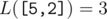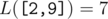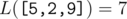本文主要是介绍【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)D】【线段树 or ST-RMQ 初始化78msAC】Lipshitz Sequence 若干区间询问所有子区间的答案和,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)D】【线段树 即时处理询问】Lipshitz Sequence 若干区间询问所有子区间的答案和 850ms
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<algorithm>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
void fre(){freopen("c://test//input.in","r",stdin);freopen("c://test//output.out","w",stdout);}
#define MS(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MC(x,y) memcpy(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MP(x,y) make_pair(x,y)
#define ls o<<1
#define rs o<<1|1
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long UL;
typedef unsigned int UI;
template <class T> inline void gmax(T &a,T b){if(b>a)a=b;}
template <class T> inline void gmin(T &a,T b){if(b<a)a=b;}
const int N=1e5+10,M=0,Z=1e9+7,ms63=1061109567;
int n,m;
int l,r;
int vv[N],v[N];
struct A
{int l,r,max;
}a[1<<18];
void build(int o,int l,int r)
{a[o].l=l;a[o].r=r;if(l==r){a[o].max=v[l];return;}int mid=(l+r)>>1;build(ls,l,mid);build(rs,mid+1,r);a[o].max=max(a[ls].max,a[rs].max);
}
int V;
int trylft(int o,int l,int r)
{if(a[o].max<V)return l;else if(a[o].l==a[o].r)return r+1;int mid=(a[o].l+a[o].r)>>1;if(a[o].l==l&&a[o].r==r){if(a[rs].max<V)return trylft(ls,l,mid);else return trylft(rs,mid+1,r);}if(r<=mid)return trylft(ls,l,r);else if(l>mid)return trylft(rs,l,r);else{int pos=trylft(rs,mid+1,r);if(pos>mid+1)return pos;else return trylft(ls,l,mid);}
}
int tryrgt(int o,int l,int r)
{if(a[o].max<=V)return r;else if(a[o].l==a[o].r)return l-1;int mid=(a[o].l+a[o].r)>>1;if(a[o].l==l&&a[o].r==r){if(a[ls].max<=V)return tryrgt(rs,mid+1,r);else return tryrgt(ls,l,mid);}if(r<=mid)return tryrgt(ls,l,r);else if(l>mid)return tryrgt(rs,l,r);else{int pos=tryrgt(ls,l,mid);if(pos<mid)return pos;else return tryrgt(rs,mid+1,r);}
}
int main()
{while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)scanf("%d",&vv[i]);--n;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)v[i]=abs(vv[i+1]-vv[i]);build(1,1,n);for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);--r;LL ans=0;for(int j=l;j<=r;j++){V=v[j];LL lft=j;if(l<j)lft=trylft(1,l,j-1);LL rgt=j;if(r>j)rgt=tryrgt(1,j+1,r);ans+=(j+1-lft)*(rgt+1-j)*V;}printf("%lld\n",ans);}}return 0;
}
/*
【trick&&吐槽】
这道题我一开始时,用的是线段树,常数本来就大。
自己写的时候还没做什么优化,于是提交时就被卡掉了啊TwT。
而且这还是——我在比赛结束倒计时7s时过了第一组数据的代码,在倒计时5s点到提交的代码,在倒计时1s交上去的代码哇!
瞬间跑到第46组数据,瞬间喜极而泣。
然而下一瞬间就tle on test 77了 QwQ。为何这样捉弄我?!
估计自己的代码,AC时间最多也就是1.2s,伤心!优化之后变成850ms,就AC掉了>_<后来再经过离线预处理,时间可以降低到250ms(ST-RMQ)甚至是78ms(线段树)【题意】
给你一个长度为n(2<=n<=1e5)的数vv[],每个数的数值为[0,1e9]范围。
然后再给你m(1<=m<=100)个询问,对于每个询问,给你一个[l,r]的区间(1<=l<r<=n),
我们的问题是,对于这个区间的所有子区间(C(len,2)+C(len,1)个),所有去年L()值的和是多少。L(区间)所返回的结果是这样计算的,定理len为区间长度——
1,如果len<2,返回0;
2,如果len>=2,返回max{向上取整(abs(vv[i]-vv[j])/(j-i)),j>i}【类型】
线段树【分析】
如何简化问题?
