点的最短距离值。
1.2 Dijkstra算法的示例
为了理解Dijkstra算法,我们来看一个图,并找到从起点到所有节点的最短路径。
考虑下面的图和起点src = 0。
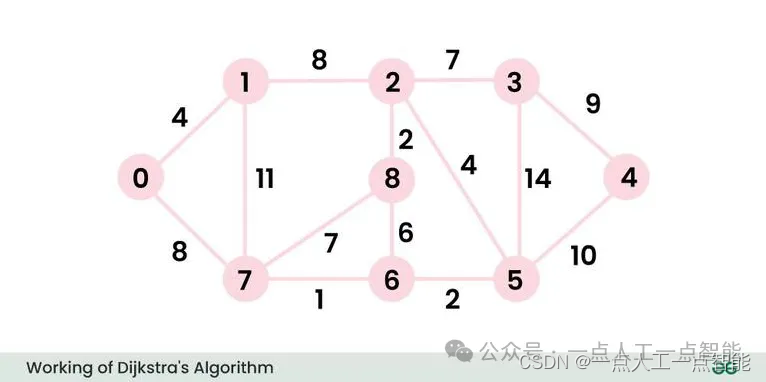
步骤1:
· 集合sptSet最初为空,节点的距离值分别是{0, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, INF},其中INF表示无穷大。
· 现在选择具有最小距离值的节点。选择节点0,并将其包含在sptSet中。因此,sptSet变为{0}。将0包含在sptSet中后,更新其相邻节点的距离值。
· 节点0的相邻节点是1和7。将1和7的距离值更新为4和8。
以下子图显示了节点及其距离值,只显示具有有限距离值的节点。包含在最短路径树中的节点以绿色显示。
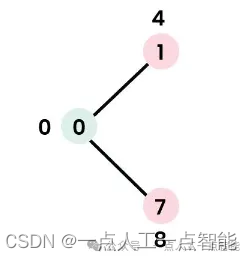
步骤2:
· 选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在SPT中(不在sptSet中)的节点。选择节点1并将其添加到sptSet中。
· 因此,sptSet现在变为{0, 1}。更新节点1的相邻节点的距离值。
· 节点2的距离值变为12。
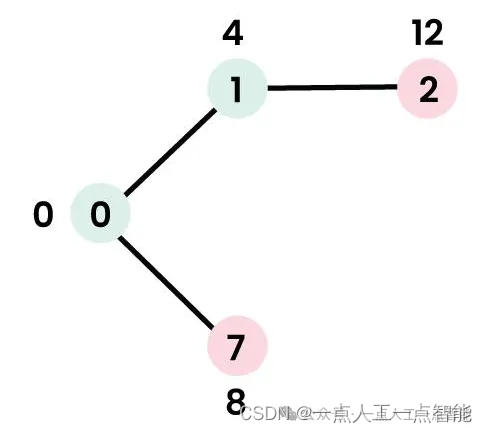
步骤3:
· 选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在SPT中(不在sptSet中)的节点。选择节点7。因此,sptSet现在变为{0, 1, 7}。
· 更新节点7的相邻节点的距离值。节点6和8的距离值变为有限值(分别为15和9)。
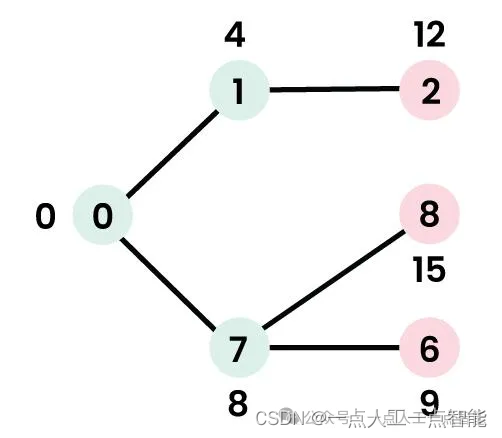
步骤4:
· 选择具有最小距离值且尚未包含在SPT中(不在sptSet中)的节点。选择节点6。因此,sptSet现在变为{0, 1, 7, 6}。
· 更新节点6的相邻节点的距离值。节点5和8的距离值被更新。

我们重复上述步骤,直到sptSet包含了给定图的所有节点。最后,我们得到以下最短路径树(SPT)。

02 代码实现
C++语言:
// C++ Program to find Dijkstra's shortest path using
// priority_queue in STL
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f// iPair ==> Integer Pair
typedef pair<int, int> iPair;// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph {int V; // No. of vertices// In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex// and weight pair for every edgelist<pair<int, int> >* adj;public:Graph(int V); // Constructor// function to add an edge to graphvoid addEdge(int u, int v, int w);// prints shortest path from svoid shortestPath(int s);
};// Allocates memory for adjacency list
Graph::Graph(int V)
{this->V = V;adj = new list<iPair>[V];
}void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v, int w)
{adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v, w));adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u, w));
}// Prints shortest paths from src to all other vertices
void Graph::shortestPath(int src)
{// Create a priority queue to store vertices that// are being preprocessed. This is weird syntax in C++.// Refer below link for details of this syntax// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/implement-min-heap-using-stl/priority_queue<iPair, vector<iPair>, greater<iPair> >pq;// Create a vector for distances and initialize all// distances as infinite (INF)vector<int> dist(V, INF);// Insert source itself in priority queue and initialize// its distance as 0.pq.push(make_pair(0, src));dist[src] = 0;/* Looping till priority queue becomes empty (or alldistances are not finalized) */while (!pq.empty()) {// The first vertex in pair is the minimum distance// vertex, extract it from priority queue.// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it// has to be done this way to keep the vertices// sorted distance (distance must be first item// in pair)int u = pq.top().second;pq.pop();// 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a// vertexlist<pair<int, int> >::iterator i;for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i) {// Get vertex label and weight of current// adjacent of u.int v = (*i).first;int weight = (*i).second;// If there is shorted path to v through u.if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight) {// Updating distance of vdist[v] = dist[u] + weight;pq.push(make_pair(dist[v], v));}}}// Print shortest distances stored in dist[]printf("Vertex Distance from Source\n");for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)printf("%d \t\t %d\n", i, dist[i]);
