本文主要是介绍企业级实战项目:基于 pycaret 自动化预测公司是否破产,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本文系数据挖掘实战系列文章,我跟大家分享一个数据挖掘实战,与以往的数据实战不同的是,用自动机器学习方法完成模型构建与调优部分工作,深入理解由此带来的便利与效果。
1. Introduction
本文是一篇数据挖掘实战案例,详细探索了从台湾经济杂志收集的1999年到2009年的数据,看看在数据探索过程中,可以洞察出哪些有用的信息,判断哪一个模型能够最准确地预测公司是否破产。
公司破产的定义是根据台湾证券交易所的商业规则而定的。
该建模将尝试使用自动机器学习库pycaret来构建机器学习模型,pycaret是一个用python编写的开源低代码机器学习库,它将机器学习工作流程自动化。如果你想探索这个库并更好地理解它的功能。推荐查看
设置环境并读取数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
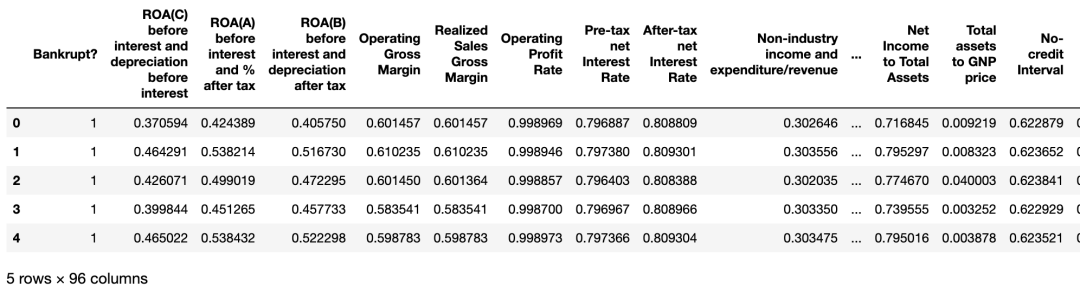
import seaborn as sns bankruptcy_df = pd.read_csv("Bankruptcy.csv") bankruptcy_df.head()
技术交流&源码获取
技术要学会交流、分享,不建议闭门造车。一个人可以走的很快、一堆人可以走的更远。
好的文章离不开粉丝的分享、推荐,资料干货、资料分享、数据、技术交流提升,均可加交流群获取,群友已超过2000人,添加时最好的备注方式为:来源+兴趣方向,方便找到志同道合的朋友。
本文数据&源码,技术交流、按照如下方式获取:
方式①、添加微信号:dkl88194,备注:资料
方式②、微信搜索公众号:Python学习与数据挖掘,后台回复:资料
资料1

资料2
我们打造了《100个超强算法模型》,特点:从0到1轻松学习,原理、代码、案例应有尽有,所有的算法模型都是按照这样的节奏进行表述,所以是一套完完整整的案例库。
很多初学者是有这么一个痛点,就是案例,案例的完整性直接影响同学的兴致。因此,我整理了 100个最常见的算法模型,在你的学习路上助推一把!

2. 理解数据
bankruptcy_df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 6819 entries, 0 to 6818
Data columns (total 96 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 Bankrupt? 6819 non-null int64 1 ROA(C) before interest and depreciation before interest 6819 non-null float64 2 ROA(A) before interest and % after tax 6819 non-null float64 3 ROA(B) before interest and depreciation after tax 6819 non-null float64 4 Operating Gross Margin 6819 non-null float64 5 Realized Sales Gross Margin 6819 non-null float64 6 Operating Profit Rate 6819 non-null float64 7 Pre-tax net Interest Rate 6819 non-null float64 8 After-tax net Interest Rate 6819 non-null float64 9 Non-industry income and expenditure/revenue 6819 non-null float64 10 Continuous interest rate (after tax) 6819 non-null float64 11 Operating Expense Rate 6819 non-null float64 12 Research and development expense rate 6819 non-null float64 13 Cash flow rate 6819 non-null float64 14 Interest-bearing debt interest rate 6819 non-null float64 15 Tax rate (A) 6819 non-null float64 16 Net Value Per Share (B) 6819 non-null float64 17 Net Value Per Share (A) 6819 non-null float64 18 Net Value Per Share (C) 6819 non-null float64 19 Persistent EPS in the Last Four Seasons 6819 non-null float64 20 Cash Flow Per Share 6819 non-null float64 21 Revenue Per Share (Yuan ¥) 6819 non-null float64 22 Operating Profit Per Share (Yuan ¥) 6819 non-null float64 23 Per Share Net profit before tax (Yuan ¥) 6819 non-null float64 24 Realized Sales Gross Profit Growth Rate 6819 non-null float64 25 Operating Profit Growth Rate 6819 non-null float64 26 After-tax Net Profit Growth Rate 6819 non-null float64 27 Regular Net Profit Growth Rate 6819 non-null float64 28 Continuous Net Profit Growth Rate 6819 non-null float64 29 Total Asset Growth Rate 6819 non-null float64 30 Net Value Growth Rate 6819 non-null float64 31 Total Asset Return Growth Rate Ratio 6819 non-null float64 32 Cash Reinvestment % 6819 non-null float64 33 Current Ratio 6819 non-null float64 34 Quick Ratio 6819 non-null float64 35 Interest Expense Ratio 6819 non-null float64 36 Total debt/Total net worth 6819 non-null float64 37 Debt ratio % 6819 non-null float64 38 Net worth/Assets 6819 non-null float64 39 Long-term fund suitability ratio (A) 6819 non-null float64 40 Borrowing dependency 6819 non-null float64 41 Contingent liabilities/Net worth 6819 non-null float64 42 Operating profit/Paid-in capital 6819 non-null float64 43 Net profit before tax/Paid-in capital 6819 non-null float64 44 Inventory and accounts receivable/Net value 6819 non-null float64 45 Total Asset Turnover 6819 non-null float64 46 Accounts Receivable Turnover 6819 non-null float64 47 Average Collection Days 6819 non-null float64 48 Inventory Turnover Rate (times) 6819 non-null float64 49 Fixed Assets Turnover Frequency 6819 non-null float64 50 Net Worth Turnover Rate (times) 6819 non-null float64 51 Revenue per person 6819 non-null float64 52 Operating profit per person 6819 non-null float64 53 Allocation rate per person 6819 non-null float64 54 Working Capital to Total Assets 6819 non-null float64 55 Quick Assets/Total Assets 6819 non-null float64 56 Current Assets/Total Assets 6819 non-null float64 57 Cash/Total Assets 6819 non-null float64 58 Quick Assets/Current Liability 6819 non-null float64 59 Cash/Current Liability 6819 non-null float64 60 Current Liability to Assets 6819 non-null float64 61 Operating Funds to Liability 6819 non-null float64 62 Inventory/Working Capital 6819 non-null float64 63 Inventory/Current Liability 6819 non-null float64 64 Current Liabilities/Liability 6819 non-null float64 65 Working Capital/Equity 6819 non-null float64 66 Current Liabilities/Equity 6819 non-null float64 67 Long-term Liability to Current Assets 6819 non-null float64 68 Retained Earnings to Total Assets 6819 non-null float64 69 Total income/Total expense 6819 non-null float64 70 Total expense/Assets 6819 non-null float64 71 Current Asset Turnover Rate 6819 non-null float64 72 Quick Asset Turnover Rate 6819 non-null float64 73 Working capitcal Turnover Rate 6819 non-null float64 74 Cash Turnover Rate 6819 non-null float64 75 Cash Flow to Sales 6819 non-null float64 76 Fixed Assets to Assets 6819 non-null float64 77 Current Liability to Liability 6819 non-null float64 78 Current Liability to Equity 6819 non-null float64 79 Equity to Long-term Liability 6819 non-null float64 80 Cash Flow to Total Assets 6819 non-null float64 81 Cash Flow to Liability 6819 non-null float64 82 CFO to Assets 6819 non-null float64 83 Cash Flow to Equity 6819 non-null float64 84 Current Liability to Current Assets 6819 non-null float64 85 Liability-Assets Flag 6819 non-null int64 86 Net Income to Total Assets 6819 non-null float64 87 Total assets to GNP price 6819 non-null float64 88 No-credit Interval 6819 non-null float64 89 Gross Profit to Sales 6819 non-null float64 90 Net Income to Stockholder's Equity 6819 non-null float64 91 Liability to Equity 6819 non-null float64 92 Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL) 6819 non-null float64 93 Interest Coverage Ratio (Interest expense to EBIT) 6819 non-null float64 94 Net Income Flag 6819 non-null int64 95 Equity to Liability 6819 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(93), int64(3)
memory usage: 5.0 MB
bankruptcy_df.shape
(6819, 96)
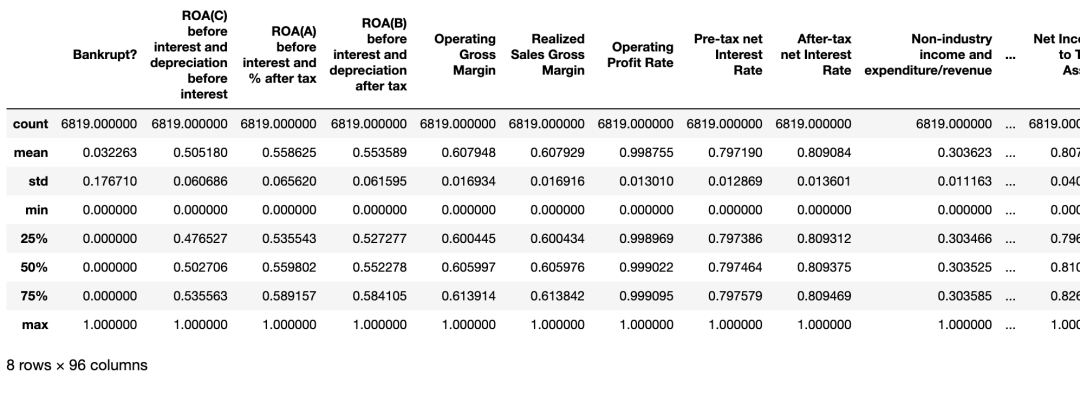
bankruptcy_df.describe()
3. 数据探索与清洗
3.1 缺失值处理
bankruptcy_df.columns[bankruptcy_df.isna().any()]
Index([], dtype='object')
从结果看,改数据集非常完整,没有缺失值!
