本文主要是介绍[Java] Java 并发包中并发原理剖析之ConcurrentLinkedQueue,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- [Java] Java 并发包中并发原理剖析之ConcurrentLinkedQueue
- 类图结构
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue 原理介绍
- 小结
- REFERENCES
- 更多
[Java] Java 并发包中并发原理剖析之ConcurrentLinkedQueue
ConcurrentLinkedQueue是线程安全的无界非阻塞队列,其底层数据结构使用单向链表实现,对于入队和出队操作使用CAS来实现线程安全。
手机用户请
横屏获取最佳阅读体验,REFERENCES中是本文参考的链接,如需要链接和更多资源,可以关注其他博客发布地址。
| 平台 | 地址 |
|---|---|
| CSDN | https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_28690417 |
| 简书 | https://www.jianshu.com/u/3032cc862300 |
| 个人博客 | https://yiyuery.club |
类图结构

ConcurrentLinkedQueue内部的队列使用单向链表方式实现,其中有两个volatile类型的Node节点分别用来存放队列的首、尾节点。从下面的无参构造函数可知,默认的头、尾节点都是指向item为null的哨兵节点。新元素会被插入队列末尾,出队时从队列头部获取一个元素。
/*** Creates a {@code ConcurrentLinkedQueue} that is initially empty.*/
public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() {head = tail = new Node<E>(null);
}
在Node节点内部维护一个使用volatile修饰的变量item,用来存放节点的值;next用来存放链表的下一个节点,从而链接为一个单向无界链表。其内部则使用UNSafe工具类提供的CAS算法来保证出入队时操作链表的原子性。
private static class Node<E> {volatile E item;volatile Node<E> next;/*** Constructs a new node. Uses relaxed write because item can* only be seen after publication via casNext.*/Node(E item) {UNSAFE.putObject(this, itemOffset, item);}boolean casItem(E cmp, E val) {return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, itemOffset, cmp, val);}void lazySetNext(Node<E> val) {UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this, nextOffset, val);}boolean casNext(Node<E> cmp, Node<E> val) {return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);}// Unsafe mechanicsprivate static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;private static final long itemOffset;private static final long nextOffset;static {try {UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();Class<?> k = Node.class;itemOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("item"));nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("next"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new Error(e);}}
}
注意,像这个包中大多数的非阻塞算法一样,这个实现依赖于,在垃圾收集系统,没有ABA的可能性问题的事实。由于回收节点,因此没有必要使用“数指针”或在版本中使用“ non-GC”设置的相关技术。
基本保持不变的特性有:
- 假如正好有一个(最后一个)引用为空的节点next,在排队时使用CAS算法。最后一个节点可以在O(1)时间内从tail到达,但tail只是一个优化——它也总是可以在O(N)时间内从head到达。
- 队列中包含的元素是从head访问的非空节点。通过CAS将节点的引用指向null,自动的会将它从队列中移除。来自head的所有元素的可达性必须保持true,即使在导致head前进的并发修改的情况下也是如此。由于创建了一个迭代器,或者是一个丢失了时间片的poll()操作,一个离开队列的节点可能会无限期地继续使用。
一个基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列。此队列按照 FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素进行排序。队列的头部 是队列中时间最长的元素。队列的尾部 是队列中时间最短的元素。新的元素插入到队列的尾部,队列获取操作从队列头部获得元素。当多个线程共享访问一个公共 collection 时,ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是一个恰当的选择。此队列不允许使用 null 元素。
此实现采用了有效的“无等待 (wait-free)”算法,该算法基于 Maged M. Michael 和 Michael L. Scott 合著的 Simple, Fast, and Practical Non-Blocking and Blocking Concurrent Queue Algorithms 中描述的算法。适用于垃圾收集环境,支持内部节点删除(以支持删除(对象))。
需要小心的是,与大多数 collection 不同,size 方法不是 一个固定时间操作。由于这些队列的异步特性,确定当前元素的数量需要遍历这些元素。
此类及其迭代器实现了 Collection 和 Iterator 接口的所有可选 方法。
内存一致性效果:当存在其他并发 collection 时,将对象放入 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 之前的线程中的操作 happen-before 随后通过另一线程从 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 访问或移除该元素的操作。
此类是 Java Collections Framework 的成员。
方法摘要
| 返回值 | 方法 |
|---|---|
boolean | add(E e) 将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。 |
boolean | contains(Object o) 如果此队列包含指定元素,则返回 true。 |
boolean | isEmpty() 如果此队列不包含任何元素,则返回 true。 |
Iterator<E> | iterator() 返回在此队列元素上以恰当顺序进行迭代的迭代器。 |
boolean | offer(E e) 将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。 |
E | peek() 获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null。 |
E | poll() 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。 |
boolean | remove(Object o) 从队列中移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)。 |
int | size() 返回此队列中的元素数量。 |
Object[] | toArray() 返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组。 |
<T> T[] | toArray(T[] a) 返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。 |
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 原理介绍
offer
