本文主要是介绍【超分辨率】Enhanced Deep Residual Networks for Single Image Super-Resolution,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
这篇文章是NTIRE2017 Super-Resolution Challenge 夺冠文章。
机器之心对此进行了简单的翻译,还是比较详细的:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/xpvGz1HVo9eLNDMv9v7vqg
这篇博客主要记录我对这篇文章的理解:
一、本文主要内容:
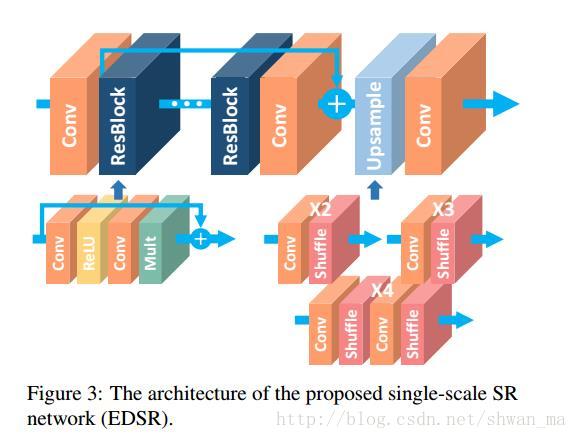
该文章提出了两种模型EDSR(单一尺度网络) 和 MDSR(多尺度超分辨率架构)。
目前一个DL网络往往对应着一个超分尺度upscaling factor
most existing SR algorithms treat superresolution of different scale factors as independent problems without considering and utilizing mutual relationships among different scales in SR. As such, those algorithms require many scale-specific networks that need to to be trained independently to deal with various scales.
文章在单一尺度网络EDSR的基础上同时也提出了MDSR(多尺度超分辨率架构)
二、文章模型:
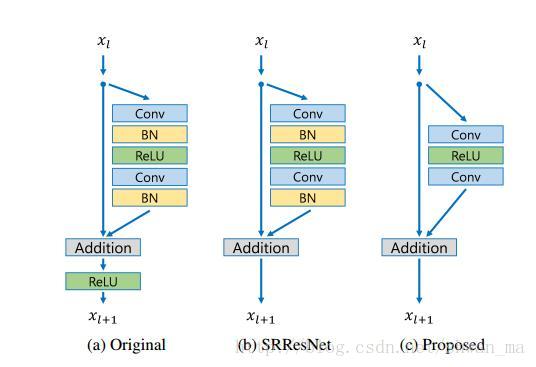
该论文模型主要来自何凯明的ResNet,不过在Residual block上有着细微的差距:
可以看到模型的residual block在SRResNet的基础上去掉了BN,
原文解释是:
Since batch normalization layers normalize the features, they get rid of range flexibility from networks by normalizing the features, it
is better to remove them.
去掉BN带来的好处是1)训练速度加快,2)使用显存减少
(因为BN层会消耗与之前卷积层等量的内存)
1) EDSR:
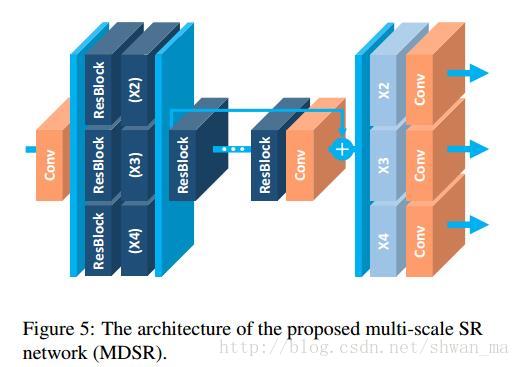
1) MDSR:
可以从图上看出,很多参数在MDSR之间是可以被共享的,因此MDSR比多个独立尺度的网络具有更少的参数,更快的收敛性。
most of the parameters are shared across different scales
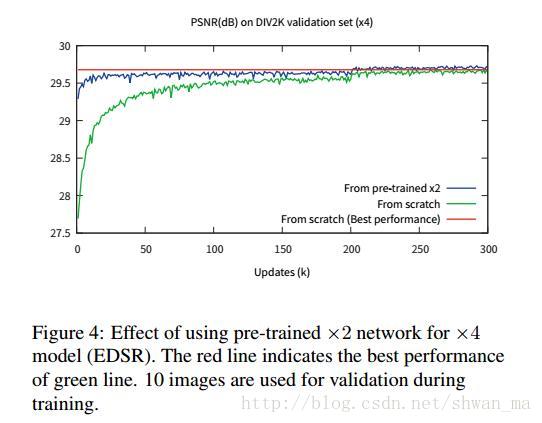
From the observation in Fig. 4, we conclude that superresolution at multiple scales is inter-related tasks.
对图4的描述:当在升采样因子(upsampling factor)为 ×3 和 ×4 的时候,我们用预训练的 ×2 网络初始化了模型参数。这一预训练方法加速了训练进程,也提升了最终的性能表现,详见图 4 。对于升采样 ×4 的情况,如果我们使用了一个预训练的 scale×2 模型(蓝线),训练就会比随机初始化的训练(绿线)收敛的更快。
这篇关于【超分辨率】Enhanced Deep Residual Networks for Single Image Super-Resolution的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!