本文主要是介绍Vue3全家桶 - Pinia - 【1】(安装与使用 + Store + State + Getters + Actions),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Pinia
pinia是Vue的专属状态管理库,它允许你跨组件或跨页面共享状态;
一、 安装与使用 pinia
- 安装语法:
yarn add pinia npm install pinia - 创建一个
pinia(根存储)并将其传递给应用程序:- 目标文件:
main.js:import { createApp } from 'vue' import App from './App.vue'// 导入 createPinia 函数 import { createPinia } from 'pinia'const app = createApp(App)// 使用 createPinia() 来创建 Pinia(根存储),并应用到整个程序中 app.use(createPinia())app.mount('#app')
- 目标文件:
二、Store
-
store是一个 保存状态 和 业务逻辑 的 实体,它并不与你的组件树绑定;换句话说,它 承载着全局状态;它有点像一个永远存在的组件,每个组件都可以读取和写入它; -
store它有三个概念,state、getters、actions,我们可以理解成组件的data、computed、methods; -
🔺创建
store:- 在项目中
src/store文件夹下新建store.js; store是用defineStore(name, fucntion | options)定义的,建议其函数返回值命名为use...Store方便理解;- 参数:
name:- 当前这个
store名字,必填 且 唯一;
- 当前这个
function | options:- 函数 或 对象 形式;
- 函数【组合模式,类似组件组合式API的书写方式】:定义响应式变量和方法,并且
return对应的 变量 和 方法;ref()相当于state,computed()相当于getters、function()相当于actions; - 对象【选项模式】:其中配置
state、getters、actions选项;
- 示例展示:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';// TODO 选项式API /*** 参数1 - store的名称,保证在整个应用中是唯一的* 参数2:* 对象形式 - 选项式API:* state - 函数* getters - 对象* actions - 对象*/ const userStore = defineStore('main', {// 共享数据state: () => ({}),// 共享通过计算得到的数据getters: {},// 共享函数actions: {} });// TODO 组合式API /*** 参数1 - store的名称,保证在整个应用中是唯一的* 参数2:* 函数形式 - 组合式API:* state -> ref() - 共享数据* getters -> computed() - 共享计算得到的数据* actions -> function() - 共享方法* 注意:最后 必须 return 出去 才会 生效*/ const userStore = defineStore('main', () => {// 最后必须返回组件需要的变量、计算属性、函数return ({}); });export default userStore;
- 在项目中
三、State
state是store的核心部分,主要存储的是共享的数据;
3.1 定义 state
store采用的是 选项模式:state选项 为 函数返回的对象,在其定义共享的数据;
store采用的是 组合式模式:- 在其函数内定义的
ref变量,最终return出去来提供共享的数据;
- 在其函数内定义的
- 示例展示:
- 组合式:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; import { ref } from 'vue';// TODO 组合式API const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => {// 1. 声明 ref 变量const userName = ref('禁止摆烂_才浅')const age = ref(22)const gender = ref('男')const city = ref('兰州')const work = ref('初级前端开发工程师')// 最后必须 return 出去return ({userName,age,gender,city,work}) });export default useUserStore; - 选项式:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';// TODO 选项式API const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {// 定义共享数据state: () => ({userName: '禁止摆烂_才浅',age: 22,gender: '男',city: '兰州',work: '初级前端开发工程师'}),getters: {},actions: {} });export default useUserStore;
- 组合式:
3.2 组件中访问 state
- 组合式API:
- 直接引入对应的
store,通过state对象直接获取和修改state; - 注意:
- 如果想在组件中 自定义变量名 来接收
store中的state中 共享的数据,我们可以这样做:- 使用
computed(() => store.dataName),具有 响应式,但是 只读形式; - ✅ 使用
storeToRefs(store)从store解构想要的state,具有 响应式,可 直接修改,可 自定义名称;
- 使用
- 如果想在组件中 自定义变量名 来接收
- 示例展示:
<script setup> import { ref, reactive, computed, onMounted } from 'vue'; import useUserStore from '@/store/useUserStore' import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia';// TODO 获取 useUserStore 示例 const user_store = useUserStore()// TODO 将 store 中 state 的数据映射为当前组件的计算属性 - 具有响应式,但是是只读 const user_userName = computed(() => user_store.userName) const user_age = computed(() => user_store.age) const user_work = computed(() => user_store.work)// TODO 使用 storeToRefs() 从 store 解构想要的 state,具有响应式,可直接修改,可自定义名称 const { userName: myName, age: myAge } = storeToRefs(user_store)onMounted(() => {}); </script><template><h2>组合式API</h2><hr><h4>从 store 直接获取 state,具有响应式,可修改</h4><ul><li>{{user_store.userName}}</li><li>{{user_store.age}}</li><li>{{user_store.gender}}</li><li>{{user_store.city}}</li><li>{{user_store.work}}</li></ul><hr><button @click="user_store.age = 23">修改 - user_store.age</button> | <button @click="user_store.city = '北京 / 上海 / 武汉 / 杭州 / 深圳'">修改 - user_store.city</button><hr><br><h4>通过 computed 将 store 中的 state 数据,映射为当前组件中的计算属性 - 具有响应式,但是是只读</h4><ul><li>{{user_userName}}</li><li>{{user_age}}</li><li>{{user_work}}</li></ul><hr><button @click="user_work = '中级前端开发工程师'">修改 - user_city</button><button @click="user_age = 23">修改 - user_age</button> | <hr><br><h4>使用 storeToRefs() 从 store 解构想要的 state 为当前组件的数据,具有响应式,可直接修改,可自定义名称</h4><ul><li>{{myName}}</li><li>{{myAge}}</li></ul><hr><button @click="myAge = 23"> 修改 - myAge </button> </template> - 运行展示:

- 直接引入对应的
- 选项式API:
- 可以使用
mapState(storeObj, array | object)辅助函数将状态属性映射为 只读计算属性; - 要映射到 computed 中;
storeObj引入的store对象;array | object:字符串数组形式 或 对象形式;- 【字符串数组形式】:
- 直接将
store中state的数据映射为当前组件的 计算属性,但是 不能自定义名称;
- 直接将
- 【对象形式】:
key为自定义当前组件的 计算属性名,value字符串形式,是store中state的共享数据;
- 【字符串数组形式】:
- 🔺注意:
mapState()函数映射到组件中的计算属性是 只读的,如果想在组件中 响应式修改state的数据,则应该选择mapWritableState()函数 来映射计算属性;- 在导入
mapState后,保存的时候可能会报错:
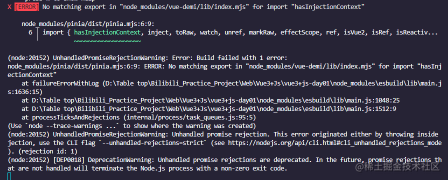
- 原因:
Pinia和vue版本不匹配导致的;Pinia 2.1.0及以上版本需要引入vue3.3及以上版本;
- 解决方法:
- 升级
vue版本:- 将 vue 升级到 3.3 及以上版本,将 pinia 升级到 2.1.0 及以上版本;
- 指定
Pinia版本:- 如果无法升级到 3.3 及以上版本,可以锁定 pinia 的版本为 2.0.36;
- 升级
- 原因:
- 示例展示:
<script> /*** 选项式API 使用 Pinia* 1. 导入 mapState 函数(mapState 函数需要写在 计算属性中)* 2. 导入 对应的 store 对象,作为 mapState 的第一个参数*/ import { mapState, mapWritableState } from 'pinia'; import useUserStore from '@/store/useUserStore.js';export default {name: 'App',component: {},props: {},data () {return {}},computed: {/*** mapState - 有两个参数:* 参数1:导入的 store 对象* 参数2:array(字符串数组) / object* array(字符串数组):* 将当前组件需要用到的数据(字符串形式)放到这个数组中;* 不能进行重命名* object:* 可以重命名,key 就是行变量名, value 就是旧名* 注意:* mapState 将 store 的 state 映射为当前组件的计算属性* 具有响应式(修改store中的state,当前组件中的数据也会发生变化),但是是只读的(不能修改)*/...mapState(useUserStore, ['userName', 'age']),...mapState(useUserStore, {u_gender: 'gender',u_work: 'work',u_city: 'city'}),...mapWritableState(useUserStore, {user_age: 'age',user_city: 'city'})},methods: {},watch: {} }; </script><template><h2> 使用 mapState 访问 state - 映射为计算属性 - 具有响应式,但是是只读</h2><ul><li> {{ userName }} </li><li> {{ age }} </li><li> {{ u_gender }} </li><li> {{ u_city }} </li><li> {{ u_work }} </li></ul><hr><button @click="age++">修改 - age</button><h2> 使用 mapWritableState 访问 state - 映射为计算属性 - 具有响应式,可修改</h2><ul><li>{{ user_age }}</li><li>{{ user_city }}</li></ul><button @click="user_age = 23">修改 - user_age</button><button @click="user_city = '武汉 / 北京 / 上海 / 杭州'">修改 - user_city</button> </template> - 运行展示:

- 修改
mapState映射的数据:- 修改不成功,会在控制台报警告;
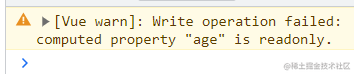
- 修改不成功,会在控制台报警告;
- 修改
mapWritableState映射的数据:- 修改成功;

- 修改成功;
- 修改
- 可以使用
四、Getters
getters是计算得到的新的共享数据,当 依赖 发生变化 时 则 重新计算,所以其他组件包括store自己不要直接对其修改;
4.1 定义 getters
- 组合式
store:- 可通过
computed()函数通过计算得到新的数据,再将其 return 暴露出去即可; - 🔺 注意:
- 在
getters中访问state中的数据,需要添加后缀.value;
- 在
- 示例展示:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; import {computed, ref} from 'vue'; // TODO 组合式API const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => { // 1. 声明 state,使用 ref() 函数 const userName = ref('禁止摆烂_才浅') const age = ref(22) const gender = ref('男') const city = ref('兰州') const work = ref('初级前端开发工程师') const birthday = ref('2000-01-01') // 2.声明 getters ,使用 computed() 函数// 只读 - 如果依赖的数据发生该改变,对应的 getters 也会重新计算const month = computed( () => birthday.value.split('-')[1] ) const ageStage = computed( () => age.value >= 18 ? '成年' : '未成年') // 最后必须 return 出去 return ({ // state userName, age, gender, city, work, birthday, // getters month, ageStage }) }); export default useUserStore; - 可通过
- 选项式
store:getters选项中 声明的 函数 即为 计算属性;- 在其函数内可通过
this关键字获取store实例【this.state中的变量名】,也可通过 方法 的 第一个参数 得到store实例; - 如果采用的是箭头函数的话,无法使用
this关键字,为了更方便使用store中实例,可为其箭头函数设置第一个参数来获取store实例; - 示例展示:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; // TODO 选项式API const useUserStore = defineStore('user', { // 定义共享数据 state: () => ({ userName: '禁止摆烂_才浅', age: 22, gender: '男', city: '兰州', work: '初级前端开发工程师', birthday: '2000-1-1' }), // 通过计算属性得到的新的共享数据,只读,不能修改,只有当依赖发生变化的时候,getters中的数据才会重i性能计算 getters: { // 非箭头函数 - 通过 this 访问 store 实例 month () { return this.birthday.split('-')[1] }, // 箭头函数 - 函数的第一个参数,为 store 实例 ageStage: store => { if (store.age < 18) return '未成年' return '成年' } }, actions: {} }); export default useUserStore;
4.2 在组件中使用 getters
-
组合式API:
- 访问
store中的getters和访问state类似,直接引入对应的store,通过store对象直接获取getters,但是如果 对其 进行修改 则 会报错;- 注意:
- 如果想将
store中的getters中共享的数据映射为本地组件的计算属性,我们可以这样做:- 使用
computed(() => store.gettersName),具有响应式,但是 只读形式; - 使用
storeToRefs(store)从store解构getters依旧是计算属性,所以是 只读的,一旦 对其 进行修改 会 报错,但是 具有响应式,可自定义名称;
- 使用
- 如果想将
- 注意:
- 示例展示:
