本文主要是介绍3_流量预测综述阅读_Cellular traffic prediction with machine learning: A survey,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
为了方便学习英语书写,总结的一些话用英语书写
♥目录♥
- 0、文献来源and摘要
- 1、introduction
- 2、prediction problems and datasets
- 2.1 prediction problems
- 2.2 dataset
- (1)Telecom Italia 意大利电信 2015
- (2)City Cellular Traffic Map (C2TM) 2015
- (3)、LTE Network Traffic Data_kaggle
- (4)、Cellular Traffic Analysis Data 2019
- (5)、China Unicom One Cell Data
- (6)、Shanghai Telecom dataset 2020
- (7)、The AIIA data
- 3、数据预处理和预测模型
- 3.1 data preprocessing
- 3.1.1 直接预测 direct-prediction
- 3.1.2 先分类然后预测
- 3.1.3 先分解然后预测
- 3.3 预测模型
- 3.3.1 统计模型 statistical models
- (1)ARIMA : Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average自回归移动平均模型
- (2)HW:Holt–Winters三次指数平滑模型
- 3.3.2 机器学习模型 machine learning models
- (1)RF:random forest 随机森林
- (2)LightGBM
- (3)GPR:Gaussian progress regression
- (4)MLR:multiple linear regression
- (5)Prohet
- 3.3.3 深度学习模型 deep learning models
- (1)FFNNs:feed-forward neural networks前馈神经网络
- (2)CNN
- (3)RNN
- (4)LSTM
- (5)GRU
- (6)ConvLSTM
- (7)LSTM+attention
- (8)CNN+RNN
0、文献来源and摘要

- 摘要:
- review the relevant studies on cellular traffic prediction
- classify the prediction problems as the temporal(时间的)and spatiotemporal prediction problems
- 人工智能的预测模型分为:statistical, machine learning, deep learning
1、introduction
流量预测的challenge:
- complex internal(内部的)patterns hidden in the historical traffic data
- pratical deployment(实际部署):a gap between high-preformance prediction model and real-world systems
这篇综述的贡献性: - classification of cellular prediction problems to four workflows and three model
- workflow : direct-prediction, classification-then-prediction, decomposition-then-prediction, and clustering-then-
prediction - model : statistical, machine learning, and deep learning
- workflow : direct-prediction, classification-then-prediction, decomposition-then-prediction, and clustering-then-
- a comprehensive(广泛的) collection of eight open datasets
- evaluation metrics 评估指标
- potential applications and directions
2、prediction problems and datasets
2.1 prediction problems
- temporal prediction problem:

在这种最简单的类型中,只使用历史流量数据中的时间依赖性 - spatiotemporal prediction problem:
- the connected users have moved and connected from one base station to another base station, with the process of handover(切换)

在多个基站或多个区域内的流量,除了时间依赖关系,还考虑了它们的空间依赖关系
the objective is to predict the entire traffic distribution in a given area or only at the hotspots(热点地区)
- the connected users have moved and connected from one base station to another base station, with the process of handover(切换)
- 这两种问题都可以看做监督学习:moving windows
- 收集到的流量数据被视为univariate单变量时间序列,对未来的时间步(time steps)的流量预测基于固定长度的历史数据

- 收集到的流量数据被视为univariate单变量时间序列,对未来的时间步(time steps)的流量预测基于固定长度的历史数据
- 衡量流量:
- SMS/call service/internet usage service
- physical resource block utilization (利用率)
- number of connected users
- 流量数据通过基站收集,然后通过cellular network operator 将不同时间粒度的数据进行聚合
- 流量需求是由网关上布置的专用探头来监控GPRS隧道协议?(这是啥?)
- 一般的假设流量数据只在一个基站内使用(没有传输)或者传输到一个central server中央服务器中(需要足够的计算资源)
- 小的改进: 流量数据不再是全部传输到中央服务器中,而是按照数据对预测精度的贡献性先对数据进行排序,然后再从基站传输到中央服务器中
- 少数情况下,流量数据是由用户端收集的
- 大多数时间粒度是5min到1h
- 流量预测问题的分类:

