本文主要是介绍高数考研 -- 公式总结(更新中),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1. 两个重要极限
(1) lim x → 0 sin x x = 1 \lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sin x}{x}=1 limx→0xsinx=1, 推广形式 lim f ( x ) → 0 sin f ( x ) f ( x ) = 1 \lim _{f(x) \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sin f(x)}{f(x)}=1 limf(x)→0f(x)sinf(x)=1.
(2) lim x → ∞ ( 1 + 1 x ) x = e \lim _{x \rightarrow \infty}\left(1+\frac{1}{x}\right)^x=\mathrm{e} limx→∞(1+x1)x=e, 推广形式 lim x → 0 ( 1 + x ) 1 x = e , lim f ( x ) → ∞ [ 1 + 1 f ( x ) ] f ( x ) = e \lim _{x \rightarrow 0}(1+x)^{\frac{1}{x}}=\mathrm{e}, \lim _{f(x) \rightarrow \infty}\left[1+\frac{1}{f(x)}\right]^{f(x)}=\mathrm{e} limx→0(1+x)x1=e,limf(x)→∞[1+f(x)1]f(x)=e
2. 常用的等价无穷小量及极限公式
(1) 当 x → 0 x \rightarrow 0 x→0 时,常用的等价无穷小
- (1) x ∼ sin x ∼ tan x ∼ arcsin x ∼ arctan x ∼ ln ( 1 + x ) ∼ e x − 1 x \sim \sin x \sim \tan x \sim \arcsin x \sim \arctan x \sim \ln (1+x) \sim \mathrm{e}^x-1 x∼sinx∼tanx∼arcsinx∼arctanx∼ln(1+x)∼ex−1.
- (2) 1 − cos x ∼ 1 2 x 2 , 1 − cos b x ∼ b 2 x 2 ( b ≠ 0 ) 1-\cos x \sim \frac{1}{2} x^2, 1-\cos ^b x \sim \frac{b}{2} x^2(b \neq 0) 1−cosx∼21x2,1−cosbx∼2bx2(b=0).
- (3) a x − 1 ∼ x ln a ( a > 0 a^x-1 \sim x \ln a(a>0 ax−1∼xlna(a>0, 且 a ≠ 1 ) a \neq 1) a=1).
- (4) ( 1 + x ) α − 1 ∼ α x ( α ≠ 0 ) (1+x)^\alpha-1 \sim \alpha x (\alpha \neq 0) (1+x)α−1∼αx(α=0).
(2) 当 n → ∞ n \rightarrow \infty n→∞ 或 x → ∞ x \rightarrow \infty x→∞ 时,常用的极限公式
- (1) lim n → ∞ n n = 1 , lim n → ∞ a n = 1 ( a > 0 ) \lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} \sqrt[n]{n}=1, \lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} \sqrt[n]{a}=1(a>0) limn→∞nn=1,limn→∞na=1(a>0).
- (2) lim x → ∞ a n x n + a n − 1 x n − 1 + ⋯ + a 1 x + a 0 b m x m + b m − 1 x m − 1 + ⋯ + b 1 x + b 0 = { a n b m , n = m , 0 , n < m , ∞ , n > m , \lim _{x \rightarrow \infty} \frac{a_n x^n+a_{n-1} x^{n-1}+\cdots+a_1 x+a_0}{b_m x^m+b_{m-1} x^{m-1}+\cdots+b_1 x+b_0}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}\frac{a_n}{b_m}, & n=m, \\ 0, & n<m, \\ \infty, & n>m,\end{array}\right. limx→∞bmxm+bm−1xm−1+⋯+b1x+b0anxn+an−1xn−1+⋯+a1x+a0=⎩ ⎨ ⎧bman,0,∞,n=m,n<m,n>m, 其中 a n , b m a_n, b_m an,bm 均不
为 0 .
- (3) lim n → ∞ x n = { 0 , ∣ x ∣ < 1 , ∞ , ∣ x ∣ > 1 , 1 , x = 1 , 不存在, x = − 1 ; lim n → ∞ e n x = { 0 , x < 0 , + ∞ , x > 0 , 1 , x = 0. \lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} x^n=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}0, & |x|<1, \\ \infty, & |x|>1, \\ 1, & x=1, \\ \text { 不存在, } & x=-1 ;\end{array} \lim _{n \rightarrow \infty} \mathrm{e}^{n x}= \begin{cases}0, & x<0, \\ +\infty, & x>0, \\ 1, & x=0 .\end{cases}\right. limn→∞xn=⎩ ⎨ ⎧0,∞,1, 不存在, ∣x∣<1,∣x∣>1,x=1,x=−1;limn→∞enx=⎩ ⎨ ⎧0,+∞,1,x<0,x>0,x=0.
