本文主要是介绍gem5 garnet l1 l2 cache的创建与相连,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
gem5 garnet l1 l2 cache的创建与相连
主要就是这个图:
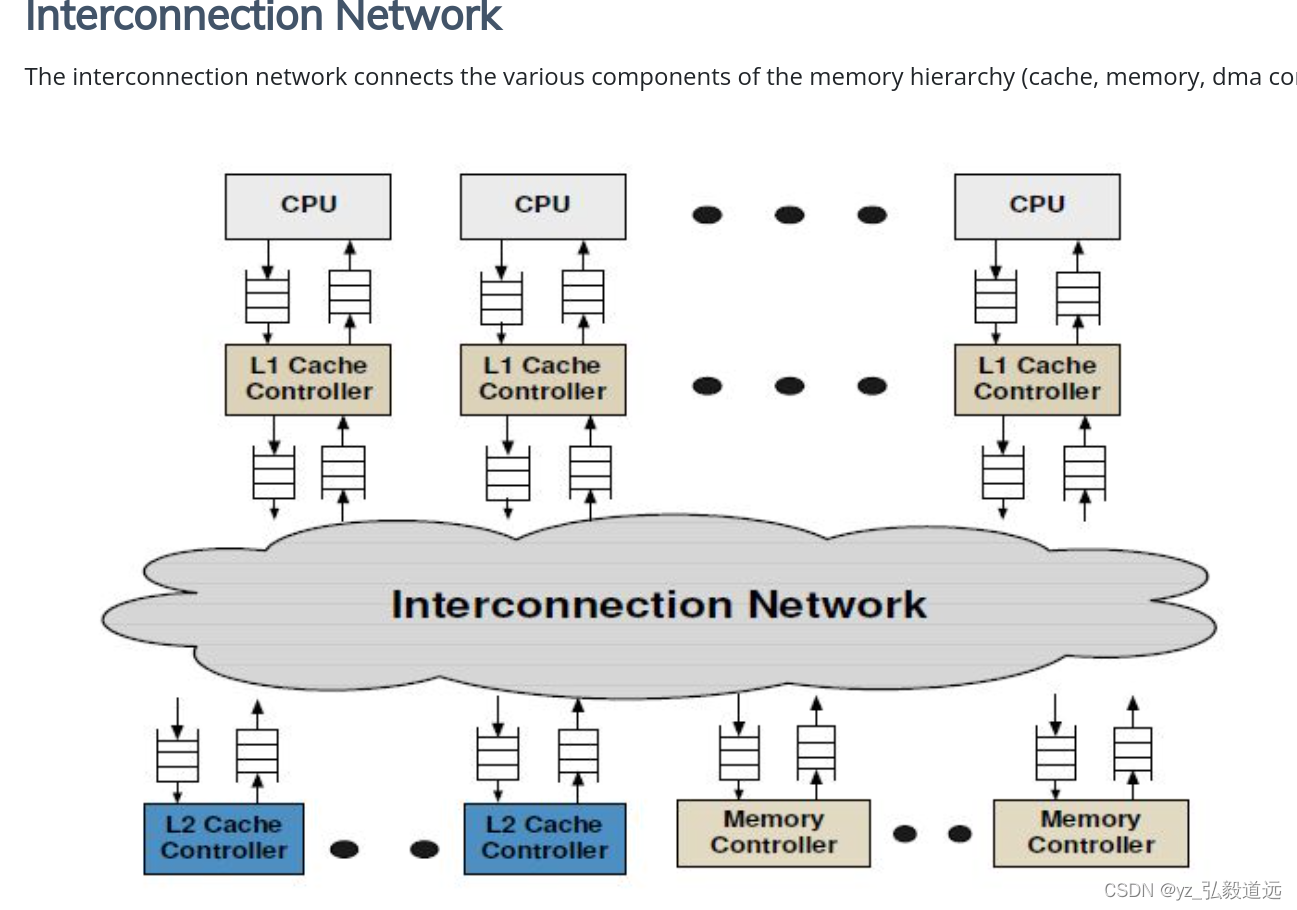
细节
我们用的是gem5/configs/deprecated/example/fs.py
#fs.py 引入了上两层路径,也就是当前可以看到 gem5/configs/路径。
addToPath("../../")
#fs.py引入了gem5/configs/ruby/Ruby.py
from ruby import Ruby
#fs.py 使用了gem5/configs/ruby/Ruby.py 中的 create_system
Ruby.create_system(args, True, test_sys, test_sys.iobus, test_sys._dma_ports, bootmem)
#fs.py 还使用了gem5/configs/ruby/Ruby.py 中的 Ruby.define_options(parser)
我们去看gem5/configs/ruby/Ruby.py 中的 create_system 和 define_options。
第1段代码关注于根据用户选择的协议创建和配置仿真系统。
第2段代码关注于定义用户可以通过命令行设置的仿真选项。
虽然两者都动态导入并利用了特定的协议模块,但它们各自处理的是仿真配置的不同方面。
#1 gem5/configs/ruby/Ruby.py 中的 create_system 使用了 buildEnv
# buildEnv来自于 from m5.defines import buildEnv
...