首先,我们不考虑询问有m个,对于一个询问区间,要如何求解?
然后,我们不考虑这个询问区间内的所有子区间,只拿出一个子区间出来,要如何求解?
这里就发现要先研究max{向上取整(abs(vv[i]-vv[j])/(j-i)),j>i}了。
然而我们很容易就发现,max{向上取整(abs(vv[i]-vv[j])/(j-i)),j>i}一定是取自——
max{向上取整(abs(vv[i]-vv[j])/(j-i)),j==i+1}中。为什么呢?
我们用v[i]表示abs(vv[i+1]-v[i])/(i+1-i)=abs(vv[i+1]-v[i])
那比如对于abs(vv[i+k]-vv[i])/k,其实可以表示为(±v[i]±v[i+1]±...±vv[i+k-1])/k
也就是说,如果j和i的差值大于1,那么得到的abs(vv[i]-vv[j])/(j-i),最大也不过是若干个v的平均值。
所以,得证:
max{向上取整(abs(vv[i]-vv[j])/(j-i)),j>i}一定是取自——
max{向上取整(abs(vv[i]-vv[j])/(j-i)),j==i+1}中。这个结论有什么用呢?
我们可以只用v[]就求出关于子区间权值的答案。
于是,对于一个询问区间,我们就有一种思路啦。
我们枚举子区间权值,然后看多少个子区间拥有这个权值就好。具体如何实现呢?
就是我们在[l,r)范围,枚举每个v[],看看这个v[]向左向右做多能覆盖到哪里。
然后这个v[]对答案的贡献就是左区间个数*右区间个数*v[]。
假设对于一个v[]的贡献计算时间为w
这样,对于一个询问区间,时间复杂度就是O(len*w),总的时间复杂度是O(m*len*w),可达O(1e7w)
于是w就要求尽量在O(1)内完成,而O(log(n))的时间复杂度下TLE也就一点也不冤了。然而我还是O(log(n))的时间复杂度。
我的做法是通过线段树来求:
1,某个点向左第一个比它大的位点,(为了防止重复,这里其实是向左第一个大于等于它的位置)
2,这个点向右第一个比它大的位点。
然后计算贡献,然后就AC啦~~不过——我们还是要引入其他做法
比如说:ST+二分。
我们可以先用ST初始化所有区间最值,然后再对于一个询问区间每个点,向左向右二分走到最左和最右的位置。
这种做法常数小很多,然而算法比较固定,出错率和稳定性大大提升。
然后在这个时候,我们发现了每个点可以向左向右延展的量,可以先做全局初始化。大大提高效率。【时间复杂度&&优化】
O(m*len*log(n))*/【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)D】【ST-RMQ+二分】Lipshitz Sequence 若干区间询问所有子区间的答案和 250ms
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<algorithm>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
void fre(){freopen("c://test//input.in","r",stdin);freopen("c://test//output.out","w",stdout);}
#define MS(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MC(x,y) memcpy(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MP(x,y) make_pair(x,y)
#define ls o<<1
#define rs o<<1|1
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long UL;
typedef unsigned int UI;
template <class T> inline void gmax(T &a,T b){if(b>a)a=b;}
template <class T> inline void gmin(T &a,T b){if(b<a)a=b;}
const int N=1e5+10,M=0,Z=1e9+7,ms63=1061109567;
int n,m;
int l,r;
int vv[N],v[N],L[N],R[N];
int b[18];
int f[N][18];
void RMQinit()
{int L=log(n+0.5)/log(2.0);for(int j=0;j<=L;++j)b[j]=1<<j;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)f[i][0]=v[i];for(int j=1;j<=L;++j){int len=b[j-1]-1;for(int i=1;i+len<=n;++i){f[i][j]=max(f[i][j-1],f[i+b[j-1]][j-1]);}}
}
int RMQmax(int l,int r)
{int len=r-l+1;int k=log(len+0.5)/log(2.0);return max(f[l][k],f[r-b[k]+1][k]);
}
void init()
{int l,r;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){l=1;r=i;while(l<r){int m=(l+r)>>1;if(RMQmax(m,i-1)<v[i])r=m;else l=m+1;}L[i]=l;l=i,r=n;while(l<r){int m=(l+r+1)>>1;if(RMQmax(i+1,m)<=v[i])l=m;else r=m-1;}R[i]=l;}
}
int main()
{while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)scanf("%d",&vv[i]);--n;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)v[i]=abs(vv[i+1]-vv[i]);RMQinit();init();for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);--r;LL ans=0;for(int j=l;j<=r;++j)ans+=(LL)(j-max(L[j],l)+1)*(min(R[j],r)-j+1)*v[j];printf("%lld\n",ans);}}return 0;
}【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)D】【线段树 全局初始化】Lipshitz Sequence 若干区间询问所有子区间的答案和 78ms
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<algorithm>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
void fre(){freopen("c://test//input.in","r",stdin);freopen("c://test//output.out","w",stdout);}