- (4) 若 lim g ( x ) = 0 , lim f ( x ) = ∞ \lim g(x)=0, \lim f(x)=\infty limg(x)=0,limf(x)=∞, 且 lim g ( x ) f ( x ) = A \lim g(x) f(x)=A limg(x)f(x)=A, 则有
lim [ 1 + g ( x ) ] f ( x ) = e A . \lim [1+g(x)]^{f(x)}=\mathrm{e}^A . lim[1+g(x)]f(x)=eA.
3. x → 0 x \rightarrow 0 x→0 时常见的麦克劳林公式
sin x = x − 1 3 ! x 3 + o ( x 3 ) , cos x = 1 − 1 2 ! x 2 + 1 4 ! x 4 + o ( x 4 ) , tan x = x + 1 3 x 3 + o ( x 3 ) , arcsin x = x + 1 3 ! x 3 + o ( x 3 ) , arctan x = x − 1 3 x 3 + o ( x 3 ) , ln ( 1 + x ) = x − 1 2 x 2 + 1 3 x 3 + o ( x 3 ) , e x = 1 + x + 1 2 ! x 2 + 1 3 ! x 3 + o ( x 3 ) , ( 1 + x ) a = 1 + a x + a ( a − 1 ) 2 ! x 2 + o ( x 2 ) . \begin{aligned} & \sin x=x-\frac{1}{3 !} x^3+o\left(x^3\right), \quad \cos x=1-\frac{1}{2 !} x^2+\frac{1}{4 !} x^4+o\left(x^4\right),\\ \\ & \tan x=x+\frac{1}{3} x^3+o\left(x^3\right), \quad \arcsin x=x+\frac{1}{3 !} x^3+o\left(x^3\right), \\ \\ & \arctan x=x-\frac{1}{3} x^3+o\left(x^3\right), \quad \ln (1+x)=x-\frac{1}{2} x^2+\frac{1}{3} x^3+o\left(x^3\right), \\ \\ & \mathrm{e}^x=1+x+\frac{1}{2 !} x^2+\frac{1}{3 !} x^3+o\left(x^3\right),(1+x)^a=1+a x+\frac{a(a-1)}{2 !} x^2+o\left(x^2\right) . \end{aligned} sinx=x−3!1x3+o(x3),cosx=1−2!1x2+4!1x4+o(x4),tanx=x+31x3+o(x3),arcsinx=x+3!1x3+o(x3),arctanx=x−31x3+o(x3),ln(1+x)=x−21x2+31x3+o(x3),ex=1+x+2!1x2+3!1x3+o(x3),(1+x)a=1+ax+2!a(a−1)x2+o(x2).
当 x → 0 x \rightarrow 0 x→0 时,由以上公式可以得到以下几组“差函数”的等价无穷小代换式:
x − sin x ∼ x 3 6 , tan x − x ∼ x 3 3 , x − ln ( 1 + x ) ∼ x 2 2 x-\sin x \sim \frac{x^3}{6}, \quad \tan x-x \sim \frac{x^3}{3}, \quad x-\ln (1+x) \sim \frac{x^2}{2} x−sinx∼6x3,tanx−x∼3x3,x−ln(1+x)∼2x2, arcsin x − x ∼ x 3 6 , x − arctan x ∼ x 3 3 \arcsin x-x \sim \frac{x^3}{6}, \quad x-\arctan x \sim \frac{x^3}{3} arcsinx−x∼6x3,x−arctanx∼3x3.