}// Driver's code
int main()
{// create the graph given in above figureint V = 9;Graph g(V);// making above shown graphg.addEdge(0, 1, 4);g.addEdge(0, 7, 8);g.addEdge(1, 2, 8);g.addEdge(1, 7, 11);g.addEdge(2, 3, 7);g.addEdge(2, 8, 2);g.addEdge(2, 5, 4);g.addEdge(3, 4, 9);g.addEdge(3, 5, 14);g.addEdge(4, 5, 10);g.addEdge(5, 6, 2);g.addEdge(6, 7, 1);g.addEdge(6, 8, 6);g.addEdge(7, 8, 7);// Function callg.shortestPath(0);return 0;
}Java语言:
import java.util.*;class Graph {private int V;private List<List<iPair>> adj;Graph(int V) {this.V = V;adj = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {adj.add(new ArrayList<>());}}void addEdge(int u, int v, int w) {adj.get(u).add(new iPair(v, w));adj.get(v).add(new iPair(u, w));}void shortestPath(int src) {PriorityQueue<iPair> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(V, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.first));int[] dist = new int[V];Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);pq.add(new iPair(0, src));dist[src] = 0;while (!pq.isEmpty()) {int u = pq.poll().second;for (iPair v : adj.get(u)) {if (dist[v.first] > dist[u] + v.second) {dist[v.first] = dist[u] + v.second;pq.add(new iPair(dist[v.first], v.first));}}}System.out.println("Vertex Distance from Source");for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {System.out.println(i + "\t\t" + dist[i]);}}static class iPair {int first, second;iPair(int first, int second) {this.first = first;this.second = second;}}
}public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {int V = 9;Graph g = new Graph(V);g.addEdge(0, 1, 4);g.addEdge(0, 7, 8);g.addEdge(1, 2, 8);g.addEdge(1, 7, 11);g.addEdge(2, 3, 7);g.addEdge(2, 8, 2);g.addEdge(2, 5, 4);g.addEdge(3, 4, 9);g.addEdge(3, 5, 14);g.addEdge(4, 5, 10);g.addEdge(5, 6, 2);g.addEdge(6, 7, 1);g.addEdge(6, 8, 6);g.addEdge(7, 8, 7);g.shortestPath(0);}
}Python 3 语言:
import heapq# iPair ==> Integer Pair
iPair = tuple# This class represents a directed graph using
# adjacency list representation
class Graph:def __init__(self, V: int): # Constructorself.V = Vself.adj = [[] for _ in range(V)]def addEdge(self, u: int, v: int, w: int):self.adj[u].append((v, w))self.adj[v].append((u, w))# Prints shortest paths from src to all other verticesdef shortestPath(self, src: int):# Create a priority queue to store vertices that# are being preprocessedpq = []heapq.heappush(pq, (0, src))# Create a vector for distances and initialize all# distances as infinite (INF)dist = [float('inf')] * self.Vdist[src] = 0while pq:# The first vertex in pair is the minimum distance# vertex, extract it from priority queue.# vertex label is stored in second of paird, u = heapq.heappop(pq)# 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a# vertexfor v, weight in self.adj[u]:# If there is shorted path to v through u.if dist[v] > dist[u] + weight:# Updating distance of vdist[v] = dist[u] + weightheapq.heappush(pq, (dist[v], v))# Print shortest distances stored in dist[]for i in range(self.V):print(f"{i} \t\t {dist[i]}")# Driver's code
