本文主要是介绍超分之SwinIR官方代码解读,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 一、解读SwinIR模型文件:network_swinir.py
- 1. 带有相对为位置偏置的(W-MSA)
- 2. STL(Swin Transformer)
- 3. RSTB(Residual Swin Transformer Block)
- 4. SwinIR(主框架网络)
- 二、解读SwinIR测试主文件:main_test_swinir.py
一、解读SwinIR模型文件:network_swinir.py

1. 带有相对为位置偏置的(W-MSA)
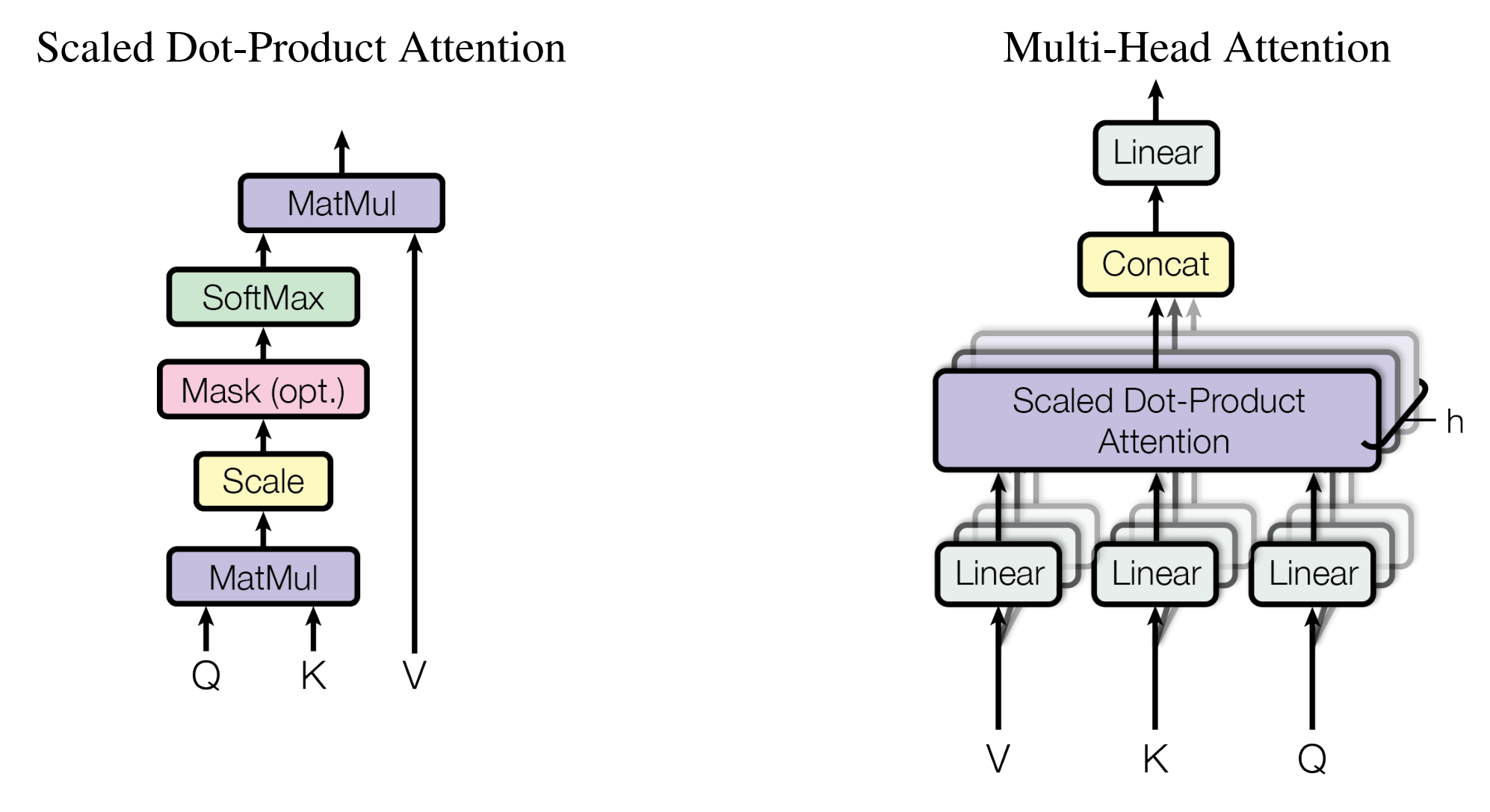
如何在图像中加入W-MSA
Swin Transformer之相对位置编码详解
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.models.layers import trunc_normal_class WindowAttention(nn.Module):r""" (带有相对位置偏置的基于窗口的多头自注意力(W-MSA))Window based multi-head self attention (W-MSA) module with relative position bias. W-MSAIt supports both of shifted and non-shifted window.Args:dim (int): Number of input channels. (输入通道数)window_size (tuple[int]): The height and width of the window. (窗口的尺寸)num_heads (int): Number of attention heads. (MSA的头数)qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: True (Q、K、V是否需要偏置)qk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set ()attn_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of attention weight. Default: 0.0 (是否使用dropout)proj_drop (float, optional): Dropout ratio of output. Default: 0.0"""def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):super().__init__()self.dim = dim # 180self.window_size = window_size # Wh, Ww:(8, 8)self.num_heads = num_heads # 6head_dim = dim // num_heads # 160//6 = 30self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5 # 1/sqrt(30)# define a parameter table of relative position bias(定义相对位置偏置的参数表)self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1),num_heads)) # [225, 6]= [(2*8-1) * (2*8-1), 6]# get pair-wise relative position index for each token inside the window(获取窗口内每个token的成对相对位置索引)coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0]) # (8, )coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1]) # (8, )# torch.meshgrid(a, b):生成网格,可以用于生成坐标,行数为第一个输入张量的元素个数,列数为第二个输入张量的元素个数coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w], indexing='ij')) # (2, Wh, Ww) (2, 8, 8)coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # (2, Wh*Ww) (2, 64)=(2, 8*8)relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None,:] # (2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) (2, 64, 64)= (2, 61, 1) - (2, 1, 64)relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # (Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2)relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # shift to start from 0relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # Wh*Ww, Wh*Wwself.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index)self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias) # 180 ---> 540self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop)self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop)trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02) # 截断正太分布self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)def forward(self, x, mask=None):"""Args:x: input features with shape of (num_windows*B, N, C) (2145, 64, 180)mask: (0/-inf) mask with shape of (num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww) or None"""B_, N, C = x.shape # 2145, 64, 180# (2145, 64, 180) --> (2415, 64, 540) ---> (2145, 64, 3, 6, 30) = (3, 2145, 6, 64, 30) :(3, B_, head, N, head_dim)qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # [2145, 6, 64, 30] make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)q = q * self.scaleattn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) # [2145, 6, 64, 30] @ [2145, 6, 30, 64] = [2145, 6, 64, 64]relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1],-1) # [64, 64, 6] [Wh*Ww,Wh*Ww,nH]relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous() # [64, 64, 6] --> [6, 64, 64] [nH, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww]attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0) # [2145, 6, 64, 30] + [1, 6, 64, 64] = [2145, 6, 64, 30]if mask is not None:nW = mask.shape[0] # 2145# [1, 2145, 6, 64, 64] + [1, 2145, 1, 64, 64] = [1, 2145, 6, 64, 64]attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N) # [1, 2145, 6, 64, 64] --> [2145, 6, 64, 64]attn = self.softmax(attn)else:attn = self.softmax(attn)attn = self.attn_drop(attn)# [2145, 6, 64, 64] @ [2145, 6, 64, 30] = [2145, 6, 64, 30] --> [2145, 64, 6, 30] --> [2145, 64, 180]x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)x = self.proj(x) # [2145, 64, 180] --> [2145, 64, 180]x = self.proj_drop(x)return xdef extra_repr(self) -> str:return f'dim={self.dim}, window_size={self.window_size}, num_heads={self.num_heads}'def flops(self, N):# calculate flops for 1 window with token length of Nflops = 0# qkv = self.qkv(x)flops += N * self.dim * 3 * self.dim# attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1))flops += self.num_heads * N * (self.dim // self.num_heads) * N# x = (attn @ v)flops += self.num_heads * N * N * (self.dim // self.num_heads)# x = self.proj(x)flops += N * self.dim * self.dimreturn flopsdef window_partition(x, window_size):""" (将输入张量x按照指定的窗口大小window_size划分成小的窗口。)Args:x: (B, H, W, C)window_size (int): window sizeReturns:windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C)"""B, H, W, C = x.shapex = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)return windowsdef calculate_mask(x_size):# calculate attention mask for SW-MSAH, W = x_sizewindow_size, shift_size = 8, 0img_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 1 H W 1h_slices = (slice(0, window_size),slice(-window_size, -shift_size),slice(-shift_size, None))w_slices = (slice(0, -window_size),slice(-window_size, -shift_size),slice(-shift_size, None))cnt = 0for h in h_slices:for w in w_slices:img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cntcnt += 1mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, window_size * window_size)attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))return attn_maskif __name__ == '__main__':attn = WindowAttention(dim=180, window_size=(8, 8), num_heads=6,qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.)print(attn)x_windows = torch.randn(2145, 64, 180)attn_mask = torch.randn(2145, 64, 64)attn_windows = attn(x_windows, mask=attn_mask)print(attn_windows.shape)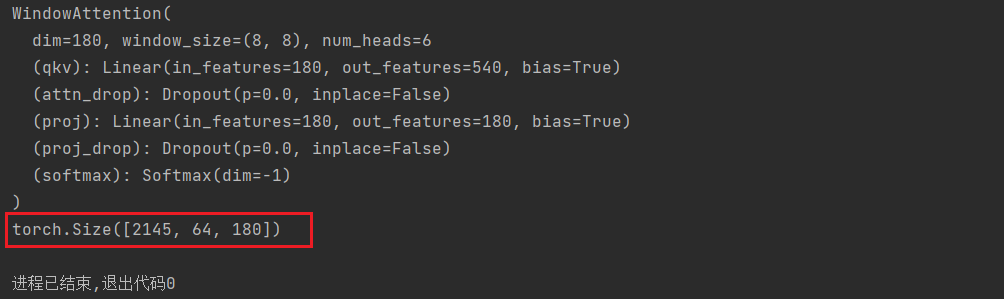