- univariate temporal prediction 单变量时域预测
- 前 N N N个时间步的历史数据: X = { x 1 , x 2 , . . . , x N } \mathcal{X}=\{x_1,x_2,...,x_N\} X={x1,x2,...,xN}
- 预测第 N + 1 N+1 N+1个时间步的 x N + 1 x_{N+1} xN+1
- y = f ( X ) y=f(\mathcal{X}) y=f(X)
- univariate spatiotemporal prediction 单变量时空预测
- 流量数据从标量 x i x_i xi变成矢量 x i ⃗ \vec{x_i} xi
- x i ⃗ \vec{x_i} xi:不同基站的数据使用率
- multivariate temporal prediction 多变量时域预测
- x i ⃗ \vec{x_i} xi:SMS, call, and data usages from the same base station
- multivariate spatiotemporal prediction 多变量时空预测
- 里面的元素是 x i ⃗ \vec{x_i} xi: 不同空间区域的不同变量
- 把整个的矩阵变成向量:当不同的空间区域存在于一个规则的网格中时,可以将流量格式化为具有相同网格大小的矩阵
- univariate temporal prediction 单变量时域预测
2.2 dataset
(1)Telecom Italia 意大利电信 2015
链接指路
- 数据集介绍:
- This dataset was collected in the city of Milan, Italy, from November 1, 2013, to January 1, 2014.
- 空域被分为100x100的网格,每个网格是235x235平方米
- 通过分析call detail record(CDR)每十分钟每个网格提取不同的信息(SMSs, calls, and Internet usage data)
- 这个数据集可以用于单变量、多变量的时空预测流量问题
(2)City Cellular Traffic Map (C2TM) 2015
链接:https://github.com/caesar0301/city-cellular-traffic-map
- 数据集介绍:
- 13,269 base stations in a medium-sized city in China from August 19, 2012, to August 26, 2012.
- Each data record contains the base station id(基站id), a timestamp(时间戳), number of mobile users(用户数), number of transferred packets(传输包的数量), and number of transferred bytes(传输字节数) every hour. base station location(基站位置)
(3)、LTE Network Traffic Data_kaggle
click on this link:https://www.kaggle.com/naebolo/predict-traffic-of-lte-network(sos没有了)
- 数据集介绍:
- 4G data usage within 57 cells in 24 h for one year, from October 23, 2017, to October 22, 2018
- the locations of these 57 cells are not available->temporal type
(4)、Cellular Traffic Analysis Data 2019
https://github.com/AminAzari/cellular-traffic-analysis
- 数据集介绍:
- the traffic packets captured from the user side on several Android devices by using virtual private network tunneling
- packet arrival/departure time, source/destination IP addresses, communication protocol (e.g., UDP, TCP, SSL), and encrypted payload
(5)、China Unicom One Cell Data
链接:https://github.com/JinScientist/traffic-data-5min/blob/master/traffic_one_cell.csv
- 数据集介绍:
- 2016年1月1日至2017年5月1日17个月
- time steps: 5 min
- 对中国移动的4G网络的CDR data进行统计
- 只有一个基站
- 适用于单变量时间预测问题
(6)、Shanghai Telecom dataset 2020
链接:http://sguangwang.com/TelecomDataset.html
- 数据集介绍:
- 2014年6月1日至11月30日在中国上海收集了3233个基站和9481部手机
- 这个数据集提功力每个用户会话的开始时间和结束时间以及对应基站的位置
- 这个数据集本来适用于边缘计算的,但是也可以用于流量预测
(7)、The AIIA data
link: https://github.com/Phil-Shawn/DMNN
- 数据集介绍:
- 2017年1月1日至2018年11月15日三个匿名区域的小时流量数据
- 预测问题属于时间类型
3、数据预处理和预测模型
3.1 data preprocessing
4种workflows:direct-prediction, classification-then-prediction, decomposition-then-prediction, and clustering-then-prediction
需要不同的数据预处理方式
3.1.1 直接预测 direct-prediction
在大多研究中输入的histical data and prediction target已经是正确的格式了(time series or input vectors)
只需要通用的数据预处理:
- 数据归一化:data scaling through data standardization or min-max normalization
- 数据缺失问题:data imputation
- forward filling
- moving average
- bayesian gaussian tensor decomposition 贝叶斯高斯张量分解

