本文主要是介绍2023-简单点-picamera的bayer数据获取抽丝剥茧,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
capture函数,设置bayer=True
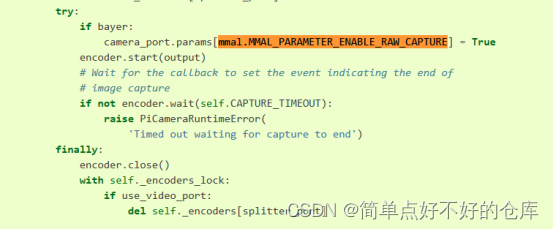
啥是mmal.xxxx? 啥是camera_port?
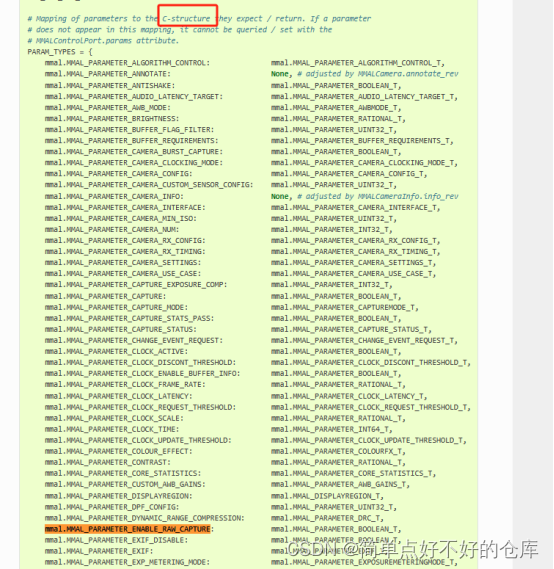
看起来是个设置标志,产生buffer,获取针对对应格式的c数据结构

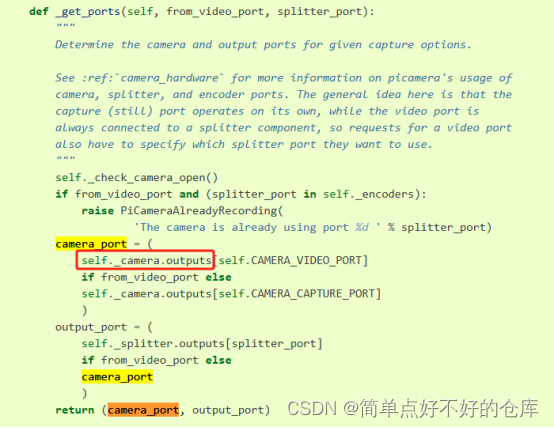
camera_port与self._camera.outputs有关
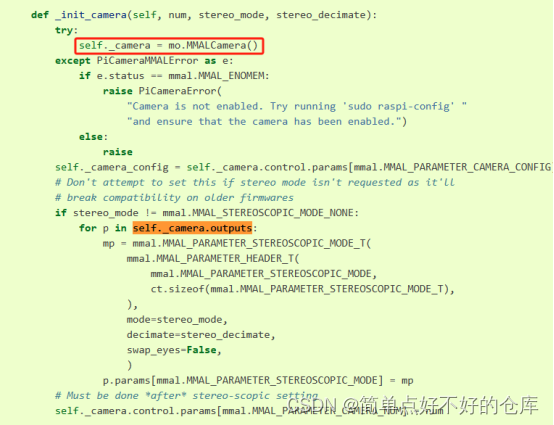
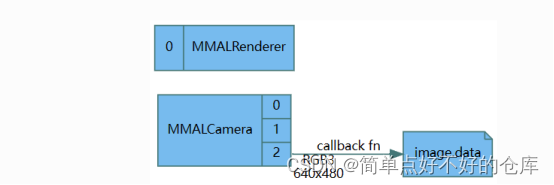
啥是mmalcamera
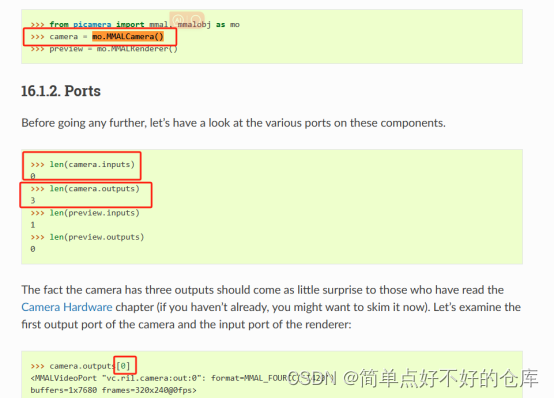
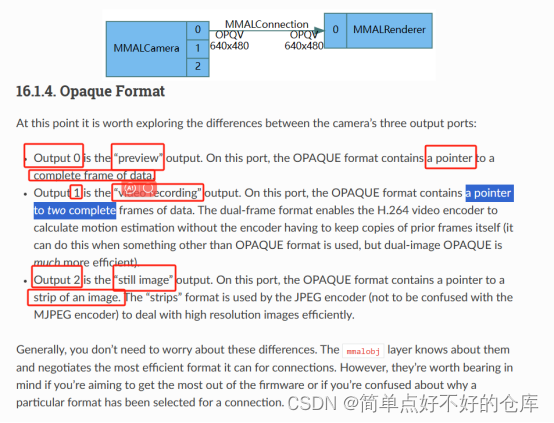
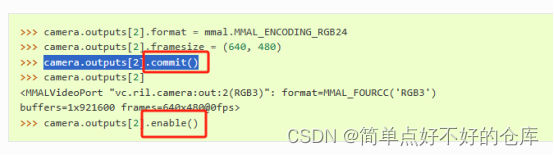

总之,找到Outputs有3个,disable()一下,然后配置相机参数,commit提交一下;
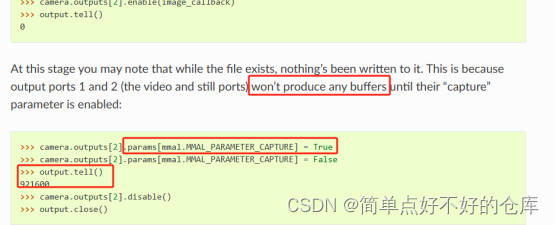
enable output with 回调函数,然后设置output.param【某某】为True产生buffers然后才能得到最终数据。
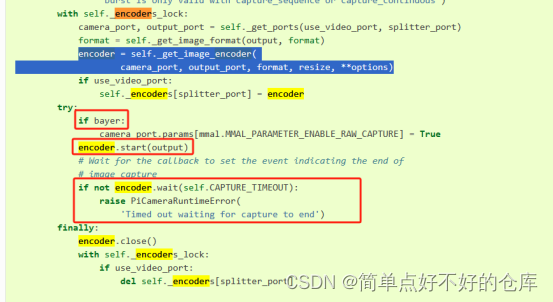
看完了例子,还有个encoder.start()
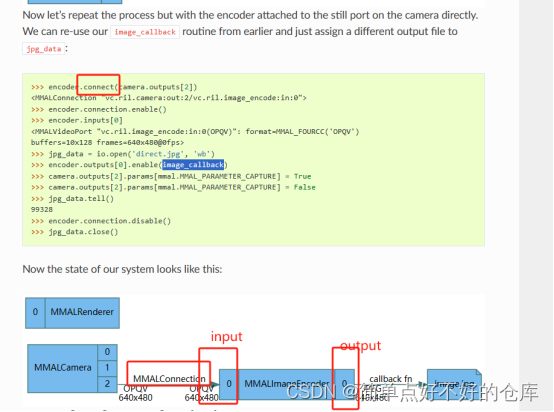
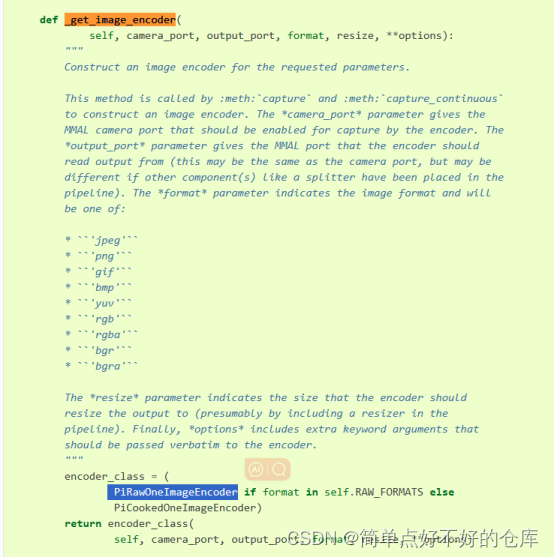
最后就追溯到这了。。。。
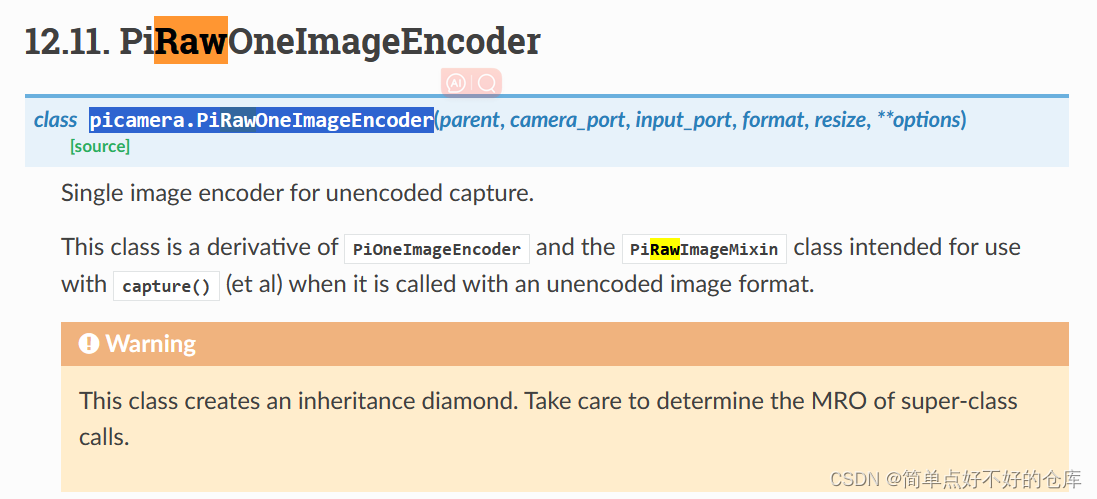

看来是多重继承
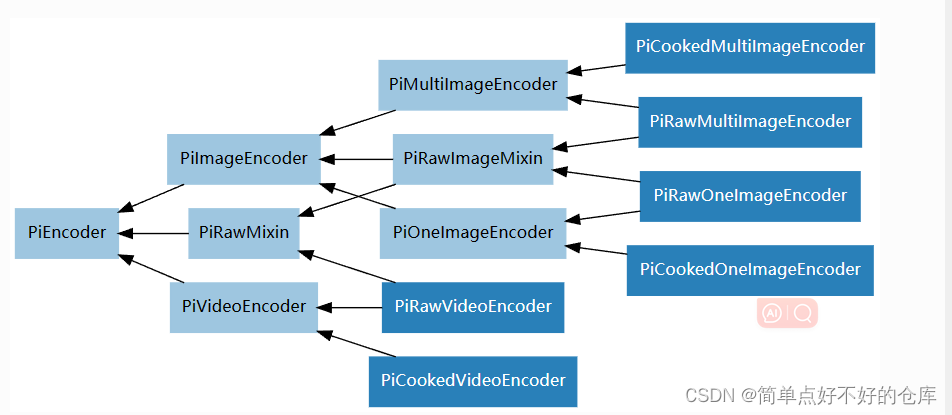
继续
又是多重
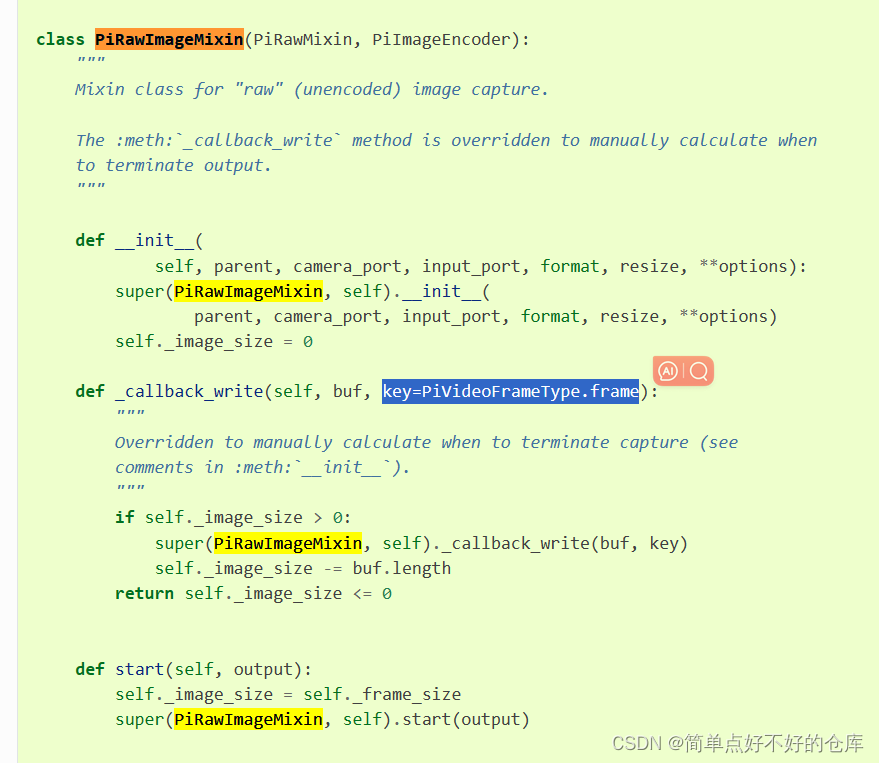
class PiRawMixin(PiEncoder):"""Mixin class for "raw" (unencoded) output.This mixin class overrides the initializer of :class:`PiEncoder`, alongwith :meth:`_create_resizer` and :meth:`_create_encoder` to configure thepipeline for unencoded output. Specifically, it disables the constructionof an encoder, and sets the output port to the input port passed to theinitializer, unless resizing is required (either for actual resizing, orfor format conversion) in which case the resizer's