本文主要是介绍Android LruCache源码分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- Android LruCache源码分析
- 概述
- LruCache和LinkedHashMap关系
- 源码分析
- 属性
- 写入数据
- 读取数据
- 删除缓存
Android LruCache源码分析
概述
LruCache(Least Recently Used Cache,最近最少使用缓存)是 Android 中的一种缓存机制。
根据数据的使用频率淘汰减少使用的数据,当需要缓存新数据时,如果缓存已满,LruCache 会淘汰最近最少使用的数据,腾出空间给新数据。
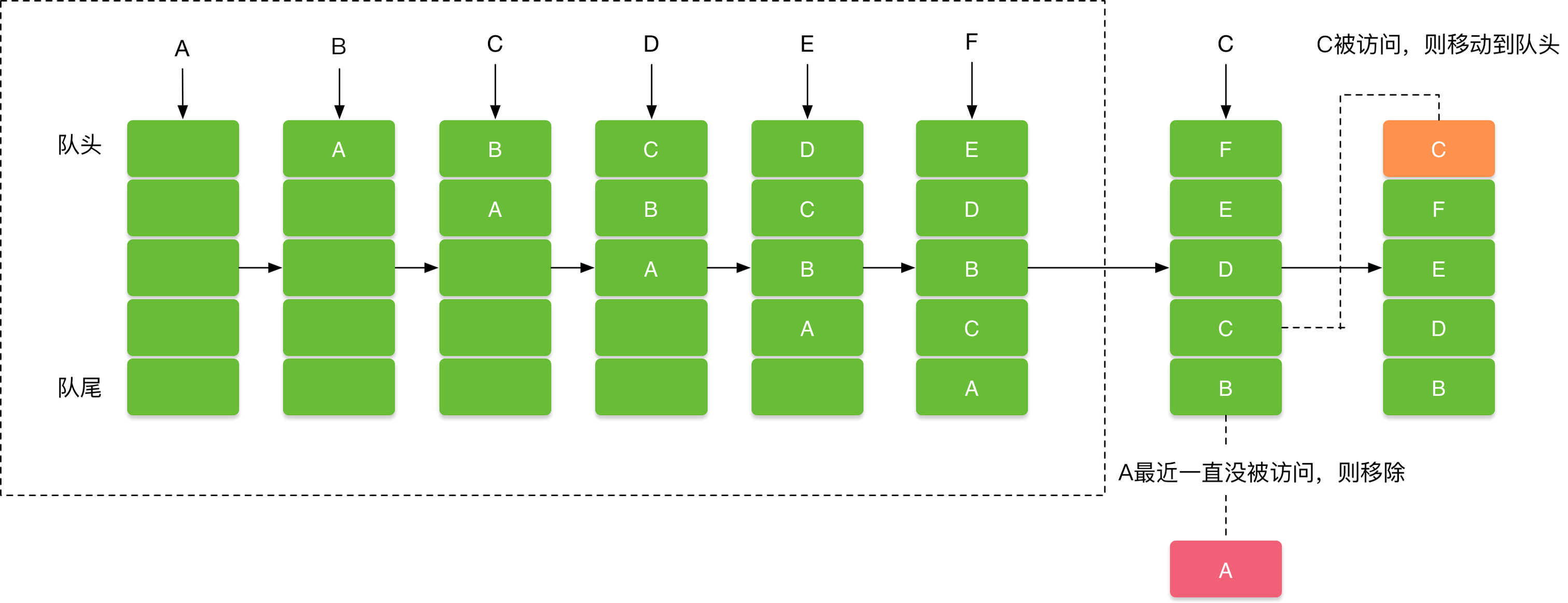
LruCache和LinkedHashMap关系
LruCache 内部使用的是 LinkedHashMap(链式哈希表),这是因为 LinkedHashMap 的构造函数里有个布尔参数 accessOrder,当它为 true 时,LinkedHashMap 会以访问顺序的方式排列元素,如下:
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(5, 0.75F, true);
map.put(1, 1);
map.put(2, 2);
map.put(3, 3);
map.put(4, 4);
map.put(5, 5);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}/** 1* 2* 3* 4* 5*/
// 访问2个元素
map.get(3);
map.get(4);
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}/** 1* 2* 5* 3* 4*/
最近访问的2个元素被移动到尾部,LruCache 也是从尾部访问数据,在表头删除数据。
源码分析
属性
public class LruCache<K, V> {private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map; // 当前缓存大小private int size;// 最大缓存容量private int maxSize;// 写入计数private int putCount;// 创建计数private int createCount;// 淘汰计数private int evictionCount;// 缓存命中计数private int hitCount;// 缓存未命计数private int missCount;
}
写入数据
public final V put(K key, V value) {// 如果值为null,则抛出异常if (key == null || value == null) {throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");}V previous;// 加锁,线程安全synchronized (this) {// 写入计数putCount++;// 通过sizeOf()计算当前项的大小,并累加已有缓存大小size += safeSizeOf(key, value);// 写入操作previous = map.put(key, value);// 如果previous为null表示为新增数据,如果previous不为null表示为修改数据if (previous != null) {// 修改数据需要将size恢复到以前的大小size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);}}// 回调entryRemoved()方法if (previous != null) {entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);}// 调整缓存大小trimToSize(maxSize);return previous;
}// 调整缓存大小
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {// 死循环while (true) {K key;V value;synchronized (this) {// 缓存未满,直接返回if (size <= maxSize || map.isEmpty()) {break;}// 缓存已满情况// 从表头遍历,获取元素Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.entrySet().iterator().next();key = toEvict.getKey();value = toEvict.getValue();// 删除元素map.remove(key);// 减少删除元素的缓存size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);// 删除计数evictionCount++;}// 回调entryRemoved()方法entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);}
}
- 插入元素,并增加已缓存的大小。
- 调用 trimToSize() 方法,调整缓存大小。
读取数据
public final V get(@NonNull K key) {if (key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("key == null");}V mapValue;synchronized (this) {// 获取元素,LinkedHashMap会将这个元素移动到表尾mapValue = map.get(key);if (mapValue != null) {hitCount++;return mapValue;}missCount++;}// 没有元素时,会回调create()方法V createdValue = create(key);if (createdValue == null) {return null;}// 下面和put()流程相同synchronized (this) {createCount++;mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);if (mapValue != null) {map.put(key, mapValue);} else {size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);}}if (mapValue != null) {entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);return mapValue;} else {trimToSize(maxSize);return createdValue;}
}
- 最终调用 LinkedHashMap#get() 方法,因为accessOrder为true ,因此元素会移动到表尾。
- 如果没有获取到元素时,会调用 create() 方法创建元素,接着执行put()流程。
删除缓存
public final V remove(@NonNull K key) {if (key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("key == null");}V previous;synchronized (this) {// 调用LinkedHashMap#remove()方法删除元素previous = map.remove(key);if (previous != null) {size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);}}if (previous != null) {entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);}return previous;
}
- 调用 LinkedHashMap#remove() 方法删除元素。
这篇关于Android LruCache源码分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







