本文主要是介绍嵌入式C基础——循环队列 ringbuffer 讲解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本期主题:
讲解ARRAY_SIZE的作用以及定义,还有一个踩坑分析
往期链接:
- 数据结构系列——先进先出队列queue
- 数据结构系列——栈 stack
- Linux内核链表
- 零长度数组的使用
- inline的作用
- 嵌入式C基础——ARRAY_SIZE使用以及踩坑分析
目录
- 1. Ringbuffer定义及特点
- 2.ringbuffer实例(rtos实例)
- 2.1 ringbuffer结构体
- 2.2 ringbuffer获取当前长度
- 2.3 ringbuffer put
- 3.根据rtos代码,设计ringbuffer,并测试
1. Ringbuffer定义及特点
Ringbuffer的定义:
环形缓冲区(Ring Buffer),也称为循环缓冲区、环形队列(Ring Queue)或循环队列(Circular Queue),是一种用于在固定大小的存储区域中存储数据的数据结构。
环形缓冲区通常由一个固定大小的数组和两个指针组成,分别用于指示缓冲区的起始位置和结束位置。数据被顺序地存储在数组中,当到达数组的末尾时,数据会“循环”回到数组的起始位置,实现了环形的存储结构。
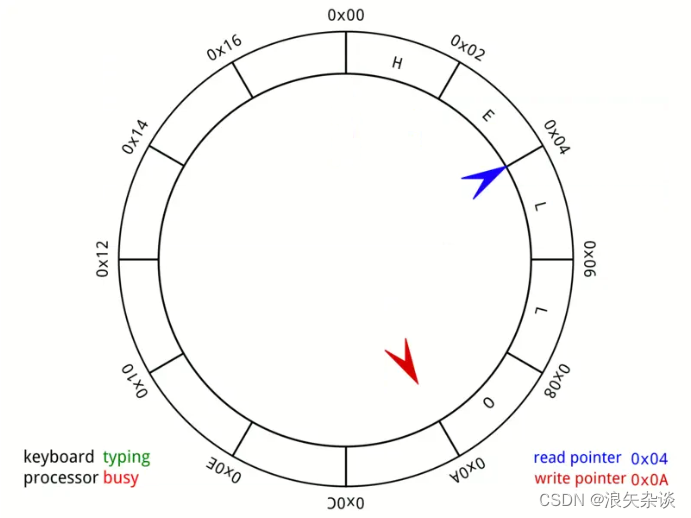
Ringbuffer的特点:
环形缓冲区通常用于实现数据在生产者和消费者之间的高效传输,特别是在多线程或多任务环境中。它具有以下特点和优势:
- 高效性: 环形缓冲区采用循环结构,避免了数据的频繁搬移。这使得对于生产者和消费者来说,插入和删除操作的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
- 固定大小: 环形缓冲区有一个固定的大小,这使得其占用的内存是可控的。当缓冲区已满时,生产者会被阻塞,以免过度生产数据,同时保护消费者不会因为数据积压而失去响应能力。
- 无需动态内存分配: 环形缓冲区一般使用静态数组作为存储空间,无需动态内存分配,因此可以在嵌入式系统等资源受限的环境中使用。
- 循环利用空间: 环形缓冲区的循环结构使得空间可以被循环利用,即使数据已经被消费,存储空间也可以被后续的数据重新利用。
- 并发安全: 当环形缓冲区被多个线程或任务访问时,需要通过互斥锁或其他同步机制来保护共享资源,以确保线程安全。
使用环形缓冲区时,需要注意处理好
生产者和消费者之间的同步和竞态条件,以及处理好缓冲区空间不足和溢出的情况。同时,还需要考虑如何优雅地处理缓冲区已满和已空时的阻塞与唤醒机制。
2.ringbuffer实例(rtos实例)
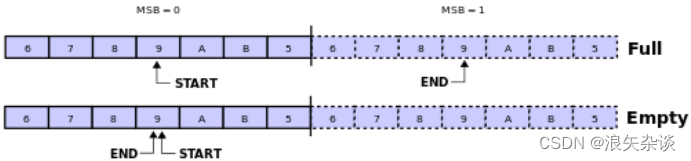
ringbuffer比较难处理的一个问题就是 当read_ptr = write_ptr 时,此时并不是很确定ringbuffer是empty还是full,rtos和Linux中的设计使用的是 镜像法,具体的意思是:
镜像扩展位是环形缓冲区中的一个额外的标志位或变量,用于指示缓冲区的填充状态。它通常有两种取值:
- 未填满(Not Full): 表示缓冲区还有空闲空间,可以继续向缓冲区写入数据。
- 填满(Full): 表示缓冲区已经填满,不能再继续向缓冲区写入数据。此时,继续写入数据可能会覆盖已有的数据,造成数据丢失。
使用镜像扩展位,当缓冲区填满时,生产者可以根据镜像扩展位的状态来判断是否继续写入数据。如果缓冲区未填满,生产者可以继续写入数据;如果缓冲区已经填满,则生产者应该等待,直到缓冲区有空间可用。
2.1 ringbuffer结构体
看rtos的实例代码:
struct rt_ringbuffer
{rt_uint8_t *buffer_ptr;/* use the msb of the {read,write}_index as mirror bit. You can see this as* if the buffer adds a virtual mirror and the pointers point either to the* normal or to the mirrored buffer. If the write_index has the same value* with the read_index, but in a different mirror, the buffer is full.* While if the write_index and the read_index are the same and within the* same mirror, the buffer is empty. The ASCII art of the ringbuffer is:** mirror = 0 mirror = 1* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+|+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+* | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 ||| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Full* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+|+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+* read_idx-^ write_idx-^** +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+|+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+* | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 ||| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Empty* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+|+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+~~~+* read_idx-^ ^-write_idx*/rt_uint32_t read_mirror : 1;rt_uint32_t read_index : 31;rt_uint32_t write_mirror : 1;rt_uint32_t write_index : 31;/* as we use msb of index as mirror bit, the size should be signed and* could only be positive. */rt_int32_t buffer_size;
};
