本文主要是介绍Android TV 焦点与按键事件分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/yummykwok/article/details/56667260
在触摸屏出现在手机上之前,焦点是手机上人机交互中最重要的一个概念。焦点即用户当前的关注点(或区域),手机上将该区域以某种形式高亮显示,人们通过上、下、左、右方向键可以移动焦点,按确认键后手机将打开(或呈显)与当前焦点关联的内容;触摸屏的出现大大地简化了人机交互,触摸事件(TouchEvent)成了核心,焦点的存在感就很小了。
但是对于电视来说,其显示屏面积大,人机距离远,触摸屏的方案显然不合理。因此目前Android电视的人机交互仍旧使用遥控器为主,焦点的重要性在电视上又显现出来了。通过遥控器将方向键或确认键信号(或信息)发送到电视端后,转换为标准按键事件(KeyEvent),而按键事件分发最终目标就是焦点。
1、初识View之焦点
View是UI组件的基本构建,也自然就是焦点的承载者。View是否可聚焦,由FOCUSABLE和FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE(触摸模式下也可以有焦点)两个FLAG标识。
- public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
- this(context);
- final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(
- attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.View, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
- final int N = a.getIndexCount();
- for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
- int attr = a.getIndex(i);
- switch (attr) {
- ……
- case com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_focusable:
- if (a.getBoolean(attr, false)) {
- viewFlagValues |= FOCUSABLE;
- viewFlagMasks |= FOCUSABLE_MASK;
- }
- break;
- case com.android.internal.R.styleable.View_focusableInTouchMode:
- if (a.getBoolean(attr, false)) {
- viewFlagValues |= FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE | FOCUSABLE;
- viewFlagMasks |= FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE | FOCUSABLE_MASK;
- }
- break;
- ……
- }
- }
- ……
- }
从上面
View
的构建方法上看,在
xml
里即可为其设置是否可聚焦,以
Button
举个栗子,
- public class Button extends TextView {
- ……
- public Button(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
- this(context, attrs, com.android.internal.R.attr.buttonStyle);
- }
- ……
- }
Button设置了一个默认的style,我们找出源码看看,
- <stylenamestylename="Widget.Button">
- <itemnameitemname="background">@drawable/btn_default</item>
- <strong><itemnameitemname="focusable">true</item></strong>
- <itemnameitemname="clickable">true</item>
- <itemnameitemname="textAppearance">?attr/textAppearanceSmallInverse</item>
- <itemnameitemname="textColor">@color/primary_text_light</item>
- <itemnameitemname="gravity">center_vertical|center_horizontal</item>
- </style>
聚焦后,
Button
背景将发生改变,向用户表示该
View
已聚焦。我们可以打开该
style
设置的
background
的源文件
btn_default
看看,
- <selectorxmlns:androidselectorxmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
- ......
- <itemandroid:state_focuseditemandroid:state_focused="true"
- android:drawable="@drawable/btn_default_normal_disable_focused"/>
- <item
- android:drawable="@drawable/btn_default_normal_disable"/>
- </selector>
可以看到,这是个
selector
,状态变成已聚焦后,使用另一
drawable
做为背景(这个过程具体是怎么实现的,我们后面分析)。从上面分析看,
TextView
变成
Button
只需要为其
style
设置几个关键的属性即可,最主要的是
clickable,focusable, background
,以下
TextView
即相当于
Button
了,
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:focusable="true"
- android:clickable="true"
- android:background=”@drawable/btn_default” />
对于设置是否可聚焦,
View
还提供以下方法
:
- public void setFocusable(boolean focusable) ;
- public void setFocusableInTouchMode(boolean focusableInTouchMode);
2、请求焦点
2.1 View的焦点请求
焦点的请求,View提供了以下几个方法,
- public final boolean requestFocus();
- public final boolean requestFocus(int direction);
- public boolean requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect);
我们打开源码看,这些方法都做了些什么
[File]android/view/View.java
- public final boolean requestFocus() {
- return requestFocus(View.FOCUS_DOWN);
- }
-
- public final boolean requestFocus(int direction) {
- return requestFocus(direction, null);
- }
-
- public boolean requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
- return requestFocusNoSearch(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
- }
- private boolean requestFocusNoSearch(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