#define MS(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MC(x,y) memcpy(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define MP(x,y) make_pair(x,y)
#define ls o<<1
#define rs o<<1|1
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long UL;
typedef unsigned int UI;
template <class T> inline void gmax(T &a,T b){if(b>a)a=b;}
template <class T> inline void gmin(T &a,T b){if(b<a)a=b;}
const int N=1e5+10,M=0,Z=1e9+7,ms63=1061109567;
int n,m;
int l,r;
int vv[N],v[N],L[N],R[N];
struct A
{int l,r,max;
}a[1<<18];
void build(int o,int l,int r)
{a[o].l=l;a[o].r=r;if(l==r){a[o].max=v[l];return;}int mid=(l+r)>>1;build(ls,l,mid);build(rs,mid+1,r);a[o].max=max(a[ls].max,a[rs].max);
}
int V;
int trylft(int o,int l,int r)
{if(a[o].max<V)return l;else if(a[o].l==a[o].r)return r+1;int mid=(a[o].l+a[o].r)>>1;if(a[o].l==l&&a[o].r==r){if(a[rs].max<V)return trylft(ls,l,mid);else return trylft(rs,mid+1,r);}if(r<=mid)return trylft(ls,l,r);else if(l>mid)return trylft(rs,l,r);else{int pos=trylft(rs,mid+1,r);if(pos>mid+1)return pos;else return trylft(ls,l,mid);}
}
int tryrgt(int o,int l,int r)
{if(a[o].max<=V)return r;else if(a[o].l==a[o].r)return l-1;int mid=(a[o].l+a[o].r)>>1;if(a[o].l==l&&a[o].r==r){if(a[ls].max<=V)return tryrgt(rs,mid+1,r);else return tryrgt(ls,l,mid);}if(r<=mid)return tryrgt(ls,l,r);else if(l>mid)return tryrgt(rs,l,r);else{int pos=tryrgt(ls,l,mid);if(pos<mid)return pos;else return tryrgt(rs,mid+1,r);}
}
void init()
{for(int j=1;j<=n;++j){V=v[j];if(j==1)L[j]=1;else L[j]=trylft(1,1,j-1);if(j==n)R[j]=n;else R[j]=tryrgt(1,j+1,n);}
}
int main()
{while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)scanf("%d",&vv[i]);--n;for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)v[i]=abs(vv[i+1]-vv[i]);build(1,1,n);init();for(int i=1;i<=m;++i){scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);--r;LL ans=0;for(int j=l;j<=r;++j)ans+=(LL)(j-max(L[j],l)+1)*(min(R[j],r)-j+1)*v[j];printf("%lld\n",ans);}}return 0;
}这篇关于【Codeforces Round 333 (Div 2)D】【线段树 or ST-RMQ 初始化78msAC】Lipshitz Sequence 若干区间询问所有子区间的答案和的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!
 is called Lipschitz continuous if there is a real constant
is called Lipschitz continuous if there is a real constant 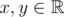 . We'll deal with a more... discrete version of this term.
. We'll deal with a more... discrete version of this term.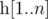 , we define it's Lipschitz constant
, we define it's Lipschitz constant 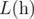 as follows:
as follows: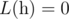
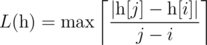 over all
over all 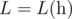 is the smallest non-negative integer such that
is the smallest non-negative integer such that  of size
of size 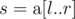 ; determine the sum of Lipschitz constants of
; determine the sum of Lipschitz constants of  .
.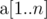 (
(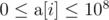 ).
).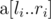 .
. with length at least
with length at least