protocol = buildEnv["PROTOCOL"]
exec(f"from . import {protocol}")
try:(cpu_sequencers, dir_cntrls, topology) = eval("%s.create_system(options, full_system, system, dma_ports,\bootmem, ruby, cpus)"% protocol)
except:print(f"Error: could not create sytem for ruby protocol {protocol}")raise#2 gem5/configs/ruby/Ruby.py 中的 def define_options(parser): 使用了 buildEnv
...
protocol = buildEnv["PROTOCOL"]exec(f"from . import {protocol}")eval(f"{protocol}.define_options(parser)")Network.define_options(parser)
这时候我们看gem5/build/X86/python/m5/defines.py 中的buildEnv
# gem5/build/X86/python/m5/defines.py 中只有下面一行代码。 全是关于 buildEnv的。
buildEnv = {'USE_SYSTEMC': True, 'HAVE_FENV': True, 'HAVE_PNG': True, 'HAVE_POSIX_CLOCK': True, 'HAVE_VALGRIND': False, 'HAVE_DEPRECATED_NAMESPACE': 1, 'HAVE_HDF5': True, 'HAVE_TUNTAP': True, 'HAVE_PROTOBUF': True, 'KVM_ISA': 'x86', 'HAVE_KVM': True, 'HAVE_PERF_ATTR_EXCLUDE_HOST': 1, 'EXTRAS': '', 'BATCH': False, 'BATCH_CMD': 'qdo', 'M5_BUILD_CACHE': False, 'USE_EFENCE': False, 'BUILD_GPU': False, 'USE_POSIX_CLOCK': True, 'NUMBER_BITS_PER_SET': '128', 'SLICC_HTML': False, 'USE_NULL_ISA': False, 'USE_X86_ISA': True, 'USE_RISCV_ISA': False, 'USE_POWER_ISA': False, 'USE_SPARC_ISA': False, 'USE_ARM_ISA': False, 'USE_ARM_FASTMODEL': False, 'PVLIB_HOME': '', 'PVLIB_FLAVOR': 'Linux64_GCC-7.3', 'MAXCORE_HOME': '', 'ARMLMD_LICENSE_FILE': '', 'ARMLMD_LICENSE_COUNT': 1, 'SIMGEN': '${MAXCORE_HOME}/bin/simgen', 'USE_MIPS_ISA': False, 'PROTOCOL': 'MESI_Two_Level', 'USE_KVM': True, 'TARGET_GPU_ISA': 'gcn3'}
fs.py 中create_system创立的l1 l2 们 但是先不相连
fs.py中创建了system,其中包括了l1 l2 , 主要是create system创建了硬件。 具体的是fs.py使用Ruby.create_system,然后 调用了MESI_Two_Level.create_system。
eval是Python的一个内置函数,功能十分强大,这个函数的作用是,返回传入字符串的表达式的结果。就是说:将字符串当成有效的表达式 来求值 并 返回计算结果。
fs.py中怎么创建硬件系统的?