结构体中有一个read_mirror和write_mirror,看注释可以知道是表示,read/write的指针是否到了mirror区,并且:
- read_index = write_index, read_mirror和write_mirror不同,此时为FULL
- read_index = write_index, read_mirror和write_mirror相同,此时为EMPTY
2.2 ringbuffer获取当前长度
RTOS中代码:
rt_size_t rt_ringbuffer_data_len(struct rt_ringbuffer *rb)
{switch (rt_ringbuffer_status(rb)){case RT_RINGBUFFER_EMPTY:return 0;case RT_RINGBUFFER_FULL:return rb->buffer_size;case RT_RINGBUFFER_HALFFULL:default:{rt_size_t wi = rb->write_index, ri = rb->read_index;if (wi > ri)return wi - ri;elsereturn rb->buffer_size - (ri - wi);}}
}
有三种情况:
- 当rt_status为空时,len为0
- 当rt_status为满时,len为buffer_size
- 当ringbuffer非空/满时,如果write_index>read_index,那么buffer_size为 wi-ri,否则为 rb->buffer_size - (ri - wi)
2.3 ringbuffer put
put代码如下:
rt_size_t rt_ringbuffer_put(struct rt_ringbuffer *rb,const rt_uint8_t *ptr,rt_uint32_t length)
{rt_uint32_t size;RT_ASSERT(rb != RT_NULL);/* whether has enough space */size = rt_ringbuffer_space_len(rb);/* no space */if (size == 0)return 0;/* drop some data */if (size < length)length = size;if (rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index > length){/* read_index - write_index = empty space */rt_memcpy(&rb->buffer_ptr[rb->write_index], ptr, length);/* this should not cause overflow because there is enough space for* length of data in current mirror */rb->write_index += length;return length;}rt_memcpy(&rb->buffer_ptr[rb->write_index],&ptr[0],rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index);rt_memcpy(&rb->buffer_ptr[0],&ptr[rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index],length - (rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index));/* we are going into the other side of the mirror */rb->write_mirror = ~rb->write_mirror;rb->write_index = length - (rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index);return length;
}逻辑是:
- 判断剩余空间的size是否足够放下数据,如果不够则需要drop一些数据
- 如果可以直接放,不需要循环回来,那么就直接Memcpy就行
- 如果需要循环回来,write_mirror需要取反
3.根据rtos代码,设计ringbuffer,并测试
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "main.h"struct rt_ringbuffer
{rt_uint8_t *buffer_ptr;rt_uint32_t read_mirror : 1;rt_uint32_t read_index : 31;rt_uint32_t write_mirror : 1;rt_uint32_t write_index : 31;rt_int32_t buffer_size;
};enum rt_ringbuffer_state rt_ringbuffer_status(struct rt_ringbuffer *rb)
{if (rb->read_index == rb->write_index){if (rb->read_mirror == rb->write_mirror)return RT_RINGBUFFER_EMPTY;elsereturn RT_RINGBUFFER_FULL;}return RT_RINGBUFFER_HALFFULL;
}int rt_ringbuffer_data_len(struct rt_ringbuffer *rb)
{switch (rt_ringbuffer_status(rb)){case RT_RINGBUFFER_EMPTY:return 0;case RT_RINGBUFFER_FULL:return rb->buffer_size;case RT_RINGBUFFER_HALFFULL:default:{rt_size_t wi = rb->write_index, ri = rb->read_index;if (wi > ri)return wi - ri;elsereturn rb->buffer_size - (ri - wi);}}
}struct rt_ringbuffer *ringbuffer_init(rt_int32_t size)
{struct rt_ringbuffer *rb;rt_uint8_t *pool;rb = (struct rt_ringbuffer *)malloc(sizeof(struct rt_ringbuffer));if (!rb) {printf("rb is null\n");return NULL;}pool = (rt_uint8_t *)malloc(size);if (!pool) {printf("pool is null\n");return NULL;}rb->buffer_ptr = pool;rb->buffer_size = size;rb->read_mirror = rb->read_index = 0;rb->write_mirror = rb->write_index = 0;return rb;
