本文主要是介绍RealSense D435 的开发日记(API 汇总),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
🌞欢迎来到机器学习的世界
🌈博客主页:卿云阁💌欢迎关注🎉点赞👍收藏⭐️留言📝
🌟本文由卿云阁原创!
🌠本阶段属于练气阶段,希望各位仙友顺利完成突破
📆首发时间:🌹2021年6月23日🌹
✉️希望可以和大家一起完成进阶之路!
🙏作者水平很有限,如果发现错误,请留言轰炸哦!万分感谢!
目录
🍈 获得相机不同传感器之间的外参转换矩阵以及内参矩阵
🍉获取设备的传感器信息
🍊获得深度图单位和米之间的映射
🍋深度图与RGB图配准
🍌获取深度图中像素点的深度值
🍍使用API进行拍照
🥭Realsense获取像素点在相机坐标系下的三维坐标
🍎其它相关内容的介绍
🍆校准编辑

🍈 获得相机不同传感器之间的外参转换矩阵以及内参矩阵
import pyrealsense2 as rspipeline = rs.pipeline() config = rs.config() config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30) config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 1280, 720, rs.format.rgb8, 30) cfg = pipeline.start(config) device = cfg.get_device() name = device.get_info(rs.camera_info.name) print(name) profile = cfg.get_stream(rs.stream.depth) profile1 = cfg.get_stream(rs.stream.color) intr = profile.as_video_stream_profile().get_intrinsics() intr1 = profile1.as_video_stream_profile().get_intrinsics() extrinsics = profile1.get_extrinsics_to(profile) print(extrinsics) print("深度传感器内参:", intr) print("RGB相机内参:", intr1)Intel RealSense D435 rotation: [0.999641, -0.0260036, 0.00641907, 0.0260053, 0.999662, -0.000173101, -0.0064124, 0.000339969, 0.999979] translation: [-0.0147544, -0.000367906, -0.000408054] 深度传感器内参: [ 640x480 p[322.424 239.496] f[386.034 386.034] Brown Conrady [0 0 0 0 0] ] RGB相机内参: [ 1280x720 p[643.807 366.839] f[930.979 930.957] Inverse Brown Conrady [0 0 0 0 0] ]注意
不同分辨率的深度相机和RGB相机对应不同的内参参数,但是外参矩阵是一样的(上述代码的外参指的是RGB相机转换到深度相机的转换矩阵),可以观察到RGB相机有畸变参数,深度相机无畸变参数。import pyrealsense2 as rspipeline = rs.pipeline() config = rs.config() config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30) config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 960, 540, rs.format.bgr8, 30) profile = pipeline.start(config) frames = pipeline.wait_for_frames() depth = frames.get_depth_frame() color = frames.get_color_frame() # 获取内参 depth_profile = depth.get_profile() print(depth_profile) # <pyrealsense2.video_stream_profile: Depth(0) 640x480 @ 30fps Z16> print(type(depth_profile)) # <class 'pyrealsense2.pyrealsense2.stream_profile'> print(depth_profile.fps()) # 30 print(depth_profile.stream_index()) # 0 print(depth_profile.stream_name()) # Depth print(depth_profile.stream_type()) # stream.depth print('', depth_profile.unique_id) # <bound method PyCapsule.unique_id of <pyrealsense2.video_stream_profile: Depth(0) 640x480 @ 30fps Z16>>color_profile = color.get_profile() print(color_profile) # <pyrealsense2.video_stream_profile: Color(0) 960x540 @ 30fps BGR8> print(type(color_profile)) # <class 'pyrealsense2.pyrealsense2.stream_profile'> print(depth_profile.fps()) # 30 print(depth_profile.stream_index()) # 0cvsprofile = rs.video_stream_profile(color_profile) dvsprofile = rs.video_stream_profile(depth_profile)color_intrin = cvsprofile.get_intrinsics() print(color_intrin) # 960x540 p[493.975 265.065] f[673.775 673.824] Brown Conrady [0.151657 -0.50863 -0.000700379 -0.000860805 0.471284] depth_intrin = dvsprofile.get_intrinsics() print(depth_intrin) # [ 640x480 p[306.57 254.527] f[461.453 461.469] None [0 0 0 0 0] ] extrin = depth_profile.get_extrinsics_to(color_profile) print(extrin) # rotation: [0.999965, 0.00762357, 0.00331248, -0.00754261, 0.999688, -0.0238027, -0.0034929, 0.0237769, 0.999711] # translation: [0.000304107, 0.0142351, -0.00695471]🍉获取设备的传感器信息