.any()指的是有没有(缺失值),而与之对应的.all()指的是是否都是(缺失值)
调整数据列名
def clean_col_names(col_name): col_name = ( col_name.strip() .replace("?", "_") .replace("(", "_") .replace(")", "_") .replace(" ", "_") .replace("/", "_") .replace("-", "_") .replace("__", "_") .replace("'", "") .lower() ) return col_name bank_columns = list(bankruptcy_df.columns)
bank_columns = [clean_col_names(col_name) for col_name in bank_columns]
bankruptcy_df.columns = bank_columns
display(bankruptcy_df.columns)
Index(['bankrupt_', 'roa_c_before_interest_and_depreciation_before_interest', 'roa_a_before_interest_and_%_after_tax', 'roa_b_before_interest_and_depreciation_after_tax', 'operating_gross_margin', 'realized_sales_gross_margin', 'operating_profit_rate', 'pre_tax_net_interest_rate', 'after_tax_net_interest_rate', 'non_industry_income_and_expenditure_revenue', 'continuous_interest_rate_after_tax_', 'operating_expense_rate', 'research_and_development_expense_rate', 'cash_flow_rate', 'interest_bearing_debt_interest_rate', 'tax_rate_a_', 'net_value_per_share_b_', 'net_value_per_share_a_', 'net_value_per_share_c_', 'persistent_eps_in_the_last_four_seasons', 'cash_flow_per_share', 'revenue_per_share_yuan_¥_', 'operating_profit_per_share_yuan_¥_', 'per_share_net_profit_before_tax_yuan_¥_', 'realized_sales_gross_profit_growth_rate', 'operating_profit_growth_rate', 'after_tax_net_profit_growth_rate', 'regular_net_profit_growth_rate', 'continuous_net_profit_growth_rate', 'total_asset_growth_rate', 'net_value_growth_rate', 'total_asset_return_growth_rate_ratio', 'cash_reinvestment_%', 'current_ratio', 'quick_ratio', 'interest_expense_ratio', 'total_debt_total_net_worth', 'debt_ratio_%', 'net_worth_assets', 'long_term_fund_suitability_ratio_a_', 'borrowing_dependency', 'contingent_liabilities_net_worth', 'operating_profit_paid_in_capital', 'net_profit_before_tax_paid_in_capital', 'inventory_and_accounts_receivable_net_value', 'total_asset_turnover', 'accounts_receivable_turnover', 'average_collection_days', 'inventory_turnover_rate_times_', 'fixed_assets_turnover_frequency', 'net_worth_turnover_rate_times_', 'revenue_per_person', 'operating_profit_per_person', 'allocation_rate_per_person', 'working_capital_to_total_assets', 'quick_assets_total_assets', 'current_assets_total_assets', 'cash_total_assets', 'quick_assets_current_liability', 'cash_current_liability', 'current_liability_to_assets', 'operating_funds_to_liability', 'inventory_working_capital', 'inventory_current_liability', 'current_liabilities_liability', 'working_capital_equity', 'current_liabilities_equity', 'long_term_liability_to_current_assets', 