本文主要是介绍C/C++,组合算法——K人活动选择问题(Activity-Selection-Problem)的源程序,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
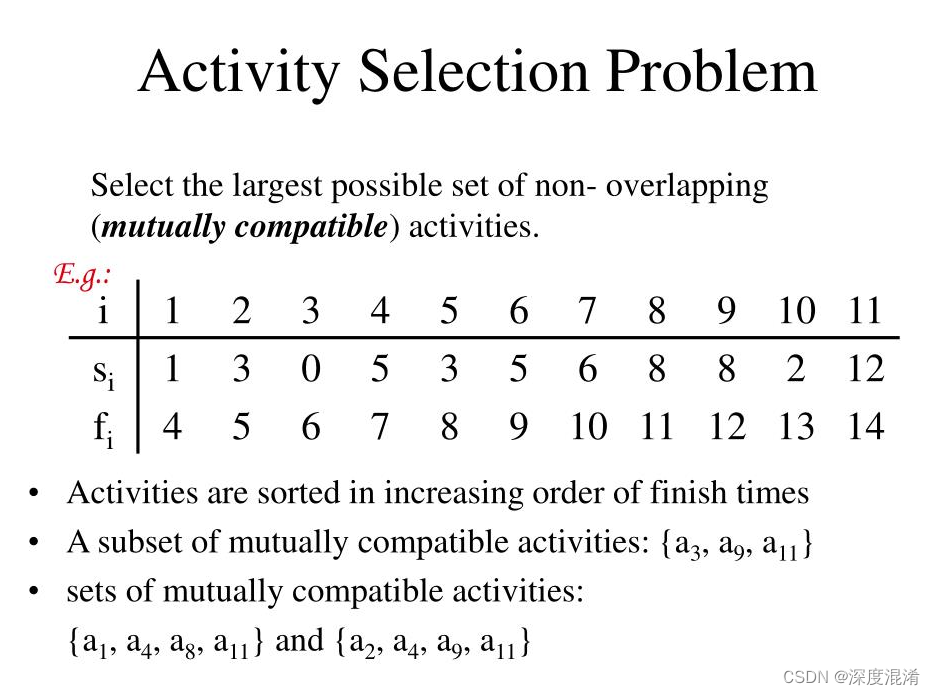
1 活动选择问题
Activity-Selection-Problem with k persons
给定两个大小为 N 的数组S[]和E[]表示商店的开始和结束时间,以及一个整数值 K 表示人数,
任务是找出如果他们基于以下条件最佳地访问每个商店,他们总共可以访问的商店的最大数量:
(1)一家商店只能被一个人光顾;
(2)一个人不能去另一家商店,如果它的时间与它冲突;
Activity Selection problem is a approach of selecting non-conflicting tasks based on start and end time and can be solved in O(N logN) time using a simple greedy approach. Modifications of this problem are complex and interesting which we will explore as well. Suprising, if we use a Dynamic Programming approach, the time complexity will be O(N^3) that is lower performance.
The problem statement for Activity Selection is that "Given a set of n activities with their start and finish times, we need to select maximum number of non-conflicting activities that can be performed by a single person, given that the person can handle only one activity at a time." The Activity Selection problem follows Greedy approach i.e. at every step, we can make a choice that looks best at the moment to get the optimal solution of the complete problem.
Our objective is to complete maximum number of activities. So, choosing the activity which is going to finish first will leave us maximum time to adjust the later activities. This is the intuition that greedily choosing the activity with earliest finish time will give us an optimal solution. By induction on the number of choices made, making the greedy choice at every step produces an optimal solution, so we chose the activity which finishes first. If we sort elements based on their starting time, the activity with least starting time could take the maximum duration for completion, therefore we won't be able to maximise number of activities.
2 文本格式
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Comparator
bool compareBy(const pair<int, int>& a,
const pair<int, int>& b)
{
if (a.second != b.second)
return a.second < b.second;
return a.first < b.first;
}
// Function to find maximum shops
// that can be visited by K persons
int maximumShops(int* opening, int* closing,
int n, int k)
{
// Store opening and closing
// time of shops
pair<int, int> a[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i].first = opening[i];
a[i].second = closing[i];
}
// Sort the pair of array
sort(a, a + n, compareBy);
// Stores the result
int count = 0;
// Stores current number of persons visiting
// some shop with their ending time
multiset<int> st;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Check if current shop can be
// assigned to a person who's
// already visiting any other shop
bool flag = false;
if (!st.empty()) {
auto it = st.upper_bound(a[i].first);
if (it != st.begin()) {
it--;
// Checks if there is any person whose
// closing time <= current shop opening
// time
if (*it <= a[i].first) {
// Erase previous shop visited by the
// person satisfying the condition
st.erase(it);
// Insert new closing time of current
// shop for the person satisfying ṭhe
// condition
st.insert(a[i].second);
// Increment the count by one
count++;
flag = true;
}
}
}
// In case if no person have closing
// time <= current shop opening time
// but there are some persons left
if (st.size() < k && flag == false) {
st.insert(a[i].second);
count++;
}
}
// Finally print the ans
return count;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given starting and ending time
int S[] = { 1, 8, 3, 2, 6 };
int E[] = { 5, 10, 6, 5, 9 };
// Given K and N
int K = 2, N = sizeof(S) / sizeof(S[0]);
// Function call
cout << maximumShops(S, E, N, K) << endl;
}
3 代码格式
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;// Comparator
bool compareBy(const pair<int, int>& a,const pair<int, int>& b)
{if (a.second != b.second)return a.second < b.second;return a.first < b.first;
}
// Function to find maximum shops
// that can be visited by K persons
int maximumShops(int* opening, int* closing,int n, int k)
{// Store opening and closing// time of shopspair<int, int> a[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {a[i].first = opening[i];a[i].second = closing[i];}// Sort the pair of arraysort(a, a + n, compareBy);// Stores the resultint count = 0;// Stores current number of persons visiting// some shop with their ending timemultiset<int> st;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// Check if current shop can be// assigned to a person who's// already visiting any other shopbool flag = false;if (!st.empty()) {auto it = st.upper_bound(a[i].first);if (it != st.begin()) {it--;// Checks if there is any person whose// closing time <= current shop opening// timeif (*it <= a[i].first) {// Erase previous shop visited by the// person satisfying the conditionst.erase(it);// Insert new closing time of current// shop for the person satisfying ṭhe// conditionst.insert(a[i].second);// Increment the count by onecount++;flag = true;}}}// In case if no person have closing// time <= current shop opening time// but there are some persons leftif (st.size() < k && flag == false) {st.insert(a[i].second);count++;}}// Finally print the ansreturn count;
}// Driver Code
int main()
{// Given starting and ending timeint S[] = { 1, 8, 3, 2, 6 };int E[] = { 5, 10, 6, 5, 9 };// Given K and Nint K = 2, N = sizeof(S) / sizeof(S[0]);// Function callcout << maximumShops(S, E, N, K) << endl;
}
这篇关于C/C++,组合算法——K人活动选择问题(Activity-Selection-Problem)的源程序的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



