本文主要是介绍第21讲 Java并发类库提供的线程池有哪几种? 分别有什么特点?,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- Java并发类库提供的线程池有哪几种? 分别有什么特点?
- 1.为什么要使用线程池?:
- 2.Executors和ThreadPoolExecutor
- 2.1Executors工厂创建线程池
- 2.1.1Executors
- 提交任务
- 关闭线程池
- Executor框架基本使用
- 2.1.2原理:
- Executor框架结构
- 2.2ThreadPoolExecutor
- 2.2.1ThreadPoolExecutor使用
- 2.2.1.1 原理:
- 2.1.1.2 参数的含义
- 我们再将ThreadPoolExecutor的size参数形象化一下:
- 2.2.1.2例子:
- 2.2.2 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor使用
- 1.以10秒的延迟运行:
- newScheduledThreadPool :
- newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor
- 2.周期性执行方法:
- 3.初始延迟并且开始定期执行。延迟时间是从线程完成执行的时间开始
- 2.3线程池大小的选择策略
- 参考
Java并发类库提供的线程池有哪几种? 分别有什么特点?
通常开发者都是利用Executors提供的通用线程池创建方法,去创建不同配置的线程池,主要区别在于不同的ExecutorService类型或者不同的初始参数。
Executors目前提供了5种不同的线程池创建配置:
- newCachedThreadPool(),它是一种用来处理大量短时间工作任务的线程池,具有几个鲜明特点:它会试图缓存线程并重用,当无缓存线程可用时,就会创建新的工作线程;如
果线程闲置的时间超过60秒,则被终止并移出缓存;长时间闲置时,这种线程池,不会消耗什么资源。 - newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads),重用指定数目(nThreads)的线程,其背后使用的是无界的工作队列,任何时候最多有nThreads个工作线程是活动的。这意味着,如
果任务数量超过了活动队列数目,将在工作队列中等待空闲线程出现;如果有工作线程退出,将会有新的工作线程被创建,以补足指定的数目nThreads。 - newSingleThreadExecutor(),它的特点在于工作线程数目被限制为1,操作一个无界的工作队列,所以它保证了所有任务的都是被顺序执行,最多会有一个任务处于活动状
态,并且不允许使用者改动线程池实例,因此可以避免其改变线程数目。 - newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()和newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize),创建的是个ScheduledExecutorService,可以进行定时或周期性的工作调度,
区别在于单一工作线程还是多个工作线程。 - newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism),这是一个经常被人忽略的线程池, Java 8才加入这个创建方法,其内部会构建ForkJoinPool,利用Work-Stealing算法,并行地处理任务,不保证处理顺序。
1.为什么要使用线程池?:
- 降低资源的消耗。降低线程创建和销毁的资源消耗
- 提高响应速度:线程的创建时间为T1,执行时间T2,销毁时间T3,免去T1和T3的时间
- 提高线程的可管理性。
2.Executors和ThreadPoolExecutor
能实例化的有两个:
- Executors:Executors工厂创建线程池。
- ThreadPoolExecutor:使用上不是很方便,需要传入多个参数。
2.1Executors工厂创建线程池
2.1.1Executors
- newCachedThreadPool使用:
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {private String username;public MyRunnable(String username) {this.username = username;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "username= "+username +"begin" + System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "username= "+username +"end" + System.currentTimeMillis());} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}public class ExecutorsDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {executorService.execute(new MyRunnable(" " + (i+1)));}Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(" ");System.out.println(" ");for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {executorService.execute(new MyRunnable(" " + (i+1)));}}
}
从结果来看,线程池得到了复用。
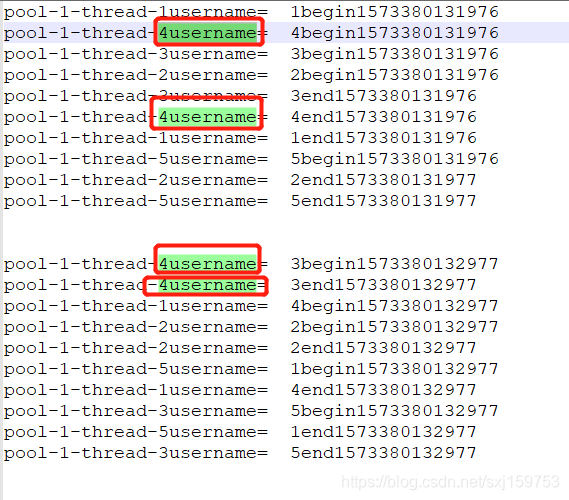 其他基本写法也都类似都是通过工厂来调用方法,之后通过execute方法来进行任务执行。
其他基本写法也都类似都是通过工厂来调用方法,之后通过execute方法来进行任务执行。
//xxx代表那几种创建方式
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newXXXThreadPool();executorService.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {}});
提交任务
有两种方式:除了execute,还有submit。
execute(Runnable command) 不需要返回
Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) 需要返回
关闭线程池
- shutdownNow():设置线程池的状态,还会尝试停止正在运行或者暂停任务的线程。
- shutdown()设置线程池的状态,只会中断所有没有执行任务的线程。
Executor框架基本使用
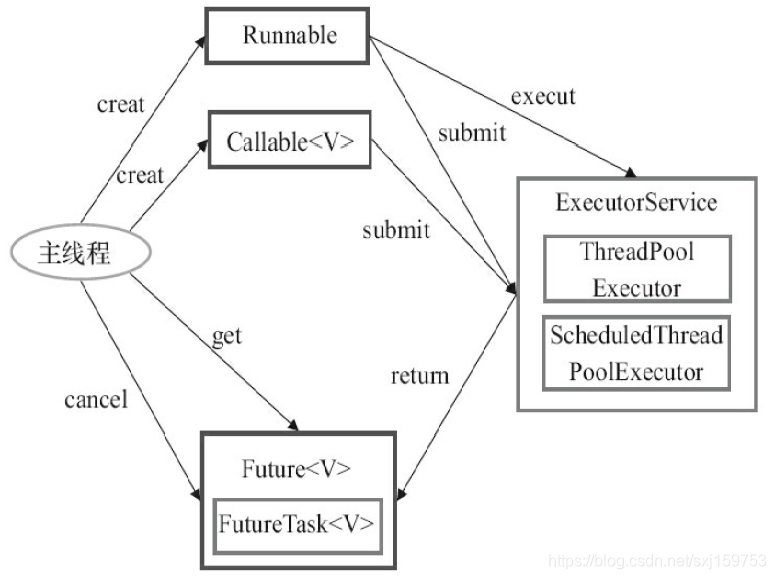
2.1.2原理:
- newCachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());}
- newFixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),threadFactory);}
- newSingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));}
- newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1));}
- newWorkStealingPool
public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool() {return new ForkJoinPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory,null, true);}
除了新加的newWorkStealingPool,其他内部都是使用的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
Executor框架结构
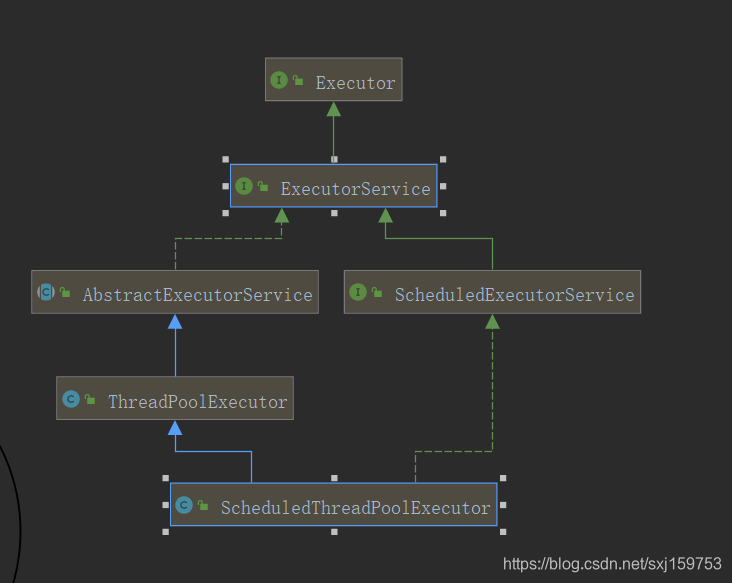
2.2ThreadPoolExecutor
2.2.1ThreadPoolExecutor使用
ThreadPoolExecutor构造方法:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);}
2.2.1.1 原理:
参数太多,通过知道原理可以对各个参数更加的理解:
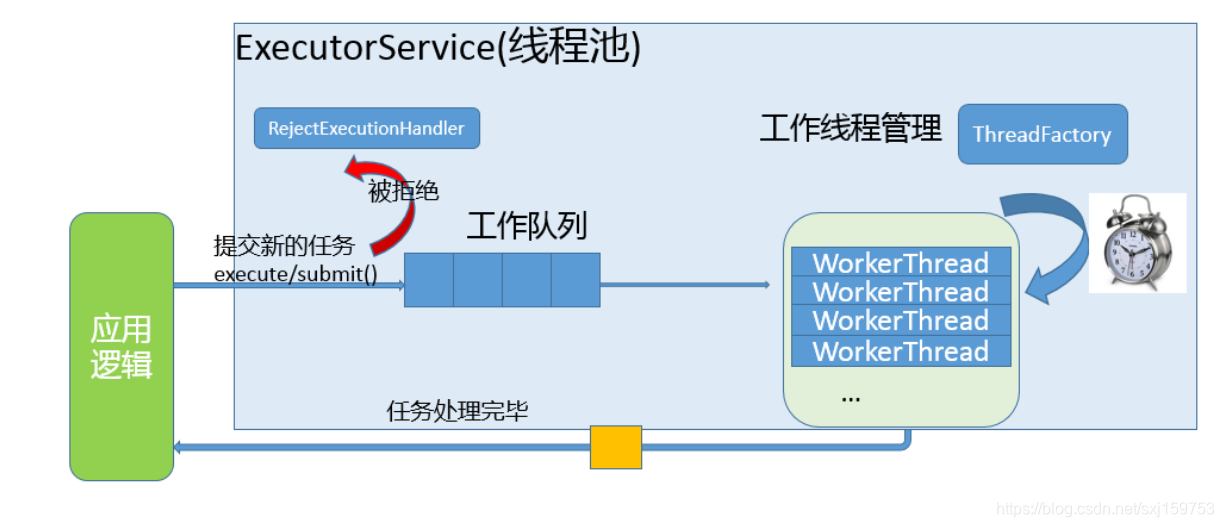
- 工作队列负责存储用户提交的各个任务,这个工作队列,可以是容量为0的SynchronousQueue(使用newCachedThreadPool),也可以是像固定大小线程池
(newFixedThreadPool)那样使用LinkedBlockingQueue。如果execute执行runnable小于corePoolSize,则不放入扩展队列。 - 内部的“线程池”,这是指保持工作线程的集合,线程池需要在运行过程中管理线程创建、销毁。例如,对于带缓存的线程池,当任务压力较大时,线程池会创建新的工作线程;当
业务压力退去,线程池会在闲置一段时间(默认60秒)后结束线程。 - RejectedExecutionHandler handler :如果任务提交时被拒绝,比如线程池已经处于SHUTDOWN状态,需要为其提供处理逻辑。
2.1.1.2 参数的含义
知道原理,再看一下各个参数的含义:
- int corePoolSize:所谓的核心线程数,可以大致理解为长期驻留的线程数目(除非设置了allowCoreThreadTimeOut)。对于不同的线程池,这个值可能会有很大区别,比
