本文主要是介绍Codeforces Round 899 (Div. 2)(C手玩? D换根dp+贪心),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
A - Increasing Sequence
直接从1开始模拟就行
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N =2e5+10,mod=998244353;
#define int long long
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const long long inf=1e17;
using node=tuple<int,int,int>;
int n,m,k;
int a[N];
void solve()
{cin>>n;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];int idx=1;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(idx==a[i]) idx++;idx++;}cout<<idx-1<<"\n";
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int t=1;cin>>t;while(t--) solve();
}B - Sets and Union
我看着范围小直接枚举缺哪个数的时候能选的最大值即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N =2e5+10,mod=998244353;
#define int long long
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const long long inf=1e17;
using node=tuple<int,int,int>;
int n,m,k;
int a[N];
void solve()
{cin>>n;set<int> st;vector<set<int>> a(n+1); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){cin>>m;for(int j=0;j<m;j++){int x;cin>>x;a[i].insert(x);st.insert(x);}}int res=0;for(auto x:st){set<int> mp;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(a[i].count(x)) continue;for(auto y:a[i]) mp.insert(y);}res=max(res,(int)(mp.size()));}cout<<res<<"\n";
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int t=1;cin>>t;while(t--) solve();
}C:
老规矩:操作题先想操作有啥性质
考虑到从后往前选数字是不会对前面的数字造成影响的,我们可以不停先删去奇数编号大于0的数字,这样子剩下大于0的数字全部为偶数编号,如果第一个数字 ≥ 0显然,我们可以在取完第一个数字后使得偶数编号变为奇数编号,如果第二个数字 ≤ 0我们可以删去它使得后面的奇偶序翻转,但当第一个数字小于0,第二个数字大于0的时候,我们要考虑舍弃第二个数字的贡献还是选择第一个负数(容易发现对这两个数字操作改变奇偶的代价是最小的)。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N =2e5+10,mod=998244353;
#define int long long
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const long long inf=1e17;
using node=tuple<int,int,int>;
int n,m,k;