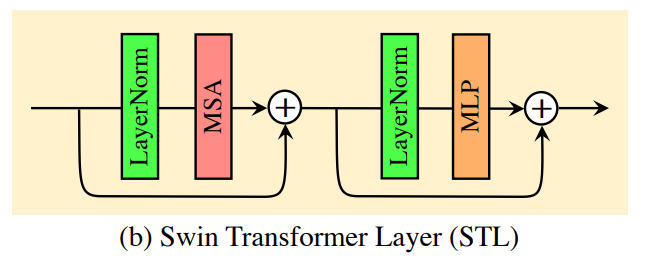
2. STL(Swin Transformer)
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):r""" Swin Transformer Block.Args:dim (int): Number of input channels.input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resulotion.num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.window_size (int): Window size.shift_size (int): Shift size for SW-MSA.mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: Trueqk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0drop_path (float, optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0act_layer (nn.Module, optional): Activation layer. Default: nn.GELUnorm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm"""def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0,mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.,act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):super().__init__()self.dim = dim # 180self.input_resolution = input_resolution # (64, 64)self.num_heads = num_heads # 6self.window_size = window_size # 8self.shift_size = shift_size # 0self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio # 2# 如果输入图像的尺寸小于窗口划分的尺寸,那么窗口就是找个输入图像的尺寸if min(self.input_resolution) <= self.window_size:# if window size is larger than input resolution, we don't partition(分区) windowsself.shift_size = 0self.window_size = min(self.input_resolution)assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size"self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)self.attn = WindowAttention(dim, window_size=to_2tuple(self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads,qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)# 根据移位窗口,来决定是否使用maskif self.shift_size > 0:attn_mask = self.calculate_mask(self.input_resolution)else:attn_mask = Noneself.register_buffer("attn_mask", attn_mask)def calculate_mask(self, x_size):# calculate attention mask for SW-MSAH, W = x_sizeimg_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 1 H W 1# slice(起始位置索引,结束位置索引) :从已有的数组中返回选定的元素(数组单元的截取) (左开右闭)h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),slice(-self.shift_size, None))w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),slice(-self.shift_size, None))cnt = 0for h in h_slices:for w in w_slices:img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cntcnt += 1mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # nW, window_size, window_size, 1mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size)attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2)attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))return attn_maskdef forward(self, x, x_size):H, W = x_sizeB, L, C = x.shape# assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"shortcut = x # [1, 137289, 180]x = self.norm1(x)x = x.view(B, H, W, C) # [1, 264, 520, 180]# cyclic shiftif self.shift_size > 0:shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))else:shifted_x = x# partition windows [1, 264, 520, 180] ---> [2145, 8, 8, 180]x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # nW*B, window_size, window_size, Cx_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, C# W-MSA/SW-MSA (to be compatible for testing on images whose shapes are the multiple of window size# 根据测试图像形状是否为窗口大小倍数, 使用W-MSA/SW-MSAif self.input_resolution == x_size:attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=self.attn_mask) # nW*B, window_size*window_size, Celse:attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=self.calculate_mask(x_size).to(x.device)) # [2145, 64, 180]# merge windows 在把窗口拼到一起attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size,C) # [2145, 64, 180] --> [2145, 8, 8, 180]shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H,W) # B H' W' C [2145, 8, 8, 180] --> [1, 264, 520, 180]# reverse cyclic shiftif self.shift_size > 0:x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))else:x = shifted_xx = x.view(B, H * W, C)# FFN STL层的前向传播过程x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x)x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))return xdef extra_repr(self) -> str:return f"dim={self.dim}, input_resolution={self.input_resolution}, num_heads={self.num_heads}, " \f"window_size={self.window_size}, shift_size={self.shift_size}, mlp_ratio={self.mlp_ratio}"def flops(self):flops = 0H, W = self.input_resolution# norm1flops += self.dim * H * W# W-MSA/SW-MSAnW = H * W / self.window_size / self.window_sizeflops += nW * self.attn.flops(self.window_size * self.window_size)# mlpflops += 2 * H * W * self.dim * self.dim * self.mlp_ratio# norm2flops += self.dim * H * Wreturn flopsif __name__ == '__main__':STL = SwinTransformerBlock(dim=180, input_resolution=(64, 64),num_heads=6, window_size=8,shift_size=0,mlp_ratio=2,qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,drop=0., attn_drop=0.,drop_path=0.,norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm)print(STL)x = torch.randn(1, 137280, 180)x_size = [264, 520]out_BasicLayer = STL(x, x_size)print(out_BasicLayer.shape)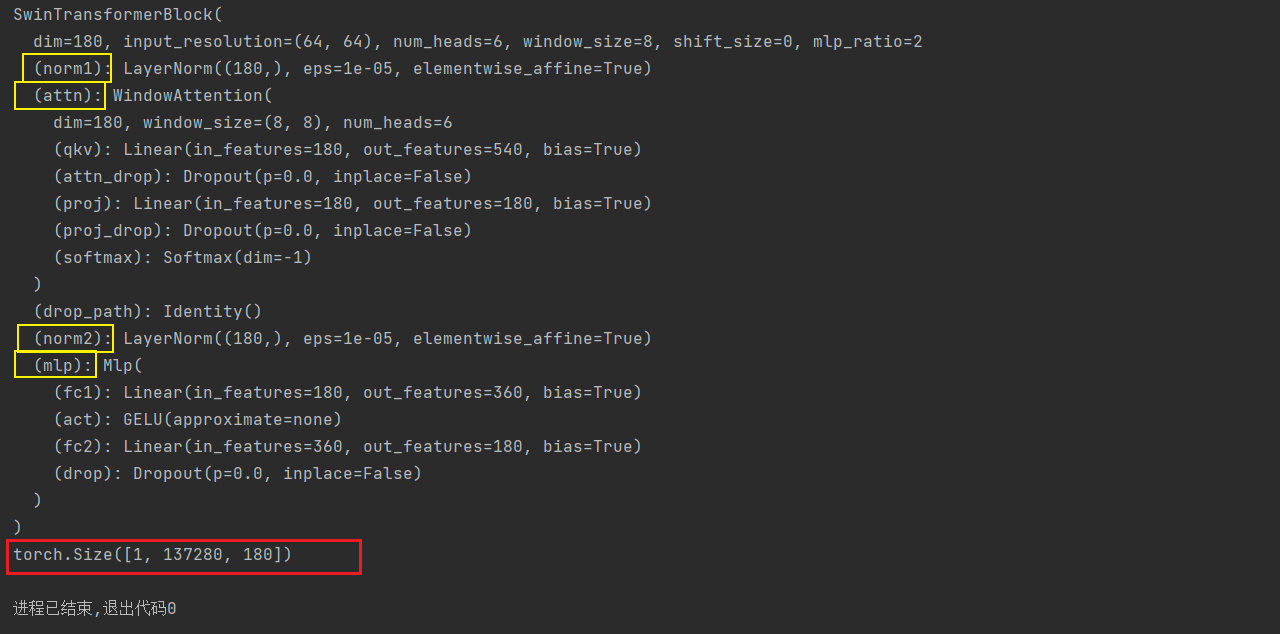