3.1.2 先分类然后预测
the raw data packets: 从一个基站或者一个用户端收集到的不同应用或者服务的流量数据
流量分类的基础:deep packet inspection(检测) techniques
绕后使用ML或者DL将数据包分为:Email, text message, video streaming, audio chat, or video call
然后分别对每一种业务进行聚类
使用不同的预测模型来预测不同应用数据的未来流量

先分类然后预测的好处:
- 在后续的预测过程中,单个应用的流量预测比或者流量预测更加稳定,更容易达到好的效果
- 通过对不同应用的数据使用率的观察可以设计相应的管理措施:当更重要的应用需要额外的传输带宽时,可以降低视频流的质量
另一种分类方式:判断单个小区的流量数据是可预测还是不可预测的(通过朴素贝叶斯分类器)就是用过预测误差实现的
只有预测误差小的贾占数据才能在之后的预测中使用,减少了训练成本
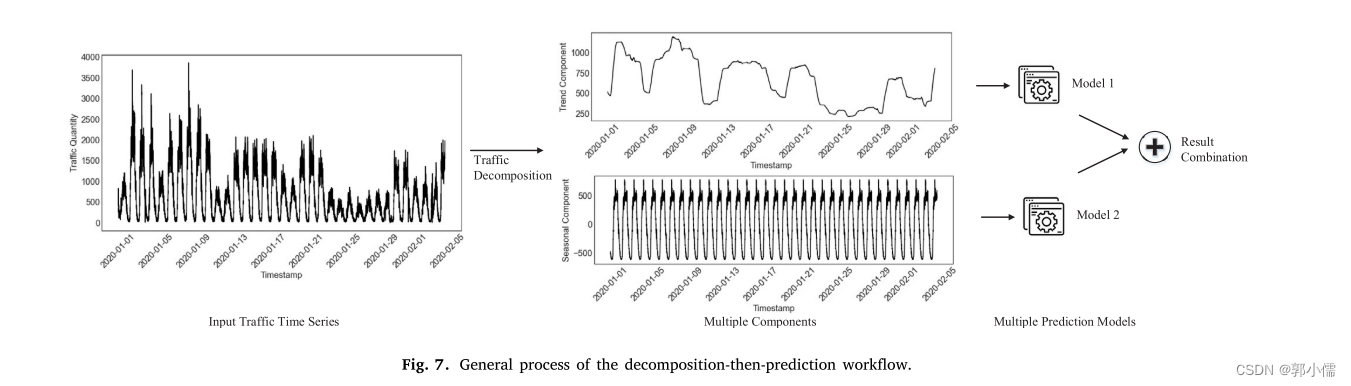
3.1.3 先分解然后预测
将单个变量的输入流量时间序列分解为多个组件
分别预测每个不同的组件
最终预测的结果是组件的输出的叠加
和先分类在预测不同,组件本身是没有物理意义的
3.3 预测模型
3.3.1 统计模型 statistical models
(1)ARIMA : Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average自回归移动平均模型
- 单变量时间序列模型
- 基于三种分量的加权线性组合:自回归分量(AR)、差分分量(I)、移动平均分量(MA)
(2)HW:Holt–Winters三次指数平滑模型
- 单变量时间序列模型
- 基于三种分量的组合:simple exponential smoothing, Holt’s ES, Winter’s ES

3.3.2 机器学习模型 machine learning models
(1)RF:random forest 随机森林
(2)LightGBM
(3)GPR:Gaussian progress regression
(4)MLR:multiple linear regression
(5)Prohet

3.3.3 深度学习模型 deep learning models
(1)FFNNs:feed-forward neural networks前馈神经网络
(2)CNN
(3)RNN
(4)LSTM
(5)GRU
(6)ConvLSTM
(7)LSTM+attention
(8)CNN+RNN



这篇关于3_流量预测综述阅读_Cellular traffic prediction with machine learning: A survey的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!