<script setup> import { ref, reactive, computed, onMounted } from 'vue'; import useUserStore from '@/store/useUserStore' import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; // TODO 获取 useUserStore 示例 const user_store = useUserStore() // TODO 使用 computed 将 store 中 getters 的数据映射为当前组件的计算属性,只读 - 不能修改,一旦修改就会在控制台打印警告 const month = computed(() => user_store.month ) const ageStage = computed(() => user_store.ageStage) // TODO 使用 storeToRefs() 将 store 中的 getters 的数据 解构 为 当前组件 的 计算属性,具有响应式,可重命名,只读 - 一旦修改,就会报错 const { month: bir_month, ageStage: age_stage } = storeToRefs(user_store) onMounted(() => {}); </script> <template> <h4>通过 store 直接获取 getters,具有响应式,只读 - 不能修改(修改会报错)</h4> <ul> <li>月份:{{ user_store.month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ user_store.ageStage }}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="(user_store.month)++">修改 - month</button> <button @click="user_store.ageStage = '嘻嘻哈哈'">修改 - age - 改变 ageStage</button> <hr> <br> <h4>通过 computed 将 store 中的 getters 映射为 当前组件 的 计算属性,具有响应式,只读 - 修改会在控制台打印警告</h4> <ul> <li>月份:{{ month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ ageStage }}</li> </ul> <button @click="month++">修改 - month</button> <button @click="ageStage = '嘻嘻哈哈'">修改 - ageStage</button> <hr> <br> <h4>通过 storeToRefs() 将 store 中的 getters 映射为 当前组件 的 计算属性,只读 - 修改会报错</h4> <ul> <li>月份:{{ bir_month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ age_stage }}</li> </ul> <button @click="bir_month++">修改 - month</button> <button @click="age_stage = '嘻嘻哈哈'">修改 - ageStage</button> </template> - 运行展示:
- 对 直接从
store获取的getters进行修改:
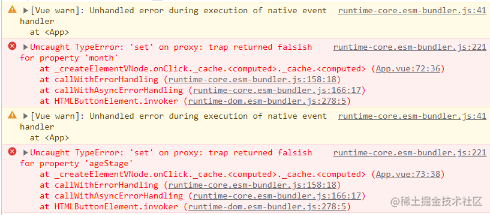
- 对 通过
computed映射的getters进行修改:
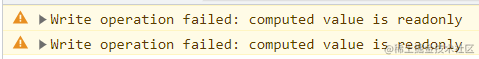
- 对 通过
storeToRefs解构的getters进行修改:
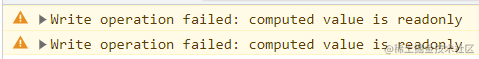
- 对 直接从
- 访问
-
选项式API:
- 访问
store中的getters和 访问state类似,同样可使用mapState()辅助函数将getters属性映射为 只读属性; - 🔺注意:
- 如果采用
mapWritableState()辅助函数 将store中的getters映射为 组件内部的计算属性,依旧可以 具有响应式,一旦对其进行修改则会报错;
- 如果采用
- 示例展示:
<script> import { mapState, mapWritableState } from 'pinia'; import useUserStore from '@/store/useUserStore.js'; export default { name: 'App', component: {}, props: {}, data () { return {} }, computed: { // 从 store 取 getters 和 取 state 用法相同,都可以使用 mapState // 具有响应式,但是不能修改 // 映射 getters(数组 + 对象) ...mapState(useUserStore, ['month']), ...mapState(useUserStore, { age_Stage: 'ageStage' }), // 使用 mapWritableState 解构 ...mapWritableState(useUserStore, ['ageStage']), ...mapWritableState(useUserStore, { bir_month: 'month' }) }, methods: {}, watch: {} }; </script> <template><h2> 使用 mapState 解构 getters - 映射为计算属性 - 不能修改</h2> <ul> <li>月份:{{ month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ age_Stage }}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="month++">修改 - month</button> <hr> <br> <h2> 使用 mapWritableState 解构 getters - 映射 getters 为当前组件的计算属性 - 具有响应式,一修改就会报错</h2> <ul> <li>月份:{{ bir_month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ ageStage }}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="bir_month++">修改 - month</button> </template>