3. RSTB(Residual Swin Transformer Block)
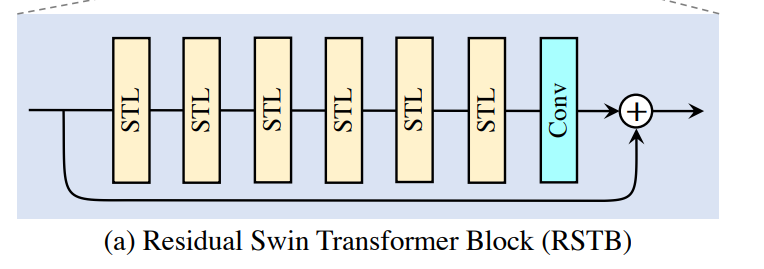
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):""" A basic Swin Transformer layer for one stage. STLArgs:dim (int): Number of input channels.input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resolution.depth (int): Number of blocks.num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.window_size (int): Local window size.mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: Trueqk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNormdownsample (nn.Module | None, optional): Downsample layer at the end of the layer. Default: Noneuse_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False."""def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, depth, num_heads, window_size,mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False):super().__init__()self.dim = dim # 180self.input_resolution = input_resolution # [64, 64]self.depth = depth # 6self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint# build blocks 每个STL存储6个STBself.blocks = nn.ModuleList([SwinTransformerBlock(dim=dim, input_resolution=input_resolution,num_heads=num_heads, window_size=window_size,shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2,mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,norm_layer=norm_layer)for i in range(depth)])# patch merging layerif downsample is not None:self.downsample = downsample(input_resolution, dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer)else:self.downsample = Nonedef forward(self, x, x_size):for blk in self.blocks:if self.use_checkpoint:x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x, x_size)else:x = blk(x, x_size)if self.downsample is not None:x = self.downsample(x)return xdef extra_repr(self) -> str:return f"dim={self.dim}, input_resolution={self.input_resolution}, depth={self.depth}"def flops(self):flops = 0for blk in self.blocks:flops += blk.flops()if self.downsample is not None:flops += self.downsample.flops()return flopsclass RSTB(nn.Module):"""Residual Swin Transformer Block (RSTB).Args:dim (int): Number of input channels.input_resolution (tuple[int]): Input resolution.depth (int): Number of blocks.num_heads (int): Number of attention heads.window_size (int): Local window size.mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.qkv_bias (bool, optional): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: Trueqk_scale (float | None, optional): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set.drop (float, optional): Dropout rate. Default: 0.0attn_drop (float, optional): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0.0drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.0norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNormdownsample (nn.Module | None, optional): Downsample layer at the end of the layer. Default: Noneuse_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: False.img_size: Input image size.patch_size: Patch size.resi_connection: The convolutional block before residual connection."""def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, depth, num_heads, window_size,mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False,img_size=224, patch_size=4, resi_connection='1conv'):super(RSTB, self).__init__()self.dim = dim # 180self.input_resolution = input_resolution # [64, 64]# STLself.residual_group = BasicLayer(dim=dim,input_resolution=input_resolution,depth=depth,num_heads=num_heads,window_size=window_size,mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,drop_path=drop_path,norm_layer=norm_layer,downsample=downsample,use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)if resi_connection == '1conv':self.conv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1)elif resi_connection == '3conv':# to save parameters and memoryself.conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(dim, dim // 4, 3, 1, 1), nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(dim // 4, dim // 4, 1, 1, 0),nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(dim // 4, dim, 3, 1, 1))self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=0, embed_dim=dim,norm_layer=None)self.patch_unembed = PatchUnEmbed(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=0, embed_dim=dim,norm_layer=None)def forward(self, x, x_size):return self.patch_embed(self.conv(self.patch_unembed(self.residual_group(x, x_size), x_size))) + xdef flops(self):flops = 0flops += self.residual_group.flops()H, W = self.input_resolutionflops += H * W * self.dim * self.dim * 9flops += self.patch_embed.flops()flops += self.patch_unembed.flops()return flopsclass PatchEmbed(nn.Module):r""" Image to Patch EmbeddingArgs:img_size (int): Image size. Default: 224.patch_size (int): Patch token size. Default: 4.in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3.embed_dim (int): Number of linear projection output channels. Default: 96.norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: None"""def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):super().