本文主要是介绍next-generation sequencing analysis method——paper1,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
半路出家会有很多困惑,我想若要踏实基础,一步步了解二代测序所有过程,读paper应该是正统。因此今天在Web of Science中检索"next-generation sequencing analysis method",找到多篇关于二代测序的发展历史,分析方法及应用等方面的文章,并在读后记录下来心得,应该会有所提高。
第一篇:

来自于:Omics Technologies and Bio-engineering: Towards Improving Quality of Life
文中主要介绍了,sequencing platforms, the characteristics of the data produced by each of them, the main tools for de novo and reference genome assembly, the effects of the assembly process on genome annotation will be discussed. The concepts related to RNA-Seq data analysis with the most used software, ChIP-Seq technology, and the protocols and pipelines used in metagenomic approaches will be discussed. The sequencing chemistry of some of these NGS technologies is described below.
11.1 主流平台
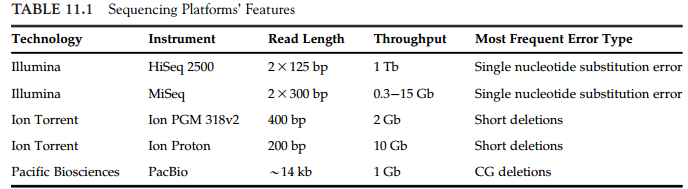
Illumina Platform, Ion Torrent Platform, PacBio Platform
STRUCTURAL GENOMICS
11.3.1 De Novo Assembly(不依赖于参考基因组的直接拼接)
Different computational approaches:
greedy algorithms, overlap-layout-consensus (OLC), and De Bruijn graphs
11.3.1.1 greedy algorithms
software: SSAKE, SHARCGS and VCAKE,对计算机要求高。
目前通常将这种方法与后两者结合使用
11.3.1.2 OLC
分为三步:识别reads中可能有overlap的区域;基于overlaps作图;根据算法生成最终序列。
software: Newbler、Mira、Edena
11.3.1.3 De Bruijn
最常用于组装原核基因组(short reads)的软件:Velvet
SPADES用于Ion Torrent platform产生的random lenghts reads
常用语真核基因组拼装的软件:SOAPdenovo、ALL-PATHS-LG
拼装过程中产生的gaps通常用“N”表示,这些区域通常是由于基因组中重复序列产生的,可以通过不同手段解决这些区域。如Paired genomic libraries(paired-end and mate-pair libraries)
用于基因组拼接之后,产生scaffolds并解决gap区域的软件:
其一通过分析contigs的末尾区域之间的overlap,确定两侧序列,如SSPACE
其二通过paired libraries解决gaps,如GAPFILLER
拼接结果评估:
(1)assembly process:metrics such as N50(评估产生序列的长度,contigs的平均长度和数量,最长和最短contigs)
(2)assembled contigs:通过mapping of paired reads进行评估。
在assembly sequence中寻找真核关键基因: Genome Assembly Gold-standard Evaluation (GAGE) tool
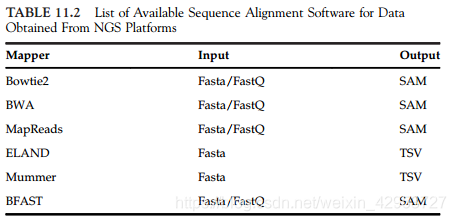
11.3.2 Reference Assembly
Software:
(1)Bowtie: efficient in terms of memory management but has some issues regarding reads that do not exhibit a perfect match, though its parameters can be adjusted
(2)BWA: Burrows-Wheeler transformation algorithm to increase mapping speed
(3)SHRiMP: compatible with data in letter space and color space format produced by the SOLiD platform
(4)SOAP2:single nucleotide polymorphism
(5)TopHat2:Ion Torrent platform
(6)mrsFAST:examines all possibilities for mapping to the reference genome, making it useful for variance detection studies
11.3.3 Genome Annotation
Describing the function of the product of a predicted gene
Bioinformatics software:
(1) signal sensors (e.g., for TATA box, start and stop codon, or poly-A signal detection),
(2) content sensors (e.g., for G + C content, codon usage, or dicodon frequency detection), and
(3) similarity detection (e.g., between proteins from closely related organisms, mRNA from the same organism, or reference genomes)
Three basic categories:
(1)nucleotidelevel annotation, which seeks to identify the physical location of DNA sequences to determine where components such as genes, RNAs, and repetitive elements are located. Sequencing and/or assembly errors at this stage can result in false pseudogenes through indels.
(2)protein-level annotation, which seeks to determine the possible functions of genes, identifying which one a given organism does or does not have.
(3)process-level annotation, which aims to identify the pathways and processes in which different genes interact, assembling an efficient functional annotation.
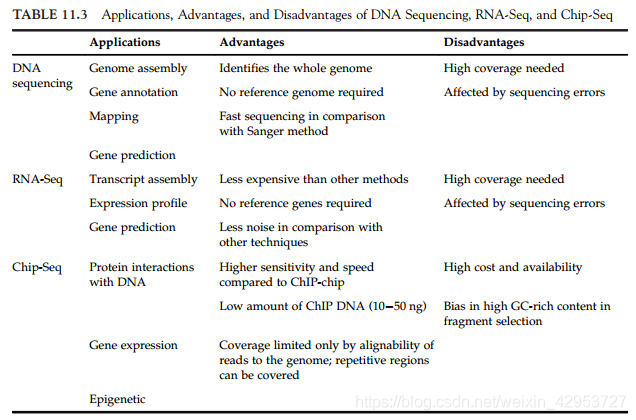
11.4.1 RNA-Seq: De Novo and Reference-Based Approaches
Identification, measurement, and comparison of gene expression in a target transcriptome
Applied to functional studies, such as expression profile analysis, annotation correction, characterization of differentially expressed genes, and gene prediction
(1)Annotated reference:
choose 1:
mapping reads software: Bioscope (quantifies the expression of each gene)
analyzing results software: DEGseq (statistical analysis of gene expression under the different conditions studied, to identify differentially expressed genes)
choose 2:
TopHat: maps the reads to the annotated reference genes, generating a mapping file in bam format.
Cufflinks: calculate the expression of the genes and identify the genes that are differentially expressed between the analyzed samples
(2)De novo:
most widely used software: SOAPdenovo-Trans、Trans-AByss、Trinity
Trinity: produce a high-quality assembly of a transcriptome with a low error rate and identify multiple isoforms.
** Trans-Abyss**: generates optimized assemblies, high coverage transcripts, assemblies with different k-mers.
SOAPdenovo-Trans: greatest transcript contiguity, least amount of redundancy, fastest of three.
(3)correction of genome annotations:
Mapping of the reads to the annotation (mapping coverage to be evaluated for all annotated genes and intergenic regions, allowing the identification of potential new transcripts)
software: Cufflinks and Scripture
(4)gene prediction:
identify new genes and incorporate into an existing annotation
software: GeneMark-ET tool
11.4.2 ChIP-Seq
MACS: empirically calculates the change in the coverage of ChIP-Seq reads and uses this measure to improve the resolution of the prediction of the binding sites
** ChIPDiff**、ODIN: identify the significant differences in two ChIP-Seq signals under different biological conditions using hidden Markov models
这篇关于next-generation sequencing analysis method——paper1的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