int a[N];
void solve()
{cin>>n;vector<int> suf(n+10);int res=0;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){res+=max(0ll,a[i]);}int t;if(n>=2) t=max(a[1],a[1]+a[2]);else t=a[1];cout<<max(res,res+t)<<"\n";
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int t=1;cin>>t;while(t--) solve();
}D:
首先一眼换根dp和最优点选的值最后肯定是根的值
为啥呢
首先我们无论怎么选,都要让当前叶子节点先变成和他父节点的值一样
这样就算父节点改变了,他的子树也不会改变
否则,如果让父节点变成叶子节点,如果父节点的祖宗节点改变了,那么父节点的子树也可能要改变,会增加额外次数
然后就是为啥选根为最后相等的值
图:
上面为选根,下面选3点
感性理解一下,就是如果根确定了,你变成其他值,其他值得系数会增加
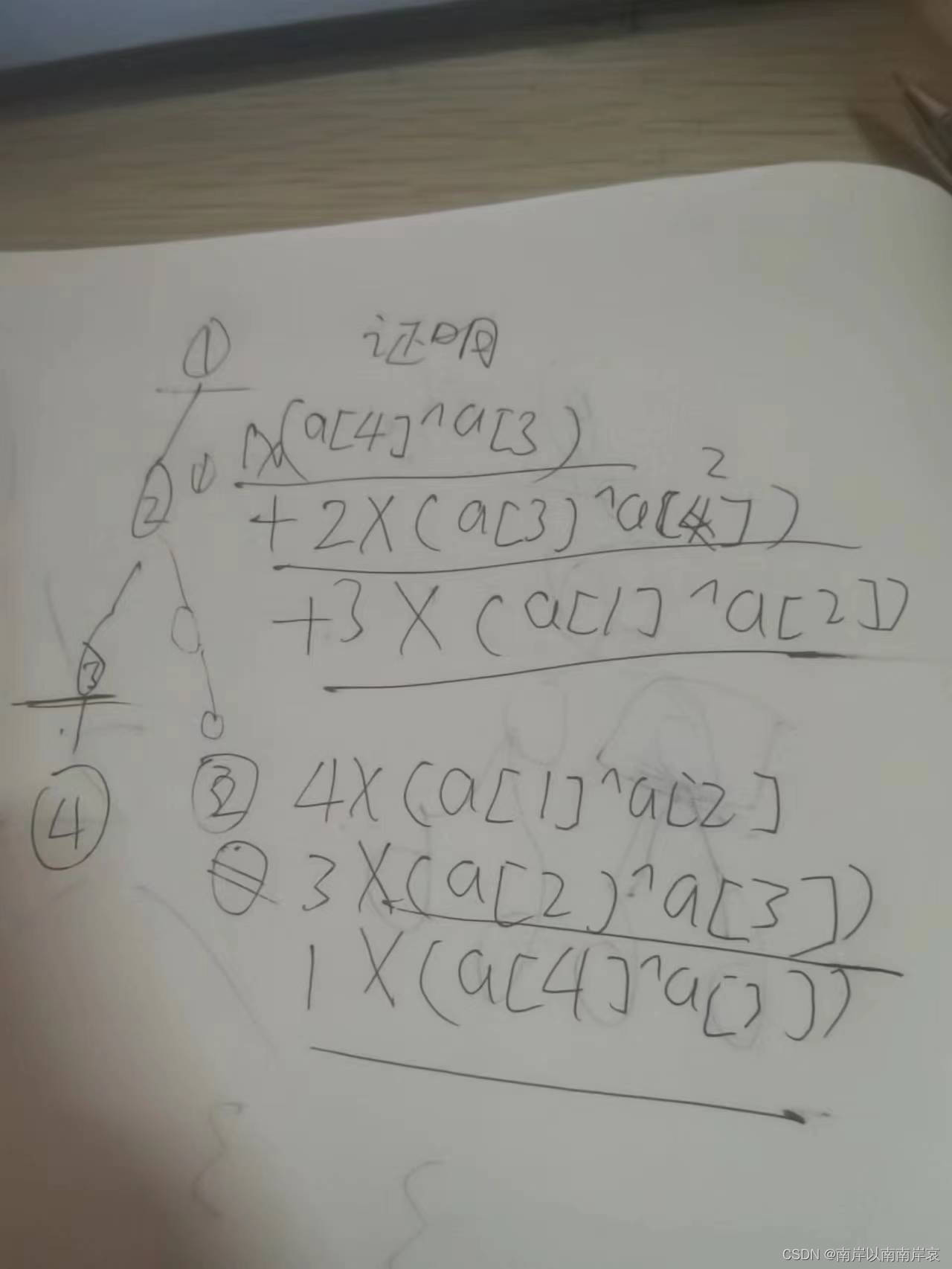
然后就换根dp了,
预处理出1点的贡献
我是分成三部分得
- res[u]=w[u]-sz[u]*(a[fa]^a[u]) 当前点为子树得代价
- +(res[fa]-w[u]) 父亲节点的子节点的代价
- +(n-sz[u])*(a[fa]^a[u]) 父亲节点到当前点的代价
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N =2e5+10,mod=998244353; #define int long long typedef long long LL; typedef pair<int, int> PII; const long long inf=1e17; using node=tuple<int,int,int>; int n,m,k; int a[N]; vector<int> g[N]; int res[N]; int sz[N]; int w[N]; void dfs(int u,int fa) {sz[u]=1;for(auto v:g[u]){if(v==fa) continue;dfs(v,u);sz[u]+=sz[v];w[u]+=w[v];}w[u]+=sz[u]*(a[u]^a[fa]);res[1]+=sz[u]*(a[u]^a[fa]); } void dfs1(int u,int fa){res[u]=w[u]-sz[u]*(a[fa]^a[u])+(res[fa]-w[u])+(n-sz[u])*(a[fa]^a[u]); for(auto v:g[u]){if(fa==v) continue;dfs1(v,u);} } void solve() {cin>>n;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){cin>>a[i];g[i].clear();res[i]=w[i]=0;}for(int i=1;i<n;i++){int x,y;cin>>x>>y;g[x].emplace_back(y);g[y].emplace_back(x);}dfs(1,1);// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<w[i]<<" \n"[i==n];dfs1(1,1);for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<res[i]<<" \n"[i==n]; }signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int t=1;cin>>t;while(t--) solve(); }
这篇关于Codeforces Round 899 (Div. 2)(C手玩? D换根dp+贪心)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