4. 基本导数公式
( x μ ) ′ = μ x μ − 1 ( μ 为常数 ) , ( a x ) ′ = a x ln a ( a > 0 , a ≠ 1 ) , ( log a x ) ′ = 1 x ln a ( a > 0 , a ≠ 1 ) , ( ln x ) ′ = 1 x , ( sin x ) ′ = cos x , ( cos x ) ′ = − sin x , ( arcsin x ) ′ = 1 1 − x 2 , ( arccos x ) ′ = − 1 1 − x 2 , ( tan x ) ′ = sec 2 x , ( cot x ) ′ = − csc 2 x , ( arctan x ) ′ = 1 1 + x 2 , ( arccot x ) ′ = − 1 1 + x 2 , ( sec x ) ′ = sec x tan x , ( csc x ) ′ = − csc x cot x , [ ln ( x + x 2 + 1 ) ] ′ = 1 x 2 + 1 , , [ ln ( x + x 2 − 1 ) ] ′ = 1 x 2 − 1 \begin{array}{ll} \left(x^\mu\right)^{\prime}=\mu x^{\mu-1} ( \mu 为常数), & \left(a^x\right)^{\prime}=a^x \ln a(a>0, a \neq 1), \\ \\ \left(\log _a x\right)^{\prime}=\frac{1}{x \ln a}(a>0, a \neq 1) , & (\ln x)^{\prime}=\frac{1}{x}, \\ \\ (\sin x)^{\prime}=\cos x, & (\cos x)^{\prime}=-\sin x, \\ \\ (\arcsin x)^{\prime}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}, & (\arccos x)^{\prime}=-\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}}, \\ \\ (\tan x)^{\prime}=\sec ^2 x, & (\cot x)^{\prime}=-\csc ^2 x, \\ \\ (\arctan x)^{\prime}=\frac{1}{1+x^2}, & (\operatorname{arccot} x)^{\prime}=-\frac{1}{1+x^2}, \\ \\ (\sec x)^{\prime}=\sec x \tan x, & (\csc x)^{\prime}=-\csc x \cot x, \\ \\ {\left[\ln \left(x+\sqrt{x^2+1}\right)\right]^{\prime}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{x^2+1}},}, & {\left[\ln \left(x+\sqrt{x^2-1}\right)\right]^{\prime}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{x^2-1}}} \end{array} (xμ)′=μxμ−1(μ为常数),(logax)′=xlna1(a>0,a=1),(sinx)′=cosx,(arcsinx)′=1−x21,(tanx)′=sec2x,(arctanx)′=1+x21,(secx)′=secxtanx,[ln(x+x2+1)]′=x2+11,,(ax)′=axlna(a>0,a=1),(lnx)′=x1,(cosx)′=−sinx,(arccosx)′=−1−x21,(cotx)′=−csc2x,(arccotx)′=−1+x21,(cscx)′=−cscxcotx,[ln(x+x2−1)]′=x2−11
三角函数六边形记忆法:
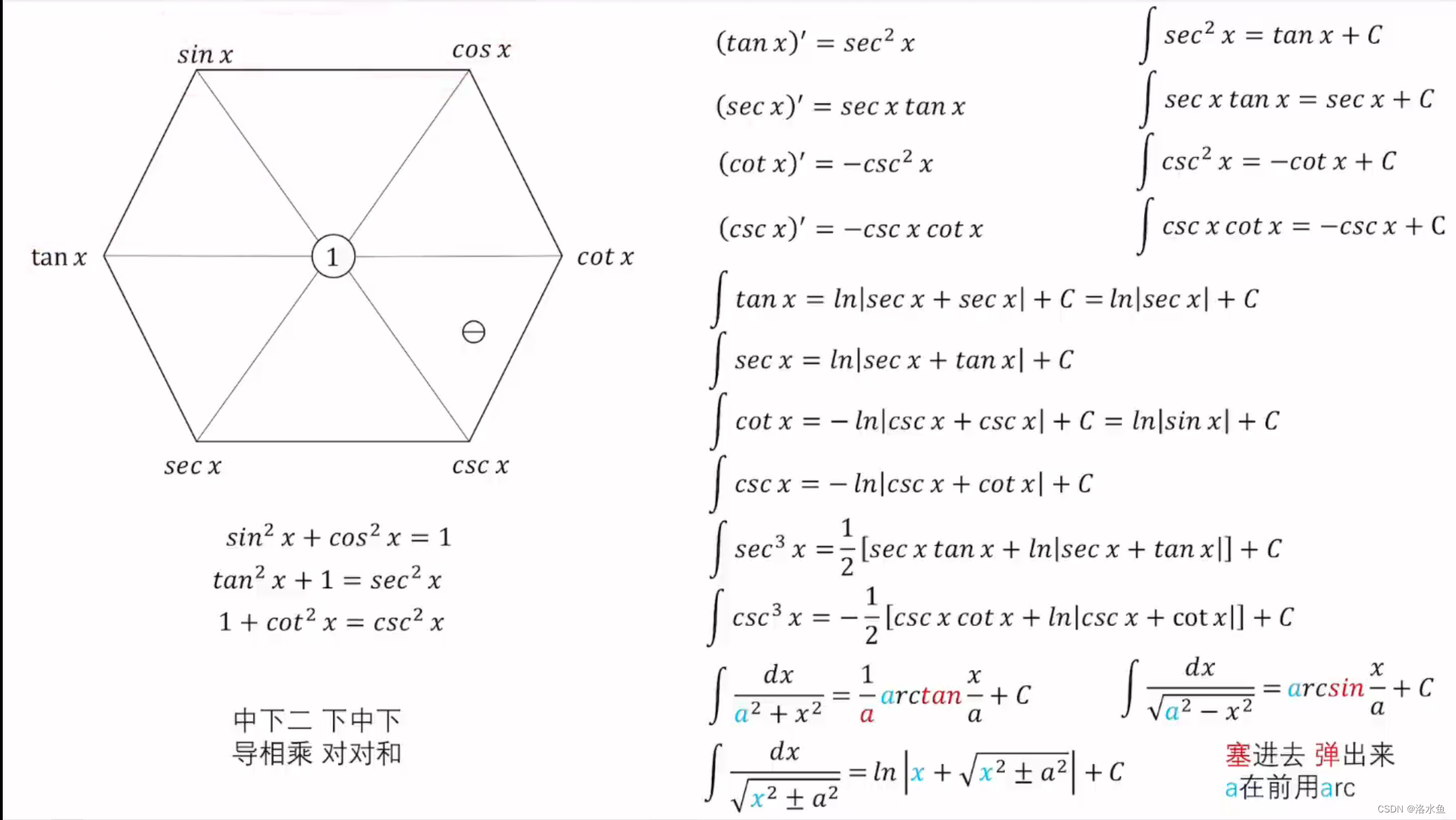
注: 变限积分求导公式.
