本文主要是介绍JavaWeb Cookie 原理分析 存活时间,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
会话技术
HTTP协议是无状态的,每次浏览器向服务器请求时,服务器都会将该请求视为新的请求。请求与请求之间独立后,就无法实现多次请求之间的数据共享,所以需要用到会话技术。
会话,用户打开浏览器,访问web服务器的资源,会话建立,直到有一方断开连接,会话结束。在一次会话中可以包含多次请求和响应。
- 从浏览器发出请求到服务端响应数据给前端之后,一次会话(在浏览器和服务器之间)就被建立了
- 会话被建立后,如果浏览器或服务端都没有被关闭,则会话就会持续建立着
- 浏览器和服务器就可以继续使用该会话进行请求发送和响应,上述的整个过程就被称之为会话。
会话跟踪,一种维护浏览器状态的方法,服务器需要识别多次请求是否来自于同一浏览器,以便在同一次会话的多次请求间共享数据。
- 客户端会话技术:Cookie
- 服务器端会话技术:Session
Cookie,客户端会话技术,将数据保存到客户端,以后每次请求都携带Cookie数据进行访问。
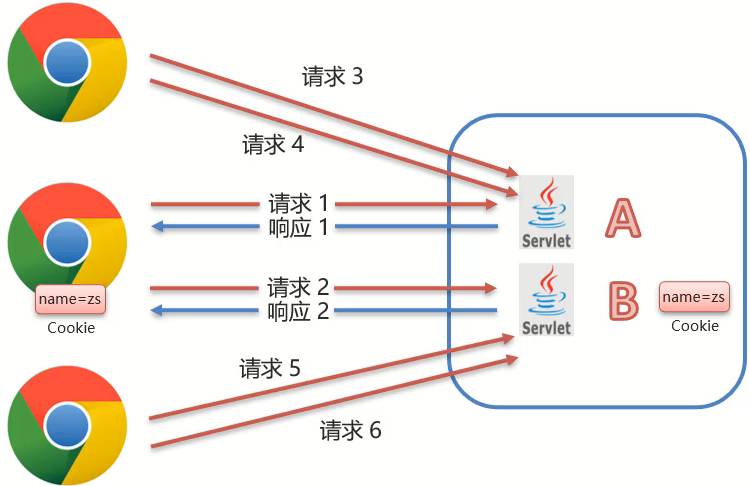
常用方法
发送Cookie
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("key","value"):创建Cookie对象,并设置数据response.addCookie(cookie):发送Cookie到客户端,使用Response对象
@WebServlet("/aServlet")
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {//发送Cookie//1. 创建Cookie对象Cookie cookie = new Cookie("username","zs");//2. 发送Cookie,responseresponse.addCookie(cookie);}@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(request, response);}
}
获取Cookie
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies():获取客户端携带的所有Cookie,使用Request对象cookie.getName():使用Cookie对象方法获取namecookie.getValue():使用Cookie对象方法获取value
@WebServlet("/bServlet")
public class BServlet extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {//获取Cookie//1. 获取Cookie数组Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();//2. 遍历数组for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {//3. 获取数据String name = cookie.getName();if("username".equals(name)){String value = cookie.getValue();System.out.println(name+":"+value);break;}}}@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(request, response);}
}
原理分析
Cookie的实现是基于HTTP协议的,其中涉及到HTTP协议中的两个请求头信息:
- 响应头:
set-cookie - 请求头:
cookie
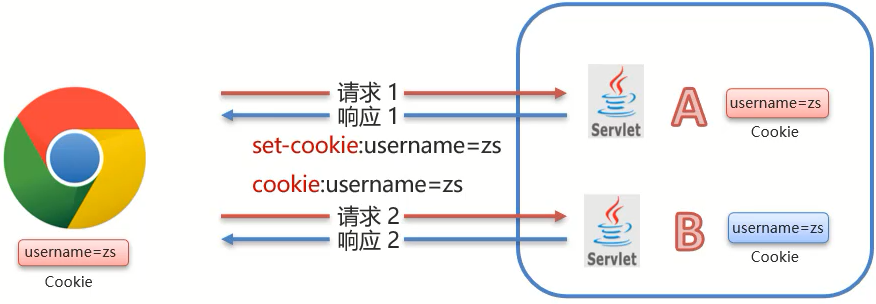
- AServlet给前端发送Cookie,BServlet从Request中获取Cookie的功能
- 对于AServlet响应数据的时候,Tomcat服务器都是基于HTTP协议来响应数据
- 当Tomcat发现后端要返回的是一个Cookie对象之后,Tomcat就会在响应头中添加一行数据
Set-Cookie:username=zs - 浏览器获取到响应结果后,从响应头中就可以获取到
Set-Cookie对应值username=zs,并将数据存储在浏览器的内存中 - 浏览器再次发送请求给BServlet的时候,浏览器会自动在请求头中添加
Cookie: username=zs发送给服务端BServlet - Request对象会把请求头中cookie对应的值封装成一个个Cookie对象,最终形成一个数组
- BServlet通过Request对象获取到
Cookie[]后,就可以从中获取自己需要的数据
存活时间
默认情况下,Cookie存储在浏览器内存中,当浏览器关闭,内存释放,则Cookie被销毁。
也可以使用下面的方法持久化到客户端本地:
setMaxAge(int seconds):设置Cookie存活时间。- 正数: 将Cookie写入浏览器所在电脑的硬盘,持久化存储。到时间自动删除。
- 负数: 默认值,Cookie在当前浏览器内存中,当浏览器关闭,则Cookie被销毁。
- 零: 删除对应Cookie。
@WebServlet("/aServlet")
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {//发送Cookie//1. 创建Cookie对象Cookie cookie = new Cookie("username","zs");//设置存活时间,1周 7天cookie.setMaxAge(60*60*24*7); //易阅读,需程序计算//cookie.setMaxAge(604800); //不易阅读(可以使用注解弥补),程序少进行一次计算//2. 发送Cookie,responseresponse.addCookie(cookie);}@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(request, response);}
}
存储中文
Cookie不能存储中文,如果有这方面的需求,需要进行转码:
- 在AServlet中对中文进行URL编码,采用
URLEncoder.encode(),将编码后的值存入Cookie中 - 在BServlet中获取Cookie中的值,获取的值为URL编码后的值
- 将获取的值在进行URL解码,采用
URLDecoder.decode(),就可以获取到对应的中文值
@WebServlet("/aServlet")
public class AServlet extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {//发送CookieString value = "张三";//对中文进行URL编码value = URLEncoder.encode(value, "UTF-8");System.out.println("存储数据:"+value);//将编码后的值存入Cookie中Cookie cookie = new Cookie("username",value);//发送Cookieresponse.addCookie(cookie);}@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(request, response);}
}
@WebServlet("/bServlet")
public class BServlet extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {//获取Cookie//1. 获取Cookie数组Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();//2. 遍历数组for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {//3. 获取数据String name = cookie.getName();if("username".equals(name)){String value = cookie.getValue();//获取的是URL编码后的值 %E5%BC%A0%E4%B8%89//URL解码value = URLDecoder.decode(value,"UTF-8");System.out.println(name+":"+value);//value解码后为 张三break;}}}@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(request, response);}
}
这篇关于JavaWeb Cookie 原理分析 存活时间的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