__init__()# to_2tuple(): 将输入对象转换为长度为2的元组img_size = to_2tuple(img_size) # 64 ---> (64, 64)patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size) # 1 ---> (1, 1)patches_resolution = [img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1]] # [64//1,64//1] ---> [64, 64]self.img_size = img_size # [64, 64]self.patch_size = patch_size # [1, 1]self.patches_resolution = patches_resolution # [64, 64]self.num_patches = patches_resolution[0] * patches_resolution[1] # 64*64=4096self.in_chans = in_chans # 180self.embed_dim = embed_dim # 180if norm_layer is not None:self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)else:self.norm = Nonedef forward(self, x):x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # B Ph*Pw C [b, c, h, w] ---> [b, h*w, c]if self.norm is not None:x = self.norm(x)return xdef flops(self):flops = 0H, W = self.img_sizeif self.norm is not None:flops += H * W * self.embed_dimreturn flopsclass PatchUnEmbed(nn.Module):r""" Image to Patch UnembeddingArgs:img_size (int): Image size. Default: 224.patch_size (int): Patch token size. Default: 4.in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3.embed_dim (int): Number of linear projection output channels. Default: 96.norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): Normalization layer. Default: None"""def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):super().__init__()img_size = to_2tuple(img_size)patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size)patches_resolution = [img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1]]self.img_size = img_sizeself.patch_size = patch_sizeself.patches_resolution = patches_resolutionself.num_patches = patches_resolution[0] * patches_resolution[1]self.in_chans = in_chansself.embed_dim = embed_dimdef forward(self, x, x_size):B, HW, C = x.shapex = x.transpose(1, 2).view(B, self.embed_dim, x_size[0], x_size[1]) # B Ph*Pw Creturn xdef flops(self):flops = 0return flopsif __name__ == '__main__':RSTB = RSTB(dim=180,input_resolution=(64, 64),depth=6,num_heads=6,window_size=8,mlp_ratio=2,qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,drop=0., attn_drop=0.,drop_path=[0.0, 0.0028571428265422583, 0.0057142856530845165, 0.008571428246796131,0.011428571306169033, 0.014285714365541935], # no impact on SR resultsnorm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,downsample=None,use_checkpoint=False,img_size=64,patch_size=1,resi_connection='1conv')print(RSTB)x = torch.randn(1, 137280, 180)x_size = [264, 520]out_RSTB =RSTB(x, x_size)print(out_RSTB.shape)

4. SwinIR(主框架网络)
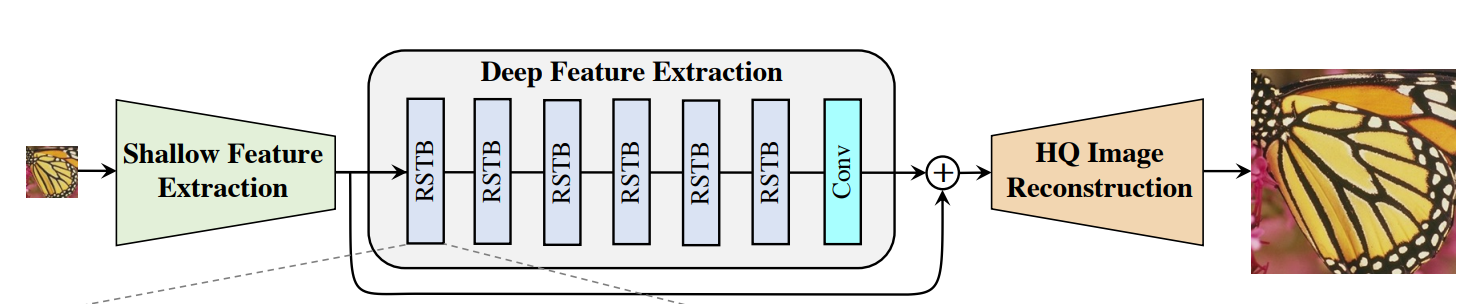
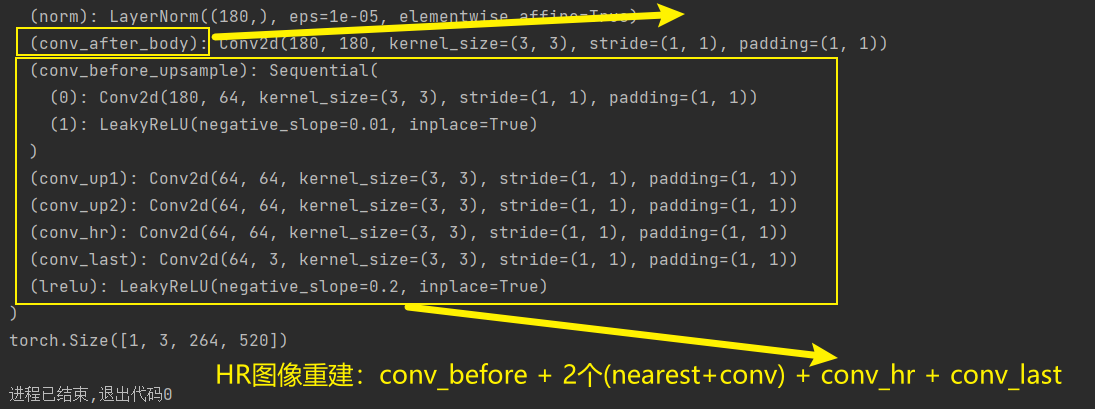
class SwinIR(nn.Module):r""" SwinIRA PyTorch impl of : `SwinIR: Image Restoration Using Swin Transformer`, based on Swin Transformer.Args:img_size (int | tuple(int)): Input image size. Default 64patch_size (int | tuple(int)): Patch size. Default: 1in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3embed_dim (int): Patch embedding dimension. Default: 96depths (tuple(int)): Depth of each Swin Transformer layer. (每个STL的深度)num_heads (tuple(int)): Number of attention heads in different layers.window_size (int): Window size. Default: 7mlp_ratio (float): Ratio of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim.Default: 4 (mlp隐藏层维度与嵌入层维度的比率)qkv_bias (bool): If True, add a learnable bias to query, key, value. Default: Trueqk_scale (float): Override default qk scale of head_dim ** -0.5 if set. Default: Nonedrop_rate (float): Dropout rate. Default: 0attn_drop_rate (float): Attention dropout rate. Default: 0drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.1norm_layer (nn.Module): Normalization layer. Default: nn.LayerNorm.ape (bool): If True, add absolute position embedding to the patch embedding. Default: False (是否使用绝对位置嵌入)patch_norm (bool): If True, add normalization after patch embedding. Default: Trueuse_checkpoint (bool): Whether to use checkpointing to save memory. Default: Falseupscale: Upscale factor. 2/3/4/8 for image SR, 1 for denoising and compress artifact reductionimg_range: Image range. 1. or 255. (输入图像像素值范围:1或者255)upsampler: The reconstruction reconstruction module. 'pixelshuffle'/'pixelshuffledirect'/'nearest+conv'/Noneresi_connection: The convolutional block before residual connection. '1conv'/'3conv'# real srmodel = net(upscale=args.scale, in_chans=3, img_size=64, window_size=8,img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=180, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='nearest+conv', resi_connection='1conv')"""def __init__(self, img_size=64, patch_size=1, in_chans=3,embed_dim=96, depths=[6, 6, 6, 6], num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6],window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1,norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, ape=False, patch_norm=True,use_checkpoint=False, upscale=2, img_range=1., upsampler='', resi_connection='1conv',**kwargs):super(SwinIR, self).__init__()num_in_ch = in_chans # 3num_out_ch = in_chans # 3num_feat = 64self.img_range = img_range# 对图像进行归一化处理if in_chans == 3:rgb_mean = (0.4488, 0.4371, 0.4040)self.mean = torch.Tensor(rgb_mean).view(1, 3, 1, 1) # mean[1, 3, 1, 1]else:self.mean = torch.zeros(1, 1, 1, 1)self.upscale = upscale # 4self.upsampler = upsampler # nearest+convself.window_size = window_size # 8######################################################################################################################################## 1, shallow feature extraction ###################################self.conv_first = nn.Conv2d(num_in_ch, embed_dim, 3, 1, 1) # 3 ---> 96######################################################################################################################################## 2, deep feature extraction ######################################self.num_layers = len(depths) # 