本文主要是介绍【PCL】pcl中是怎么计算特征的,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- 写在前面
- 四种计算特征的方法
- 1. !indices & !isurface
- 2. indices & !isurface
- 3. !indices & isurface
- 4. indices & isurface
- 三个接口辨析
- 1. setInputCloud(PointCloudConstPtr &)
- 2. setIndices(IndicesConstPtr &)
- 3. setSearchSurface(PointCloudConstPtr &)
- 例子
- 1. 直接计算全部的点云的法向量,每一个点邻域考虑本身的邻域。
- 2. 不计算每一个点的法向量,仅仅计算给的的索引的,考虑邻域为本身的邻域
- 3. 计算给定点云(下采样后)的每一个点的法向量,对每一个点考虑SearchSurface中的对应点的邻域
- 总结
- 参考
写在前面
在计算特征向量descriptors的时候,需要只对关键点keypoints计算关键点在其原始点云处的邻域特征,那么就会用到setSearchSurface这个函数。
四种计算特征的方法
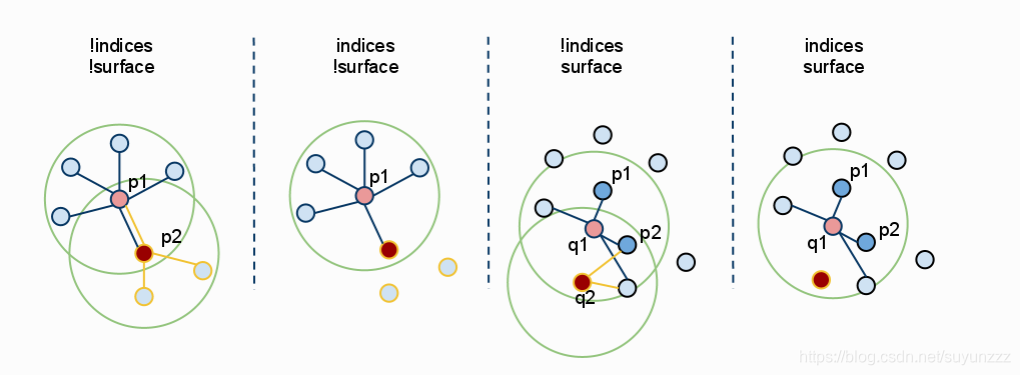
1. !indices & !isurface
无索引,搜索原点云上的每一个点的邻域。
2. indices & !isurface
有索引,搜索原点云上的每一个点的邻域。
3. !indices & isurface
无索引,搜索指定的点云上的每一个点的邻域。
4. indices & isurface
有索引,搜索指定的点云上的每一个点的邻域。
三个接口辨析
1. setInputCloud(PointCloudConstPtr &)
设置搜索的点云
2. setIndices(IndicesConstPtr &)
设置cloud的索引,类似于下采样
3. setSearchSurface(PointCloudConstPtr &)
具体计算某一个点处的特征时,设置需要考虑的哪个点云上对应于该点的邻域特征。
例子
下面例子中具体考虑哪个点云集合的邻域,是取决于tree的,看程序注释可以发现是优先考虑 search surface。
1. 直接计算全部的点云的法向量,每一个点邻域考虑本身的邻域。
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);... read, pass in or create a point cloud ...// Create the normal estimation class, and pass the input dataset to itpcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;ne.setInputCloud (cloud);// Create an empty kdtree representation, and pass it to the normal estimation object.// Its content will be filled inside the object, based on the given input dataset (as no other search surface is given).pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> ());ne.setSearchMethod (tree);// Output datasetspcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);// Use all neighbors in a sphere of radius 3cmne.setRadiusSearch (0.03);// Compute the featuresne.compute (*cloud_normals);// cloud_normals->points.size () should have the same size as the input cloud->points.size ()
}
2. 不计算每一个点的法向量,仅仅计算给的的索引的,考虑邻域为本身的邻域
The following code snippet will estimate a set of surface normals for a subset of the points in the input dataset.
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);... read, pass in or create a point cloud ...// Create a set of indices to be used. For simplicity, we're going to be using the first 10% of the points in cloudstd::vector<int> indices (std::floor (cloud->points.size () / 10));for (std::size_t i = 0; i < indices.size (); ++i) indices[i] = i;// Create the normal estimation class, and pass the input dataset to itpcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;ne.setInputCloud (cloud);// Pass the indicespcl::shared_ptr<std::vector<int> > indicesptr (new std::vector<int> (indices));ne.setIndices (indicesptr);// Create an empty kdtree representation, and pass it to the normal estimation object.// Its content will be filled inside the object, based on the given input dataset (as no other search surface is given).pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> ());ne.setSearchMethod (tree);// Output datasetspcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);// Use all neighbors in a sphere of radius 3cmne.setRadiusSearch (0.03);// Compute the featuresne.compute (*cloud_normals);// cloud_normals->points.size () should have the same size as the input indicesptr->size ()
}3. 计算给定点云(下采样后)的每一个点的法向量,对每一个点考虑SearchSurface中的对应点的邻域
Finally, the following code snippet will estimate a set of surface normals for all the points in the input dataset, but will estimate their nearest neighbors using another dataset. As previously mentioned, a good usecase for this is when the input is a downsampled version of the surface.
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_downsampled (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);... read, pass in or create a point cloud ...... create a downsampled version of it ...// Create the normal estimation class, and pass the input dataset to itpcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> ne;ne.setInputCloud (cloud_downsampled);// Pass the original data (before downsampling) as the search surfacene.setSearchSurface (cloud);// Create an empty kdtree representation, and pass it to the normal estimation object.// Its content will be filled inside the object, based on the given surface dataset.pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> ());ne.setSearchMethod (tree);// Output datasetspcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);// Use all neighbors in a sphere of radius 3cmne.setRadiusSearch (0.03);// Compute the featuresne.compute (*cloud_normals);// cloud_normals->points.size () should have the same size as the input cloud_downsampled->points.size ()
}总结
上述四种情况,!indices&SearchSurface最常用。
在计算关键点的特征向量的时会用到。
如下:
descr_est.setInputCloud (model_keypoints); //模型点云的关键点descr_est.setInputNormals (model_normals); //模型点云的法线 descr_est.setSearchSurface (model); //模型点云 descr_est.compute (*model_descriptors); //计算描述子descr_est.setInputCloud (scene_keypoints);descr_est.setInputNormals (scene_normals);descr_est.setSearchSurface (scene);descr_est.compute (*scene_descriptors);————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「JoannaJuanCV」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zfjBIT/article/details/93046902
参考
PCL学习:基于点云分类的目标识别
How 3D Features work in PCL
PCL/OpenNI tutorial 5: 3D object recognition (pipeline)
PCL/OpenNI tutorial 4: 3D object recognition (descriptors)
这篇关于【PCL】pcl中是怎么计算特征的的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








