本文主要是介绍CTPN源码解析5-文本线构造算法构造文本行,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文本检测算法一:CTPN
CTPN源码解析1-数据预处理split_label.py
CTPN源码解析2-代码整体结构和框架
CTPN源码解析3.1-model()函数解析
CTPN源码解析3.2-loss()函数解析
CTPN源码解析4-损失函数
CTPN源码解析5-文本线构造算法构造文本行
CTPN训练自己的数据集
由于解析的这个CTPN代码是被banjin-xjy和eragonruan大神重新封装过的,所以代码整体结构非常的清晰,简洁!不像上次解析FasterRCNN的代码那样跳来跳去,没跳几步脑子就被跳乱了[捂脸],向大神致敬!PS:里面肯定会有理解和注释错误的,欢迎批评指正!
解析源码地址:https://github.com/eragonruan/text-detection-ctpn
知乎:从代码实现的角度理解CTPN:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49588885
知乎:理解文本检测网络CTPN:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/77883736
知乎:场景文字检测—CTPN原理与实现:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34757009
文本线构造法(获取预测碎片框后合并成一行的后处理方法)
理论:
在上一个步骤中,已经获得了图Text proposal所示的一串或多串text proposal,接下来就要采用文本线构造法,把这些text proposal连接成一个文本检测框。

为了说明问题,假设某张图有上图所示的2个text proposal,即蓝色和红色2组Anchor,CTPN采用如下算法构造文本线:
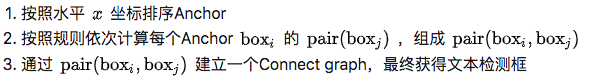
具体参考这篇文章:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_31866177/article/details/890437
代码流程:

代码:
根据文本碎片框及其得分,图像尺寸,使用文本线构造法获得文本行及其得分。步骤:
- 删除得分较低的proposal
- proposal按得分排序
- 对proposal做nms
- 根据预测的碎片框,及其得分,图像宽高进行文本行合并
- 按一定条件过滤合并后的文本行
'''根据文本碎片框及其得分,图像尺寸,使用文本线构造法获得文本行及其得分'''def detect(self, text_proposals, scores, size):# 删除得分较低的proposalkeep_inds = np.where(scores > TextLineCfg.TEXT_PROPOSALS_MIN_SCORE)[0] # 获取文本框得分大于0.7的索引text_proposals, scores = text_proposals[keep_inds], scores[keep_inds] # 根据索引获得文本框信息和得分# 按得分排序sorted_indices = np.argsort(scores.ravel())[::-1]text_proposals, scores = text_proposals[sorted_indices], scores[sorted_indices]# 对proposal做nmskeep_inds = nms(np.hstack((text_proposals, scores)), TextLineCfg.TEXT_PROPOSALS_NMS_THRESH)text_proposals, scores = text_proposals[keep_inds], scores[keep_inds]# 根据预测的碎片框,及其得分,图像宽高进行文本行合并# utils/text_connector/text_proposal_connector.pytext_recs = self.text_proposal_connector.get_text_lines(text_proposals, scores, size)# 按一定条件过滤合并后的文本行keep_inds = self.filter_boxes(text_recs)return text_recs[keep_inds]
其中的第4步:根据预测碎片框,文本框得分,图像宽高获得文本行,步骤:
- 确定每一行的碎片框(碎片框配对)
- 根据每一行的碎片框,计算每个文本行四个角的坐标及每行得分
'''根据预测碎片框,文本框得分,图像宽高获得文本行'''def get_text_lines(self, text_proposals, scores, im_size):# tp=text proposaltp_groups = self.group_text_proposals(text_proposals, scores, im_size) # 返回值里存放着每行的相似框,每个子图是一行text_lines = np.zeros((len(tp_groups), 5), np.float32)for index, tp_indices in enumerate(tp_groups):text_line_boxes = text_proposals[list(tp_indices)] # 取一行相似碎片框x0 = np.min(text_line_boxes[:, 0]) # 获取x的最小值x1 = np.max(text_line_boxes[:, 2]) # 获取x的最大值offset = (text_line_boxes[0, 2] - text_line_boxes[0, 0]) * 0.5 #第一个相似框宽度的一半,其实每个框宽度都等于16lt_y, rt_y = self.fit_y(text_line_boxes[:, 0], text_line_boxes[:, 1], x0 + offset, x1 - offset) # 左上y, 右上ylb_y, rb_y = self.fit_y(text_line_boxes[:, 0], text_line_boxes[:, 3], x0 + offset, x1 - offset) # 坐下y,右下y# the score of a text line is the average score of the scores# of all text proposals contained in the text line# 文本行的分数是该文本行中包含的所有文本碎片框的分数的平均分数score = scores[list(tp_indices)].sum() / float(len(tp_indices))text_lines[index, 0] = x0text_lines[index, 1] = min(lt_y, rt_y) # y0text_lines[index, 2] = x1text_lines[index, 3] = max(lb_y, rb_y) # y1text_lines[index, 4] = score # 得分text_lines = clip_boxes(text_lines, im_size) # 保证文本框在图像内text_recs = np.zeros((len(text_lines), 9), np.float)index = 0for line in text_lines: # 得到每一文本行四个角坐标xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = line[0], line[1], line[2], line[3]text_recs[index, 0] = xmin # 左上点xtext_recs[index, 1] = ymin # 左上点ytext_recs[index, 2] = xmax # 右上点xtext_recs[index, 3] = ymin # 右上点ytext_recs[index, 4] = xmaxtext_recs[index, 5] = ymaxtext_recs[index, 6] = xmintext_recs[index, 7] = ymaxtext_recs[index, 8] = line[4] # 得分index = index + 1return text_recs # 返回各个文本行及其得分其中的第1步:确定每一行的碎片框(碎片框配对),步骤:
- 将所有的碎片预测框,按左上点x坐标进行归类
- 定义graph,graph大小 n*n n是碎片预测框的数量
- 遍历碎片预测框,根据当前索引,先往右找满足条件的配对框,再往左找满足条件的配对框(需两两相互配对)
- 返回Graph(graph)
'''找配对相似框'''def build_graph(self, text_proposals, scores, im_size):self.text_proposals = text_proposals # 预测的文本框碎片self.scores = scores # 得分self.im_size = im_size # 图像宽高self.heights = text_proposals[:, 3] - text_proposals[:, 1] + 1 # 文本框的高度# 下面这段代码的功能是将所有的预测框,按左上点x坐标进行归类boxes_table = [[] for _ in range(self.im_size[1])] # im_size[1] = w 图像宽度for index, box in enumerate(text_proposals): # text_proposals shape(?,4)boxes_table[int(box[0])].append(index) # box[0]是预测碎片框的左上点x坐标self.boxes_table = boxes_table# graph类型 n*n n是预测框的大小graph = np.zeros((text_proposals.shape[0], text_proposals.shape[0]), np.bool)for index, box in enumerate(text_proposals): # 遍历预测出的碎片框successions = self.get_successions(index) # 在当前索引左上点x坐标一定区间范围内找与当前索引相似的预测碎片框作为返回值if len(successions) == 0: # 没有与当前索引相似的碎片框continue# 往右找相似碎片框succession_index = successions[np.argmax(scores[successions])] #取出所有相似碎片框中scores最大值所对应的索引if self.is_succession_node(index, succession_index): # 往左找相似碎片框,左右相互相似# NOTE: a box can have multiple successions(precursors) if multiple successions(precursors)# have equal scores. 一个预测框可能有多个得分一样的相似框graph[index, succession_index] = True # 当前索引和其相似索引标记为True,形成对应关系return Graph(graph)buid_graph()调用的相关函数,就不一一介绍了
# 往右边寻找# 根据当前索引,判断当前预测碎片框左上点x坐标+1,到当前预测碎片框左上点x坐标+1+最大间隙值(20)与图像宽度中取较小值# 在这个区间范围内找与当前索引相似的预测碎片框作为返回值def get_successions(self, index): # index 是当前预测碎片框的索引box = self.text_proposals[index] # 根据索引获得预测碎片框坐标 x1,y1,x2,y2results = []# left 范围是当前预测碎片框左上点x坐标+1,到当前预测碎片框左上点x坐标+1+最大间隙值(20)与图像宽度中取较小值for left in range(int(box[0]) + 1, min(int(box[0]) + TextLineCfg.MAX_HORIZONTAL_GAP + 1, self.im_size[1])):adj_box_indices = self.boxes_table[left] # 所有左上点x坐标为left的索引for adj_box_index in adj_box_indices: # 遍历左上点x坐标为left的索引if self.meet_v_iou(adj_box_index, index): # 判断两个预选框的偏差,如果差别较小则加入结果results.append(adj_box_index)if len(results) != 0:return results # 返回相关索引return results# 往左边寻找相似框,思路和向右的一样def get_precursors(self, index):box = self.text_proposals[index]results = []for left in range(int(box[0]) - 1, max(int(box[0] - TextLineCfg.MAX_HORIZONTAL_GAP), 0) - 1, -1):adj_box_indices = self.boxes_table[left]for adj_box_index in adj_box_indices:if self.meet_v_iou(adj_box_index, index):results.append(adj_box_index)if len(results) != 0:return resultsreturn results# 右边是左边的相似框,反过来判断左边是不是右边的相似框def is_succession_node(self, index, succession_index):precursors = self.get_precursors(succession_index) # 得到左边与右边相似的碎片框if self.scores[index] >= np.max(self.scores[precursors]):return Truereturn False# 判断两个预选框的偏差,高度的偏差和y坐标差与最小高度的比值def meet_v_iou(self, index1, index2): # index1 左上点x坐标为left的索引 index2 是当前预测碎片框的索引# 计算两个预选框y方向坐标差与最小高度的比值def overlaps_v(index1, index2):h1 = self.heights[index1]h2 = self.heights[index2]y0 = max(self.text_proposals[index2][1], self.text_proposals[index1][1]) # 获取两个索引左上点y坐标的最大值y1 = min(self.text_proposals[index2][3], self.text_proposals[index1][3]) # 获取两个索引右下点y坐标的最小值return max(0, y1 - y0 + 1) / min(h1, h2)# 计算两个预选框高度的比例,横小于1的情况小越接近1 说明越相似def size_similarity(index1, index2):h1 = self.heights[index1]h2 = self.heights[index2]return min(h1, h2) / max(h1, h2)return overlaps_v(index1, index2) >= TextLineCfg.MIN_V_OVERLAPS and \size_similarity(index1, index2) >= TextLineCfg.MIN_SIZE_SIM至此,CTPN源码算是粗略的解析完了,里面肯定会有理解和注释错误的,欢迎批评指正!

这篇关于CTPN源码解析5-文本线构造算法构造文本行的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