# 直接调用 fs.py 中 build_test_system
test_sys = build_test_system(np)#build_test_system中 先定义一个初步的test_sys
test_sys = makeLinuxX86System(test_mem_mode, np, bm[0], args.ruby, cmdline=cmdline)
#因为有ruby,额外操作 test_sysRuby.create_system(args, True, test_sys, test_sys.iobus, test_sys._dma_ports, bootmem)
#Ruby.create_system 中 protocol = buildEnv["PROTOCOL"] = 'MESI_Two_Level' (因为'PROTOCOL': 'MESI_Two_Level', )
#eval函数执行这个字符串表达式,相当于调用了对应协议模块中的create_system函数。这个函数负责根据给定的参数创建并配置仿真系统的组件。
#"%s.create_system(options, full_system, system, dma_ports, bootmem, ruby, cpus)" % protocol这一行是一个格式化的字符串表达式,它将protocol变量的值插入到字符串中。假设protocol的值为"MESI_Two_Level",那么格式化后的字符串将是"MESI_Two_Level.create_system(options, full_system, system, dma_ports, bootmem, ruby, cpus)"。
try:(cpu_sequencers, dir_cntrls, topology) = eval("%s.create_system(options, full_system, system, dma_ports,\bootmem, ruby, cpus)"% protocol)
小结就是,其实Ruby.create_system 调用了MESI_Two_Level.create_system,其中 “MESI_Two_Level”会根据选定的协议不同而变化。
MESI_Two_Level.create_system
gem5/configs/ruby/MESI_Two_Level.py
#遍历每一个cpu
for i in range(options.num_cpus):#实例指令cache和数据cachel1i_cache = L1Cache(size=options.l1i_size,assoc=options.l1i_assoc,start_index_bit=block_size_bits,is_icache=True,)l1d_cache = L1Cache(size=options.l1d_size,assoc=options.l1d_assoc,start_index_bit=block_size_bits,is_icache=False,)#暂未定prefetcher = RubyPrefetcher()#每一个cpu都可以有不同的时钟域clk_domain = cpus[i].clk_domain#把每个cpu的l2相连起来 Connect the L1 controllers and the networkl1_cntrl.mandatoryQueue = MessageBuffer()l1_cntrl.requestFromL1Cache = MessageBuffer()l1_cntrl.requestFromL1Cache.out_port = ruby_system.network.in_portl1_cntrl.responseFromL1Cache = MessageBuffer()l1_cntrl.responseFromL1Cache.out_port = ruby_system.network.in_portl1_cntrl.unblockFromL1Cache = MessageBuffer()l1_cntrl.unblockFromL1Cache.out_port = ruby_system.network.in_portl1_cntrl.optionalQueue = MessageBuffer()l1_cntrl.requestToL1Cache = MessageBuffer()l1_cntrl.requestToL1Cache.in_port = ruby_system.network.out_portl1_cntrl.responseToL1Cache = MessageBuffer()l1_cntrl.responseToL1Cache.in_port = ruby_system.network.out_port#然后是l2,先遍历每一个l2.数目是自己在命令行指定的,但是需要和cpu数一致。