设 F ( x ) = ∫ φ 2 ( x ) φ 1 ( x ) f ( t ) d t F(x)=\int_{\varphi_2(x)}^{\varphi_1(x)} f(t) \mathrm{d} t F(x)=∫φ2(x)φ1(x)f(t)dt, 其中 f ( x ) f(x) f(x) 在 [ a , b ] [a, b] [a,b] 上连续, 可导函数 φ 1 ( x ) \varphi_1(x) φ1(x) 和 φ 2 ( x ) \varphi_2(x) φ2(x) 的值域在 [ a , b ] [a, b] [a,b] 上, 则在函数 φ 1 ( x ) \varphi_1(x) φ1(x) 和 φ 2 ( x ) \varphi_2(x) φ2(x) 的公共定义域上有:
F ′ ( x ) = d d x [ ∫ φ 1 ( x ) φ 2 ( x ) f ( t ) d t ] = f [ φ 2 ( x ) ] φ 2 ′ ( x ) − f [ φ 1 ( x ) ] φ 1 ′ ( x ) . F^{\prime}(x)=\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d} x}\left[\int_{\varphi_1(x)}^{\varphi_2(x)} f(t) \mathrm{d} t\right]=f\left[\varphi_2(x)\right] \varphi_2^{\prime}(x)-f\left[\varphi_1(x)\right] \varphi_1^{\prime}(x) . F′(x)=dxd[∫φ1(x)φ2(x)f(t)dt]=f[φ2(x)]φ2′(x)−f[φ1(x)]φ1′(x).
5. 几个重要函数的麦克劳林展开式
(1) e x = 1 + x + 1 2 ! x 2 + ⋯ + 1 n ! x n + o ( x n ) \mathrm{e}^x=1+x+\frac{1}{2 !} x^2+\cdots+\frac{1}{n !} x^n+o\left(x^n\right) ex=1+x+2!1x2+⋯+n!1xn+o(xn).
(2) sin x = x − 1 3 ! x 3 + ⋯ + ( − 1 ) n 1 ( 2 n + 1 ) ! x 2 n + 1 + o ( x 2 n + 1 ) \sin x=x-\frac{1}{3 !} x^3+\cdots+(-1)^n \frac{1}{(2 n+1) !} x^{2 n+1}+o\left(x^{2 n+1}\right) sinx=x−3!1x3+⋯+(−1)n(2n+1)!1x2n+1+o(x2n+1).
(3) cos x = 1 − 1 2 ! x 2 + 1 4 ! x 4 − ⋯ + ( − 1 ) n 1 ( 2 n ) ! x 2 n + o ( x 2 n ) \cos x=1-\frac{1}{2 !} x^2+\frac{1}{4 !} x^4-\cdots+(-1)^n \frac{1}{(2 n) !} x^{2 n}+o\left(x^{2 n}\right) cosx=1−2!1x2+4!1x4−⋯+(−1)n(2n)!1x2n+o(x2n).
(4) 1 1 − x = 1 + x + x 2 + ⋯ + x n + o ( x n ) , ∣ x ∣ < 1 \frac{1}{1-x}=1+x+x^2+\cdots+x^n+o\left(x^n\right),|x|<1 1−x1=1+x+x2+⋯+xn+o(xn),∣x∣<1.