if __name__ == "__main__":# create the graph given in above figureV = 9g = Graph(V)# making above shown graphg.addEdge(0, 1, 4)g.addEdge(0, 7, 8)g.addEdge(1, 2, 8)g.addEdge(1, 7, 11)g.addEdge(2, 3, 7)g.addEdge(2, 8, 2)g.addEdge(2, 5, 4)g.addEdge(3, 4, 9)g.addEdge(3, 5, 14)g.addEdge(4, 5, 10)g.addEdge(5, 6, 2)g.addEdge(6, 7, 1)g.addEdge(6, 8, 6)g.addEdge(7, 8, 7)g.shortestPath(0)C#语言:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
public class Graph
{
private const int INF = 2147483647;private int V;
private List<int[]>[] adj;public Graph(int V)
{ // No. of verticesthis.V = V;// In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex// and weight pair for every edgethis.adj = new List<int[]>[V];for (int i = 0; i < V; i++){this.adj[i] = new List<int[]>();}
}public void AddEdge(int u, int v, int w)
{this.adj[u].Add(new int[] { v, w });this.adj[v].Add(new int[] { u, w });
}// Prints shortest paths from src to all other vertices
public void ShortestPath(int src)
{// Create a priority queue to store vertices that// are being preprocessed.SortedSet<int[]> pq = new SortedSet<int[]>(new DistanceComparer());// Create an array for distances and initialize all// distances as infinite (INF)int[] dist = new int[V];for (int i = 0; i < V; i++){dist[i] = INF;}// Insert source itself in priority queue and initialize// its distance as 0.pq.Add(new int[] { 0, src });dist[src] = 0;/* Looping till priority queue becomes empty (or alldistances are not finalized) */while (pq.Count > 0){// The first vertex in pair is the minimum distance// vertex, extract it from priority queue.// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it// has to be done this way to keep the vertices// sorted by distance)int[] minDistVertex = pq.Min;pq.Remove(minDistVertex);int u = minDistVertex[1];// 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a// vertexforeach (int[] adjVertex in this.adj[u]){// Get vertex label and weight of current// adjacent of u.int v = adjVertex[0];int weight = adjVertex[1];// If there is a shorter path to v through u.if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight){// Updating distance of vdist[v] = dist[u] + weight;pq.Add(new int[] { dist[v], v });}}}// Print shortest distances stored in dist[]Console.WriteLine("Vertex Distance from Source");for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)Console.WriteLine(i + "\t" + dist[i]);
}private class DistanceComparer : IComparer<int[]>
{public int Compare(int[] x, int[] y)
{if (x[0] == y[0]){return x[1] - y[1];}return x[0] - y[0];}
}
}public class Program
{
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{// create the graph given in above figureint V = 9;Graph g = new Graph(V);// making above shown graphg.AddEdge(0, 1, 4);g.AddEdge(0, 7, 8);g.AddEdge(1, 2, 8);g.AddEdge(1, 7, 11);g.AddEdge(2, 3, 7);g.AddEdge(2, 8, 2);g.AddEdge(2, 5, 4);g.AddEdge(3, 4, 9);g.AddEdge(3, 5, 14);g.AddEdge(4, 5, 10);g.AddEdge(5, 6, 2);g.AddEdge(6, 7, 1);g.AddEdge(6, 8, 6);g.AddEdge(7, 8, 7);g.ShortestPath(0);
}
}// this code is contributed by bhardwajjiJavascript:
<script>
// javascript Program to find Dijkstra's shortest path using