output is used."""RAW_ENCODINGS = {# name mmal-encoding bytes-per-pixel'yuv': (mmal.MMAL_ENCODING_I420, 1.5),'rgb': (mmal.MMAL_ENCODING_RGB24, 3),'rgba': (mmal.MMAL_ENCODING_RGBA, 4),'bgr': (mmal.MMAL_ENCODING_BGR24, 3),'bgra': (mmal.MMAL_ENCODING_BGRA, 4),}def __init__(self, parent, camera_port, input_port, format, resize, **options):encoding, bpp = self.RAW_ENCODINGS[format]# Workaround: on older firmwares, non-YUV encodings aren't supported on# the still port. If a non-YUV format is requested without resizing,# test whether we can commit the requested format on the input port and# if this fails, set resize to force resizer usageif resize is None and encoding != mmal.MMAL_ENCODING_I420:input_port.format = encodingtry:input_port.commit()except PiCameraMMALError as e:if e.status != mmal.MMAL_EINVAL:raiseresize = input_port.framesizewarnings.warn(PiCameraResizerEncoding("using a resizer to perform non-YUV encoding; ""upgrading your firmware with sudo rpi-update ""may improve performance"))# Workaround: If a non-alpha format is requested with the resizer, use# the alpha-inclusive format and set a flag to get the callback to# strip the alpha bytesself._strip_alpha = Falseif resize:width, height = resizetry:format = {'rgb': 'rgba','bgr': 'bgra',}[format]self._strip_alpha = Truewarnings.warn(PiCameraAlphaStripping("using alpha-stripping to convert to non-alpha ""format; you may find the equivalent alpha format ""faster"))except KeyError:passelse:width, height = input_port.framesize# Workaround (#83): when the resizer is used the width must be aligned# (both the frame and crop values) to avoid an error when the output# port format is set (height is aligned too, simply for consistency# with old picamera versions). Warn the user as they're not going to# get the resolution they expectif not resize and format != 'yuv' and input_port.name.startswith('vc.ril.video_splitter'):# Workaround: Expected frame size is rounded to 16x16 when splitter# port with no resizer is used and format is not YUVfwidth = bcm_host.VCOS_ALIGN_UP(width, 16)else:fwidth = bcm_host.VCOS_ALIGN_UP(width, 32)fheight = bcm_host.VCOS_ALIGN_UP(height, 16)if fwidth != width or fheight != height:warnings.warn(PiCameraResolutionRounded("frame size rounded up from %dx%d to %dx%d" % (width, height, fwidth, fheight)))if resize:resize = (fwidth, fheight)# Workaround: Calculate the expected frame size, to be used by the# callback to decide when a frame ends. This is to work around a# firmware bug that causes the raw image to be returned twice when the# maximum camera resolution is requestedself._frame_size = int(fwidth * fheight * bpp)super(PiRawMixin, self).__init__(parent, camera_port, input_port, format, resize, **options)def _create_encoder(self, format):"""Overridden to skip creating an encoder. Instead, this class simply usesthe resizer's port as the output port (if a resizer has beenconfigured) or the specified input port otherwise."""if self.resizer:self.output_port = self.resizer.outputs[0]else:self.output_port = self.input_porttry:self.output_port.format = self.RAW_ENCODINGS[format][0]except KeyError:raise PiCameraValueError('unknown format %s' % format)self.output_port.commit()def _callback_write(self, buf, key=PiVideoFrameType.frame):"""_callback_write(buf, key=PiVideoFrameType.frame)Overridden to strip alpha bytes when required."""if self._strip_alpha:return super(PiRawMixin, self)._callback_write(MMALBufferAlphaStrip(buf._buf), key)else:return super(PiRawMixin, self)._callback_write(buf, key)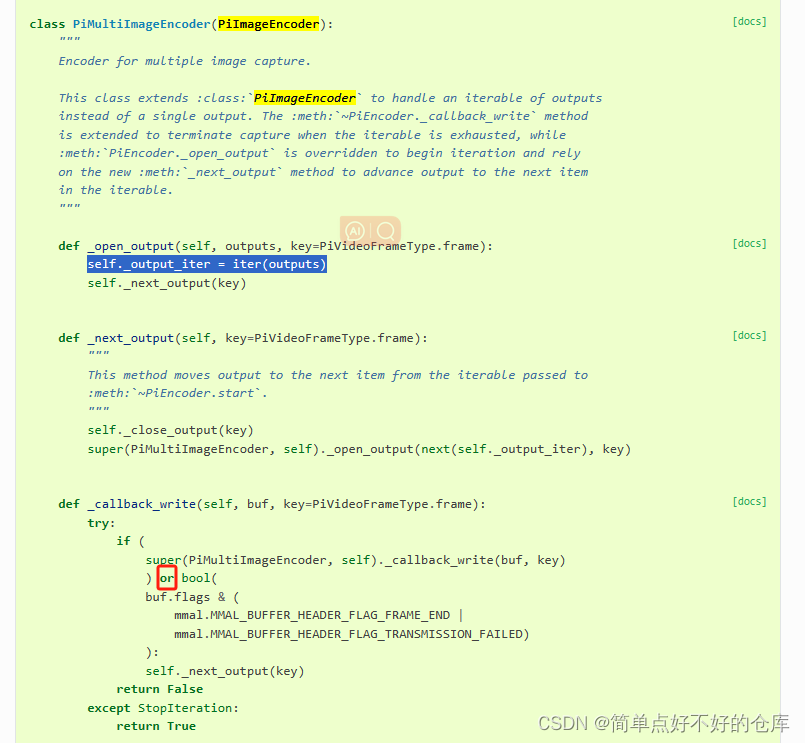
class PiVideoFrame(namedtuple('PiVideoFrame', ('index', # the frame number, where the first frame is 0'frame_type', # a constant indicating the frame type (see PiVideoFrameType)'frame_size', # the size (in bytes) of the frame's data'video_size', # the size (in bytes) of the video so far'split_size', # the size (in bytes) of the video since the last split'timestamp', # the presentation timestamp (PTS) of the frame'complete', # whether the frame is complete or not))):"""This class is a :func:`~collections.namedtuple` derivative used to storeinformation about a video frame. It is recommended that you access theinformation stored by this class by attribute name rather than position(for example: ``frame.index`` rather than ``frame[0]``)... attribute:: indexReturns the zero-based number of the frame. This is a monotonic counterthat is simply incremented every time the camera starts outputting anew frame. As a consequence, this