本文主要是介绍g2o--icp代码解析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
概要
个人理解Icp是一种location算法。我们先将全局的事物特征化,提取出特征点。在求解过程中,将观察的的图像,同样进行特征化。将全局点与当前特征点进行匹配,就可以求得观察者当前的位姿。
Icp算法通常分为粗匹配和精细匹配两部分。粗匹配是将观察特征点移动到对应全局特征点的附近,而精细匹配这是将一个一个对应的特征点,使用最小二乘优化进行调整。在精细匹配的过程中,特征点对的选取也很重要,icp是一套迭代的算法,每次变换后都需要重新选取特征点对。

在求解一次特征点对匹配过程中,也存在很多中算法。笔者接触过的牛顿法思路比较简单,效果也很好。网上还推荐一种常用的方法svd,也是基于矩阵进行运算。今天介绍的g2o也是一种icp的匹配算法。
所谓的图优化,就是把一个常规的优化问题,以图(Graph)的形式来表述。在图中,以顶点表示优化变量,以边表示观测方程。于是总体优化问题变为n条边加和的形式(边是约束)。
所谓的问题
观测者所在两个位姿,能够看到特征点在自我坐标下的三维位置,并且在两个位姿下的特征点对是明确的,求解两个位姿的相对关系。
建图
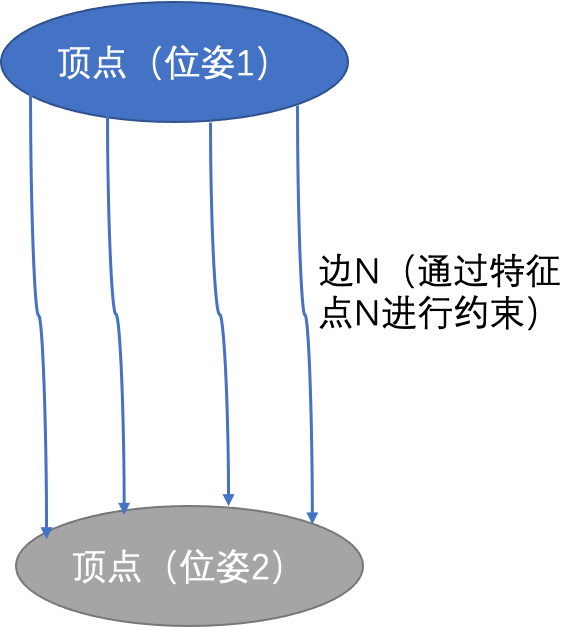
源码解析
本文分析的也是g2o自带example中的代码(gicp_demo.cpp)
初始化求解器
SparseOptimizer optimizer;optimizer.setVerbose(false);// variable-size block solverg2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg* solver =new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(std::make_unique<BlockSolverX>(std::make_unique<LinearSolverDense<g2o::BlockSolverX::PoseMatrixType>>()));optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);初始化1000个特征点
vector<Vector3d> true_points;for (size_t i = 0; i < 1000; ++i) {true_points.push_back(Vector3d((g2o::Sampler::uniformRand(0., 1.) - 0.5) * 3,g2o::Sampler::uniformRand(0., 1.) - 0.5,g2o::Sampler::uniformRand(0., 1.) + 10));}初始化观测者的两个位姿
// set up two posesint vertex_id = 0;for (size_t i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {// set up rotation and translation for this nodeVector3d t(0, 0, i);Quaterniond q;q.setIdentity();Eigen::Isometry3d cam; // camera posecam = q;cam.translation() = t;// set up nodeVertexSE3* vc = new VertexSE3();vc->setEstimate(cam); // 设定初始位姿vc->setId(vertex_id); // vertex idcerr << t.transpose() << " | " << q.coeffs().transpose() << endl;// set first cam pose fixedif (i == 0) vc->setFixed(true); // 将第一个点固定// add to optimizeroptimizer.addVertex(vc); // 将观测者的位姿添加进优化器中vertex_id++;} 添加约束
// set up point matchesfor (size_t i = 0; i < true_points.size(); ++i) { // 遍历所有特征点// get two posesVertexSE3* vp0 =dynamic_cast<VertexSE3*>(optimizer.vertices().find(0)->second); // 取出观测者第一个位姿VertexSE3* vp1 =dynamic_cast<VertexSE3*>(optimizer.vertices().find(1)->second); // 取出观测者第二个位姿// calculate the relative 3D position of the pointVector3d pt0, pt1;pt0 = vp0->estimate().inverse() * true_points[i]; // 计算特征点在第一个位姿坐标系下的位置pt1 = vp1->estimate().inverse() * true_points[i]; // 计算特征点在第二个位姿坐标系下的位置// add in noisept0 += Vector3d(g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(0., euc_noise), // 添加误差g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(0., euc_noise),g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(0., euc_noise));pt1 += Vector3d(g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(0., euc_noise),g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(0., euc_noise),g2o::Sampler::gaussRand(0., euc_noise));// form edge, with normals in varioius positionsVector3d nm0, nm1;nm0 << 0, i, 1;nm1 << 0, i, 1;nm0.normalize();nm1.normalize();Edge_V_V_GICP* e // new edge with correct cohort for caching= new Edge_V_V_GICP();e->setVertex(0, vp0); // first viewpoint 设定边的第一个顶点 e->setVertex(1, vp1); // second viewpoint 设定边的第二个顶点 EdgeGICP meas;meas.pos0 = pt0; // 设定边中第一个观测点的观测值meas.pos1 = pt1; // 设定边中第二个观测点的观测值meas.normal0 = nm0;meas.normal1 = nm1;e->setMeasurement(meas); // 设定观测值// e->inverseMeasurement().pos() = -kp;meas = e->measurement();// use this for point-planee->information() = meas.prec0(0.01); // 设定权重optimizer.addEdge(e); // 将该边添加进求解器中}求解结果
cout << endl << "Second vertex should be near 0,0,1" << endl;cout << dynamic_cast<VertexSE3*>(optimizer.vertices().find(0)->second)->estimate().translation().transpose()<< endl;cout << dynamic_cast<VertexSE3*>(optimizer.vertices().find(1)->second) // 第二个点的位姿是我们最关心的->estimate().translation().transpose()<< endl;注:
关于边中的normal0和normal1参数的解释 -- https://github.com/RainerKuemmerle/g2o/issues/266
这篇关于g2o--icp代码解析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