/*** Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue.* As the queue is unbounded, this method will never return {@code false}.** @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null*/public boolean offer(E e) {//[1]抛出空指针异常checkNotNull(e);//[2]构造Node节点,在构造函数内部调用unsafe.putObjectfinal Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);//[3]从尾节点进行插入for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {Node<E> q = p.next;//[4]如果q==null说明p是尾节点,则执行插入if (q == null) {// p is last node//[5]使用CAS设置p节点的next节点if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {// Successful CAS is the linearization point// for e to become an element of this queue,// and for newNode to become "live".//[6] CAS成功,则说明新增节点已经被放入链表,然后设置当前尾节点(包含head,第//1, 3 , 5 . . .个节点为尾节点)if (p != t) // hop two nodes at a timecasTail(t, newNode); // Failure is OK.return true;}// Lost CAS race to another thread; re-read next}else if (p == q)// We have fallen off list. If tail is unchanged, it// will also be off-list, in which case we need to// jump to head, from which all live nodes are always// reachable. Else the new tail is a better bet.//[7]多线程操作时,由于poll操作移除元素后可能会把head变为自引用,也就是head的next变//成了 head,所以这里需要重新找新的headp = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;else// Check for tail updates after two hops.//[8]寻找尾节点p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;}}
offer 操作时在队列末尾添加一个元素,如果该元素为null,则抛出NPE异常,否则由于ConcurrentLinkedQueue是无界队列,该方法一直会返回true。由于使用CAS无阻塞算法,因此该方法不会阻塞挂起调用的线程。
add
add操作是在链表末尾添加一个元素,其实在内部调用的还是offer操作。
/*** Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue.* As the queue is unbounded, this method will never throw* {@link IllegalStateException} or return {@code false}.** @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null*/
public boolean add(E e) {return offer(e);
}
poll
poll操作是在队列头部获取并移除一个元素,如果队列为空则返回null。
public E poll() {//[1]goto标记restartFromHead://[2]无限循环for (;;) {for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {//[3]保存当前节点值E item = p.item;//[4]当前节点有值则用CAS变为nullif (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) {// Successful CAS is the linearization point// for item to be removed from this queue.//[5]CAS成功则标记当前节点并从链表中删除if (p != h) // hop two nodes at a timeupdateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p);return item;}//[6]当前队列为空则返回nullelse if ((q = p.next) == null) {updateHead(h, p);return null;}//[7]如果当前节点被自引用了,则重新寻找新的队列头节点else if (p == q)continue restartFromHead;elsep = q;}}
}
peek
获取队列头部的一个元素(只获取不移除),如果队列为空则返回null。
public E peek() {//[1]restartFromHead:for (;;) {for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {//[2]E item = p.item;//[3]if (item != null || (q = p.next) == null) {updateHead(h, p);return item;}else if (p == q)continue restartFromHead;elsep = q;}}
}
peek与poll操作类似,不同之处在于代码[3]处少了castItem操作,其实这很正常,因为peek只是获取队列头元素,并不清空值。第一次调用peek操作的时候会删除哨兵节点,并让队列的head节点指向队列的第一个元素或是null。
size
计算当前队列元素的个数,在并发环境下不是很有用,因为CAS没有加锁,所以从调用size函数到返回结果期间有可能增删元素,导致统计的元素个数不精确。
/*** Returns the number of elements in this queue. If this queue* contains more than {@code Integer.MAX_VALUE} elements, returns* {@code Integer.MAX_VALUE}.** <p>Beware that, unlike in most collections, this method is* <em>NOT</em> a constant-time operation. Because of the* asynchronous nature of these queues, determining the current* number of elements requires an O(n) traversal.* Additionally, if elements are added or removed during execution* of this method, the returned result may be inaccurate. Thus,* this method is typically not very useful in concurrent* applications.** @return the number of elements in this queue*/
public int size() {int count = 0;for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p))if (p.item != null)// Collection.size() spec says to max outif (++count == Integer.MAX_VALUE)break;return count;
}/*** Returns the first live (non-deleted) node on list, or null if none.* This is yet another variant of poll/peek; here returning the* first node, not element. We could make peek() a wrapper around* first(), but that would cost an extra volatile read of item,* and the need to add a retry loop to deal with the possibility* of losing a race to a concurrent poll().*/
Node<E> first() {restartFromHead:for (;;) {for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {boolean hasItem = (p.item != null);if (hasItem || (q = p.next) == null) {updateHead(h, p);return hasItem ? p : null;}else if (p == q)continue restartFromHead;elsep = q;}}
}/**
* Returns the successor of p, or the head node if p.next has been
* linked to self, which will only be true if traversing with a
* stale pointer that is now off the list.