} /** return the size of empty space in rb */
#define rt_ringbuffer_space_len(rb) ((rb)->buffer_size - rt_ringbuffer_data_len(rb))int rt_ringbuffer_put(struct rt_ringbuffer *rb,const rt_uint8_t *ptr,rt_uint32_t length)
{rt_uint32_t size;/* whether has enough space */size = rt_ringbuffer_space_len(rb);/* no space */if (size == 0)return 0;/* drop some data */if (size < length)length = size;if (rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index > length){/* read_index - write_index = empty space */memcpy(&rb->buffer_ptr[rb->write_index], ptr, length);/* this should not cause overflow because there is enough space for* length of data in current mirror */rb->write_index += length;return length;}memcpy(&rb->buffer_ptr[rb->write_index],&ptr[0],rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index);memcpy(&rb->buffer_ptr[0],&ptr[rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index],length - (rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index));/* we are going into the other side of the mirror */rb->write_mirror = ~rb->write_mirror;rb->write_index = length - (rb->buffer_size - rb->write_index);return length;
}int rt_ringbuffer_get(struct rt_ringbuffer *rb,rt_uint8_t *ptr,rt_uint32_t length)
{int size;/* whether has enough data */size = rt_ringbuffer_data_len(rb);/* no data */if (size == 0)return 0;/* less data */if (size < length)length = size;if (rb->buffer_size - rb->read_index > length){/* copy all of data */memcpy(ptr, &rb->buffer_ptr[rb->read_index], length);/* this should not cause overflow because there is enough space for* length of data in current mirror */rb->read_index += length;return length;}memcpy(&ptr[0],&rb->buffer_ptr[rb->read_index],rb->buffer_size - rb->read_index);memcpy(&ptr[rb->buffer_size - rb->read_index],&rb->buffer_ptr[0],length - (rb->buffer_size - rb->read_index));/* we are going into the other side of the mirror */rb->read_mirror = ~rb->read_mirror;rb->read_index = length - (rb->buffer_size - rb->read_index);return length;
}int main(void)
{int ret;struct rt_ringbuffer *rb = NULL;rb = ringbuffer_init(4);if (!rb) {printf("rb init failed\n");return -1;}uint8_t a[4] = {0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x4};uint8_t read[4] = { 0 };ret = rt_ringbuffer_put(rb, a, 4);ret = rt_ringbuffer_get(rb, read, 1);for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {printf("0x%x\n", read[i]);}ret = rt_ringbuffer_put(rb, a, 4);ret = rt_ringbuffer_get(rb, read, 4);for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {printf("0x%x\n", read[i]);}return 0;
}
//main.h
#ifndef __MAIN_H__
#define __MAIN_H__#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>typedef uint8_t rt_uint8_t;
typedef uint32_t rt_uint32_t;
typedef int32_t rt_int32_t;
typedef int rt_size_t;enum rt_ringbuffer_state
{RT_RINGBUFFER_EMPTY,RT_RINGBUFFER_FULL,/* half full is neither full nor empty */RT_RINGBUFFER_HALFFULL,
};#endif
测试结果:

这篇关于嵌入式C基础——循环队列 ringbuffer 讲解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