// priority_queue in STL
const INF = 2147483647;// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph {constructor(V){// No. of verticesthis.V = V;// In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex// and weight pair for every edgethis.adj = new Array(V);for(let i = 0; i < V; i++){this.adj[i] = new Array();}}addEdge(u, v, w){this.adj[u].push([v, w]);this.adj[v].push([u, w]);}// Prints shortest paths from src to all other verticesshortestPath(src){// Create a priority queue to store vertices that// are being preprocessed. This is weird syntax in C++.// Refer below link for details of this syntax// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/implement-min-heap-using-stl/let pq = [];// Create a vector for distances and initialize all// distances as infinite (INF)let dist = new Array(V).fill(INF);// Insert source itself in priority queue and initialize// its distance as 0.pq.push([0, src]);dist[src] = 0;/* Looping till priority queue becomes empty (or alldistances are not finalized) */while (pq.length > 0) {// The first vertex in pair is the minimum distance// vertex, extract it from priority queue.// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it// has to be done this way to keep the vertices// sorted distance (distance must be first item// in pair)let u = pq[0][1];pq.shift();// 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a// vertexfor(let i = 0; i < this.adj[u].length; i++){// Get vertex label and weight of current// adjacent of u.let v = this.adj[u][i][0];let weight = this.adj[u][i][1];// If there is shorted path to v through u.if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight) {// Updating distance of vdist[v] = dist[u] + weight;pq.push([dist[v], v]);pq.sort((a, b) =>{if(a[0] == b[0]) return a[1] - b[1];return a[0] - b[0];});}}}// Print shortest distances stored in dist[]document.write("Vertex Distance from Source");for (let i = 0; i < V; ++i)document.write(i, " ", dist[i]);}
}// Driver's code
// create the graph given in above figure
let V = 9;
let g = new Graph(V);// making above shown graph
g.addEdge(0, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(0, 7, 8);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 8);
g.addEdge(1, 7, 11);
g.addEdge(2, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(2, 8, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 4, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 14);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 10);
g.addEdge(5, 6, 2);
g.addEdge(6, 7, 1);
g.addEdge(6, 8, 6);
g.addEdge(7, 8, 7);// Function call
g.shortestPath(0);// The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
</script>输出:
时间复杂度:O(V^2)
辅助空间:O(V)
注意:
· 该代码计算了最短距离,但没有计算路径信息。可以创建一个父节点数组,在更新距离时更新父节点数组,并使用它来显示从源到不同节点的最短路径。
· 该实现的时间复杂度是O(V^2)。如果使用邻接表表示输入图,可以借助二叉堆将其减少为O(E * log V)。更多详情,请参阅邻接表表示的Dijkstra算法。
· Dijkstra算法对具有负权重环的图不起作用。
03 Dijkstra算法的应用
谷歌地图使用Dijkstra算法显示起点和目标点之间的最短距离。
在计算机网络中,Dijkstra算法是各种路由协议的基础,例如OSPF(开放最短路径优先)和IS-IS(中间系统到中间系统)。
交通和交通管理系统使用Dijkstra算法来优化交通流量,减少拥堵,并计划车辆的最高效路径。
航空公司使用Dijkstra算法来规划最小化燃料消耗、减少旅行时间的飞行路径。
Dijkstra算法在电子设计自动化中用于在集成电路和大规模集成(VLSI)芯片上进行路由连接。
这篇关于5种语言实现 | 使用Dijkstra算法从起点到所有节点找到最短路径的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