6, 默认4self.embed_dim = embed_dim # 180, 默认96self.ape = ape # 默认falseself.patch_norm = patch_norm # 默认trueself.num_features = embed_dim # 180, 默认96self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio # 2, 默认4# split image into non-overlapping patches (把图像分割成patches)self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=embed_dim, embed_dim=embed_dim,norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches # 64*64=4096, 默认264*184= 48576patches_resolution = self.patch_embed.patches_resolution # [64, 64]self.patches_resolution = patches_resolution # [64, 64]# merge non-overlapping patches into image (把多个patches在合成一张图像)self.patch_unembed = PatchUnEmbed(img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=embed_dim, embed_dim=embed_dim,norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)# absolute position embedding # 使用绝对位置嵌入if self.ape:self.absolute_pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, embed_dim))trunc_normal_(self.absolute_pos_embed, std=.02)self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate)# stochastic depth 随机深度: 从 0 到 drop_path_rate 之间均匀分布的数字序列。# torch.linspace(0, 0.1, sum([6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6])): 生成从0开始到0.1结束的等差数列(公差大约是0.002857),总共有36个元素dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] # stochastic depth decay rule# build Residual Swin Transformer blocks (RSTB)self.layers = nn.ModuleList()for i_layer in range(self.num_layers):layer = RSTB(dim=embed_dim,input_resolution=(patches_resolution[0],patches_resolution[1]),depth=depths[i_layer],num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],window_size=window_size,mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])], # no impact on SR resultsnorm_layer=norm_layer,downsample=None,use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,img_size=img_size,patch_size=patch_size,resi_connection=resi_connection)self.layers.append(layer)self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features)# build the last conv layer in deep feature extractionif resi_connection == '1conv':self.conv_after_body = nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, embed_dim, 3, 1, 1)elif resi_connection == '3conv':# to save parameters and memoryself.conv_after_body = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, embed_dim // 4, 3, 1, 1),nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(embed_dim // 4, embed_dim // 4, 1, 1, 0),nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(embed_dim // 4, embed_dim, 3, 1, 1))##################################################################################################################################### 3, high quality image reconstruction ################################if self.upsampler == 'pixelshuffle':# for classical SRself.conv_before_upsample = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, num_feat, 3, 1, 1),nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True))self.upsample = Upsample(upscale, num_feat)self.conv_last = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_out_ch, 3, 1, 1)elif self.upsampler == 'pixelshuffledirect':# for lightweight SR (to save parameters)self.upsample = UpsampleOneStep(upscale, embed_dim, num_out_ch,(patches_resolution[0], patches_resolution[1]))elif self.upsampler == 'nearest+conv':# for real-world SR (less artifacts)self.conv_before_upsample = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, num_feat, 3, 1, 1),nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True))self.conv_up1 = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1)if self.upscale == 4:self.conv_up2 = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1)self.conv_hr = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1)self.conv_last = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_out_ch, 3, 1, 1)self.lrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True)else:# for image denoising and JPEG compression artifact reductionself.conv_last = nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, num_out_ch, 3, 1, 1)self.apply(self._init_weights)def _init_weights(self, m):if isinstance(m, nn.Linear): # 对于线性层,权重使用截断正态分布初始化,trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None: # 对于含有偏置的线性层,将偏置项 m.bias 初始化为零。nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm): # 对于layerNorm,将权重初始化为1,偏置初始化为0nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)@torch.jit.ignoredef no_weight_decay(self):return {'absolute_pos_embed'}@torch.jit.ignoredef no_weight_decay_keywords(self):return {'relative_position_bias_table'}def check_image_size(self, x):_, _, h, w = x.size()mod_pad_h = (self.window_size - h % self.window_size) % self.window_sizemod_pad_w = (self.window_size - w % self.window_size) % self.window_sizex = F.pad(x, (0, mod_pad_w, 0, mod_pad_h), 'reflect')return xdef forward_features(self, x):x_size = (x.shape[2], x.shape[3])x = self.patch_embed(x)if self.ape:x = x + self.absolute_pos_embedx = self.pos_drop(x)for layer in self.layers:x = layer(x, x_size)x = self.norm(x) # B L Cx = self.patch_unembed(x, x_size)return xdef forward(self, x):H, W = x.shape[2:]x = self.check_image_size(x)self.mean = self.mean.type_as(x)x = (x - self.mean) * self.img_rangeif self.upsampler == 'pixelshuffle':# for classical SRx = self.conv_first(x)x = self.conv_after_body(self.forward_features(x)) + xx = self.conv_before_upsample(x)x = self.conv_last(self.upsample(x))elif self.upsampler == 'pixelshuffledirect':# for lightweight SRx = self.conv_first(x)x = self.conv_after_body(self.forward_features(x)) + xx = self.upsample(x)elif self.upsampler == 'nearest+conv':# for real-world SRx = self.conv_first(x)x = self.conv_after_body(self.forward_features(x)) + xx = self.conv_before_upsample(x)x = self.lrelu(self.conv_up1(torch.nn.functional.