本文主要是介绍Spark学习笔记(详解,附代码实列和图解)----------RDD(四)分区器,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
七.RDD分区器
Spark 目前支持 Hash 分区和 Range 分区,和用户自定义分区。Hash 分区为当前的默认分区。分区器直接决定了 RDD 中分区的个数、RDD 中每条数据经过 Shuffle 后进入哪个分区,进而决定了 Reduce 的个数。
➢ 只有 Key-Value 类型的 RDD 才有分区器,非 Key-Value 类型的 RDD 分区的值是 None
➢ 每个 RDD的分区 ID 范围:0 ~ (numPartitions - 1),决定这个值是属于那个分区的。
1.Hash 分区:(默认的分区就是HashPartition分区)
对于给定的 key,计算其 hashCode,并除以分区个数取余,并除以分区的个数取余,如果余数小于0,则用余数+分区的个数(否则加0),最后返回的值就是这个key所属的分区ID。
Rdd.partitionBy(new spark.HashPartitioner(2))//2为分区数
源码:
class HashPartitioner(partitions: Int) extends Partitioner {require(partitions >= 0, s"Number of partitions ($partitions) cannot be negative.")def numPartitions: Int = partitionsdef getPartition(key: Any): Int = key match {case null => 0//key为0则统统放入0号分区case _ => Utils.nonNegativeMod(key.hashCode, numPartitions)
//否则调用这个方法,根据key的hashcode和分区数,得到分区号}def nonNegativeMod(x: Int, mod: Int): Int = {val rawMod = x % modrawMod + (if (rawMod < 0) mod else 0)
}
2.Range 分区:
将一定范围内的数据映射到一个分区中,尽量保证每个分区数据均匀,而且分区间有序。但是分区内的元素是不能保证顺序的。
实现过程为:
第一步:先从整个RDD中抽取出样本数据,将样本数据排序,计算出每个分区的最大key值,形成一个Array[KEY]类型的数组变量rangeBounds;
第二步:判断key在rangeBounds中所处的范围,给出该key值在RDD中的分区id下标;该分区器要求RDD中的KEY类型必须是可以排序的
Rdd.partitionBy(new RangePartitioner(3,Rdd))//3为要分区的个数
3.自定义分区器
需要继承org.apache.spark.Partitioner类,实现如下:
def numPartitions:这个方法需要返回你想要创建分区的个数;
def getPartition:这个函数需要对输入的key做计算,然后返回该key的分区ID,范围一定是0到numPartitions-1;
equals():这个是Java标准的判断相等的函数,之所以要求用户实现这个函数是因为Spark内部会比较两个RDD的分区是否一样,默认equals已经去区分两个RDD了 可以不重写
class MySparkPartition(numParts: Int) extends Partitioner {override def numPartitions: Int = numParts/*** 可以自定义分区算法* @param key* @return*/override def getPartition(key: Any): Int = {val domain = new java.net.URL(key.toString).getHost()val code = (domain.hashCode % numPartitions)if (code < 0) {code + numPartitions} else {code}}override def equals(other: Any): Boolean = other match {case mypartition: MySparkPartition =>mypartition.numPartitions == numPartitionscase _ =>false}override def hashCode: Int = numPartitions}示例:
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{HashPartitioner, Partitioner, SparkConf, SparkContext}
object RDD_PART {def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val sparConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("WordCount").set("spark.testing.memory", "2147480000")val sc = new SparkContext(sparConf)val rdd = sc.makeRDD(List(("nba", "xxxxxxxxx"),("cba", "xxxxxxxxx"),("wnba", "xxxxxxxxx"),("nba", "xxxxxxxxx")), 2)val partRDD: RDD[(String, String)] = rdd.partitionBy(new MyPartitioner)partRDD.saveAsTextFile("output1")sc.stop()}/*** 自定义分区器* 1. 继承Partitioner* 2. 重写方法*/class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner {// 分区数量override def numPartitions: Int = 3// 根据数据的key值返回数据所在的分区索引(从0开始)override def getPartition(key: Any): Int = {key match {case "nba" => 0case "wnba" => 1case _ => 2}}}}
输出:
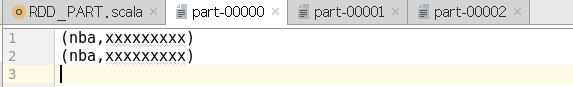
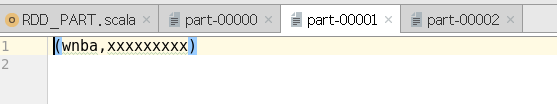
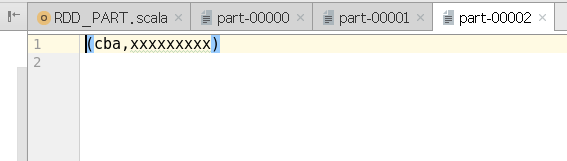
这篇关于Spark学习笔记(详解,附代码实列和图解)----------RDD(四)分区器的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