import pyrealsense2 as rs import pyrealsense2 as rspipeline = rs.pipeline() config = rs.config() pipeline_wrapper = rs.pipeline_wrapper(pipeline) pipeline_profile = config.resolve(pipeline_wrapper) device = pipeline_profile.get_device() for s in device.sensors:print(s.get_info(rs.camera_info.name))cfg = pipeline.start(config) device1 = cfg.get_device() for s in device1.sensors:print(s.get_info(rs.camera_info.name))aaaa
Stereo Module RGB Camera Stereo Module RGB Camera两个语句得到的都是pipeline_profile的类,有get_device的方法
pipeline.start(config)config.resolve(pipeline_wrapper)🍊获得深度图单位和米之间的映射
import pyrealsense2 as rs import pyrealsense2 as rs# Create a pipeline pipeline = rs.pipeline() # Start streaming profile = pipeline.start()# Getting the depth sensor's depth scale (see rs-align example for explanation) depth_sensor = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor() depth_scale = depth_sensor.get_depth_scale() print("Depth Scale is: ", depth_scale)Depth Scale is: 0.0010000000474974513get_depth_scale的目标是获得深度图单位与米单位之间的映射关系,所以上述表示一个深度图单位等于0.00025米。第二个例子通过get_data方法获得的数值与米单位之间需要乘以一个比例系数。
🍋深度图与RGB图配准
# First import the library import pyrealsense2 as rs # Import Numpy for easy array manipulation import numpy as np # Import OpenCV for easy image rendering import cv2# Create a pipeline pipeline = rs.pipeline()# Create a config and configure the pipeline to stream # different resolutions of color and depth streams config = rs.config()# Get device product line for setting a supporting resolution pipeline_wrapper = rs.pipeline_wrapper(pipeline) pipeline_profile = config.resolve(pipeline_wrapper) device = pipeline_profile.get_device() device_product_line = str(device.get_info(rs.camera_info.product_line))found_rgb = False for s in device.sensors:if s.get_info(rs.camera_info.name) == 'RGB Camera':found_rgb = Truebreak if not found_rgb:print("The demo requires Depth camera with Color sensor")exit(0)config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30)if device_product_line == 'L500':config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 1280, 720, rs.format.bgr8, 30) else:config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.bgr8, 30)# Start streaming profile = pipeline.start(config)# Getting the depth sensor's depth scale (see rs-align example for explanation) depth_sensor = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor() depth_scale = depth_sensor.get_depth_scale() print("Depth Scale is: ", depth_scale)# We will be removing the background of objects more than # clipping_distance_in_meters meters away clipping_distance_in_meters = 1 # 1 meter clipping_distance = clipping_distance_in_meters / depth_scale# Create an align object # rs.align allows us to perform alignment of depth frames to others frames # The "align_to" is the stream type to which we plan to align depth frames. align_to = rs.stream.color align = rs.align(align_to)# Streaming loop try:while True:# Get frameset of color and depthframes = pipeline.wait_for_frames()# frames.get_depth_frame() is a 