本文主要是介绍161 Linux C++ 通讯架构实战15,线程池代码分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
线程池应该使用的地方 和 epoll 技术结合

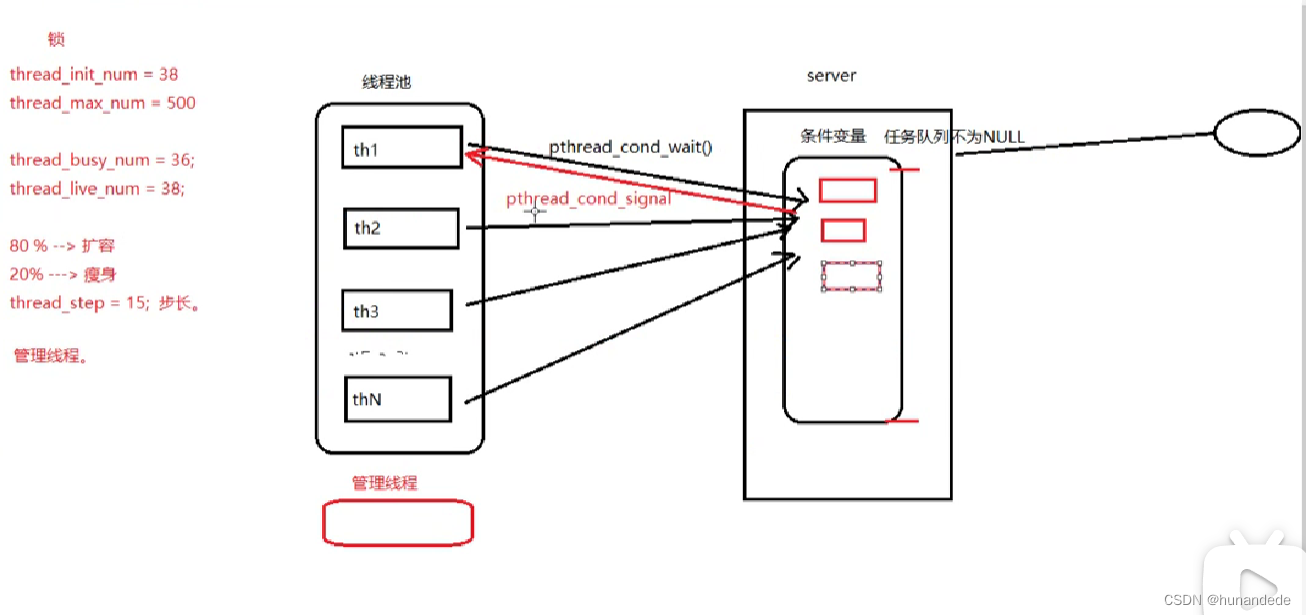
线程池代码处理数据的地方。

线程池分析:
线程池代码1 threadpool_create
//Tencent8888 start threadpool_create函数的目的初始化线程池,对应的struct是 threadpool_t
/*
1.先malloc整个线程池的大小
2.这里使用的 do while实现的好处是,如果哪里有问题,则可以直接break出来,这里要学习的是这种技巧,实际上是为了避免使用goto 语句
3.锁子和 条件变量的初始化
4.将存放线程池中每个线程的tid。数组 进行分配空间。pthread_t *threads
5.将 任务队列 task_queue 进行分配空间
6.对于最小数量的thread,进行初始化
7.对管理线程进行初始化
8.如果有有问题 free相关的信息
9.下来我们就要看 thread 的初始化的回调函数 threadpool_thread
10.然后再看 管理线程 的初始化的回调函数 adjust_thread
*/
//Tencent8888 end
//Tencent8888 start threadpool_create函数的目的初始化线程池,对应的struct是 threadpool_t
/*1.先malloc整个线程池的大小2.这里使用的 do while实现的好处是,如果哪里有问题,则可以直接break出来,这里要学习的是这种技巧,实际上是为了避免使用goto 语句3.锁子和 条件变量的初始化4.将存放线程池中每个线程的tid。数组 进行分配空间。pthread_t *threads5.将 任务队列 task_queue 进行分配空间6.对于最小数量的thread,进行初始化7.对管理线程进行初始化8.如果有有问题 free相关的信息9.下来我们就要看 thread 的初始化的回调函数 threadpool_thread10.然后再看 管理线程 的初始化的回调函数 adjust_thread
*/
//Tencent8888 endthreadpool_t *threadpool_create(int min_thr_num, int max_thr_num, int queue_max_size)
{int i;threadpool_t *pool = NULL;do {if((pool = (threadpool_t *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_t))) == NULL) { printf("malloc threadpool fail");break;/*跳出do while*/}pool->min_thr_num = min_thr_num; /* 线程池最小线程数 */pool->max_thr_num = max_thr_num; /* 线程池最大线程数 */pool->busy_thr_num = 0; /* 忙状态线程个数 */pool->live_thr_num = min_thr_num; /* 活着的线程数 初值=最小线程数 */pool->queue_size = 0; /* 有0个产品 */pool->queue_max_size = queue_max_size; /* task_queue队列可容纳任务数上限*/pool->queue_front = 0; /* task_queue队头下标 */pool->queue_rear = 0; /* task_queue队尾下标 */pool->shutdown = false; /* 不关闭线程池 *//* 根据最大线程上限数, 给工作线程数组开辟空间, 并清零 */pool->threads = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t)*max_thr_num); if (pool->threads == NULL) {printf("malloc threads fail");break;}memset(pool->threads, 0, sizeof(pthread_t)*max_thr_num);/* 队列开辟空间 */pool->task_queue = (threadpool_task_t *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_task_t)*queue_max_size);if (pool->task_queue == NULL) {printf("malloc task_queue fail");break;}/* 初始化互斥琐、条件变量 */if (pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->lock), NULL) != 0|| pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->thread_counter), NULL) != 0|| pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_empty), NULL) != 0|| pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_full), NULL) != 0){printf("init the lock or cond fail");break;}/* 启动 min_thr_num 个 work thread */for (i = 0; i < min_thr_num; i++) {pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool);/*pool指向当前线程池*/printf("start thread 0x%x...\n", (unsigned int)pool->threads[i]);}pthread_create(&(pool->adjust_tid), NULL, adjust_thread, (void *)pool);/* 启动管理者线程 */return pool;} while (0);threadpool_free(pool); /* 前面代码调用失败时,释放poll存储空间 */return NULL;