for i in range(options.num_l2caches):## First create the Ruby objects associated with this cpu#l2_cache = L2Cache(size=options.l2_size,assoc=options.l2_assoc,start_index_bit=l2_index_start,)l2_cntrl = L2Cache_Controller(version=i,L2cache=l2_cache,transitions_per_cycle=options.ports,ruby_system=ruby_system,)exec("ruby_system.l2_cntrl%d = l2_cntrl" % i)l2_cntrl_nodes.append(l2_cntrl)# Connect the L2 controllers and the networkl2_cntrl.DirRequestFromL2Cache = MessageBuffer()l2_cntrl.DirRequestFromL2Cache.out_port = ruby_system.network.in_portl2_cntrl.L1RequestFromL2Cache = MessageBuffer()l2_cntrl.L1RequestFromL2Cache.out_port = ruby_system.network.in_portl2_cntrl.responseFromL2Cache = MessageBuffer()l2_cntrl.responseFromL2Cache.out_port = ruby_system.network.in_portl2_cntrl.unblockToL2Cache = MessageBuffer()l2_cntrl.unblockToL2Cache.in_port = ruby_system.network.out_portl2_cntrl.L1RequestToL2Cache = MessageBuffer()l2_cntrl.L1RequestToL2Cache.in_port = ruby_system.network.out_portl2_cntrl.responseToL2Cache = MessageBuffer()l2_cntrl.responseToL2Cache.in_port = ruby_system.network.out_port
#3个vn
ruby_system.network.number_of_virtual_networks = 3#后面创建topology会把all_cntrls 传递进去。
all_cntrls = (l1_cntrl_nodes + l2_cntrl_nodes + dir_cntrl_nodes + dma_cntrl_nodes)#topology是调用的 from .Ruby import create_topology, create_directories
#然后ruby.py也是调用的 gem5/configs/topologies/Mesh_XY.py里的Mesh_XY(controllers),这意味着它会创建一个Mesh_XY类型的网络拓扑实例,并将controllers作为参数传递给它。topology = create_topology(all_cntrls, options)
return (cpu_sequencers, mem_dir_cntrl_nodes, topology)
Mesh_XY(SimpleTopology) 的创立(先不相连)
路径如下是:
- fs.py 调用了 gem5/configs/ruby/Ruby.py 中的 Ruby.create_system( args, True, test_sys, test_sys.iobus, test_sys._dma_ports, bootmem )
- Ruby.create_system 调用了MESI_Two_Level.create_system
- MESI_Two_Level.create_system底部 内嵌了Ruby.create_topology
- Ruby.create_topology调用了 TopoPython.topoClass(controllers),其中TopoPython 是 import topologies.{options.topology} as TopoPython. {options.topology} 是我们命令行输入的,也就是import了 Mesh_XY.py 。 topoClass,是Mesh_XY.py 中的一个class ,定义是 class Mesh_XY(SimpleTopology):。
- 之后我们就详解,class Mesh_XY(SimpleTopology):如何处理传递进来的 all_cntrls。
1.本身的类型是SimpleTopology
如下,就是简单的说一下自己继承自哪个类型。这个类型来自于 from topologies.BaseTopology import SimpleTopology。 引用的文件的路径是gem5/configs/topologies/BaseTopology.py。
class Mesh_XY(SimpleTopology):description = "Mesh_XY"
2. 初始化需要controller
def __init__(self, controllers):self.nodes = controllers
这时候把MESI_Two_Level.create_system 传递进来的 l1 l2 nodes等传递给mesh_xy.py中的代码,但是没有进一步操作。
3. 将controller们 相连
调用流程是 fs.py中 ruby.create_system,其中内嵌的ruby.create_topology 调用了topology.makeTopology( options, network, IntLinkClass, ExtLinkClass, RouterClass ), topology是mesh_xy,所以调用了gem5/configs/topologies/Mesh_XY.py中的 def makeTopology(self, options, network, IntLink, ExtLink, Router):这个函数 .