'retained_earnings_to_total_assets', 'total_income_total_expense', 'total_expense_assets', 'current_asset_turnover_rate', 'quick_asset_turnover_rate', 'working_capitcal_turnover_rate', 'cash_turnover_rate', 'cash_flow_to_sales', 'fixed_assets_to_assets', 'current_liability_to_liability', 'current_liability_to_equity', 'equity_to_long_term_liability', 'cash_flow_to_total_assets', 'cash_flow_to_liability', 'cfo_to_assets', 'cash_flow_to_equity', 'current_liability_to_current_assets', 'liability_assets_flag', 'net_income_to_total_assets', 'total_assets_to_gnp_price', 'no_credit_interval', 'gross_profit_to_sales', 'net_income_to_stockholders_equity', 'liability_to_equity', 'degree_of_financial_leverage_dfl_', 'interest_coverage_ratio_interest_expense_to_ebit_', 'net_income_flag', 'equity_to_liability'], dtype='object')
统计并绘制目标变量
该步骤的目的是查看目标变量是否平衡,如果不平衡,则需要针对性处理。
class_bar=sns.countplot(data=bankruptcy_df,x="bankrupt_")
ax = plt.gca()
for p in ax.patches: ax.annotate('{:.1f}'.format(p.get_height()), (p.get_x()+0.3, p.get_height()+500))
class_bar
3.2 特征分布
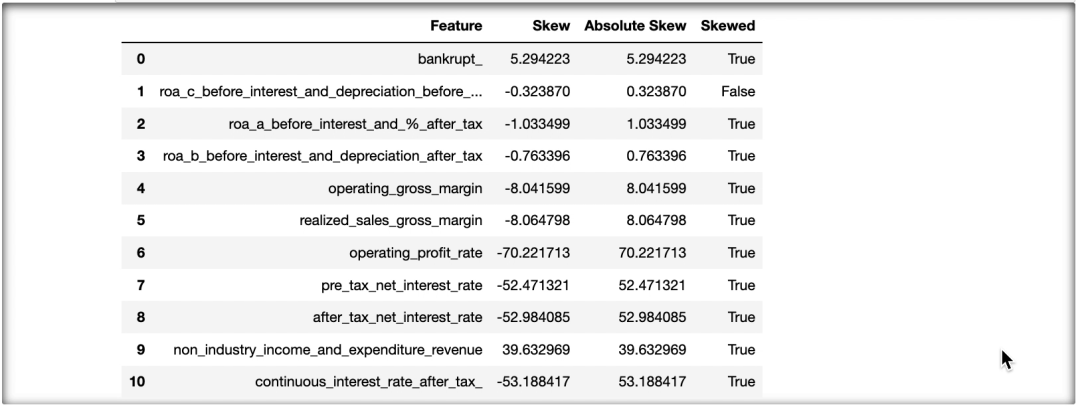
检查偏态
# Return true/false if skewed
import scipy.stats
skew_df = pd.DataFrame(bankruptcy_df.select_dtypes(np.number).columns, columns = ['Feature']) skew_df['Skew'] = skew_df['Feature'].apply(lambda feature: scipy.stats.skew(bankruptcy_df[feature])) skew_df['Absolute Skew'] = skew_df['Skew'].apply(abs)
# 得到与方向无关的倾斜幅度
skew_df['Skewed']= skew_df['Absolute Skew'].apply(lambda x: True if x>= 0.5 else False)
with pd.option_context("display.max_rows", 1000): display(skew_df)
可视化分布
cols = list(bankruptcy_df.columns)
ncols = 8
nrows = math.ceil(len(cols) / ncols) fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize = (4.5 * ncols, 4 * nrows))
for i in range(len(cols)): sns.kdeplot(bankruptcy_df[cols[i]], ax = ax[i // ncols, i % ncols]) if i % ncols != 0: ax[i // ncols, i % ncols].set_ylabel(" ")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
查看有偏态的特征
query_skew=skew_df.query("Skewed == True")["Feature"]
with pd.option_context("display.max_rows", 1000): display(query_skew)
0 bankrupt_
2 roa_a_before_interest_and_%_after_tax
3 roa_b_before_interest_and_depreciation_after_tax
4 operating_gross_margin
5 realized_sales_gross_margin
6 operating_profit_rate
7 pre_tax_net_interest_rate
8 after_tax_net_interest_rate
9 non_industry_income_and_expenditure_revenue
10 continuous_interest_rate_after_tax_
11 operating_expense_rate
12 research_and_development_expense_rate
13 cash_flow_rate
14 interest_bearing_debt_interest_rate
15 tax_rate_a_
16 net_value_per_share_b_
17 net_value_per_share_a_