640x360 depth image# Align the depth frame to color framealigned_frames = align.process(frames)# Get aligned framesaligned_depth_frame = aligned_frames.get_depth_frame() # aligned_depth_frame is a 640x480 depth imagecolor_frame = aligned_frames.get_color_frame()# Validate that both frames are validif not aligned_depth_frame or not color_frame:continuedepth_image = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data())color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())# the size of color_frame is (720,1280,3)# Remove background - Set pixels further than clipping_distance to greygrey_color = 153depth_image_3d = np.dstack((depth_image, depth_image, depth_image))# depth image is 1 channel, color is 3 channels# depth_image_3d shape is (720,1280,3)bg_removed = np.where((depth_image_3d > clipping_distance) | (depth_image_3d <= 0), grey_color, color_image)# the size of bg_removed is (720,1280,3)# Render images:# depth align to color on left# depth on rightdepth_colormap = cv2.applyColorMap(cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)images = np.hstack((bg_removed, depth_colormap))cv2.namedWindow('Align Example', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)cv2.imshow('Align Example', images)key = cv2.waitKey(1)# Press esc or 'q' to close the image windowif key & 0xFF == ord('q') or key == 27:cv2.destroyAllWindows()break finally:pipeline.stop()无论初始对于彩色流或是深度流是如何设置分辨率的,经过align.process之后的彩色流和深度流都是(720,1280)大小的(这个大小根据彩色流的设置而定),虽然深度流需要重构为三维来让彩色流和深度流拼接。虽然深度流的大小转换为和彩色流一样的大小,但是分辨率还是根据深度流的设置参数而定的,与大小无关
🍌获取深度图中像素点的深度值
get_distance()方法得到的数据是以米为单位的
import cv2 import numpy as np import pyrealsense2 as rspipeline = rs.pipeline() config = rs.config() config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30) # Start streaming profile = pipeline.start(config) while True:frames = pipeline.wait_for_frames()depth_frames = frames.get_depth_frame()depth_image = np.asarray(depth_frames.get_data())depth_colormap = cv2.applyColorMap(cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)distance = depth_frames.get_distance(100, 200)print(distance)cv2.imshow("depth image:", depth_colormap)key = cv2.waitKey(1)if key == 27:break pipeline.stop()3.8570001125335693 3.8570001125335693 3.8570001125335693 4.11400032043457 3.809000253677368 3.8330001831054688 3.763000249862671 4.25600004196167 5.27400016784668
🍍使用API进行拍照
import cv2 import numpy as np import pyrealsense2 as rs import os# 配置 pipe = rs.pipeline() cfg = rs.config() cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 1280, 720, rs.format.rgb8, 30)i = 0 profile = pipe.start(cfg)while True:# 获取图片帧frameset = pipe.wait_for_frames()color_frame = frameset.get_color_frame()color_img = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())# 更改通道的顺序为RGBcv2.namedWindow('RealSense', cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)cv2.imshow('RealSense', color_img)k = cv2.waitKey(1)# Esc退出,if k == 27:cv2.destroyAllWindows()break# 输入空格保存图片elif k == ord(' '):i = i + 1cv2.imwrite(os.path.join("D:\\Realsense\\pic_capture", str(i) + '.jpg'), color_img)print("Frames{} Captured".format(i))pipe.stop()
只要将数据转换为numpy数组的方式,就可以通过opencv库进行图片的保存
🥭Realsense获取像素点在相机坐标系下的三维坐标