因为这里很重要,单独一个大节来写。
ruby. create_system里 将controller们 相连: 调用mesh_xy.makeTopology
fs.py调用了 ruby.create_system,
- 先调用 MESI_Two_Level.create_system
1.1 MESI_Two_Level.create_system 底部 内嵌了Ruby.create_topology 创建了 这个topology但是没有相连。 这里的create 只是调用mesh_xy(ctrls)进行初始化。 - ruby.create_system 紧接着 topology.makeTopology( options, network, IntLinkClass, ExtLinkClass, RouterClass ),调用了 gem5/configs/topologies/Mesh_XY.py中的Mesh_XY. makeTopology. 进行相连
2.1 其中,from network import Network 是创建了network,会要在互联时使用。gem5/configs/
下面是相连的代码
Mesh_XY类定义了一个基于XY路由算法的二维网格(mesh)拓扑结构。这个拓扑用于在gem5仿真中配置处理器核心、缓存和其他控制器之间的网络连接。代码中定义了如何将控制器(controllers)连接到网格中的路由器,并设置了路由器之间的内部链接(int_links)。这里的controllers是传入的参数,包含了L1控制器、L2控制器、目录控制器和DMA控制器的节点。
下面是对代码中关键部分的解释:
控制器与路由器的连接(External Links)
控制器(如缓存控制器和DMA控制器)通过外部链接(ExtLink)连接到网格中的路由器。
代码首先将大部分控制器平均分配给所有路由器,每个路由器连接相同数量的控制器。
如果有剩余的控制器(比如由于控制器数量不能被路由器数量整除),这些控制器将被连接到网格中的第一个路由器。
路由器间的内部连接(Internal Links)
网格中的每个路由器通过内部链接(IntLink)相互连接,形成网格结构。
东西方向的链接(East-West)和南北方向的链接(North-South)被创建,以实现网格的二维结构。
每个链接的权重和延迟设置反映了网格的物理和性能特性。在XY路由中,通常东西方向和南北方向的链接权重会有所不同,以支持死锁避免算法。
网格拓扑的构建过程
计算路由器数量、行数和列数。
为每个路由器创建Router对象,并将它们存储在一个列表中。
根据提供的控制器节点创建外部链接(ExtLink),将控制器连接到相应的路由器。
创建内部链接(IntLink),根据网格拓扑将路由器彼此连接。
将所有创建的外部链接和内部链接分别存储在network.ext_links和network.int_links中。
通过这种方式,Mesh_XY类构建了一个基于XY路由的网格网络拓扑,它连接了仿真中的各个控制器和路由器,从而实现了复杂的网络通信模式。
在仿真中,这个网格拓扑模型被用来研究不同网络配置和通信模式对整体系统性能的影响,特别是在处理多核处理器和复杂内存系统的场景中。
代码逐行解读: def makeTopology(self, options, network, IntLink, ExtLink, Router):
我们诸行解读,从不跳过。为了方便阅读,直接写在注释里了。
def makeTopology(self, options, network, IntLink, ExtLink, Router):nodes = self.nodes # 来自于自己的init时读的all_cntrls <- def __init__(self, controllers): self.nodes = controllersnum_routers = options.num_cpus#命令行给的输入,例如64 或1 ,我们先用64做个例子num_rows = options.mesh_rows# #命令行给的输入,例如8 或1 我们用64作为例子,这里再用8x8作为例子(2x32,4x16 也可以,但是8x8常见)# default values for link latency and router latency.# Can be over-ridden on a per link/router basislink_latency = options.link_latency # used by simple and garnet #我们命令行没有输入,使用默认值router_latency = options.router_latency # only used by garnet #我们命令行没有输入,使用默认值# There must be an evenly divisible number of cntrls to routers# Also, obviously the number or rows must be <= the number of routers#len(nodes) = 是这么计算的: 64 +64+ 64 + 0#all_cntrls = ( l1_cntrl_nodes + l2_cntrl_nodes + dir_cntrl_nodes + dma_cntrl_nodes ) #分为l1 ctrl num = cpu num,是64, l2 ctrl num是 单独命令行输入的 64# dir和dma是 gem5/configs/ruby/MESI_Two_Level.py 中 from .Ruby import create_topology, create_directories,然后 gem5/configs/ruby/Ruby.py 中 def create_directories(options, bootmem, ruby_system, system): return (dir_cntrl_nodes, None) 。 其中for i in range(options.num_dirs): dir_cntrl_nodes.append(dir_cntrl) 。# dir num是 单独命令行输入的 l2 dir num 64 dma_cntrl_nodes是返回的none也就是 0.cntrls_per_router, remainder = divmod(len(nodes), num_routers)#然后每个router分到了3个cntrls 没有remainder#64个节点整除8行,得到8列。 如果router数目不够而row太大,就报错。 如果除不尽(通过检查相乘是否相等)就报错。assert num_rows > 0 and num_rows <= num_routersnum_columns = int(num_routers / num_rows)assert num_columns * num_rows == num_routers#遍历64个路由器,实例话64个router。