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')))if self.upscale == 4:x = self.lrelu(self.conv_up2(torch.nn.functional.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')))x = self.conv_last(self.lrelu(self.conv_hr(x)))else:# for image denoising and JPEG compression artifact reductionx_first = self.conv_first(x)res = self.conv_after_body(self.forward_features(x_first)) + x_firstx = x + self.conv_last(res)x = x / self.img_range + self.meanreturn x[:, :, :H * self.upscale, :W * self.upscale]def flops(self):flops = 0H, W = self.patches_resolutionflops += H * W * 3 * self.embed_dim * 9flops += self.patch_embed.flops()for i, layer in enumerate(self.layers):flops += layer.flops()flops += H * W * 3 * self.embed_dim * self.embed_dimflops += self.upsample.flops()return flopsif __name__ == '__main__':SwinIR = SwinIR(upscale=4, in_chans=3, img_size=64, window_size=8,img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=180, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='nearest+conv', resi_connection='1conv')print(SwinIR)x = torch.randn(1, 3, 264, 520)out_SwinIR = SwinIR(x)print(x.shape)

二、解读SwinIR测试主文件:main_test_swinir.py
import argparse
import cv2
import glob
import numpy as np
from collections import OrderedDict
import os
import torch
import requestsfrom models.network_swinir import SwinIR as net
from utils import util_calculate_psnr_ssim as util# 测试:python main_test_swinir.py --task real_sr --scale 4 --model_path model_zoo/swinir/003_realSR_BSRGAN_DFO_s64w8_SwinIR-M_x4_GAN.pth --folder_lq testsets/RealSRSet+5images --tiledef main():parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()# IR中的三种任务parser.add_argument('--task', type=str, default='real_sr', help='classical_sr, lightweight_sr, real_sr, ''gray_dn, color_dn, jpeg_car, color_jpeg_car')# 缩放尺寸parser.add_argument('--scale', type=int, default=4, help='scale factor: 1, 2, 3, 4, 8') # 1 for dn and jpeg car# 添加噪声的程度parser.add_argument('--noise', type=int, default=15, help='noise level: 15, 25, 50')# jpeg压缩程度parser.add_argument('--jpeg', type=int, default=40, help='scale factor: 10, 20, 30, 40')# 训练的patch尺寸parser.add_argument('--training_patch_size', type=int, default=128, help='patch size used in training SwinIR. ''Just used to differentiate two different settings in Table 2 of the paper. ''Images are NOT tested patch by patch.')# 是否使用real image sr的大模型parser.add_argument('--large_model', action='store_true', help='use large model, only provided for real image sr')# 训练好的模型路径parser.add_argument('--model_path', type=str,default='model_zoo/swinir/003_realSR_BSRGAN_DFO_s64w8_SwinIR-M_x4_GAN.pth')# 测试的LQ图像文件路径parser.add_argument('--folder_lq', type=str, default='testsets/RealSRSet+5images', help='input low-quality test image folder')parser.add_argument('--folder_gt', type=str, default=None, help='input ground-truth test image folder')# 测试时,是否将图像分成多个小块进行测试。(超出显存时,使用)parser.add_argument('--tile', type=int, default=None,help='Tile size, None for no tile during testing (testing as a whole)')# 不同小块的重叠区域parser.add_argument('--tile_overlap', type=int, default=32, help='Overlapping of different tiles')args = parser.parse_args()device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')# set up model 加载训练后的SwinIR模型if os.path.exists(args.model_path):print(f'loading model from {args.model_path}')else:os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(args.model_path), exist_ok=True)url = 'https://github.com/JingyunLiang/SwinIR/releases/download/v0.0/{}'.format(os.path.basename(args.model_path))r = requests.get(url, allow_redirects=True)print(f'downloading model {args.model_path}')open(args.model_path, 'wb').write(r.content)model = define_model(args) # 根据model.task的选择,设置不同的网络模型model.eval()model = model.to(device)# setup folder: 测试LQ图像的文件路径, save_dir: 保存的HQ文件路径, border: 0, window_size: 8folder, save_dir, border, window_size = setup(args)os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)test_results = OrderedDict() # 按照有序插入顺序存储 的有序字典test_results['psnr'] = []test_results['ssim'] = []test_results['psnr_y'] = []test_results['ssim_y'] = []test_results['psnrb'] = []test_results['psnrb_y'] = []psnr, ssim, psnr_y, ssim_y, psnrb, psnrb_y = 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0# 整个循环会依次处理文件夹 folder 中的每个文件,并对其进行排序。在每次迭代中,idx: 文件在列表中的索引,path: 文件的完整路径。# glob.glob(): 函数用于获取匹配指定模式的文件路径列表# os.path.join(folder, '*'): 会生成一个匹配指定文件夹下所有文件的模式for idx, path in enumerate(sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(folder, '*')))):# read image 获取图像的名字,获取图像[h, w, c],(float32,0-1之间)imgname, img_lq, img_gt = get_image_pair(args, path) # image to HWC-BGR, float32# 先把使用CV2获取的图像颜色通道BGR转换成RGB,然后在将图像[h, w, c] ---> [c, h, w]img_lq = np.transpose(img_lq if img_lq.shape[2] == 1 else img_lq[:, :, [2, 1, 0]],(2, 0, 1)) # HCW-BGR to CHW-RGB# ndarry[c, h, w] ---> tensor[1, c, h, w]img_lq = torch.from_numpy(img_lq).float().unsqueeze(0).to(device) # CHW-RGB to NCHW-RGB# inferencewith torch.no_grad():# pad input image to be a multiple of window_size 将输入图像填充至window_size的倍数_, _, h_old, w_old = img_lq.size() # h_old:256 w_old:512h_pad = (h_old // window_size + 1) * window_size - h_old # 需要填充的高度:8w_pad = (w_old // window_size + 1) * window_size - w_old # 需要填充的宽度:8# torch.flip(img_lq, [dim]):对输入的 img_lq 图像进行第dim维度(水平/垂直)方向上的镜像翻转。