18 net_value_per_share_c_
19 persistent_eps_in_the_last_four_seasons
20 cash_flow_per_share
21 revenue_per_share_yuan_¥_
22 operating_profit_per_share_yuan_¥_
23 per_share_net_profit_before_tax_yuan_¥_
24 realized_sales_gross_profit_growth_rate
25 operating_profit_growth_rate
26 after_tax_net_profit_growth_rate
27 regular_net_profit_growth_rate
28 continuous_net_profit_growth_rate
29 total_asset_growth_rate
30 net_value_growth_rate
31 total_asset_return_growth_rate_ratio
32 cash_reinvestment_%
33 current_ratio
34 quick_ratio
35 interest_expense_ratio
36 total_debt_total_net_worth
37 debt_ratio_%
38 net_worth_assets
39 long_term_fund_suitability_ratio_a_
40 borrowing_dependency
41 contingent_liabilities_net_worth
42 operating_profit_paid_in_capital
43 net_profit_before_tax_paid_in_capital
44 inventory_and_accounts_receivable_net_value
45 total_asset_turnover
46 accounts_receivable_turnover
47 average_collection_days
48 inventory_turnover_rate_times_
49 fixed_assets_turnover_frequency
50 net_worth_turnover_rate_times_
51 revenue_per_person
52 operating_profit_per_person
53 allocation_rate_per_person
57 cash_total_assets
58 quick_assets_current_liability
59 cash_current_liability
60 current_liability_to_assets
61 operating_funds_to_liability
62 inventory_working_capital
63 inventory_current_liability
64 current_liabilities_liability
65 working_capital_equity
66 current_liabilities_equity
67 long_term_liability_to_current_assets
68 retained_earnings_to_total_assets
69 total_income_total_expense
70 total_expense_assets
71 current_asset_turnover_rate
72 quick_asset_turnover_rate
73 working_capitcal_turnover_rate
74 cash_turnover_rate
75 cash_flow_to_sales
76 fixed_assets_to_assets
77 current_liability_to_liability
78 current_liability_to_equity
79 equity_to_long_term_liability
81 cash_flow_to_liability
83 cash_flow_to_equity
84 current_liability_to_current_assets
85 liability_assets_flag
86 net_income_to_total_assets
87 total_assets_to_gnp_price
88 no_credit_interval
89 gross_profit_to_sales
90 net_income_to_stockholders_equity
91 liability_to_equity
92 degree_of_financial_leverage_dfl_
93 interest_coverage_ratio_interest_expense_to_ebit_
95 equity_to_liability
Name: Feature, dtype: object
进行下采样,直至样本集中的破产与非破产比例为50/50。完成之后再次对数据进行偏态检查,决定是否需要做log转换,另外进行相关矩阵分析。
3.3 下采样
首先对数据集进行下采样,目标比例为bankrupt vs non bankrupt = 50 vs 50。
bankruptcy_df2 = bankruptcy_df.sample(frac=1) #Shuffle Bankruptcy df bankruptcy_df_b = bankruptcy_df2.loc[bankruptcy_df2["bankrupt_"] == 1]
bankruptcy_df_nb = bankruptcy_df2.loc[bankruptcy_df2["bankrupt_"] == 0][:220] bankruptcy_subdf_comb = pd.concat([bankruptcy_df_b,bankruptcy_df_nb])