如newFixedThreadPool会将其设置为nThreads,而对于newCachedThreadPool则是为0。 - maximumPoolSize:线程不够时能够创建的最大线程数。同样进行对比,对于newFixedThreadPool,当然就是nThreads,因为其要求是固定大小,
而newCachedThreadPool则是Integer.MAX_VALUE。 - long keepAliveTime:线程空闲下来后,存活的时间
- TimeUnit unit, 存活时间的单位值
- BlockingQueue workQueue, 保存任务的阻塞队列,如果execute执行runnable小于corePoolSize,则不放入扩展队列。
- ThreadFactory threadFactory, 创建线程的工厂,给新建的线程赋予名字
- RejectedExecutionHandler handler :饱和策略
- AbortPolicy :直接抛出异常,默认;
- CallerRunsPolicy:用调用者所在的线程来执行任务
- DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃阻塞队列里最老的任务,队列里最靠前的任务
- DiscardPolicy :当前任务直接丢弃
- 实现自己的饱和策略,实现RejectedExecutionHandler接口即可。
我们再将ThreadPoolExecutor的size参数形象化一下:
//车中可载的标准人数System.out.println(executorPool.getCorePoolSize());//车中可载的最大人数System.out.println(executorPool.getMaximumPoolSize());//正在载的人数System.out.println(executorPool.getPoolSize());//扩展车中正在载的人数System.out.println(executorPool.getQueue().size());
上面的图可以更形象化:
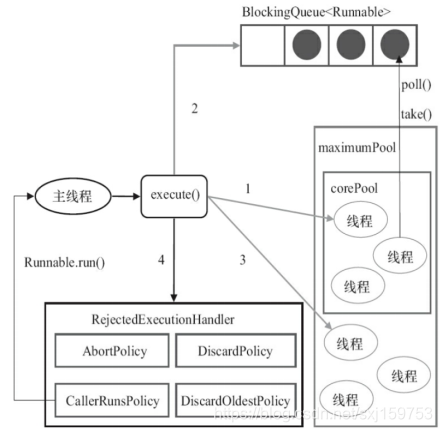
2.2.1.2例子:
我们需要有一个名为WorkerThread.java的Runnable类
package Executor;
public class WorkerThread implements Runnable {private String command;public WorkerThread(String s){this.command=s;}@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Start. Command = "+command);processCommand();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" End.");}private void processCommand() {try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic String toString(){return this.command;}
}RejectedExecutionHandlerImpl
package Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;public class RejectedExecutionHandlerImpl implements RejectedExecutionHandler {@Overridepublic void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {System.out.println(r.toString() + " is rejected");}}
MyMonitorThread:
有一个监视线程,该线程将在特定时间间隔打印执行程序信息
package Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;public class MyMonitorThread implements Runnable {private ThreadPoolExecutor executor;private int seconds;private boolean run = true;public MyMonitorThread(ThreadPoolExecutor executor, int delay) {this.executor = executor;this.seconds = delay;}public void shutdown() {this.run = false;}@Overridepublic void run() {while (run) {System.out.println(String.format("[monitor] [%d/%d] Active: %d, Completed: %d, Task: %d, isShutdown: %s, isTerminated: %s",this.executor.getPoolSize(),this.executor.getCorePoolSize(),this.executor.getActiveCount(),this.executor.getCompletedTaskCount(),this.executor.getTaskCount(),this.executor.isShutdown(),this.executor.isTerminated()));try {Thread.sleep(seconds * 1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
使用:
package Executor;import java.util.concurrent.*;public class ExecutorsDemo {public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException{//RejectedExecutionHandler的实现类RejectedExecutionHandlerImpl rejectionHandler = new RejectedExecutionHandlerImpl();//Get the ThreadFactory implementation 实现ThreadFactory threadFactory = Executors.defaultThreadFactory();//创建ThreadPoolExecutorThreadPoolExecutor executorPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 4, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(2), threadFactory, rejectionHandler);//开始监控线程池 monitoring threadMyMonitorThread monitor = new MyMonitorThread(executorPool, 3);Thread monitorThread = new Thread(monitor);monitorThread.start();//放到线程池for(int i=0; i<10; i++){executorPool.execute(new WorkerThread("cmd"+i));}Thread.sleep(30000);//shut down the poolexecutorPool.shutdown();//shut down the monitor threadThread.sleep(5000);monitor.shutdown();}
}注意创建的时候
初始池大小保持为2,最大池大小保持为4,工作队列大小保持为2。
如果有4个或者更多的任务提交,那么工作队列将只容纳其中的2个任务,其余的任务将由RejectedExecutionHandlerImpl处理。
打印:
cmd6 is rejected
cmd7 is rejected
cmd8 is rejected
cmd9 is rejected
pool-1-thread-3 Start. Command = cmd4
pool-1-thread-2 Start. Command = cmd1
pool-1-thread-1 Start. Command = cmd0
pool-1-thread-4 Start. Command = cmd5
[monitor] [0/2] Active: 0, Completed: 0, Task: 0, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
[monitor] [4/2] Active: 4, Completed: 0, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
pool-1-thread-3 End.
pool-1-thread-2 End.
pool-1-thread-3 Start. Command = cmd2
pool-1-thread-2 Start. Command = cmd3
pool-1-thread-1 End.
pool-1-thread-4 End.
[monitor] [4/2] Active: 2, Completed: 4, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
[monitor] [4/2] Active: 2, Completed: 4, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
pool-1-thread-3 End.
pool-1-thread-2 End.