-
- if ((mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_MASK) != FOCUSABLE ||
- (mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != VISIBLE) {
- return false;
- }
-
- if (isInTouchMode() &&
- (FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE != (mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE))) {
- return false;
- }
-
- if (hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus()) {
- return false;
- }
- handleFocusGainInternal(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
- return true;
- }
可以看到,前两个重载方法最终都走到第三个方法内,对于
View
来讲,关键就是看这个私有方法
requestFocusNoSearch
,这个方法主要做了以下4
件事:
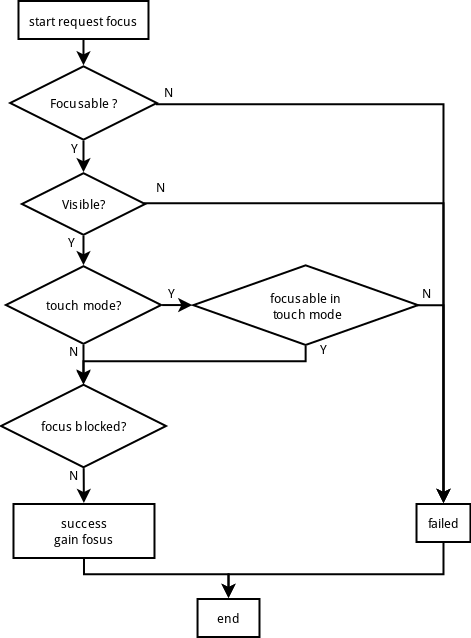
1)检查View 是否可聚焦,是否可见。聚焦前提是 FOCUSABLE并且VISIBLE
2)如果是触摸模式,则检查该模式下是否可聚焦(FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE)
3)检查是否被上一层(ViewGroup)屏蔽焦点
4)当前View获取焦点,处理焦点变动
2.2 ViewGroup的焦点请求
ViewGroup是可以包含其它View 的一种特殊的 View,各种Layout均是它的子类;对于焦点请求,与View不同的是:
1)它可以优先让下层View请求焦点,失败后再自己请求
2)可以优先于下层View请求焦点,失败后再下层View请求
3)可以屏蔽下层View请求焦点
这三种对下一层请求焦点的控制,分别用了三个FLAG记录于mGroupFlags中,依次对应为
1)FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS
2)FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS
3)FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS
设置这个控制的方法和属性为:
- public void setDescendantFocusability(int focusability);
-
- android:descendantFocusability
设置好后,那么它具体是怎么控制的呢?我们分以下几种情况来分析:
1)ViewGroup的下层View请求焦点: 按上一节说的,View请求焦点需要检查是否被上层屏蔽的,实际就是检查上层是否设置了FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS这个FLAG,我们回到View.java查看hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus这个检查方法,
- private boolean hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus() {
- final boolean focusableInTouchMode = isFocusableInTouchMode();
- ViewParent ancestor = mParent;
- while (ancestor instanceof ViewGroup) {
- final ViewGroup vgAncestor = (ViewGroup) ancestor;
- if (vgAncestor.getDescendantFocusability() == ViewGroup.FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS
- || (!focusableInTouchMode && vgAncestor.shouldBlockFocusForTouchscreen())) {
- return true;
- } else {
- ancestor = vgAncestor.getParent();
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
这个方法中,一层层往上找,看是否有ViewGroup
设置了FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS
。
2)ViewGroup请求焦点:ViewGroup重写了requestFocus方法以实现控制优先级,
- @Override
- public boolean requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
- int descendantFocusability = getDescendantFocusability();
- switch (descendantFocusability) {
- case FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS:
- return super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
- case FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS: {
- final boolean took = super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
- return took ? took : onRequestFocusInDescendants(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
- }
- case FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS: {
- final boolean took = onRequestFocusInDescendants(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
- return took ? took : super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
- }
- ……
- }
- }
- protected boolean onRequestFocusInDescendants(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
- ……
- for (int i = index; i != end; i += increment) {
- View child = children[i];
- if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {
- if (child.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect)) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
2.3焦点的变更
2.1中提到View请求焦点最后一步是处理焦点变动,我们来细看下里面都做了些什么
- void handleFocusGainInternal(@FocusRealDirection int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
- if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) == 0) {
- mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FOCUSED;
- if (mParent != null) {
- mParent.requestChildFocus(this, this);
- }
- if (mAttachInfo != null) {
-
- View oldFocus = (mAttachInfo != null) ? getRootView().findFocus() : null;
- mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnGlobalFocusChange(oldFocus, this);
- }
- onFocusChanged(true, direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
- refreshDrawableState();
- }
- }
至此,焦点请求到显示更新已经明了,但还有个问题,
同一个界面上只可以有一个焦点,当一个
View
获取焦点,应当让前一个焦点失焦。这意味着必须有个地方记录当前焦点,
担此重任的即是ViewGroup
里私有变量mFocused
,
- public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
- ……
-
- private View mFocused;
- ……
- }
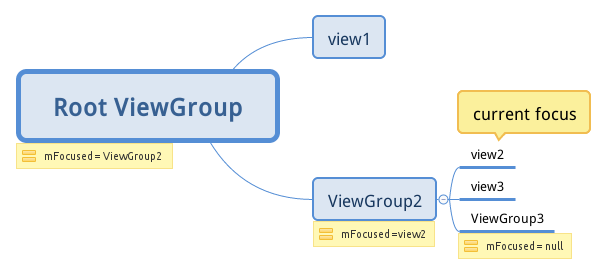
这个变量指向的可能是:
1)下一层有焦点的View(或ViewGroup)
2)焦点在其下层的ViewGroup
3)null,焦点不在它的下层
举个例子:
很明显,如果界面上有焦点的话,从上层往下一层层找,就能找到。View/ViewGroup提供findFocus方法,用于找到当前范围内的焦点,
- [File]View.java
- public View findFocus() {
- return (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) != 0 ? this : null;
- }
-
-
- [File]ViewGroup.java
-
- @Override
- public View findFocus() {
- if (isFocused()) {
- return this;
- }
- if (mFocused != null) {
- return mFocused.findFocus();
- }
- return null;
- }
那么问题来了,这个
mFocused
是怎么更新的呢,又是怎么让它失焦呢?关键就在于
handleFocusGainInternal
中的这个调用:
- mParent.requestChildFocus(this, this);
[File] ViewGroup.java
- public void requestChildFocus(View child, View focused) {
- if (getDescendantFocusability() == FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS) {
- return;
- }
-
- super.unFocus(focused);
-
- if (mFocused != child) {
- if (mFocused != null) {
- mFocused.unFocus(focused);
- }
- mFocused = child;
- }
- if (mParent != null) {
- mParent.requestChildFocus(this, focused);
- }
- }
我
们可以看
requestChildFocus
这个方法会一层层往上调用,让 mFocused
失焦,然后更新为新的 child
;具体地,前一焦点是怎么被清除的呢,我们来看下 unFocus
这个方法,
[File]View.java
- void unFocus(View focused) {
- clearFocusInternal(focused, false, false);
- }
[File]ViewGroup.java
- @Override
- void unFocus(View focused) {
- if (mFocused == null) {
- super.unFocus(focused);
- } else {
- mFocused.unFocus(focused);
- mFocused = null;
- }
- }
对于 ViewGroup
来说,如果
mFocused
有记录,则调用其
unFocus
方法,最后将其置为
null
。这样就做到了一层层住下更新mFocused,
最终调用焦点View
的
clearFocusInternal
。至此,焦点的请求到更新
的逻辑就应该了然于胸了。
2.4 <requestFocus/> 标签
这个标签用于布局文件中,如:
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent">
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/btn0"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/btn1"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content">
- <requestFocus/>
- </Button>
- </LinearLayout>
添加了该标签的可聚焦的 View ,如上布局中的 btn1, 将在加载的时候(LayoutInflater#inflate)调用它的 requestFocus 方法,
- public abstract class LayoutInflater {
- ......
- private static final String TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS = "requestFocus";
- ......
- void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, Context context,
- AttributeSet attrs, boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
- ......
- while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
- parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
- ......
- if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
- parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
-
- private void parseRequestFocus(XmlPullParser parser, View view)
- throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
- view.requestFocus();
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
3. 按键事件(KeyEvent)与焦点查找
KeyEvent的分发与 TouchEvent 的分发,大致类似,从ViewRootImpl 开始一层层往下分发,
- ViewRootImpl.java (API 25)
- private int processKeyEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
- final KeyEvent event = (KeyEvent)q.mEvent;
-
- if (mView.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
- return FINISH_HANDLED;
- }
- …...
