本文主要是介绍Springboot实现缓存预热,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
很多时候我们代码中使用缓存时都是先判断缓存中没有数据我们再读取数据库而有则直接使用缓存数据,而在系统冷启动(当系统重启或新启动时,缓存是空的,这被称为冷启动)时,我们毫无意外都是直接获取数据库的内容,这时候缓存的命中率几乎为0,这时候我们需要考虑业务系统的缓存预热功能,在系统启动之前通过预先将常用数据加载到缓存中,以提高缓存命中率和系统性能的过程。缓存预热的目的是尽可能地避免缓存击穿和缓存雪崩。
一、系统启动时加载
1、CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner是SpringBoot中用于在应用程序启动后执行特定逻辑的接口。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 缓存预热器(CommandLineRunner方式)*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheCLRunner implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {//TODO 缓存预热逻辑log.info("CommandLineRunner方式完成缓存预热");}
}import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 缓存预热器(ApplicationRunner方式)*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheAppRunner implements ApplicationRunner {@Overridepublic void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {//TODO 缓存预热逻辑log.info("ApplicationRunner方式完成缓存预热");}
}2、实现InitializingBean接口,并在afterPropertiesSet方法中执行缓存预热的逻辑。这样Spring在初始化Bean时会调用afterPropertiesSet方法
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 缓存预热器(InitializingBean方式)*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheInitializing implements InitializingBean {@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {//TODO 缓存预热逻辑log.info("InitializingBean方式完成缓存预热");}
}
3、基于ApplicationReadyEvent,我们可以在应用程序完全启动并处于可用状态后执行一些初始化逻辑。使用@EventListener注解或实现ApplicationListener接口来监听这个事件。
4、@PostConstruct注解标注一个方法,该方法将在 Bean 的构造函数执行完毕后立即被调用。
这里3、4点的例子写在一起
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;/*** 缓存预热器(ApplicationReadyEvent和@PostConstruct方式)*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CacheLoader {@EventListener(ApplicationReadyEvent.class)public void loadCache1() {//TODO 缓存预热逻辑log.info("@EventListener方式完成缓存预热");}@PostConstructpublic void loadCache2() {//TODO 缓存预热逻辑log.info("@PostConstruct方式完成缓存预热");}
}启动项目大致看一下4种方式的加载顺序,可根据自己的需求选择对应的方式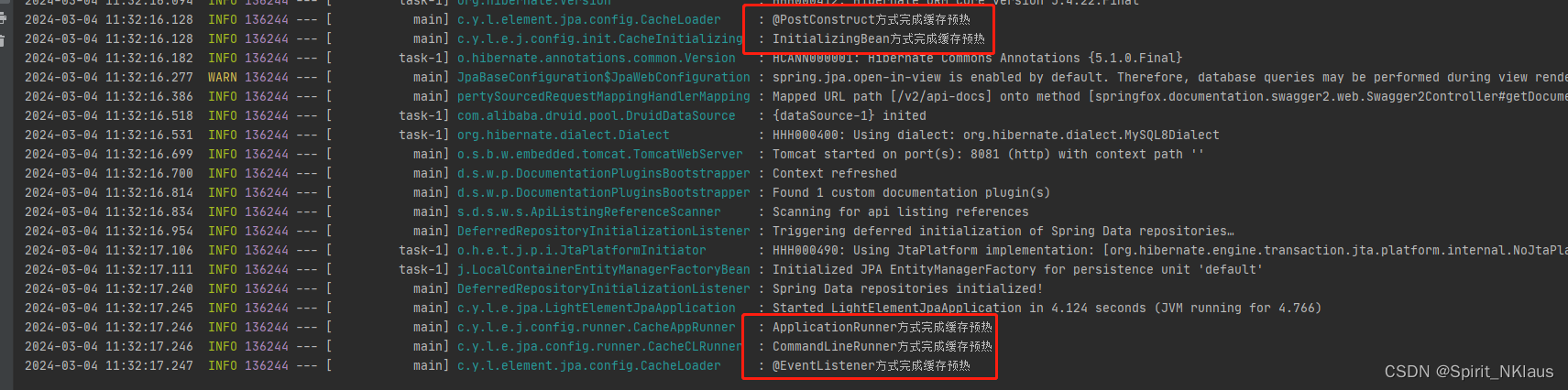
二、定时任务加载
使用Spring的@Scheduled,quartz,xxl-job都可以,@Scheduled为例
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 1 * * ?") // 每天凌晨1点执行
public void scheduledCachePreload() {//TODO 缓存预热逻辑log.info("定时任务方式完成缓存预热");
}这篇关于Springboot实现缓存预热的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