- 访问
五、Actions
actions一般情况下是对state中的 数据进行修改 的 业务逻辑 函数,actions也可以是异步的,可以在其中await任何API调用 甚至 其他操作;
5.1 定义actions
-
组合式
store:- 可通过声明函数,再将其
return暴露出去即可共享其函数; - 示例展示:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; import {computed, ref} from 'vue'; // TODO 组合式API const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => { // 1. 声明 state,使用 ref() 函数 const userName = ref('禁止摆烂_才浅') const age = ref(22) const gender = ref('男') const city = ref('兰州') const work = ref('初级前端开发工程师') const birthday = ref('2000-01-01') // 2.声明 getters ,使用 computed() 函数 // 只读 - 如果依赖的数据发生该改变,对应的 getters 也会重新计算 const month = computed( () => birthday.value.split('-')[1] ) const ageStage = computed( () => age.value >= 18 ? '成年' : '未成年') // 3.声明 actions - 声明函数 const setUserInfo = (username, ageStage) => { userName.value = username age.value = ageStage } // 最后必须 return 出去 return ({ // state userName, age, gender, city, work, birthday, // getters month, ageStage, // actions setUserInfo }) }); export default useUserStore;
- 可通过声明函数,再将其
-
选项式
store:actions选项中声明的函数即可共享函数,在其函数内可通过this来获取整个store实例;- 示例展示:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'; // TODO 选项式API const useUserStore = defineStore('user', { // 定义共享数据 state: () => ({ userName: '禁止摆烂_才浅', age: 22, gender: '男', city: '兰州', work: '初级前端开发工程师', birthday: '2000-1-1' }), // 通过计算属性得到的新的共享数据,只读,不能修改,只有当依赖发生变化的时候,getters中的数据才会重i性能计算 getters: { // 非箭头函数 - 通过 this 访问 store 实例 month () { return this.birthday.split('-')[1] }, // 箭头函数 - 函数的第一个参数,为 store 实例 ageStage: store => { if (store.age < 18) return '未成年' return '成年' } }, // 定义共享的函数(可以是异步的),其主要作用是:修改 state 中的数据 actions: { setUserInfo (username, age) { // this -> 当前 store 的实例对象 this.userName = username this.age = age } } }); export default useUserStore;
5.2 组件中访问actions
- 组合式API:
- 直接引入对应的
store,通过store对象直接获取actions; - 🔺 注意:
- 如果想将
store中的actions中函数 映射为 本地组件 的 函数,可将store解构 出 对应的 函数即可,也可自定义函数名,此处不能通过storeToRefs(store)函数;
- 如果想将
- 示例展示:
<script setup> import { ref, reactive, computed, onMounted } from 'vue'; import useUserStore from '@/store/useUserStore' import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; const userInfo = reactive({ username: '邵秋华', age: 22.5 }) // TODO 获取 useUserStore 示例 const user_store = useUserStore() // TODO 将 store 中 state 的数据映射为当前组件的计算属性 - 具有响应式,但是是只读 const user_userName = computed(() => user_store.userName) const user_age = computed(() => user_store.age) const user_work = computed(() => user_store.work) // TODO 使用 storeToRefs() 从 store 解构想要的 state,具有响应式,可直接修改,可自定义名称 const { userName: myName, age: myAge } = storeToRefs(user_store) // TODO 使用 computed 将 store 中 getters 的数据映射为当前组件的计算属性,只读 - 不能修改,一旦修改就会在控制台打印警告 const month = computed(() => user_store.month ) const ageStage = computed(() => user_store.ageStage) // TODO 使用 storeToRefs() 将 store 中的 getters 的数据 解构 为 当前组件 的 计算属性,具有响应式,可重命名,只读 - 一旦修改,就会报错 const { month: bir_month, ageStage: age_stage } = storeToRefs(user_store) // TODO 直接对 store 进行解构,得到 actions,可以进行重命名 const { setUserInfo: setStateData } = user_store onMounted(() => {}); </script> <template> <h2>组合式API</h2> <hr> <h4>从 store 直接获取 state,具有响应式,可修改</h4> <ul> <li>{{user_store.userName}}</li> <li>{{user_store.age}}</li> <li>{{user_store.gender}}</li> <li>{{user_store.city}}</li> <li>{{user_store.work}}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="user_store.age = 23">修改 - user_store.age</button> | <button @click="user_store.city = '北京 / 上海 / 武汉 / 杭州 / 深圳'">修改 - user_store.city</button> <hr> <br> <h4>通过 computed 将 store 中的 state 数据,映射为当前组件中的计算属性 - 具有响应式,但是是只读</h4> <ul> <li>{{user_userName}}</li> <li>{{user_age}}</li> <li>{{user_work}}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="user_work = '中级前端开发工程师'">修改 - user_city</button> <button @click="user_age = 23">修改 - user_age</button> | <hr> <br> <h4>使用 storeToRefs() 从 store 解构想要的 state 为当前组件的数据,具有响应式,可直接修改,可自定义名称</h4> <ul> <li>{{myName}}</li> <li>{{myAge}}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="myAge = 23"> 修改 - myAge </button> <br> <hr> <h4>通过 store 直接获取 getters,具有响应式,只读 - 不能修改(修改会报错)</h4> <ul> <li>月份:{{ user_store.month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ user_store.ageStage }}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="(user_store.month)++">修改 - month</button> <button @click="user_store.ageStage = '嘻嘻哈哈'">修改 - age - 改变 ageStage</button> <hr> <br> <h4>通过 computed 将 store 中的 getters 映射为 当前组件 的 计算属性,具有响应式,只读 - 修改会在控制台打印警告</h4> <ul> <li>月份:{{ month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ ageStage }}</li> </ul> <button @click="month++">修改 - month</button> <button @click="ageStage = '嘻嘻哈哈'">修改 - ageStage</button> <hr> <br> <h4>通过 storeToRefs() 将 store 中的 getters 映射为 当前组件 的 计算属性,只读 - 修改会报错</h4> <ul> <li>月份:{{ bir_month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ age_stage }}</li> </ul> <button @click="bir_month++">修改 - month</button> <button @click="age_stage = '嘻嘻哈哈'">修改 - ageStage</button> <br> <h4>通过 store 直接读取 actions</h4> <button @click="user_store.setUserInfo(userInfo.username, userInfo.age)">通过 store 直接读取的 actions 修改 state 中的数据</button> <br> <hr> <h4>通过 storeToRefs() 将 store 中的 actions 解构 为 当前组件 的 function</h4> <button @click="setStateData('张三', '32')">直接对 store 进行解构,得到 actions</button> </template>
- 直接引入对应的
- 选项式API:
- 可以使用
mapActions(storeObj, array | object)辅助函数将actions映射为当前组件的函数;- 映射在
methods中; storeObj: 引入的store;array | object:字符串数组形式 或 对象形式;- 【对象】:
key为自定义当前组件的函数名,value字符串形式,是store中actions的函数名;
- 【字符串数组】:
- 直接将
store中actions的函数映射为当前组件的函数,但是不能自定义名称;
- 直接将
- 【对象】:
- 映射在
- 示例展示:
<script> /** * 选项式API 使用 Pinia * 1. 导入 mapState 函数(mapState 函数需要写在 计算属性中) * 2. 导入 对应的 store 对象,作为 mapState 的第一个参数 */ import {mapActions, mapState, mapWritableState} from 'pinia'; import useUserStore from '@/store/useUserStore.js'; export default { name: 'App', component: {}, props: {}, data () { return { userInfo: { username: '邵秋华', age: 22.5 } } }, computed: { /** * mapState - 有两个参数: * 参数1:导入的 store 对象 * 参数2:array(字符串数组) / object * array(字符串数组): * 将当前组件需要用到的数据(字符串形式)放到这个数组中; * 不能进行重命名 * object: * 可以重命名,key 就是行变量名, value 就是旧名 * 注意: * mapState 将 store 的 state 映射为当前组件的计算属性 * 具有响应式(修改store中的state,当前组件中的数据也会发生变化),但是是只读的(不能修改) */ ...mapState(useUserStore, ['userName', 'age']), ...mapState(useUserStore, { u_gender: 'gender', u_work: 'work', u_city: 'city' }), ...mapWritableState(useUserStore, { user_age: 'age', user_city: 'city' }), // 从 store 取 getters 和 取 state 用法相同,都可以使用 mapState // 具有响应式,但是不能修改 // 映射 getters(数组 + 对象) ...mapState(useUserStore, ['month']), ...mapState(useUserStore, { age_Stage: 'ageStage' }), // 使用 mapWritableState 解构 ...mapWritableState(useUserStore, ['ageStage']), ...mapWritableState(useUserStore, { bir_month: 'month' }) }, methods: { // 映射 actions 有两种方式,数组 + 对象(可以自定义名称接收) // 数组形式 ...mapActions(useUserStore, ['setUserInfo']), // 对象形式 ...mapActions(useUserStore, { setStateData: 'setUserInfo' }) }, watch: {} }; </script> <template> <h2> 使用 mapState 访问 state - 映射为计算属性 - 具有响应式,但是是只读</h2> <ul> <li> {{ userName }} </li> <li> {{ age }} </li> <li> {{ u_gender }} </li> <li> {{ u_city }} </li> <li> {{ u_work }} </li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="age++">修改 - age</button> <h2> 使用 mapWritableState 访问 state - 映射为计算属性 - 具有响应式,可修改</h2> <ul> <li>{{ user_age }}</li> <li>{{ user_city }}</li> </ul> <button @click="user_age = 23">修改 - user_age</button> <button @click="user_city = '武汉 / 北京 / 上海 / 杭州'">修改 - user_city</button> <hr> <br> <h2> 使用 mapState 解构 getters - 映射为计算属性 - 不能修改</h2> <ul> <li>月份:{{ month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ age_Stage }}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="month++">修改 - month</button> <hr> <br> <h2> 使用 mapWritableState 解构 getters - 映射 getters 为当前组件的计算属性 - 具有响应式,一修改就会报错</h2> <ul> <li>月份:{{ bir_month }}</li> <li>是否成年:{{ ageStage }}</li> </ul> <hr> <button @click="bir_month++">修改 - month</button> <br> <button class="setUserInfo" @click="setUserInfo(userInfo.username, userInfo.age)">修改 state 中的数据(数组形式映射)</button> <br> <button class="setUserInfo" @click="setStateData(userInfo.username, userInfo.age)">修改 state 中的数据(对象形式映射)</button> </template> <style scoped> .setUserInfo { margin-top: 10px; background-color: #00ffe3; } </style>
- 可以使用
这篇关于Vue3全家桶 - Pinia - 【1】(安装与使用 + Store + State + Getters + Actions)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