bankruptcy_subdf = bankruptcy_subdf_comb.sample(frac=1,random_state=42) bankruptcy_subdf
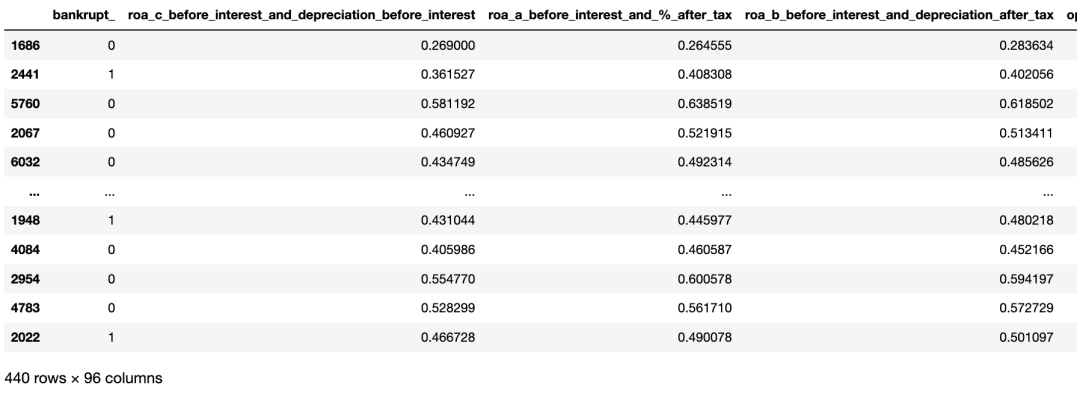
再次绘图查看正负样本数。
sns.countplot(bankruptcy_subdf["bankrupt_"])
随机选择220家非破产公司和220家破产公司。
4. 特征工程
bankruptcy_subdf2 = bankruptcy_subdf.drop(["net_income_flag"],axis=1)
bankruptcy_subdf2.shape (440, 95)
4.1 相关矩阵
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(30,20))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
sns.heatmap(bankruptcy_subdf2.corr(),ax=ax1,cmap="coolwarm")
4.1.1 找出与破产相关的最高特征
根据对破产企业的基本认识,破产企业资产少、负债高、盈利能力低、现金流少。可以朝这个方向分析我们的数据集。
corr=bankruptcy_subdf2[bankruptcy_subdf2.columns[:-1]].corr()['bankrupt_'][:] corr_df = pd.DataFrame(corr) print("Correlations to Bankruptcy:")
for index, row in corr_df["bankrupt_"].iteritems(): if row!=1.0 and row>=0.5: print(f'Positive Correlation: {index}') elif row!=1.0 and row<=-0.5: print(f'Negative Correlation: {index}')
Correlations to Bankruptcy:
Negative Correlation: roa_c_before_interest_and_depreciation_before_interest
Negative Correlation: roa_b_before_interest_and_depreciation_after_tax
Negative Correlation: net_value_per_share_b_
Negative Correlation: net_value_per_share_a_
Negative Correlation: net_value_per_share_c_
Negative Correlation: persistent_eps_in_the_last_four_seasons
Negative Correlation: per_share_net_profit_before_tax_yuan_¥_
Positive Correlation: debt_ratio_%
Negative Correlation: net_worth_assets
Negative Correlation: net_profit_before_tax_paid_in_capital
Negative Correlation: total_income_total_expense
这些特征代表什么
-
roa_c_before_interest_and_depreciation_before_interest息前资产收益率和息前折旧:总资产收益率–如果总资产收益率低,破产风险高
-
roa_a_before_interest_and_after_tax息前和税后利润:总资产回报率–如果总资产回报率较低,破产风险较高
-
roa_b_before_interest_and_depreciation_after_tax利润不计利息及税后折旧:总资产回报率–如果总资产回报率较低,破产风险较高
-
debt_ratio负债率:负债占总资产的比例–价值越高,负债占资产的比例越高,导致破产风险越高
-
net_worth_assets净资产:净资产越少,破产风险越高
-
retained_earnings_to_total_assets留存收益与总资产之比:留存收益越少,破产风险越高
-
total_income_total_expense总费用:收入与费用之比较低,破产风险较高
-
net_income_to_total_assets净收入与总资产之比:净收入越低,破产风险越高
从结果看,导致公司违约风险越高的特征,似乎与背景知识一致。
4.2 下采样后特征分布可视化
# Visualisation of distributions after sub-sampling
cols = list(bankruptcy_subdf2.columns)
ncols = 8
nrows = math.ceil(len(cols) / ncols) fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize = (4.5 * ncols, 4 * nrows))
for i in range(len(cols)): sns.kdeplot(bankruptcy_subdf2[cols[i]], ax = ax[i // ncols, i % ncols]) if i % ncols != 0: ax[i // ncols, i % ncols].set_ylabel(" ")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
4.3 所有特征的箱线图
plt.figure(figsize=(30,20))
boxplot=sns.boxplot(data=bankruptcy_subdf2,orient="h")