*/
final Node<E> succ(Node<E> p) {
Node<E> next = p.next;
return (p == next) ? head : next;
}
first获取第一个队列的元素(哨兵元素不算),没有则为null。
succ获取当前节点的next元素,如果是自引入节点则返回真正的头节点
remove
如果队列里面存在该元素则删除该元素,如果存在多个则删除第一个,并返回true,否则返回false。
/*** Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue,* if it is present. More formally, removes an element {@code e} such* that {@code o.equals(e)}, if this queue contains one or more such* elements.* Returns {@code true} if this queue contained the specified element* (or equivalently, if this queue changed as a result of the call).** @param o element to be removed from this queue, if present* @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {//[1]if (o != null) {Node<E> next, pred = null;for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; pred = p, p = next) {boolean removed = false;E item = p.item;//[2]相等则使用CAS设置为null,否则获取next节点,继续下一次循环查找是否有匹配其他元素//同时只有一个线程可以操作成功if (item != null) {if (!o.equals(item)) {next = succ(p);continue;}removed = p.casItem(item, null);}//[3]获取next节点next = succ(p);//[4]如果有前驱节点,并且next节点不为空则链接前驱节点到nextif (pred != null && next != null) // unlinkpred.casNext(p, next);if (removed)return true;}}return false;
}
contains
判断队列里面是否含有指定对象,由于是遍历整个队列,所以需要像size操作一样结果也不是那么精确,有可能调用该方法时元素还在队列里面,但是遍历过程中其他线程才把该元素删除了,那么就会返回false了。
/*** Returns {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element.* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this queue contains* at least one element {@code e} such that {@code o.equals(e)}.** @param o object to be checked for containment in this queue* @return {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {if (o == null) return false;for (Node<E> p = first(); p != null; p = succ(p)) {E item = p.item;if (item != null && o.equals(item))return true;}return false;
}
小结
-
ConcurrentLinkedQueue的底层使用单向链表数据结构来保存队列元素,每个元素被包装成一个 Node 节点。队列是靠头、尾节点来维护的,创建队列时头、尾节点指向-个 item 为 null 的哨兵节点。第一次执行 peek 或者first 操作时会把 head 指向第一个真正的队 列元素。由于使用非阻塞 CAS 算法,没有加锁,所以在计算 size 时有可能进行了 offer 、poll 或者 remove 操作 , 导致计算的元素个数不精确,所以在井发情况下 size 函数不是很 有用。 -
入队、出队都是操作使用 volatile 修饰的 tail 、 head 节点,要保证在多线程下出入队线程安全,只需要保证这两个 Node 操作的可见性和原子性即可。由于 volatile 本身可以保证可见性,所以只需要保证对两个变量操作的原子性即可。
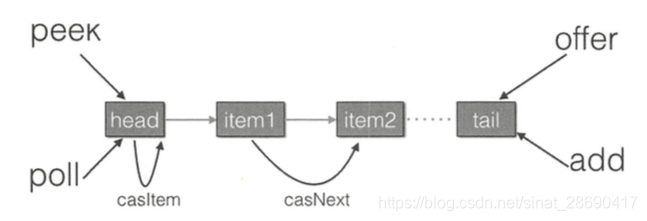
- offer 操作是在 tail 后面添加元素,也就是调用 tail.casNext 方法,而这个方法使用的是CAS 操作,只有一个线程会成功,然后失败的线程会循环,重新获取 tail , 再执行 casNext 方法。 poll 操作也通过类似 CAS 的算法保证出队时移除节点操作的原子性。
REFERENCES
- Java并发编程之美
- JDK-API-DOCS
更多
扫码关注“架构探险之道”,获取更多源码和文章资源
知识星球(扫码加入获取源码和文章资源链接)
这篇关于[Java] Java 并发包中并发原理剖析之ConcurrentLinkedQueue的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