}
线程池代码2 threadpool_thread
代码中的使用
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool);//pool指向当前线程池
pthread_create的第一个参数为传输参数,保存系统给我们分配好的线程ID。
第二个参数为NULL。表示使用线程默认属性
第三个参数为函数指针,指向线程主函数,该函数执行完毕,则线程结束
第四个参数 为第三个函数指针需要的参数,当前传递的是整个线程池pool
先复习一下 pthread_create函数 的使用
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);返回值:成功:0; 失败:错误号 -----Linux环境下,所有线程特点,失败均直接返回错误号。参数:pthread_t:当前Linux中可理解为:typedef unsigned long int pthread_t;参数1:传出参数,保存系统为我们分配好的线程ID参数2:通常传NULL,表示使用线程默认属性。若想使用具体属性也可以修改该参数。参数3:函数指针,指向线程主函数(线程体),该函数运行结束,则线程结束。参数4:线程主函数执行期间所使用的参数。下来看threadpool_thread 这个方法到底干了些啥?
1.先是将参数 threadpool 取出来,因为pthread_create使用的时候,会将整个线程池poll做为参数传递过来。这是一种poll使用的方法
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool);//pool指向当前线程池
/* 线程池中各个工作线程 */
void *threadpool_thread(void *threadpool)
{threadpool_t *pool = (threadpool_t *)threadpool;threadpool_task_t task;while (true) {/* Lock must be taken to wait on conditional variable *//*刚创建出线程,等待任务队列里有任务,否则阻塞等待任务队列里有任务后再唤醒接收任务*/pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));/*queue_size == 0 说明没有任务,调 wait 阻塞在条件变量上, 若有任务,跳过该while*/while ((pool->queue_size == 0) && (!pool->shutdown)) { printf("thread 0x%x is waiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_not_empty), &(pool->lock));/*清除指定数目的空闲线程,如果要结束的线程个数大于0,结束线程*/if (pool->wait_exit_thr_num > 0) {pool->wait_exit_thr_num--;/*如果线程池里线程个数大于最小值时可以结束当前线程*/if (pool->live_thr_num > pool->min_thr_num) {printf("thread 0x%x is exiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());pool->live_thr_num--;pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));pthread_exit(NULL);}}}/*如果指定了true,要关闭线程池里的每个线程,自行退出处理*/if (pool->shutdown) {pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));printf("thread 0x%x is exiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());pthread_exit(NULL); /* 线程自行结束 */}/*从任务队列里获取任务, 是一个出队操作*/task.function = pool->task_queue[pool->queue_front].function;task.arg = pool->task_queue[pool->queue_front].arg;pool->queue_front = (pool->queue_front + 1) % pool->queue_max_size; /* 出队,模拟环形队列 */pool->queue_size--;/*通知可以有新的任务添加进来*/pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_full));/*任务取出后,立即将 线程池琐 释放*/pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));/*执行任务*/ printf("thread 0x%x start working\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter)); /*忙状态线程数变量琐*/pool->busy_thr_num++; /*忙状态线程数+1*/pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));(*(task.function))(task.arg); /*执行回调函数任务*///task.function(task.arg); /*执行回调函数任务*//*任务结束处理*/ printf("thread 0x%x end working\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));pool->busy_thr_num--; /*处理掉一个任务,忙状态数线程数-1*/pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));}pthread_exit(NULL);
}
线程池代码3 adjust_thread
这篇关于161 Linux C++ 通讯架构实战15,线程池代码分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