boxplot.set(xscale="log")
plt.show()
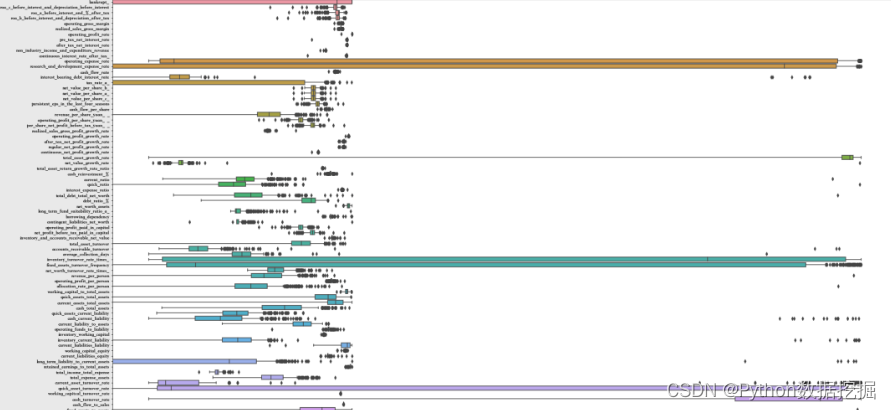
4.4 异常值处理
quartile1 = bankruptcy_subdf2.quantile(q=0.25,axis=0)
# display(quartile1)
quartile3 = bankruptcy_subdf2.quantile(q=0.75,axis=0)
# display(quartile3)
IQR = quartile3 -quartile1
lower_limit = quartile1-1.5*IQR
upper_limit = quartile3+1.5*IQR lower_limit = lower_limit.drop(["bankrupt_"])
upper_limit = upper_limit.drop(["bankrupt_"])
# print(lower_limit)
# print(" ")
# print(upper_limit) bankruptcy_subdf2_out = bankruptcy_subdf2[((bankruptcy_subdf2<lower_limit) | (bankruptcy_subdf2>upper_limit)).any(axis=1)]
display(bankruptcy_subdf2_out.shape)
display(bankruptcy_subdf2.shape)
(423, 95) (440, 95)
额外复制一份表,供后续分析处理。
bankruptcy_subdf3 = bankruptcy_subdf2_out.copy()
bankruptcy_subdf3
下采样后且去除离群值后的分布可视化。
# Visualisation of distributions after sub-sampling after outlier removal
cols = list(bankruptcy_subdf3.columns)
ncols = 8
nrows = math.ceil(len(cols) / ncols) fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize = (4.5 * ncols, 4 * nrows))
for i in range(len(cols)): sns.kdeplot(bankruptcy_subdf3[cols[i]], ax = ax[i // ncols, i % ncols],fill=True,color="red") sns.kdeplot(bankruptcy_subdf2[cols[i]], ax = ax[i // ncols, i % ncols],color="green") if i % ncols != 0: ax[i // ncols, i % ncols].set_ylabel(" ")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show() 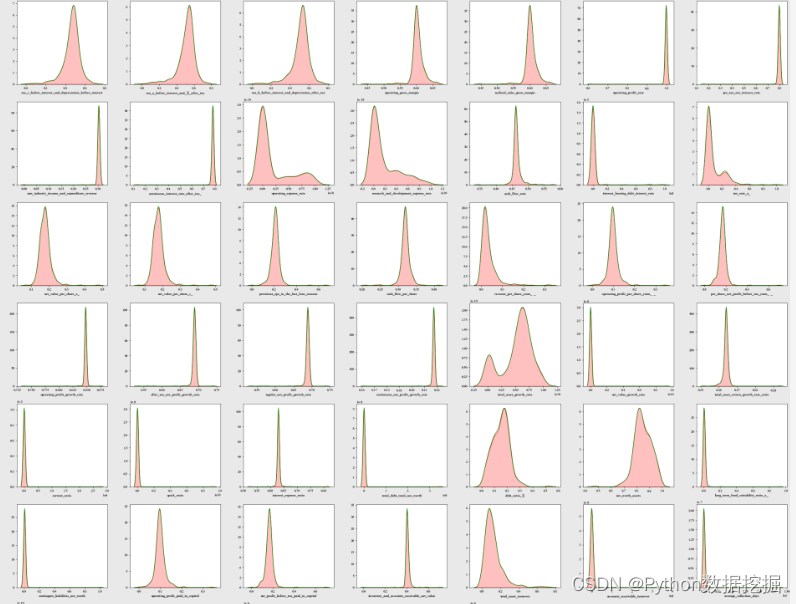
5 数据预处理
5.1 特征编码
所有类别在基础数据中都已编码完成,因此这里不需要再次编码列。在实际工作中,这一步大概率是必不可少的,编码技术也是尤其重要,需要好好掌握。如果你还不了解或不是很了解,推荐查看:
5.2 Log转换
这一步是为了去除数据中的偏态分布。
# Log transform to remove skews
target = bankruptcy_subdf3['bankrupt_']
bankruptcy_subdf4 = bankruptcy_subdf3.drop(["bankrupt_"],axis=1) def log_trans(data): for col in data: skew = data[col].skew() if skew>=0.5 or skew<=0.5: data[col] = np.log1p(data[col]) else: continue return data bankruptcy_subdf4_log = log_trans(bankruptcy_subdf4)
bankruptcy_subdf4_log.head()
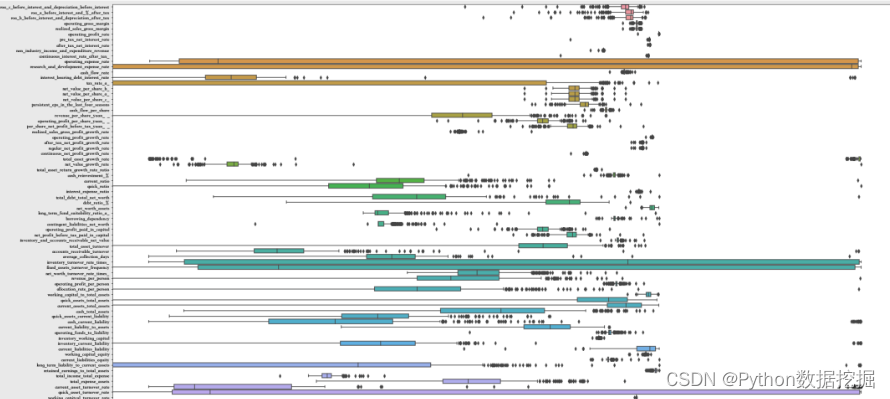
5.2.1 Log转换数据的箱线图
plt.figure(figsize=(30,20))
boxplot=sns.boxplot(data=bankruptcy_subdf4_log,orient="h")
boxplot.set(xscale="log")
plt.show()
5.2.2 Log转换后的数据分布可视化
# 在下采样后、去除离群值及log变换后的数据分布的可视化
compare_subdf2 = bankruptcy_subdf2.drop(["bankrupt_"],axis=1) cols = list(bankruptcy_subdf4.columns)
ncols = 8
nrows = math.ceil(len(cols) / ncols) fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize = (4.5 * ncols, 4 * nrows))
for i in range(len(cols)): sns.kdeplot(bankruptcy_subdf4_log[cols[i]], ax = ax[i // ncols, i % ncols],fill=True,color="red") sns.kdeplot(bankruptcy_subdf2[cols[i]], ax = ax[i // ncols, i % ncols],color="green") if i % ncols != 0: ax[i // ncols, i % ncols].set_ylabel(" ")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