[monitor] [4/2] Active: 0, Completed: 6, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
[monitor] [2/2] Active: 0, Completed: 6, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
[monitor] [2/2] Active: 0, Completed: 6, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
[monitor] [2/2] Active: 0, Completed: 6, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
[monitor] [2/2] Active: 0, Completed: 6, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
[monitor] [2/2] Active: 0, Completed: 6, Task: 6, isShutdown: false, isTerminated: false
[monitor] [0/2] Active: 0, Completed: 6, Task: 6, isShutdown: true, isTerminated: true
[monitor] [0/2] Active: 0, Completed: 6, Task: 6, isShutdown: true, isTerminated: trueProcess finished with exit code 02.2.2 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor使用
有时我们需要定期或在特定的延迟后执行任务。Java提供了Timer类,通过它可以实现此目的,但有时我们需要并行运行类似的任务
示例:
同样是WorkerThread
package Executor;public class WorkerThread implements Runnable {private String command;public WorkerThread(String s){this.command=s;}@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Start. Command = "+command);processCommand();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" End.");}private void processCommand() {try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic String toString(){return this.command;}
}1.以10秒的延迟运行:
newScheduledThreadPool :
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);}
可以包含多个线程的,线程执行周期任务,适度控制后台线程数量的时候。
package Executor;import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.*;public class ExecutorsDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);System.out.println("Current Time = "+new Date());for(int i=0; i<3; i++){Thread.sleep(1000);WorkerThread worker = new WorkerThread("do heavy processing");scheduledThreadPool.schedule(worker, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}//让一些线程产生调度程序Thread.sleep(30000);scheduledThreadPool.shutdown();while(!scheduledThreadPool.isTerminated()){//等待所有任务完成}System.out.println("Finished all threads");}}结果:
Current Time = Sun Nov 10 20:51:56 CST 2019
pool-1-thread-1 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-2 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-3 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-1 End.
pool-1-thread-2 End.
pool-1-thread-3 End.
Finished all threads
Process finished with exit code 0一个线程情况下,可以使用:
newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1));}
只包含一个线程,只需要单个线程执行周期任务,保证顺序的执行各个任务
2.周期性执行方法:
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
只需将上面代码替换为这个:
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {Thread.sleep(1000);WorkerThread worker = new WorkerThread("do heavy processing");// schedule task to execute at fixed ratescheduledThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(worker, 0, 10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);}
结果:会不断的执行下去,结果中我按了结束。
Current Time = Sun Nov 10 20:57:57 CST 2019
pool-1-thread-1 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-2 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-3 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-1 End.
pool-1-thread-2 End.
pool-1-thread-3 End.
pool-1-thread-1 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-4 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-2 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-1 End.
pool-1-thread-4 End.
pool-1-thread-2 End.
pool-1-thread-1 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-3 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-5 Start. Command = do heavy processing
pool-1-thread-1 End.
pool-1-thread-3 End.
pool-1-thread-5 End.Process finished with exit code -1注意:
scheduleAtFixedRate任务超时的情况:
例如规定60s执行一次,有任务执行了80S,则下个任务马上开始执行。
周期变为:
第一个任务 时长 80s,第二个任务20s,第三个任务 50s
第一个任务第0秒开始,第80S结束;
第二个任务第80s开始,在第100秒结束;
第三个任务第120s秒开始,170秒结束
第四个任务从180s开始
而且,使用scheduleAtFixedRate时候:ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的任务最好在run方法中try-catch住异常,如果不捕捉,则后续固定任务不再执行。
3.初始延迟并且开始定期执行。延迟时间是从线程完成执行的时间开始
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,long initialDelay,long delay,TimeUnit unit);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {Thread.sleep(1000);WorkerThread worker = new WorkerThread("do heavy processing");scheduledThreadPool.scheduleWithFixedDelay(worker, 0, 1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}2.3线程池大小的选择策略
- 如果我们的任务主要是进行计算,通常建议按照CPU核的数目N或者N+1。
- 如果是需要较多等待的任务,例如I/O操作比较多:
线程数 = CPU核数 × (1 + 平均等待时间/平均工作时间)
-
上面是仅仅考虑了CPU等限制,实际还可能受各种系统资源限制影响.在实际工作中,不要把解决问题的思路全部指望到调整线程池上,很多时候架构上的改变更能解决问题,比如利用背压机制的Reactive Stream、合理的拆分等。
-
队列的选择上,应该使用有界,无界队列可能会导致内存溢出,OOM
参考
在36讲的基础上,又参考了:
journaldev
《java并发编程核心方法与框架》
这篇关于第21讲 Java并发类库提供的线程池有哪几种? 分别有什么特点?的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






