本文主要是介绍算法学习——LeetCode力扣补充篇3(143. 重排链表、141. 环形链表、205. 同构字符串、1002. 查找共用字符、925. 长按键入),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
算法学习——LeetCode力扣补充篇3

143. 重排链表
143. 重排链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
描述
给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例
示例 1:
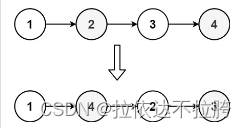
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[1,4,2,3]
示例 2:
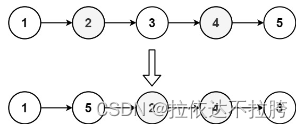
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[1,5,2,4,3]
提示
链表的长度范围为 [1, 5 * 104]
1 <= node.val <= 1000
代码解析
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:void reorderList(ListNode* head) {ListNode *tmp = head;vector<int> arr_num;while(tmp!=nullptr){arr_num.push_back(tmp->val);tmp = tmp -> next;}int node_num = arr_num.size()/2;tmp = head;ListNode *tmp_next;while(node_num--){ListNode *new_node = new ListNode(arr_num[arr_num.size() - ( arr_num.size()/2 - node_num)]);// cout<<new_node->val<<endl;tmp_next = tmp->next;tmp->next = new_node;new_node->next = tmp_next;if(node_num == 0 && arr_num.size()%2 == 0) new_node->next = nullptr;else if(node_num == 0 && arr_num.size()%2 == 1) new_node->next->next = nullptr;else tmp = tmp->next->next;}}
};141. 环形链表
141. 环形链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
描述
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例
示例 1:
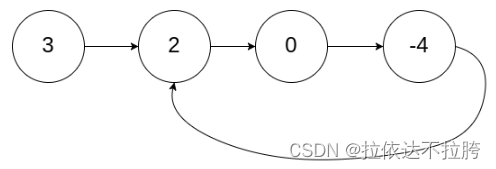
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
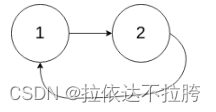
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 104]
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos 为 -1 或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
代码解析
```cpp
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {if(head==nullptr || head->next==nullptr) return false;ListNode *left = head;ListNode *right = head;while(left!=nullptr && right !=nullptr && right->next!= nullptr){left = left->next;right = right->next->next;if(left == right) return true;}return false;}
};
205. 同构字符串
205. 同构字符串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
描述
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,判断它们是否是同构的。
如果 s 中的字符可以按某种映射关系替换得到 t ,那么这两个字符串是同构的。
每个出现的字符都应当映射到另一个字符,同时不改变字符的顺序。不同字符不能映射到同一个字符上,相同字符只能映射到同一个字符上,字符可以映射到自己本身。
示例
示例 1:
输入:s = “egg”, t = “add”
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = “foo”, t = “bar”
输出:false
示例 3:
输入:s = “paper”, t = “title”
输出:true
提示
1 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
t.length == s.length
s 和 t 由任意有效的 ASCII 字符组成
代码解析
class Solution {
public:bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {if(s.size() != t.size()) return false;unordered_map<char,char> my_map_s;unordered_map<char,char> my_map_t;for(int i=0 ; i<s.size() ;i++){if(my_map_s.find(s[i]) == my_map_s.end())my_map_s[s[i]] = t[i];if(my_map_t.find(t[i]) == my_map_t.end())my_map_t[t[i]] = s[i];if(my_map_s[s[i]] != t[i] || my_map_t[t[i]] != s[i]) return false; }return true;}
};1002. 查找共用字符
1002. 查找共用字符 - 力扣(LeetCode)
描述
给你一个字符串数组 words ,请你找出所有在 words 的每个字符串中都出现的共用字符( 包括重复字符),并以数组形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例
示例 1:
输入:words = [“bella”,“label”,“roller”]
输出:[“e”,“l”,“l”]
示例 2:
输入:words = [“cool”,“lock”,“cook”]
输出:[“c”,“o”]
提示
1 <= words.length <= 100
1 <= words[i].length <= 100
words[i] 由小写英文字母组成
代码解析
class Solution {
public:vector<string> commonChars(vector<string>& words) {vector<string> result;vector<vector<int>> map(words.size() , vector<int>(26,0));for(int i=0 ; i<words.size() ;i++){for(int j=0 ; j<words[i].size() ;j++)map[i][words[i][j] - 'a'] += 1;}for(int j=0 ; j<26 ;j++){int tmp = INT_MAX;for(int i=0 ; i<words.size() ;i++){if(map[i][j] == 0 ) break;tmp = min( tmp, map[i][j]);if(i==words.size()-1){while(tmp--){string s(1,'a'+j);result.push_back(s);}} }}return result;}
};925. 长按键入
925. 长按键入 - 力扣(LeetCode)
描述
你的朋友正在使用键盘输入他的名字 name。偶尔,在键入字符 c 时,按键可能会被长按,而字符可能被输入 1 次或多次。
你将会检查键盘输入的字符 typed。如果它对应的可能是你的朋友的名字(其中一些字符可能被长按),那么就返回 True。
示例
示例 1:
输入:name = “alex”, typed = “aaleex”
输出:true
解释:‘alex’ 中的 ‘a’ 和 ‘e’ 被长按。
示例 2:
输入:name = “saeed”, typed = “ssaaedd”
输出:false
解释:‘e’ 一定需要被键入两次,但在 typed 的输出中不是这样。
提示
1 <= name.length, typed.length <= 1000
name 和 typed 的字符都是小写字母
代码解析
class Solution {
public:bool isLongPressedName(string name, string typed) {int indnx = 0;if(name[0] != typed[0]) return false;for(int i=0 ; i<typed.size() ;i++){if(typed[i] == name[indnx]) indnx++;else if(typed[i] != name[indnx] && typed[i] != name[indnx-1]) return false;}if(indnx == name.size()) return true;else return false;}
};这篇关于算法学习——LeetCode力扣补充篇3(143. 重排链表、141. 环形链表、205. 同构字符串、1002. 查找共用字符、925. 长按键入)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