print("Red represents distributions after log transforms, green represents before log transform")
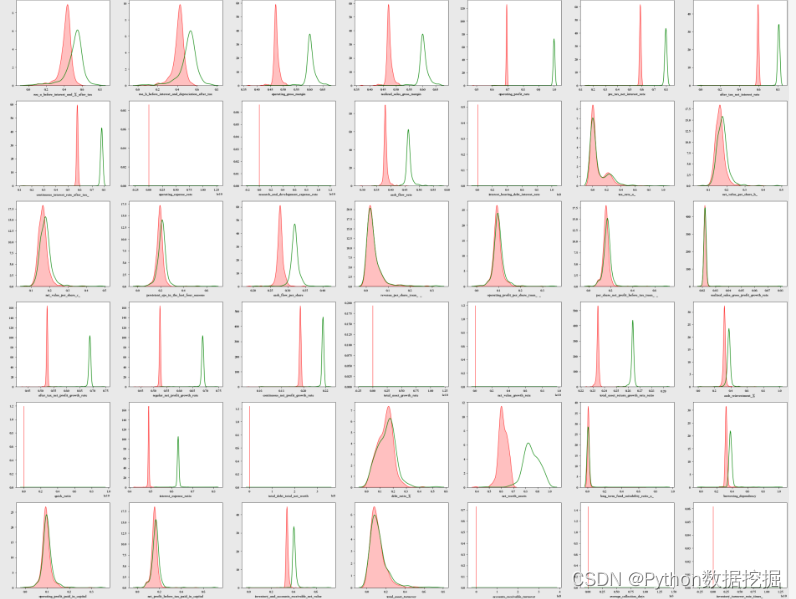
红色表示Log变换后的分布,绿色表示Log变换前的分布。(完整数据集:关注@公众号:数据STUDIO,联系云朵君获取)
6 使用Pycaret构建模型
本次模型构建使用的是自动机器学习框架pycaret,如果你还没有安装,可使用下述命令安装即可。
pip install -U --ignore-installed --pre pycaret

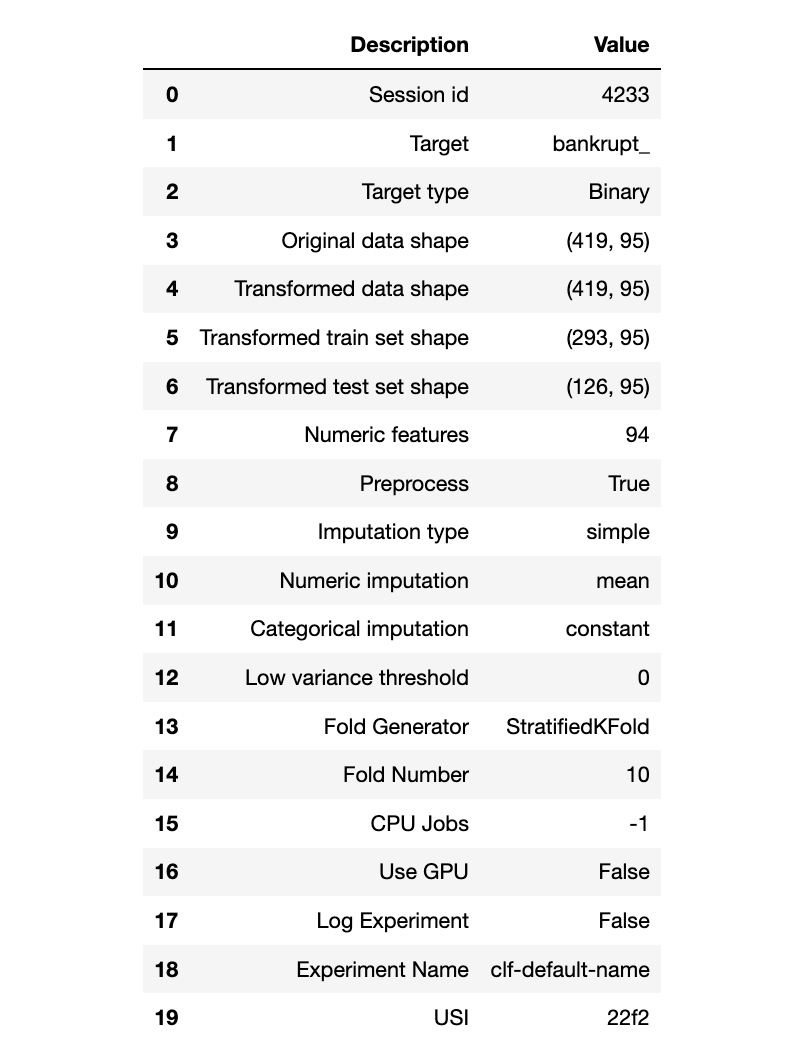
在pycaret中自动完成训练及测试数据的切分工作。
from pycaret.classification import *
exp_name = setup(data = bankruptcy_subdf4, target = bankruptcy_subdf3["bankrupt_"])
compare_models()
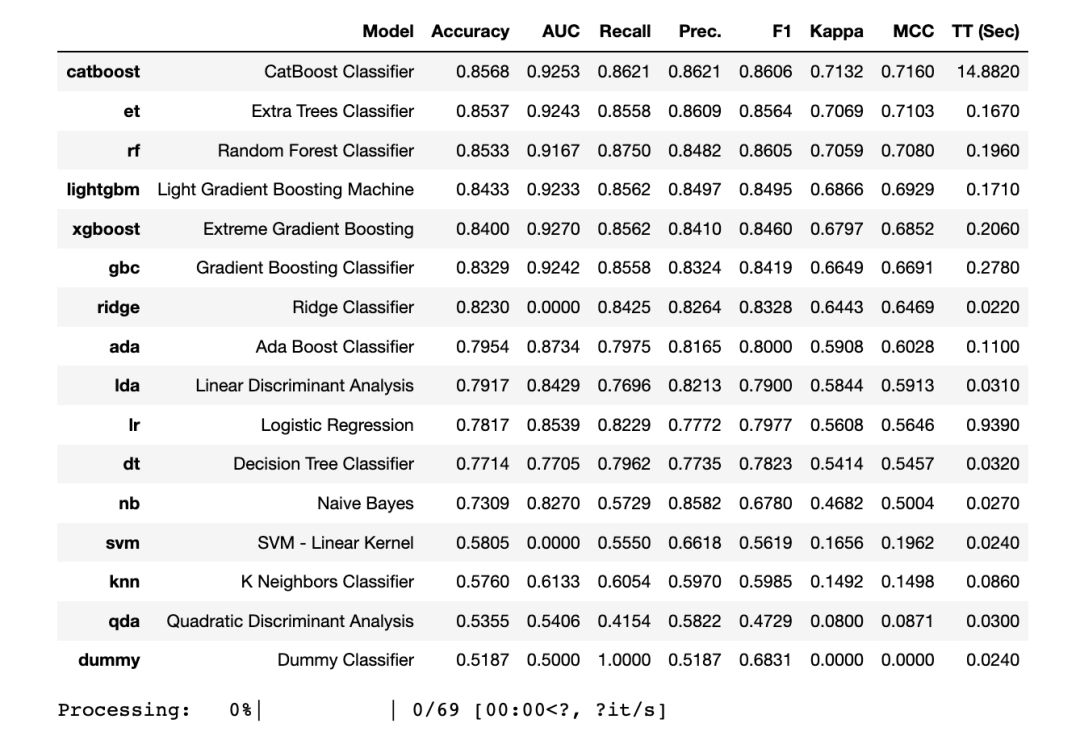
Pycaret显示,3种模型的准确性最高的是
-
LightGBM分类器
-
梯度提升GBC分类器
-
XGBoost分类器
接下来将使用这5个模型进行超参数调优。
6.1 选定模型交叉验证
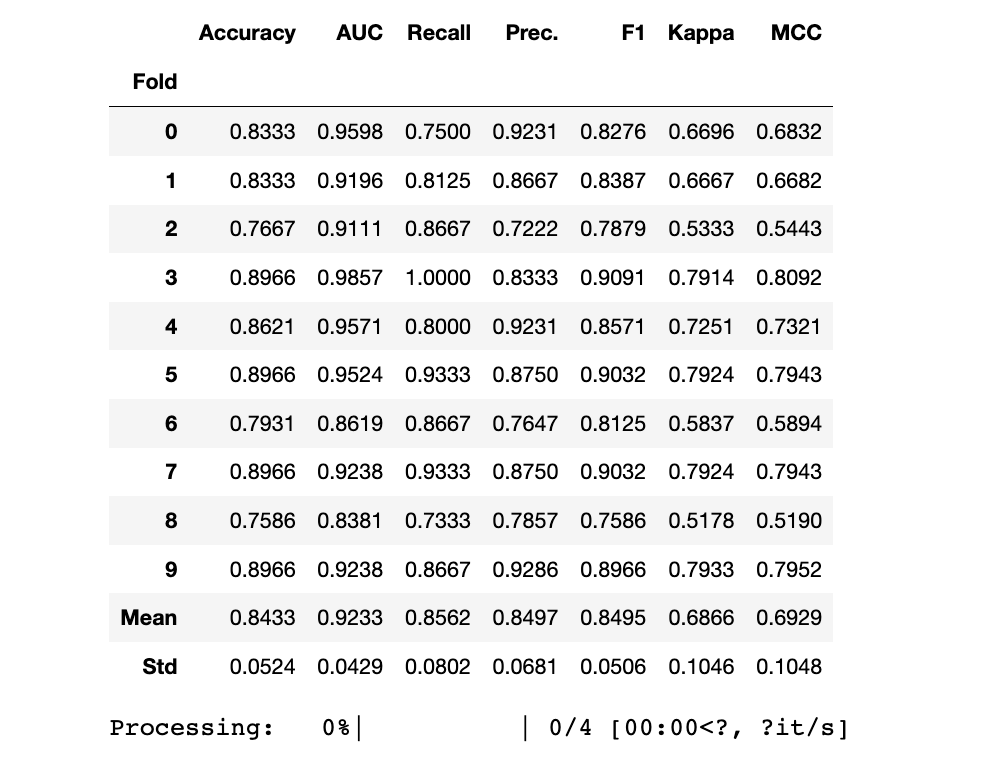
LightGBM
print("LGBM Model")
lgb_clf = create_model("lightgbm")
lgb_clf_scoregrid = pull()
LGBM Model
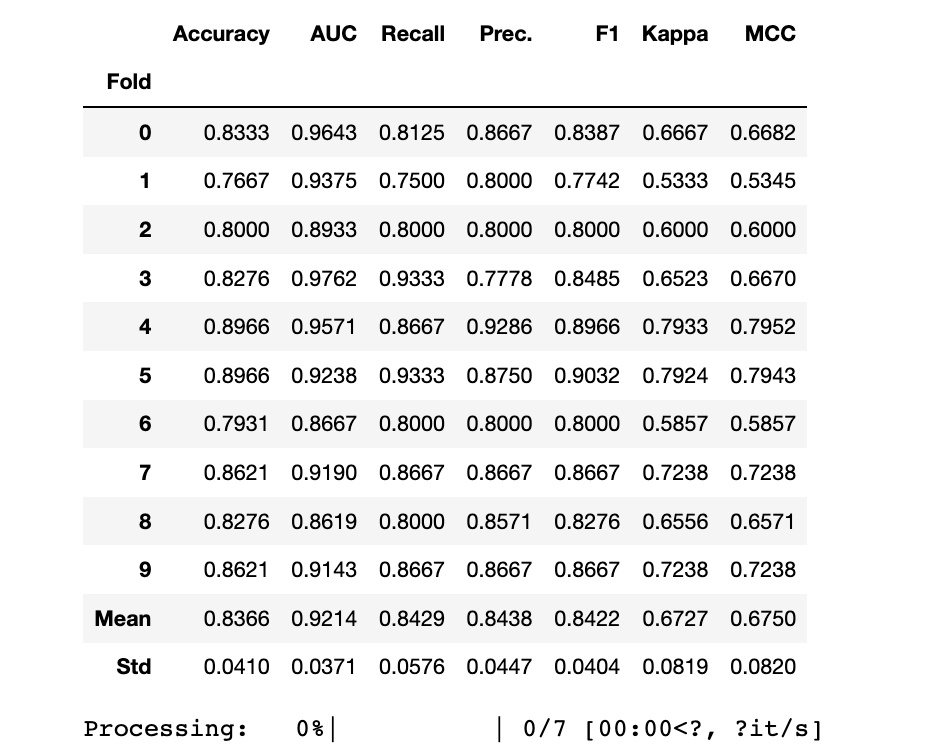
GBC
print("GBC Model")
gbc_clf = create_model("gbc")
gbc_clf_scoregrid = pull()
GBC Model
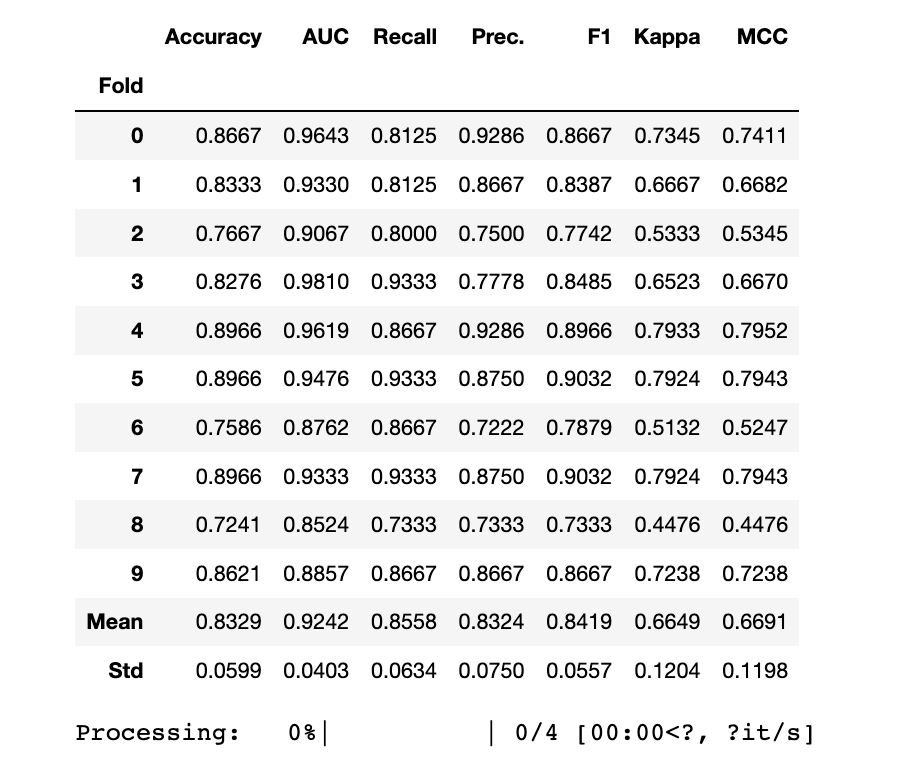
XGBoost
print("XGB Model")
xgb_clf = create_model("xgboost")
xgb_clf_scoregrid = pull()
XGB Model
7 使用Pycaret进行超参数调优
7.1 模型调优
LightGBM
print("Before Tuning")
print(lgb_clf_scoregrid.loc[["Mean","Std"]])
print("")
lgb_clf = tune_model(lgb_clf,choose_better=True)
print(lgb_clf)
Before Tuning Accuracy AUC Recall Prec. F1 Kappa MCC
Fold
Mean 0.8433 0.9233 0.8562 0.8497 0.8495 0.6866 0.6929
Std 0.0524 0.0429 0.0802 0.0681 0.0506 0.1046 0.1048
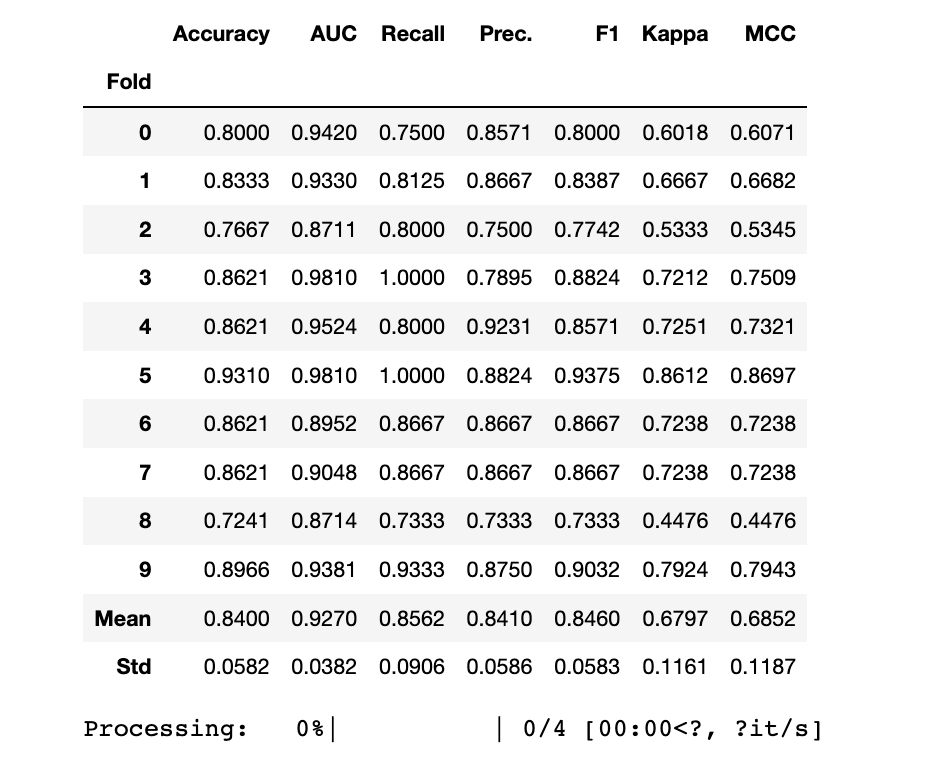
GBC
print("Before Tuning")
print(gbc_clf_scoregrid.loc[["Mean","Std"]])
print("")
gbc_clf = tune_model(gbc_clf,choose_better=True)
print(gbc_clf)
Before Tuning Accuracy AUC Recall Prec. F1 Kappa MCC
Fold
Mean 0.8329 0.9242 0.8558 0.8324 0.8419 0.6649 0.6691
Std 0.0599 0.0403 0.0634 0.0750 0.0557 0.1204 0.1198
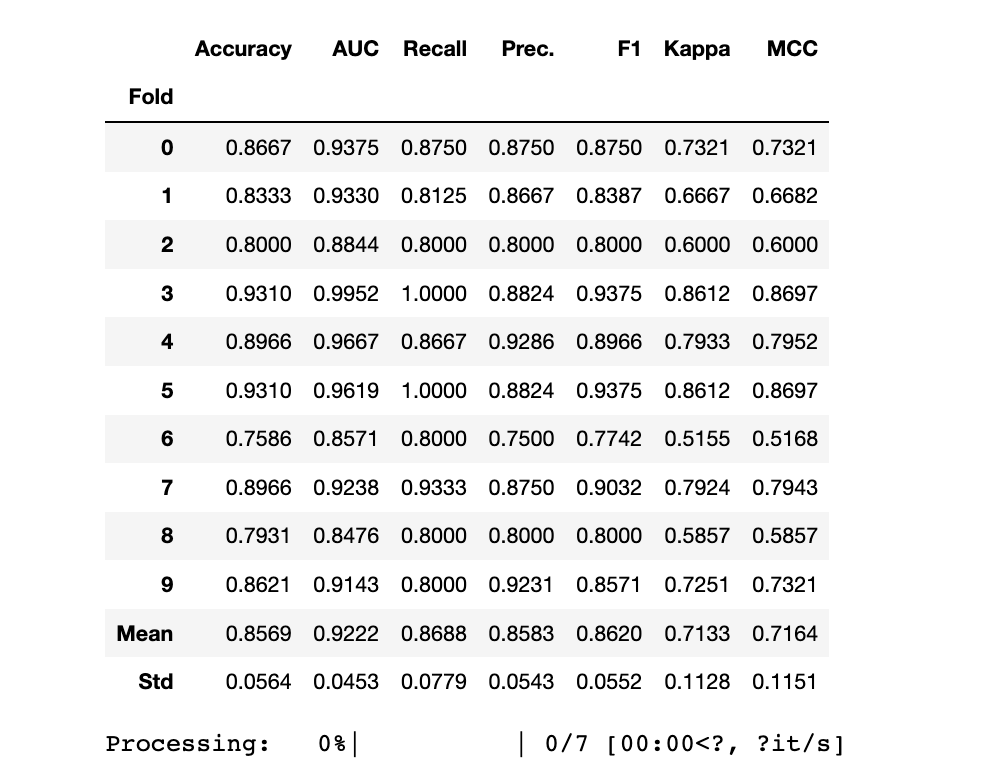
XGBoost
print("Before Tuning")
print(xgb_clf_scoregrid.loc[["Mean","Std"]])
print("")
xgb_clf = tune_model(xgb_clf,choose_better = True)
print(xgb_clf)
Before Tuning Accuracy AUC Recall Prec. F1 Kappa MCC
Fold
Mean 0.8400 0.9270 0.8562 0.8410 0.8460 0.6797 0.6852
Std 0.0582 0.0382 0.0906 0.0586 0.0583 0.1161 0.1187
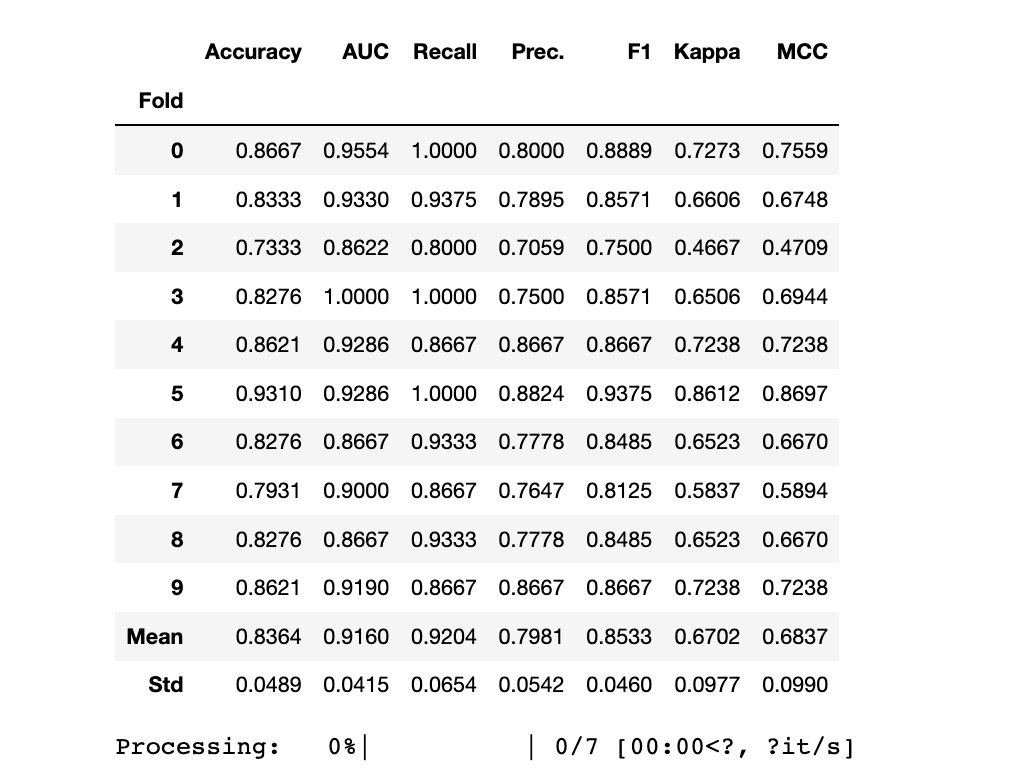
7.2 模型集成
-
Bagged & Boosting 方法
-
Blending
-
Stacking
LightGBM
# Original
print(lgb_clf_scoregrid.loc[['Mean', 'Std']]) # Compare the original against bagged and boosted # Bagged
lgb_clf = ensemble_model(lgb_clf,fold =5,choose_better = True)
# Boosted
lgb_clf = ensemble_model(lgb_clf,method="Boosting",choose_better = True)