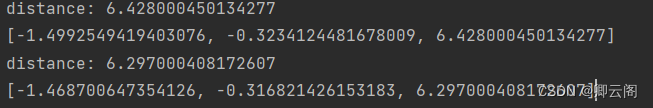
import pyrealsense2 as rs import numpy as np import cv2 import jsondef get_aligned_images():frames = pipeline.wait_for_frames() # 等待获取图像帧aligned_frames = align.process(frames) # 获取对齐帧aligned_depth_frame = aligned_frames.get_depth_frame() # 获取对齐帧中的depth帧color_frame = aligned_frames.get_color_frame() # 获取对齐帧中的color帧############### 相机参数的获取 #######################intr = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics # 获取相机内参depth_intrin = aligned_depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics # 获取深度参数(像素坐标系转相机坐标系会用到)camera_parameters = {'fx': intr.fx, 'fy': intr.fy,'ppx': intr.ppx, 'ppy': intr.ppy,'height': intr.height, 'width': intr.width,'depth_scale': profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor().get_depth_scale()}# 保存内参到本地with open('D:\\Realsense\\intrinsics.json', 'w') as fp:json.dump(camera_parameters, fp)#######################################################depth_image = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data()) # 深度图(默认16位)depth_image_8bit = cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03) # 深度图(8位)depth_image_3d = np.dstack((depth_image_8bit, depth_image_8bit, depth_image_8bit)) # 3通道深度图color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data()) # RGB图# 返回相机内参、深度参数、彩色图、深度图、齐帧中的depth帧return intr, depth_intrin, color_image, depth_image_3d, aligned_depth_framepipeline = rs.pipeline() # 定义流程pipeline config = rs.config() # 定义配置config config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30) # 配置depth流 config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 960, 540, rs.format.bgr8, 30) # 配置color流 profile = pipeline.start(config) # 流程开始 align_to = rs.stream.color # 与color流对齐 align = rs.align(align_to) while True:intr, depth_intrin, rgb, depth, aligned_depth_frame = get_aligned_images() # 获取对齐的图像与相机内参# 定义需要得到真实三维信息的像素点(x, y),本例程以中心点为例x = 320y = 240dis = aligned_depth_frame.get_distance(x, y) # (x, y)点的真实深度值print("distance:",dis)camera_coordinate = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(intr, [x, y], dis)# (x, y)点在相机坐标系下的真实值,为一个三维向量。# 其中camera_coordinate[2]仍为dis,camera_coordinate[0]和camera_coordinate[1]为相机坐标系下的xy真实距离。print(camera_coordinate)cv2.imshow('RGB image', rgb) # 显示彩色图像key = cv2.waitKey(1)# Press esc or 'q' to close the image windowif key & 0xFF == ord('q') or key == 27:pipeline.stop()break cv2.destroyAllWindows()
获得像素点在相机坐标系下的三维坐标之后,通过手眼标定就可以转化为在机械臂基底坐标系下的坐标,进而执行下一步操作。所得到的三维坐标应该是以米为单位的。
🍎其它相关内容的介绍
像素坐标:
通过SDK提供的图像流都关联一个独立的2D以像素为单位的坐标系。[0,0]点位于左上角,[w-1,h-1]点位于右下角。w和h分别代表列和行,从相机的角度来看,x轴指向右边,y轴指向下边。这个坐标系就是所谓的像素坐标系,用来索引特定的像素点。点坐标:
通过SDK提供的图像流都关联一个独立的3D以米为单位的坐标系。这个坐标系的原点[0,0,0]指的是物理成像仪的中心。在这个空间中,x轴正向指向右,y轴正向指向下,z轴正向指向前。该空间中的坐标称为“点”,用于描述三维空间中可能在特定图像中可见的位置。相机内参
流的2D和3D坐标系的转换关系是通过相机内参来描述的,包含在rs2_intrinsics结构体中。不同的RealSense设备的内参是不同的,rs2_intrinsics结构体必须要能够描述由这些设备产生的图像。相机外参
每种图像流的三维坐标系是不同的,比如说,通常来说深度图像是通过一个或多个红外成像仪生成的,而彩色流是通过一个独立的彩色成像仪形成的。这些不同的流所对应的三维坐标系之间的关系是通过外参进行描述的,包含在rs2_extrinsics的结构体中。🍆校准
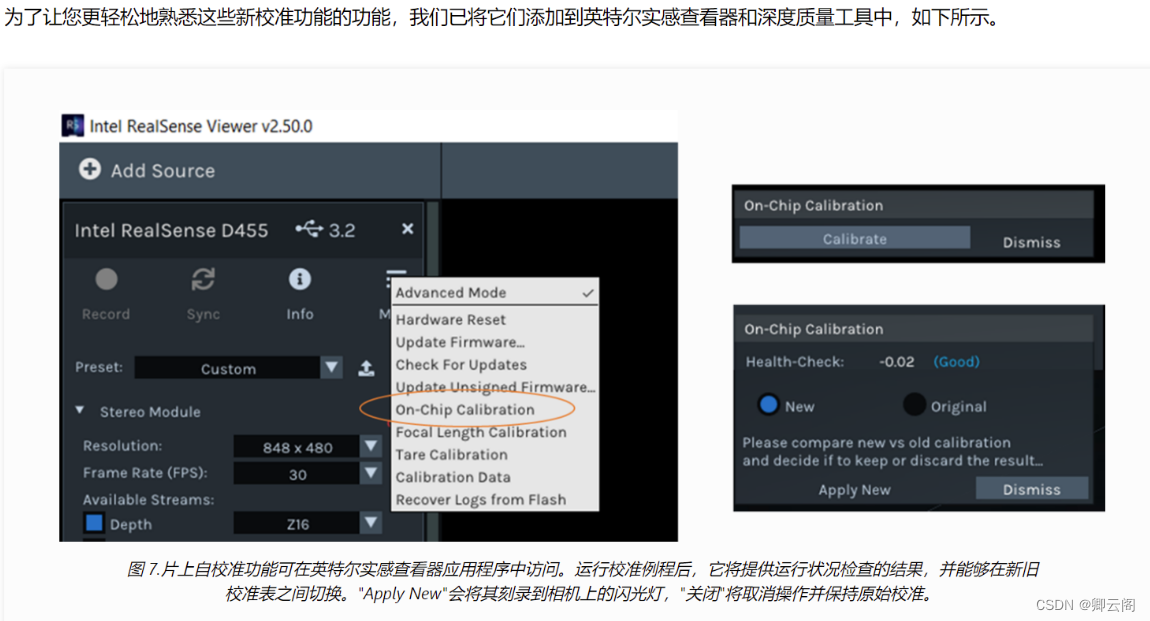
这张图片也就是说,在 Viewer 上进行校准,当误差小于一定值时,可以忽略。
如果校准过程中报错:可能是没有足够的有效深度像素,通常可以通过确保投影仪处于打开状态来补救。
这篇关于RealSense D435 的开发日记(API 汇总)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!