本文主要是介绍【C++学习手札】基于红黑树封装模拟实现map和set,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

🎬慕斯主页:修仙—别有洞天
💜本文前置知识: 红黑树
♈️今日夜电波:漂流—菅原纱由理
2:55━━━━━━️💟──────── 4:29
🔄 ◀️ ⏸ ▶️ ☰
💗关注👍点赞🙌收藏您的每一次鼓励都是对我莫大的支持😍
目录
一、前言
map和set的底层原理
二、红黑树的封装
通过模板使得map和set都可复用红黑树
迭代器类
operator++()
operator--()
红黑树类
仿函数
map
set
封装后的红黑树
begin()和end()
通过仿函数来控制要比较的值
完整封装
三、map和set的封装
封装后的set
封装后的map
四、完整代码
RBTree.h
myset.h
mymap.h
一、前言
本文主要叙述基于红黑树对于map和set的封装实现,需要有红黑树的知识前提。由于前面作者对于红黑树主要只是模拟实现了插入的功能。因此本文也只是实现map和set相应的功能,本文的主要要点在于map和set的封装以及迭代器中++和--的实现。
map和set的底层原理
C++中的map和set都是STL中的关联容器,都基于红黑树实现。其中set是K模型的容器,而map是KV模型的容器,本文主要讲述用一棵KV模型的红黑树同时实现map和set。map和set都使用红黑树的基本操作,时间复杂度为O(log n),其中n为元素数量。因此,map和set都是高效的关联容器。
二、红黑树的封装
通过模板使得map和set都可复用红黑树
可以看到我们定义了一个模板参数T,通过T的类型变化来改变红黑树中每一个节点的值,从而控制整颗红黑树的复用。
enum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;T _data;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _data(data), _col(RED){}
};迭代器类
迭代器实际上是对于指针进行操作,因此我们实例化并且重新命名了节点类的指针Node,由于迭代器分为是否常量迭代器,对此我们额外定义了两个模板参数Ref、Ptr用于控制其中重载运算符 T& operator*() 和 T* operator->()。当我们实例化时,区分Ref是const T&还是T&、Ptr是const T*还是T*。后面RBTree中会有所体现。在迭代器中,其中,operator*和operator->返回指向节点的指针,operator++和operator--实现前后缀++/--运算符,operator==和operator!=用来比较两个迭代器是否指向同一个节点。
以下为大致实现的功能:
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Self& operator--();Self& operator++();Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}};operator++()
对于map和set的遍历我们默认都是中序遍历,也就是左子树 根 右子树。因此对于++操作我们首要的是找到下一个节点,则这个下一个节点便是在这个节点的右子树,也就是而下一个节点的准确位置为:这个节点的右子树的最左节点(为什么呢?因为左 根 右我们将这个节点看作为根,则下一个节点位置为右子树,而右子树的第一个节点则为最左的节点)。 当这个节点的右为空,意味着包括这个节点在内的左 根 右都遍历完了,那么我们就需要向上遍历。则需遵循以下:如果孩子是父亲的左就返回父亲(这就是意味着遍历完了左 接下来要遍历 根),否则就继续向上遍历,如果走到nullptr那就是遍历完成。
总结一下遍历规则:
1、如果_node的右不为空,找右孩子的最左节点
2、如果_node的右为空,如果孩子是父亲的左就返回父亲,否则就继续向上遍历,如果走到nullptr那就是遍历完成
Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right){// 下一个就是右子树的最左节点Node* cur = _node->_right;while (cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}_node = cur;}else{// 左子树 根 右子树// 右为空,找孩子是父亲左的那个祖先Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;} operator--()
和上面的operator++()相似,但是我们的遍历顺序变为了右子树 根 左子树。
总结一下遍历规则:
1、如果_node的左不为空,找左孩子的最右节点
2、如果_node的左为空,如果孩子是父亲的右就返回父亲,否则就继续向上遍历,如果走到nullptr那就是遍历完成
Self& operator--(){if (_node->_left){Node* cur = _node->_left;while (cur->_right){cur = cur->_right;}_node = cur;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}红黑树类
从之前我们所学习的红黑树的模拟实现我们可以知道,红黑树的插入等等操作中会用到对于key的比较。对此,set和map的比较要求是不同的,set可以直接用key进行比较,而map中对于pair的比较是先按first比较再比价second,而我们想要的结果是只比较first,因此我们定义了个KeyofT来对map和set进行区分。这个KeyofT则是通过传递仿函数来进行控制对于要比较值的转换。
// set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
// map->RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin();iterator end();const_iterator begin();const_iterator end();//pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)pair<Node*, bool> Insert(const T& data);Node * Find(const K & key)private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};仿函数
注意:这里的仿函数是在map和set中定义的,我们在map和set中的迭代器实际上是就是间接的控制了RBTree的迭代器。
map
struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};set
struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};封装后的红黑树
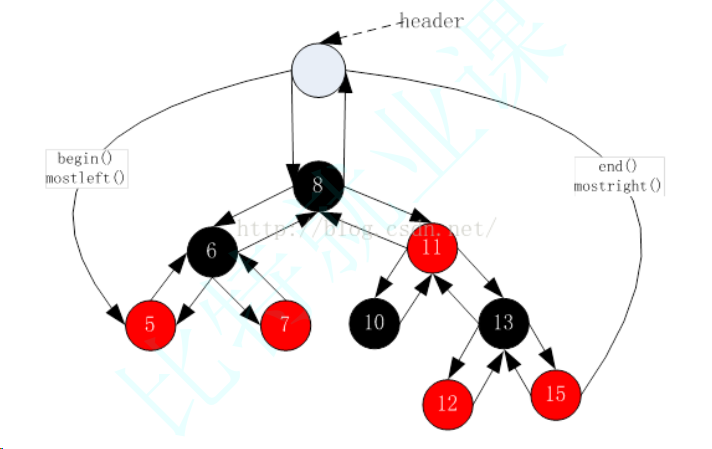
begin()和end()
STL明确规定,begin()与end()代表的是一段前闭后开的区间,而对红黑树进行中序遍历后,可以得到一个有序的序列,因此:begin()可以放在红黑树中最小节点(即最左侧节点)的位置,end()放在最大节点(最右侧节点)的下一个位置,关键是最大节点的下一个位置在哪块?能否给成nullptr呢?答案是行不通的,因为对end()位置的迭代器进行--操作,必须要能找最后一个元素,此处就不行,因此最好的方式是将end()放在头结点的位置:
虽然但是,作者还是将end()给了nullptr,事实上勉强还是可以用的哈哈哈...
iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}通过仿函数来控制要比较的值
注意:这里对于insert以及find中都定义了一个KeyOfT kot; 这个就是上面所提到的用于转化用于比较的数据的仿函数的定义。
其中对于insert有点需要注意:我们运用了pair中的特性,用pair<Node*, bool>接收了make_pair(newnode, true)的返回值,用pair构造了一个新的pair而不是拷贝构造了一个pair。后续会提到为什么(在set封装中)
//pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)pair<Node*, bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(_root, true);}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return make_pair(cur, false);}}// 新增节点给红色cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_col = RED;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}else{parent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){// g// p u// cNode* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上更新处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_left){// 单旋// g// p// cRotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// 双旋// g// p// cRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else // parent == grandfather->_right{// g// u p // c//Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// g// u p // c//RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(newnode, true);}Node * Find(const K & key){Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur!= nullptr){ if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_right;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}完整封装
// set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
// map->RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}//pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)pair<Node*, bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(_root, true);}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return make_pair(cur, false);}}// 新增节点给红色cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_col = RED;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}else{parent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){// g// p u// cNode* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上更新处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_left){// 单旋// g// p// cRotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// 双旋// g// p// cRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else // parent == grandfather->_right{// g// u p // c//Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// g// u p // c//RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(newnode, true);}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;subR->_left = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;if (_root == parent){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = parentParent;}}void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (_root == parent){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);}// 根节点->当前节点这条路径的黑色节点的数量bool Check(Node* root, int blacknum, const int refVal){if (root == nullptr){//cout << balcknum << endl;if (blacknum != refVal){cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl;return false;}return true;}if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << "有连续的红色节点" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == BLACK){++blacknum;}return Check(root->_left, blacknum, refVal)&& Check(root->_right, blacknum, refVal);}bool IsBalance(){if (_root == nullptr)return true;if (_root->_col == RED)return false;//参考值int refVal = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK){++refVal;}cur = cur->_left;}int blacknum = 0;return Check(_root, blacknum, refVal);}int Height(){return _Height(_root);}int _Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;}size_t Size(){return _Size(_root);}size_t _Size(Node* root){if (root == NULL)return 0;return _Size(root->_left)+ _Size(root->_right) + 1;}Node * Find(const K & key){Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur!= nullptr){ if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_right;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};三、map和set的封装
封装后的set
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"namespace bit
{template<class K>class set{public:struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}iterator end() const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}注意这段代码:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator; typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;其中typenam是告诉编译器这里是类型因为这里是对类模板取内嵌类型。通过set的定义我们知道set不允许被修改数值,因此我们将两个迭代器实际上都定义为const_iterator。但是这样定义其中insert又出问题了,因为其中的返回类型会出现不匹配的情况,即pair<iterator, bool> 和_t.Insert(key)不匹配。因为我们return返回的实际上是iterator,而实际上接受的类型为const_iterator。这时我们上面提到的用pair构造了一个新的pair而不是拷贝构造了一个pair就起到作用了,他使得返回的类型匹配!