Accuracy AUC Recall Prec. F1 Kappa MCC
Fold
Mean 0.8433 0.9233 0.8562 0.8497 0.8495 0.6866 0.6929
Std 0.0524 0.0429 0.0802 0.0681 0.0506 0.1046 0.1048
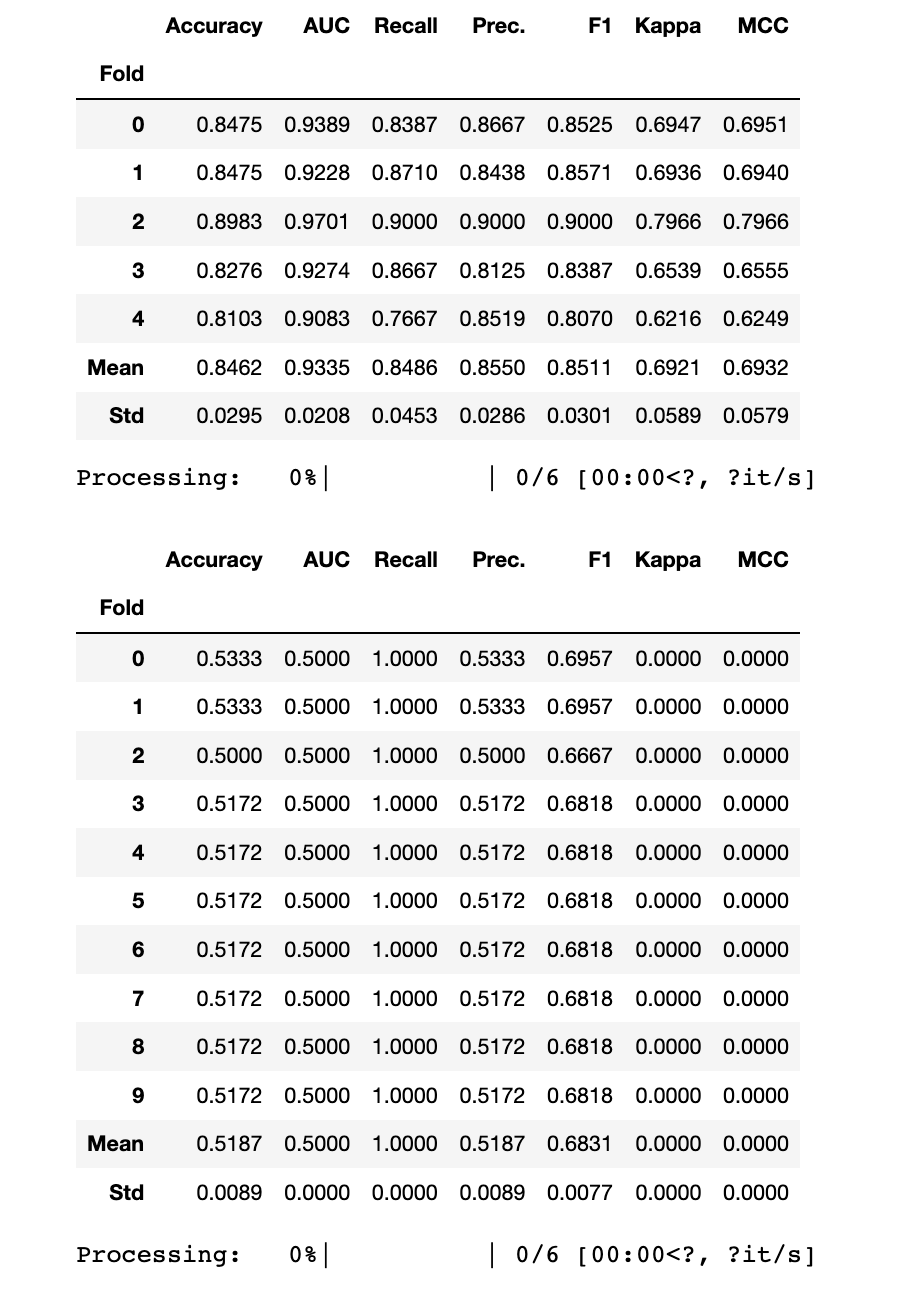
GBC
# Original
print(gbc_clf_scoregrid.loc[['Mean', 'Std']]) # Compare the original against bagged and boosted # Bagged
gbc_clf = ensemble_model(gbc_clf,fold =5,choose_better = True)
# Boosted
gbc_clf = ensemble_model(gbc_clf,method="Boosting",choose_better = True)
Accuracy AUC Recall Prec. F1 Kappa MCC
Fold
Mean 0.8329 0.9242 0.8558 0.8324 0.8419 0.6649 0.6691
Std 0.0599 0.0403 0.0634 0.0750 0.0557 0.1204 0.1198
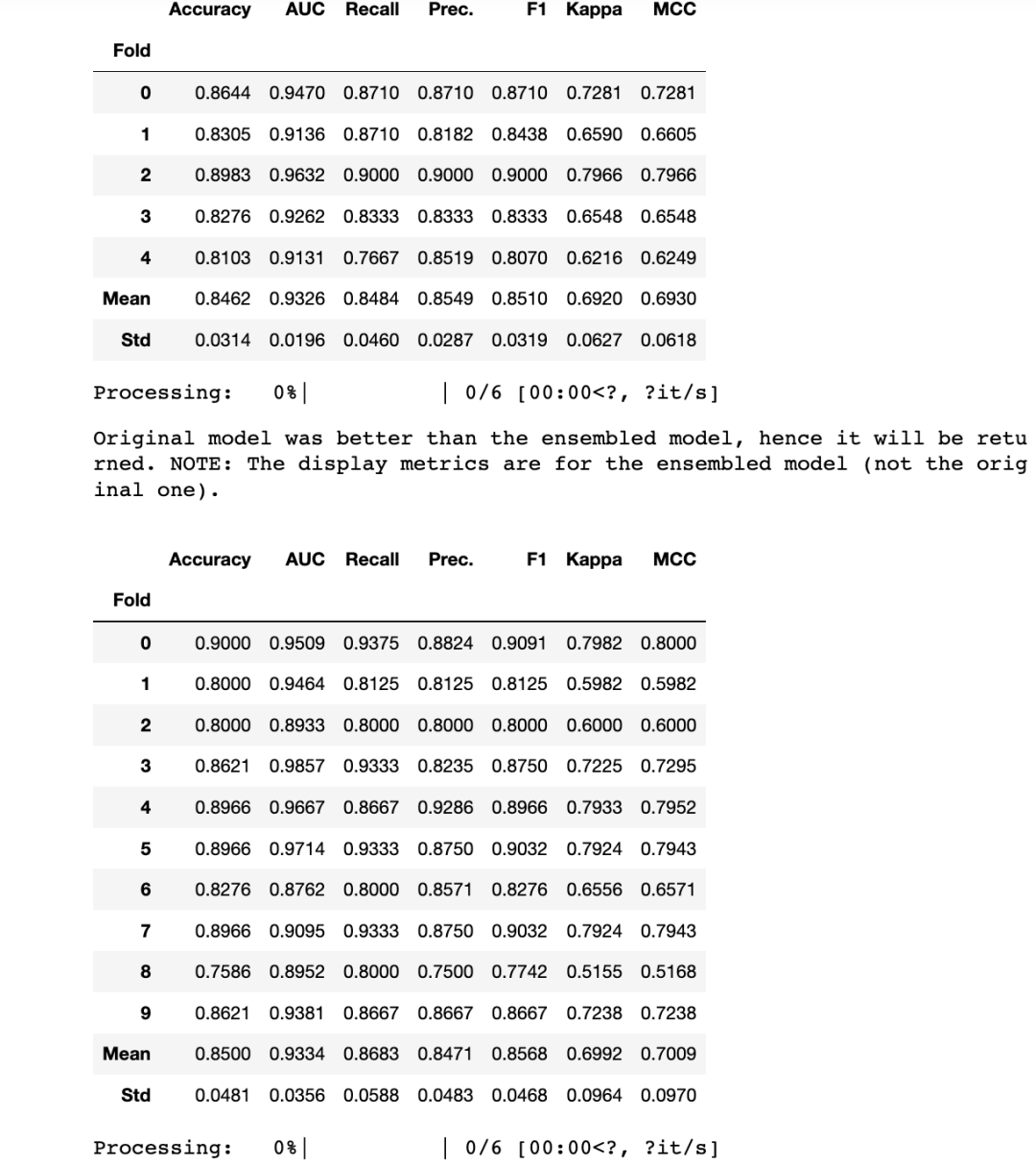
XGBoost
# Original
print(xgb_clf_scoregrid.loc[['Mean', 'Std']]) # Compare the original and boosted against bagged and boosted # Bagged
xgb_clf = ensemble_model(xgb_clf,fold =5,choose_better = True)
# Boosted
xgb_clf = ensemble_model(xgb_clf,method="Boosting",choose_better = True)
Accuracy AUC Recall Prec. F1 Kappa MCC
Fold
Mean 0.8400 0.9270 0.8562 0.8410 0.8460 0.6797 0.6852
Std 0.0582 0.0382 0.0906 0.0586 0.0583 0.1161 0.1187
7.3.1 Blend Models
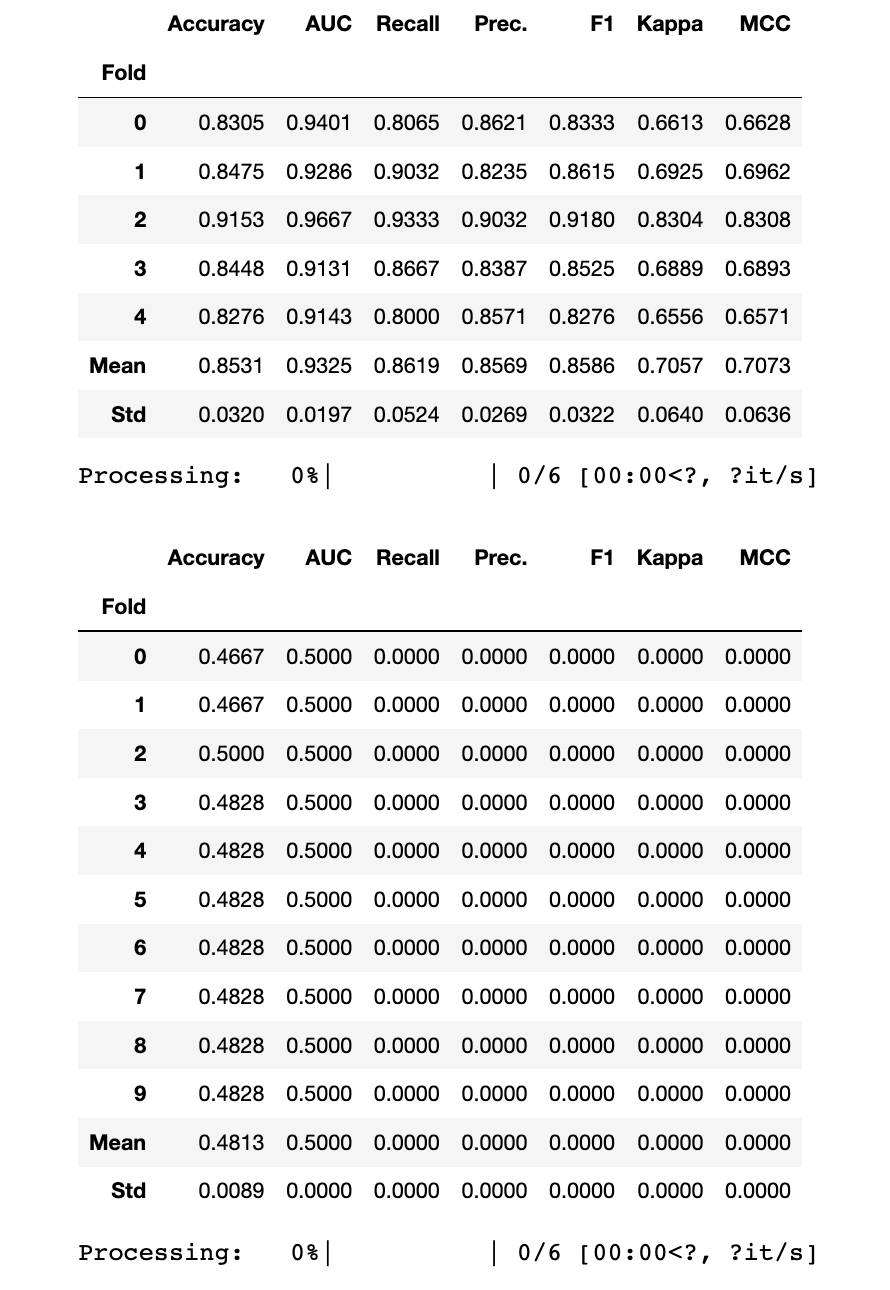
blend_models([lgb_clf, gbc_clf, xgb_clf],choose_better=True)
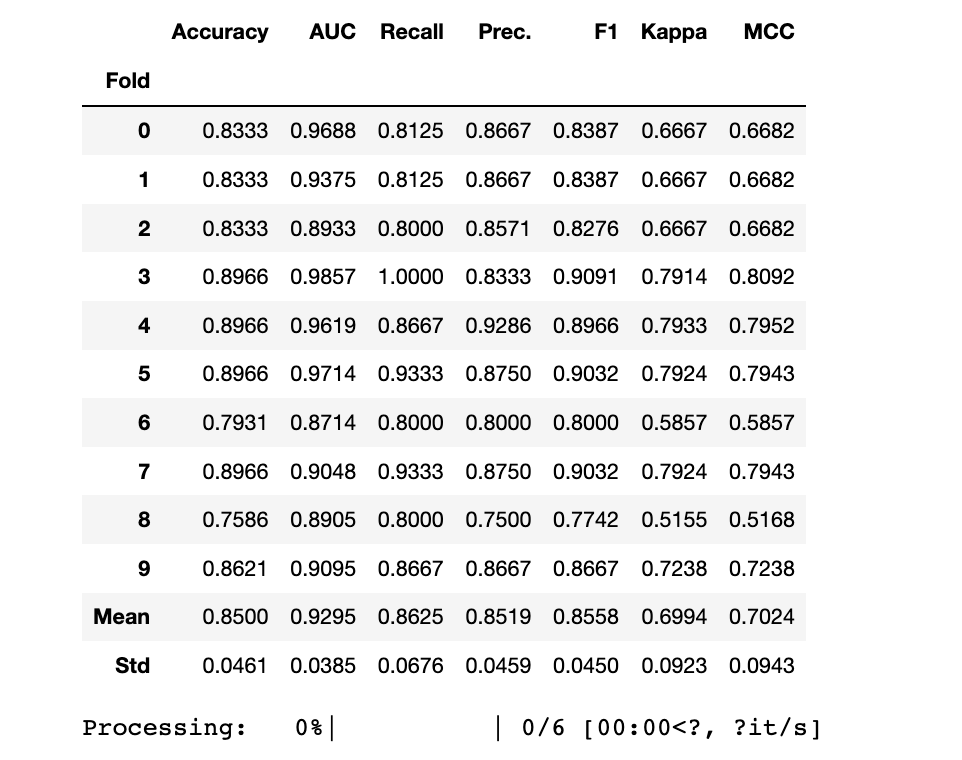
7.3.2 Stacking
stacker = stack_models(lgb_clf,gbc_clf) #remove xgb as some issues
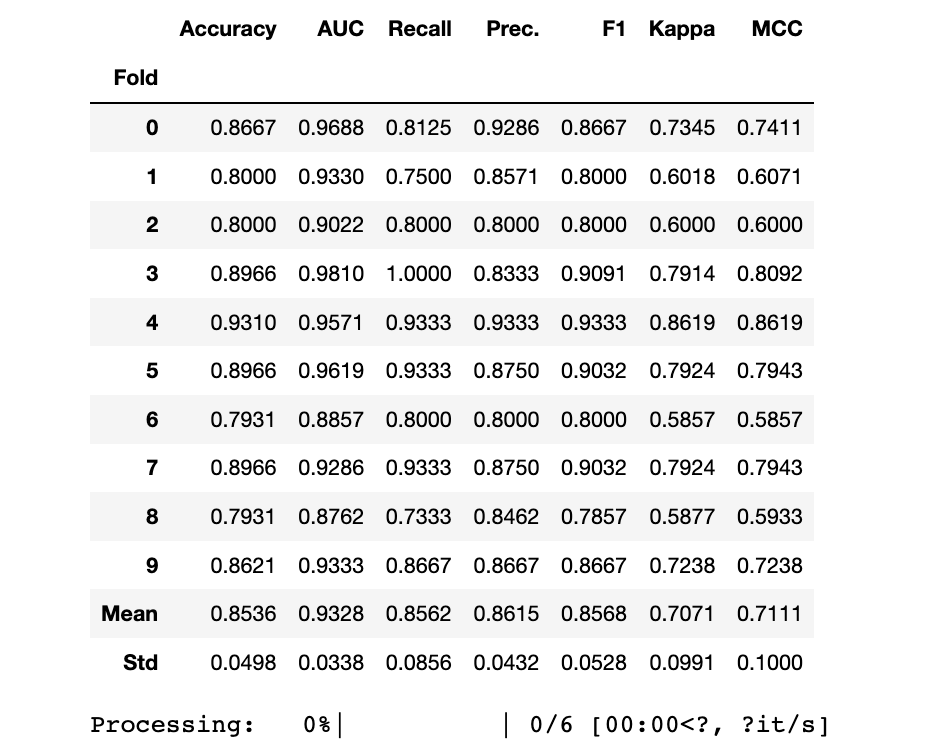
print(stacker)
8 模型评估
# evaluate_model(lgb_clf)
# evaluate_model(gbc_clf)
# evaluate_model(xgb_clf)
8.1 ROC-AUC
plot_model(stacker, plot = 'auc')
# Stacked classifier from ensembling
plot_model(lgb_clf, plot = 'auc')
# lgb最适合Bagging集成并被选中
plot_model(gbc_clf, plot = 'auc')
# gbc最适合Boosting集成并被选中
plot_model(xgb_clf, plot = 'auc')
# 基本的xgb分类器在经过调优和集成后仍然表现最好,因此选择了它 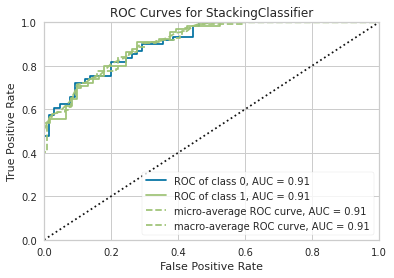
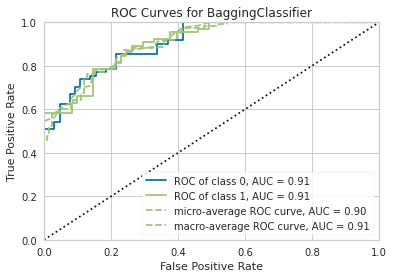
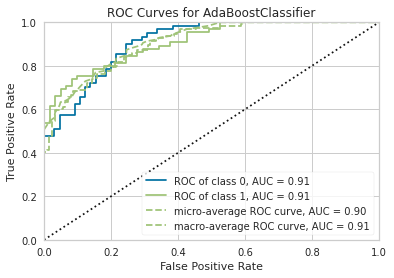
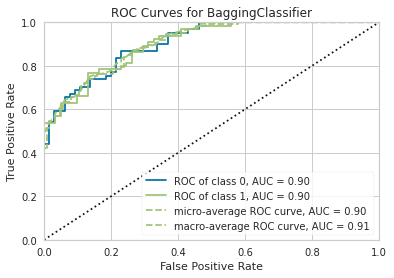
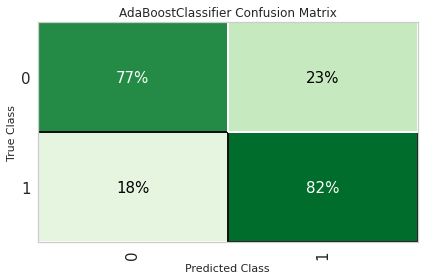
8.2 混淆矩阵
plot_model(stacker, plot = 'confusion_matrix', plot_kwargs = {'percent' : True})
plot_model(lgb_clf, plot = 'confusion_matrix', plot_kwargs = {'percent' : True})
plot_model(gbc_clf, plot = 'confusion_matrix', plot_kwargs = {'percent' : True})
plot_model(xgb_clf, plot = 'confusion_matrix', plot_kwargs = {'percent' : True}) 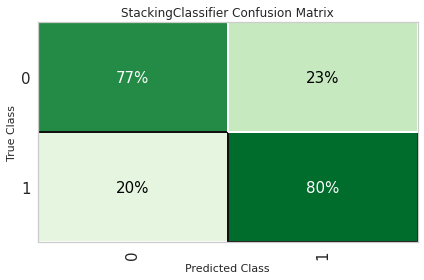
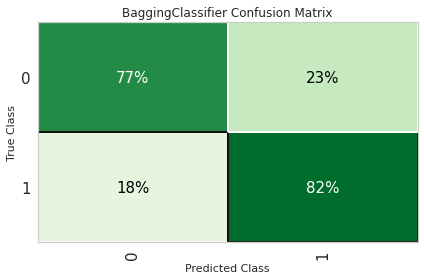

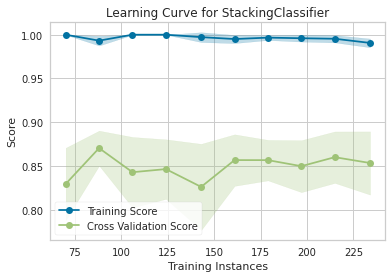
8.3 学习曲线
plot_model(stacker, plot = 'learning')
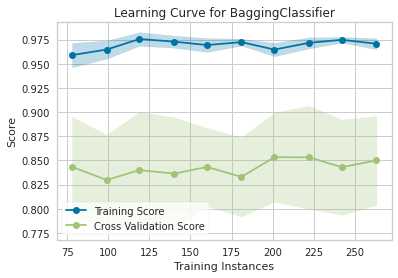
plot_model(lgb_clf, plot = 'learning')
就到这里了!
这篇关于企业级实战项目:基于 pycaret 自动化预测公司是否破产的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