(5) 1 1 + x = 1 − x + x 2 − ⋯ + ( − 1 ) n x n + o ( x n ) , ∣ x ∣ < 1 \frac{1}{1+x}=1-x+x^2-\cdots+(-1)^n x^n+o\left(x^n\right),|x|<1 1+x1=1−x+x2−⋯+(−1)nxn+o(xn),∣x∣<1.
(6) ln ( 1 + x ) = x − x 2 2 + x 3 3 − ⋯ + ( − 1 ) n − 1 x n n + o ( x n ) , − 1 < x ⩽ 1 \ln (1+x)=x-\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^3}{3}-\cdots+(-1)^{n-1} \frac{x^n}{n}+o\left(x^n\right),-1<x \leqslant 1 ln(1+x)=x−2x2+3x3−⋯+(−1)n−1nxn+o(xn),−1<x⩽1.
(7) ( 1 + x ) a = 1 + a x + a ( a − 1 ) 2 ! x 2 + ⋯ + a ( a − 1 ) ⋯ ( a − n + 1 ) n ! x n + (1+x)^a=1+a x+\frac{a(a-1)}{2 !} x^2+\cdots+\frac{a(a-1) \cdots(a-n+1)}{n !} x^n+ (1+x)a=1+ax+2!a(a−1)x2+⋯+n!a(a−1)⋯(a−n+1)xn+ o ( x n ) o\left(x^n\right) o(xn).
6. 曲率和曲率半径计算公式
(1) 曲率
- (1) (非参数方程) 曲线 y = f ( x ) y=f(x) y=f(x) 上任意一点 ( x , f ( x ) ) (x, f(x)) (x,f(x)) 处的曲率为
K = ∣ y ′ ′ ∣ [ 1 + ( y ′ ) 2 ] 3 2 . K=\frac{\left|y^{\prime \prime}\right|}{\left[1+\left(y^{\prime}\right)^2\right]^{\frac{3}{2}}} \text {. } K=[1+(y′)2]23∣y′′∣. - (2) (参数方程) { x = x ( t ) , y = y ( t ) \left\{\begin{array}{l}x=x(t), \\ y=y(t)\end{array}\right. {x=x(t),y=y(t) 上任意一点的曲率为
K = ∣ x ′ ( t ) y ′ ′ ( t ) − y ′ ( t ) x ′ ′ ( t ) ∣ { [ x ′ ( t ) ] 2 + [ y ′ ( t ) ] 2 } 3 2 . K=\frac{\left|x^{\prime}(t) y^{\prime \prime}(t)-y^{\prime}(t) x^{\prime \prime}(t)\right|}{\left\{\left[x^{\prime}(t)\right]^2+\left[y^{\prime}(t)\right]^2\right\}^{\frac{3}{2}}} . K={[x′(t)]2+[y′(t)]2}23∣x′(t)y′′(t)−y′(t)x′′(t)∣.
参数方程求导:
参数方程 { x = φ ( t ) y = ψ ( t ) \left\{\begin{array}{l}x=\varphi(t) \\ y=\psi(t)\end{array}\right. {x=φ(t)y=ψ(t)
d y d x = d y / d t d x / d t = ψ ′ ( t ) φ ′ ( t ) , 令其为 F ( t ) , \frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{d y / d t}{d x / d t}=\frac{\psi^{\prime}(t)}{\varphi^{\prime}(t)},令其为F(t),\\ dxdy=dx/dtdy/dt=φ′(t)ψ′(t),令其为F(t),
d 2 y d x 2 = d ( d y d x ) d x = d ( d y d x ) / d t d x / d t = ψ ′ ′ ( t ) φ ′ ( t ) − ψ ′ ( t ) φ ′ ′ ( t ) [ φ ′ ( t ) ] 3 = d ( F ( t ) ) / d t d x / d t = F ′ ( t ) φ ′ ( t ) \frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}=\frac{d\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right)}{d x}=\frac{d\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right) / d t}{d x / d t}=\frac{\psi^{\prime \prime}(t) \varphi^{\prime}(t)-\psi^{\prime}(t) \varphi^{\prime \prime}(t)}{\left[\varphi^{\prime}(t)\right]^{3}} = \frac{d(F(t))/dt}{dx/dt} = \frac{F^{\prime}(t)}{\varphi^{\prime}(t)} dx2d2y=dxd(dxdy)=dx/dtd(dxdy)/dt=[φ′(t)]3ψ′′(t)φ′(t)−ψ′(t)φ′′(t)=dx/dtd(F(t))/dt=φ′(t)F′(t)
可以记最后那个简单的式子
(2) 曲率半径
R = 1 K ( K ≠ 0 ) R=\frac{1}{K}(K \neq 0) R=K1(K=0)
这篇关于高数考研 -- 公式总结(更新中)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