img_lq = torch.cat([img_lq, torch.flip(img_lq, [2])], 2)[:, :, :h_old + h_pad, :] # 水平镜像填充高度 [1, 3, 256+8, 512] = [1, 3, 264, 512]img_lq = torch.cat([img_lq, torch.flip(img_lq, [3])], 3)[:, :, :, :w_old + w_pad] # 垂直镜像填充宽度 [1, 3, 256+8, 512+8] = [1, 3, 264, 520]# 前向传播,得到4倍放大的HR图像output = test(img_lq, model, args, window_size) # [1, 3, 264, 520] --> [1, 3, 264*4, 520*4] = [1, 3, 1056, 2080]# 在将填充图像剪裁为原始图像的四倍。output = output[..., :h_old * args.scale, :w_old * args.scale] # 在将图像恢复成原始图像的4倍 [1, 3, 1024, 2048]# save image将重建的HR图像[1, 3, 1024, 2048] ---> [3, 1024, 2048], 并将元素值限制在(0,1), 且转为ndarry# x.clamp_(0, 1): 将x的元素值限制到(0, 1)(<0的用0代替,>1的用1代替)output = output.data.squeeze().float().cpu().clamp_(0, 1).numpy() # [3, 1024, 2048]if output.ndim == 3:# 先将通道维度RGB---> BGR, 然后在将CHW ---> HWCoutput = np.transpose(output[[2, 1, 0], :, :], (1, 2, 0)) # CHW-RGB to HCW-BGR# 再将元素值由(0,1)的float32---> (0, 255)的uint8output = (output * 255.0).round().astype(np.uint8) # float32 to uint8# 最后使用CV2库保存生成图像cv2.imwrite(f'{save_dir}/{imgname}_SwinIR.png', output)# evaluate psnr/ssim/psnr_b (对于由GT图像的测试任务,则计算其相应的指标)if img_gt is not None:img_gt = (img_gt * 255.0).round().astype(np.uint8) # float32 to uint8img_gt = img_gt[:h_old * args.scale, :w_old * args.scale, ...] # crop gtimg_gt = np.squeeze(img_gt)psnr = util.calculate_psnr(output, img_gt, crop_border=border)ssim = util.calculate_ssim(output, img_gt, crop_border=border)test_results['psnr'].append(psnr)test_results['ssim'].append(ssim)if img_gt.ndim == 3: # RGB imagepsnr_y = util.calculate_psnr(output, img_gt, crop_border=border, test_y_channel=True)ssim_y = util.calculate_ssim(output, img_gt, crop_border=border, test_y_channel=True)test_results['psnr_y'].append(psnr_y)test_results['ssim_y'].append(ssim_y)if args.task in ['jpeg_car', 'color_jpeg_car']:psnrb = util.calculate_psnrb(output, img_gt, crop_border=border, test_y_channel=False)test_results['psnrb'].append(psnrb)if args.task in ['color_jpeg_car']:psnrb_y = util.calculate_psnrb(output, img_gt, crop_border=border, test_y_channel=True)test_results['psnrb_y'].append(psnrb_y)print('Testing {:d} {:20s} - PSNR: {:.2f} dB; SSIM: {:.4f}; PSNRB: {:.2f} dB;''PSNR_Y: {:.2f} dB; SSIM_Y: {:.4f}; PSNRB_Y: {:.2f} dB.'.format(idx, imgname, psnr, ssim, psnrb, psnr_y, ssim_y, psnrb_y))else:print('Testing {:d} {:20s}'.format(idx, imgname))# summarize psnr/ssimif img_gt is not None:ave_psnr = sum(test_results['psnr']) / len(test_results['psnr'])ave_ssim = sum(test_results['ssim']) / len(test_results['ssim'])print('\n{} \n-- Average PSNR/SSIM(RGB): {:.2f} dB; {:.4f}'.format(save_dir, ave_psnr, ave_ssim))if img_gt.ndim == 3:ave_psnr_y = sum(test_results['psnr_y']) / len(test_results['psnr_y'])ave_ssim_y = sum(test_results['ssim_y']) / len(test_results['ssim_y'])print('-- Average PSNR_Y/SSIM_Y: {:.2f} dB; {:.4f}'.format(ave_psnr_y, ave_ssim_y))if args.task in ['jpeg_car', 'color_jpeg_car']:ave_psnrb = sum(test_results['psnrb']) / len(test_results['psnrb'])print('-- Average PSNRB: {:.2f} dB'.format(ave_psnrb))if args.task in ['color_jpeg_car']:ave_psnrb_y = sum(test_results['psnrb_y']) / len(test_results['psnrb_y'])print('-- Average PSNRB_Y: {:.2f} dB'.format(ave_psnrb_y))def define_model(args):# 001 classical image srif args.task == 'classical_sr':model = net(upscale=args.scale, in_chans=3, img_size=args.training_patch_size, window_size=8,img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=180, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='pixelshuffle', resi_connection='1conv')param_key_g = 'params'# 002 lightweight image sr# use 'pixelshuffledirect' to save parameterselif args.task == 'lightweight_sr':model = net(upscale=args.scale, in_chans=3, img_size=64, window_size=8,img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=60, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='pixelshuffledirect', resi_connection='1conv')param_key_g = 'params'# 003 real-world image srelif args.task == 'real_sr':if not args.large_model:# use 'nearest+conv' to avoid block artifactsmodel = net(upscale=args.scale, in_chans=3, img_size=64, window_size=8,img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=180, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='nearest+conv', resi_connection='1conv')else:# larger model size; use '3conv' to save parameters and memory; use ema for GAN trainingmodel = net(upscale=args.scale, in_chans=3, img_size=64, window_size=8,img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=240,num_heads=[8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8, 8],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='nearest+conv', resi_connection='3conv')param_key_g = 'params_ema'# 004 grayscale image denoisingelif args.task == 'gray_dn':model = net(upscale=1, in_chans=1, img_size=128, window_size=8,img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=180, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='', resi_connection='1conv')param_key_g = 'params'# 005 color image denoisingelif args.task == 'color_dn':model = net(upscale=1, in_chans=3, img_size=128, window_size=8,img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=180, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='', resi_connection='1conv')param_key_g = 'params'# 006 grayscale JPEG compression artifact reduction# use window_size=7 because JPEG encoding uses 8x8; use img_range=255 because it's sligtly better than 1elif args.task == 'jpeg_car':model = net(upscale=1, in_chans=1, img_size=126, window_size=7,img_range=255., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=180, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='', resi_connection='1conv')param_key_g = 'params'# 006 color JPEG compression artifact reduction# use window_size=7 because JPEG encoding uses 8x8; use img_range=255 because it's sligtly better than 1elif args.task == 'color_jpeg_car':model = net(upscale=1, in_chans=3, img_size=126, window_size=7,img_range=255., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], embed_dim=180, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6],mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='', resi_connection='1conv')param_key_g = 'params'pretrained_model = torch.load(args.model_path)model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model[param_key_g] if param_key_g in pretrained_model.keys() else pretrained_model,strict=True)return modeldef setup(args):# 001 classical image sr/ 002 lightweight image srif args.task in ['classical_sr', 'lightweight_sr']:save_dir = f'results/swinir_{args.task}_x{args.scale}'folder = args.folder_gtborder = args.scalewindow_size = 8# 003 real-world image srelif args.task in ['real_sr']:save_dir = f'results/swinir_{args.task}_x{args.scale}'if args.large_model:save_dir += '_large'folder = args.folder_lqborder = 0window_size = 8# 004 grayscale image denoising/ 005 color image denoisingelif args.task in ['gray_dn', 'color_dn']:save_dir = f'results/swinir_{args.task}_noise{args.noise}'folder = args.folder_gtborder = 0window_size = 8# 006 JPEG compression artifact reductionelif args.task in ['jpeg_car', 'color_jpeg_car']:save_dir = f'results/swinir_{args.task}_jpeg{args.jpeg}'folder = args.folder_gtborder = 0window_size = 7return folder, save_dir, border, window_sizedef get_image_pair(args, path):# 用于将文件路径 path 中的文件名和扩展名分离,并将它们分别赋值给 imgname 和 imgext 变量(imgname, imgext) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(path))# 001 classical image sr/ 002 lightweight image sr (load lq-gt image pairs)if args.task in ['classical_sr', 'lightweight_sr']:img_gt = cv2.imread(path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR).astype(np.float32) / 255.img_lq = cv2.imread(f'{args.folder_lq}/{imgname}x{args.scale}{imgext}', cv2.IMREAD_COLOR).astype(np.float32) / 255.# 003 real-world image sr (load lq image only)elif args.task in ['real_sr']:img_gt = None# 读取路径为 path 的图像文件,并将其转换为浮点型(float32)数组,同时进行归一化处理,范围在0到1之间img_lq = cv2.imread(path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR).astype(np.float32) / 255.# 004 grayscale image denoising (load gt image and generate lq image on-the-fly)elif args.task in ['gray_dn']:img_gt = cv2.imread(path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE).astype(np.float32) / 255.np.random.seed(seed=0)img_lq = img_gt + np.random.normal(0, args.noise / 255., img_gt.shape)img_gt = np.expand_dims(img_gt, axis=2)img_lq = np.expand_dims(img_lq, axis=2)# 005 color image denoising (load gt image and generate lq image on-the-fly)elif args.task in ['color_dn']:img_gt = cv2.imread(path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR).astype(np.float32) / 255.np.random.seed(seed=0)img_lq = img_gt + np.random.normal(0, args.noise / 255., img_gt.shape)# 006 grayscale JPEG compression artifact reduction (load gt image and generate lq image on-the-fly)elif args.task in ['jpeg_car']:img_gt = cv2.imread(path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)if img_gt.ndim != 2:img_gt = util.bgr2ycbcr(img_gt, y_only=True)result, encimg = cv2.imencode('.jpg', img_gt, [int(cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY), args.jpeg])img_lq = cv2.imdecode(encimg, 0)img_gt = np.expand_dims(img_gt, axis=2).astype(np.float32) / 255.img_lq = np.expand_dims(img_lq, axis=2).astype(np.float32) / 255.# 006 JPEG compression artifact reduction (load gt image and generate lq image on-the-fly)elif args.task in ['color_jpeg_car']:img_gt = cv2.imread(path)result, encimg = cv2.imencode('.jpg', img_gt, [int(cv2.IMWRITE_JPEG_QUALITY), args.jpeg])img_lq = cv2.imdecode(encimg, 1)img_gt = img_gt.astype(np.float32) / 255.img_lq = img_lq.astype(np.float32) / 255.return imgname, img_lq, img_gtdef test(img_lq, model, args, window_size):# 是否将图像分成多个小块进行测试。(超出显存时,使用)if args.tile is None:# test the image as a wholeoutput = model(img_lq)else:# test the image tile by tileb, c, h, w = img_lq.size()tile = min(args.tile, h, w)assert tile % window_size == 0, "tile size should be a multiple of window_size"tile_overlap = args.tile_overlapsf = args.scale# 计算每次滑动的步长stride = tile - tile_overlap# 根据步长和图像高度计算垂直方向上分块的起始索引列表。h_idx_list = list(range(0, h - tile, stride)) + [h - tile]# 根据步长和图像宽度计算水平方向上分块的起始索引列表。w_idx_list = list(range(0, w - tile, stride)) + [w - tile]# 创建一个与输入图像相同类型的全零张量 E,用于存储每个分块的测试结果。E = torch.zeros(b, c, h * sf, w * sf).type_as(img_lq)# 创建一个与 E 相同类型的全零张量 W,用于存储每个分块的权重信息。W = torch.zeros_like(E)# 循环遍历垂直和水平方向上的分块起始索引。for h_idx in h_idx_list:for w_idx in w_idx_list:# 根据当前分块的起始索引,从输入图像中提取对应的分块。in_patch = img_lq[..., h_idx:h_idx + tile, w_idx:w_idx + tile]# 对每个块进行前向传播的超分辨率重建out_patch = model(in_patch)out_patch_mask = torch.ones_like(out_patch)# 将当前分块的测试结果和权重信息添加到全局张量 E 和 W 中的相应位置。E[..., h_idx * sf:(h_idx + tile) * sf, w_idx * sf:(w_idx + tile) * sf].add_(out_patch)W[..., h_idx * sf:(h_idx + tile) * sf, w_idx * sf:(w_idx + tile) * sf].add_(out_patch_mask)# 将 E 中的每个分块测试结果除以 W 中的相应权重,得到的结果为所有分块测试结果的加权平均值。output = E.div_(W)return outputif __name__ == '__main__':main()原图像


重建HR图像:


这篇关于超分之SwinIR官方代码解读的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