当然我们也有其他的解决办法:定义一个迭代器的拷贝构造
STL库中的普通迭代器都可以转换为const迭代器,这是迭代器类的拷贝构造所支持的。
如下:
struct __TreeIterator
{typedef RedBlackTreeNode<T> Node;Node* _node;typedef __TreeIterator<T,Ref,Ptr> Self;typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;__TreeIterator(const iterator& it):_node(it._node){}__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}
}
封装后的map
想较于set,map的key值不可修改,但是value是可以修改的,对于他的迭代器定义按照正常的const和非const就好,但是他主要做文章的地方是在RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;中,直接将K定义为const K了。
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"namespace bit
{template<class K, class V>class map{public:struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};// 对类模板取内嵌类型,加typename告诉编译器这里是类型typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end()const{return _t.end();}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}四、完整代码
RBTree.h
#pragma once// set ->key
// map ->key/valueenum Colour
{RED,BLACK
};template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;T _data;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _data(data), _col(RED){}
};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __TreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef __TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;__TreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator--(){if (_node->_left){Node* cur = _node->_left;while (cur->_right){cur = cur->_right;}_node = cur;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_left){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right){// 下一个就是右子树的最左节点Node* cur = _node->_right;while (cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}_node = cur;}else{// 左子树 根 右子树// 右为空,找孩子是父亲左的那个祖先Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};// set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
// map->RBTree<K, pair<const K, T>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef __TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __TreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}const_iterator begin() const{Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return const_iterator(cur);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(nullptr);}//pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)pair<Node*, bool> Insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(_root, true);}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return make_pair(cur, false);}}// 新增节点给红色cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;cur->_col = RED;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}else{parent->_left = cur;cur->_parent = parent;}while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (parent == grandfather->_left){// g// p u// cNode* uncle = grandfather->_right;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上更新处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_left){// 单旋// g// p// cRotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// 双旋// g// p// cRotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else // parent == grandfather->_right{// g// u p // c//Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续往上处理cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{// g// u p // c//RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return make_pair(newnode, true);}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;subR->_left = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (subRL)subRL->_parent = parent;if (_root == parent){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = parentParent;}}void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR)subLR->_parent = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (_root == parent){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = subL;}else{parentParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = parentParent;}}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);}// 根节点->当前节点这条路径的黑色节点的数量bool Check(Node* root, int blacknum, const int refVal){if (root == nullptr){//cout << balcknum << endl;if (blacknum != refVal){cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl;return false;}return true;}if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << "有连续的红色节点" << endl;return false;}if (root->_col == BLACK){++blacknum;}return Check(root->_left, blacknum, refVal)&& Check(root->_right, blacknum, refVal);}bool IsBalance(){if (_root == nullptr)return true;if (_root->_col == RED)return false;//参考值int refVal = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK){++refVal;}cur = cur->_left;}int blacknum = 0;return Check(_root, blacknum, refVal);}int Height(){return _Height(_root);}int _Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;}size_t Size(){return _Size(_root);}size_t _Size(Node* root){if (root == NULL)return 0;return _Size(root->_left)+ _Size(root->_right) + 1;}Node * Find(const K & key){Node* cur = _root;KeyOfT kot;while (cur!= nullptr){ if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_left;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_right;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};myset.h
pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"namespace bit
{template<class K>class set{public:struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}iterator end() const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}mymap.h
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"namespace bit
{template<class K, class V>class map{public:struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};// 对类模板取内嵌类型,加typename告诉编译器这里是类型typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end()const{return _t.end();}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}感谢你耐心的看到这里ღ( ´・ᴗ・` )比心,如有哪里有错误请踢一脚作者o(╥﹏╥)o!

给个三连再走嘛~
这篇关于【C++学习手札】基于红黑树封装模拟实现map和set的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!