attribute cannot be used to detectdropped frames. Nor does it necessarily represent actual frames; itwill be incremented for SPS headers and motion data buffers too... attribute:: frame_typeReturns a constant indicating the kind of data that the frame contains(see :class:`PiVideoFrameType`). Please note that certain frame typescontain no image data at all... attribute:: frame_sizeReturns the size in bytes of the current frame. If a frame is writtenin multiple chunks, this value will increment while :attr:`index`remains static. Query :attr:`complete` to determine whether the framehas been completely output yet... attribute:: video_sizeReturns the size in bytes of the entire video up to this frame. Notethat this is unlikely to match the size of the actual file/streamwritten so far. This is because a stream may utilize buffering whichwill cause the actual amount written (e.g. to disk) to lag behind thevalue reported by this attribute... attribute:: split_sizeReturns the size in bytes of the video recorded since the last call toeither :meth:`~PiCamera.start_recording` or:meth:`~PiCamera.split_recording`. For the reasons explained above,this may differ from the size of the actual file/stream written so far... attribute:: timestampReturns the presentation timestamp (PTS) of the frame. This representsthe point in time that the Pi received the first line of the frame fromthe camera.The timestamp is measured in microseconds (millionths of a second).When the camera's clock mode is ``'reset'`` (the default), thetimestamp is relative to the start of the video recording. When thecamera's :attr:`~PiCamera.clock_mode` is ``'raw'``, it is relative tothe last system reboot. See :attr:`~PiCamera.timestamp` for moreinformation... warning::Currently, the camera occasionally returns "time unknown" values inthis field which picamera represents as ``None``. If you arequerying this property you will need to check the value is not``None`` before using it. This happens for SPS header "frames",for example... attribute:: completeReturns a bool indicating whether the current frame is complete or not.If the frame is complete then :attr:`frame_size` will not incrementany further, and will reset for the next frame... versionchanged:: 1.5Deprecated :attr:`header` and :attr:`keyframe` attributes and added thenew :attr:`frame_type` attribute instead... versionchanged:: 1.9Added the :attr:`complete` attribute."""__slots__ = () # workaround python issue #24931@propertydef position(self):"""Returns the zero-based position of the frame in the stream containingit."""return self.split_size - self.frame_size@propertydef keyframe(self):"""Returns a bool indicating whether the current frame is a keyframe (anintra-frame, or I-frame in MPEG parlance)... deprecated:: 1.5Please compare :attr:`frame_type` to:attr:`PiVideoFrameType.key_frame` instead."""warnings.warn(PiCameraDeprecated('PiVideoFrame.keyframe is deprecated; please check ''PiVideoFrame.frame_type for equality with ''PiVideoFrameType.key_frame instead'))return self.frame_type == PiVideoFrameType.key_frame@propertydef header(self):"""Contains a bool indicating whether the current frame is actually anSPS/PPS header. Typically it is best to split an H.264 stream so thatit starts with an SPS/PPS header... deprecated:: 1.5Please compare :attr:`frame_type` to:attr:`PiVideoFrameType.sps_header` instead."""warnings.warn(PiCameraDeprecated('PiVideoFrame.header is deprecated; please check ''PiVideoFrame.frame_type for equality with ''PiVideoFrameType.sps_header instead'))return self.frame_type == PiVideoFrameType.sps_header

这个.frame就是0,用在encoder里


self.outputs就是个字典,以下是填入对象

mo.open_stream:
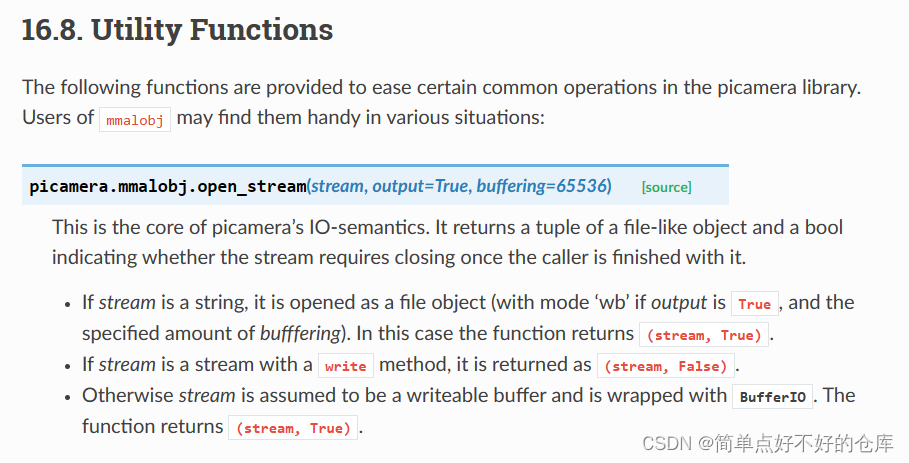
就是读写咯

乖乖,就是说encoder有outputs字典,可以存储多种output.
找了半天还是没找到关于buffer_count的

picamera2库有相关设置调整,picamera貌似内置好的

buffer_count在摄像头捕获和处理图像时起着重要作用。它表示用于存储图像数据的缓冲区数量。这些缓冲区是临时的存储空间,用于在图像从摄像头传感器读取并传输到应用程序或处理器进行进一步处理时暂存图像数据。
具体来说,buffer_count的作用包括:
图像连续性:当摄像头连续捕获图像时,每个缓冲区都会存储一帧图像的数据。通过设置足够的缓冲区数量,可以确保摄像头能够连续地捕获图像,而不会因为处理速度不够快而丢失帧。这样,就能够保证图像流的连续性。
性能优化:适当的缓冲区数量可以平衡摄像头捕获速度和应用程序处理速度之间的差异。如果缓冲区数量太少,摄像头可能会因为等待应用程序处理完前一帧而减慢捕获速度。而如果缓冲区数量过多,可能会占用过多的内存资源,导致效率下降。因此,根据系统的性能和需求,设置合适的buffer_count可以提高图像处理的效率和性能。
资源管理:缓冲区数量也涉及到内存资源的管理。每个缓冲区都需要占用一定的内存空间。通过控制buffer_count,可以管理摄像头系统所使用的内存量,以确保资源的合理利用。
综上所述,buffer_count在摄像头捕获和处理图像时起到了关键的作用,它影响着图像连续性、性能优化和资源管理。通过合理设置buffer_count,可以确保摄像头系统的高效运行和图像质量。
目前未找到硬编码位置,,,,,,,,
这篇关于2023-简单点-picamera的bayer数据获取抽丝剥茧的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