# Create the routers in the meshrouters = [Router(router_id=i, latency=router_latency)for i in range(num_routers)]#传递给network ,这里的network是一个类,名字叫garnetnetwork,继承自class RubyNetwork(ClockedObject):,s RubyNetwork中的 routers = VectorParam.BasicRouter("Network routers")network.routers = routers# link counter to set unique link idslink_count = 0# Add all but the remainder nodes to the list of nodes to be uniformly# distributed across the network.network_nodes = []remainder_nodes = []for node_index in range(len(nodes)):if node_index < (len(nodes) - remainder):network_nodes.append(nodes[node_index])else:remainder_nodes.append(nodes[node_index])# Connect each node to the appropriate routerext_links = []#这行代码使用enumerate函数遍历network_nodes列表,i是索引,n是当前迭代的节点(控制器)。#l1_cntrl_nodes + l2_cntrl_nodes + dir_cntrl_nodes + dma_cntrl_nodes# cntrl_level 分别是0,1,2。 3因为dma不存在所以没有。for (i, n) in enumerate(network_nodes):cntrl_level, router_id = divmod(i, num_routers)assert cntrl_level < cntrls_per_routerext_links.append(ExtLink(link_id=link_count,ext_node=n,int_node=routers[router_id],latency=link_latency,))#这里完成后,每个cpu和对应的router之间有3个线。分别是 l1_cntrl+ l2_cntrl + dir_cntrl。link_count += 1#我们# Connect the remainding nodes to router 0. These should only be# DMA nodes.for (i, node) in enumerate(remainder_nodes):assert node.type == "DMA_Controller"assert i < remainderext_links.append(ExtLink(link_id=link_count,ext_node=node,int_node=routers[0],latency=link_latency,))link_count += 1#这些ext links指的是l1 l2 和router相连network.ext_links = ext_links#int links指的是noc之内,router之间的相连# Create the mesh links.int_links = []#左边router的east outport 连接右边一列的router的west inport# East output to West input links (weight = 1)for row in range(num_rows):for col in range(num_columns):if col + 1 < num_columns:east_out = col + (row * num_columns)west_in = (col + 1) + (row * num_columns)int_links.append(IntLink(link_id=link_count,src_node=routers[east_out],dst_node=routers[west_in],src_outport="East",dst_inport="West",latency=link_latency,weight=1,))link_count += 1#左边router的east inport 连接右边一列的router的east outport# West output to East input links (weight = 1)for row in range(num_rows):for col in range(num_columns):if col + 1 < num_columns:east_in = col + (row * num_columns)west_out = (col + 1) + (row * num_columns)int_links.append(IntLink(link_id=link_count,src_node=routers[west_out],dst_node=routers[east_in],src_outport="West",dst_inport="East",latency=link_latency,weight=1,))link_count += 1#上边router的 North outport 连接下边一行的router的westinport# North output to South input links (weight = 2)for col in range(num_columns):for row in range(num_rows):if row + 1 < num_rows:north_out = col + (row * num_columns)south_in = col + ((row + 1) * num_columns)int_links.append(IntLink(link_id=link_count,src_node=routers[north_out],dst_node=routers[south_in],src_outport="North",dst_inport="South",latency=link_latency,weight=2,))link_count += 1#上边router的 North intport 连接下边一行的router的west outport# South output to North input links (weight = 2)for col in range(num_columns):for row in range(num_rows):if row + 1 < num_rows:north_in = col + (row * num_columns)south_out = col + ((row + 1) * num_columns)int_links.append(IntLink(link_id=link_count,src_node=routers[south_out],dst_node=routers[north_in],src_outport="South",dst_inport="North",latency=link_latency,weight=2,))link_count += 1network.int_links = int_links# Register nodes with filesystemdef registerTopology(self, options):for i in range(options.num_cpus):FileSystemConfig.register_node([i], MemorySize(options.mem_size) // options.num_cpus, i)
小结
我们这里发现,所以router都连接上了3个ext links 连上的 ctrl分别是 l1 l2 和dir,同时intlinks互相链接router。我们在之后的博客看到底数据是怎么传输的,怎么从 core 流向caches再流向 router.
这篇关于gem5 garnet l1 l2 cache的创建与相连的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