-
-
- if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
- int direction = 0;
- switch (event.getKeyCode()) {
- case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT:
- if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
- direction = View.FOCUS_LEFT;
- }
- break;
- case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT:
- if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
- direction = View.FOCUS_RIGHT;
- }
- break;
- case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_UP:
- if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
- direction = View.FOCUS_UP;
- }
- break;
- case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_DOWN:
- if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
- direction = View.FOCUS_DOWN;
- }
- break;
- case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_TAB:
- if (event.hasNoModifiers()) {
- direction = View.FOCUS_FORWARD;
- } else if (event.hasModifiers(KeyEvent.META_SHIFT_ON)) {
- direction = View.FOCUS_BACKWARD;
- }
- break;
- }
- if (direction != 0) {
- View focused = mView.findFocus();
- if (focused != null) {
- View v = focused.focusSearch(direction);
- if (v != null && v != focused) {
- ……
- if (v.requestFocus(direction, mTempRect)) {
-
- playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants
- .getContantForFocusDirection(direction));
- return FINISH_HANDLED;
- }
- }
-
- if (mView.dispatchUnhandledMove(focused, direction)) {
- return FINISH_HANDLED;
- }
- } else {
-
- View v = focusSearch(null, direction);
- if (v != null && v.requestFocus(direction)) {
- return FINISH_HANDLED;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- return FORWARD;
- }
可以
看到,dispatchKeyEvent
如果没有消费掉,将自动查找焦点。
3.1 KeyEvent分发
如果不重写dispatchKeyEvent,KeyEvent分发的最终目标是当前焦点View/ViewGroup。还是以下面这个图为例,分发的路径是RootViewGroup-->ViewGroup2-->view2

实现较TouchEvent的分发简单许多,就是根据前面提到的ViewGroup中mFocused来定位,我们来看下ViewGroup的dispatchKeyEvent的实现,
[File]ViewGroup.java
- @Override
- public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
- if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
- mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onKeyEvent(event, 1);
- }
- if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_FOCUSED | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS))
- == (PFLAG_FOCUSED | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) {
- if (super.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
- return true;
- }
- } else if (mFocused != null && (mFocused.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)
- == PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS) {
- if (mFocused.dispatchKeyEvent(event)) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
- mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 1);
- }
- return false;
- }
最终分发到焦点View上,将回调 OnKeyListener 或 KeyEvent.Callback,
[File]View.java
- public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
- if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
- mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onKeyEvent(event, 0);
- }
-
- ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
- if (li != null && li.mOnKeyListener != null && (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
- && li.mOnKeyListener.onKey(this, event.getKeyCode(), event)) {
- return true;
- }
-
-
- if (event.dispatch(this, mAttachInfo != null
- ? mAttachInfo.mKeyDispatchState : null, this)) {
- return true;
- }
- if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
- mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 0);
- }
- return false;
- }
可
以看到默认的
,ViewGroup
分发
KeyEvent
过程不会找焦点,
不消费方向键,
而是由ViewRootImpl
来处理。那么另一个重要的按键
“确认键”呢
?
如果当前有焦点,然后按
下确认键可能需要产生点击事件,这件事就是在 View
的 onKeyDown,onKeyUp
中处理的,
[File]View.java
- public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
- if (KeyEvent.isConfirmKey(keyCode)) {
- if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == DISABLED) {
- return true;
- }
-
- if (((mViewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE
- || (mViewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE)
- && (event.getRepeatCount() == 0)) {
-
-
- final float x = getWidth() / 2f;
- final float y = getHeight() / 2f;
- setPressed(true, x, y);
- checkForLongClick(0, x, y);
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- public boolean onKeyUp(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
- if (KeyEvent.isConfirmKey(keyCode)) {
- if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == DISABLED) {
- return true;
- }
- if ((mViewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE && isPressed()) {
- setPressed(false);
- if (!mHasPerformedLongPress) {
-
- removeLongPressCallback();
- return performClick();
- }
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
3.2焦点查找
前面提到ViewRootImpl里可能会根据按键方向查找焦点,如果已有聚焦的View,就调用 View 的focusSearch,从该View开始查找,否则调用自己的focusSearch 方法从顶层开始查找。我们先来看 View 的这个方法,
[File]View.java
- public View focusSearch(@FocusRealDirection int direction) {
- if (mParent != null) {
- return mParent.focusSearch(this, direction);
- } else {
- return null;
- }
- }
View
简单地让上一层ViewGroup
来查找,再来看ViewGroup
的这个方法,
[File]ViewGroup.java
- public View focusSearch(View focused, int direction) {
- if (isRootNamespace()) {
-
-
-
- return FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, focused, direction);
- } else if (mParent != null) {
- return mParent.focusSearch(focused, direction);
- }
- return null;
- }
一直调用上一层 ViewGroup
的
focusSearch
,直到当前是rootView,
使用
FocusFinder
在rootView
范围内开始查找,实际上 ViewRootImpl
里也同样是使用FocusFinder
来查找,我们下面看下
findNextFocus
这个方法,
[File]FocusFinder.java
- public final View findNextFocus(ViewGroup root, View focused, int direction) {
- if (focused != null) {
-
- View userSetNextFocus = focused.findUserSetNextFocus(root, direction);
- if (userSetNextFocus != null &&
- userSetNextFocus.isFocusable() &&
- (!userSetNextFocus.isInTouchMode() ||
- userSetNextFocus.isFocusableInTouchMode())) {
- return userSetNextFocus;
- }
-
- ……
-
- } else {
-
-
- ……
- }
- return findNextFocus(root, focused, mFocusedRect, direction);
- }
如果已经存在焦点,并且该焦点
View
设置了某方向的下一焦点
View
的
ID
,那么根据
ID
找出这个
View
即可;否则根据当前焦点区域按方向查找,这个算法这里就暂不介绍了。
这篇关于Android TV 焦点与按键事件分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







