本文主要是介绍Netty Review - 探索Pipeline的Inbound和Outbound,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 概念
- Server Code
- Client Code
- InboundHandler和OutboundHandler的执行顺序
- 在InboundHandler中不触发fire方法
- InboundHandler和OutboundHandler的执行顺序
- 如果把OutboundHandler放在InboundHandler的后面,OutboundHandler会执行吗

概念
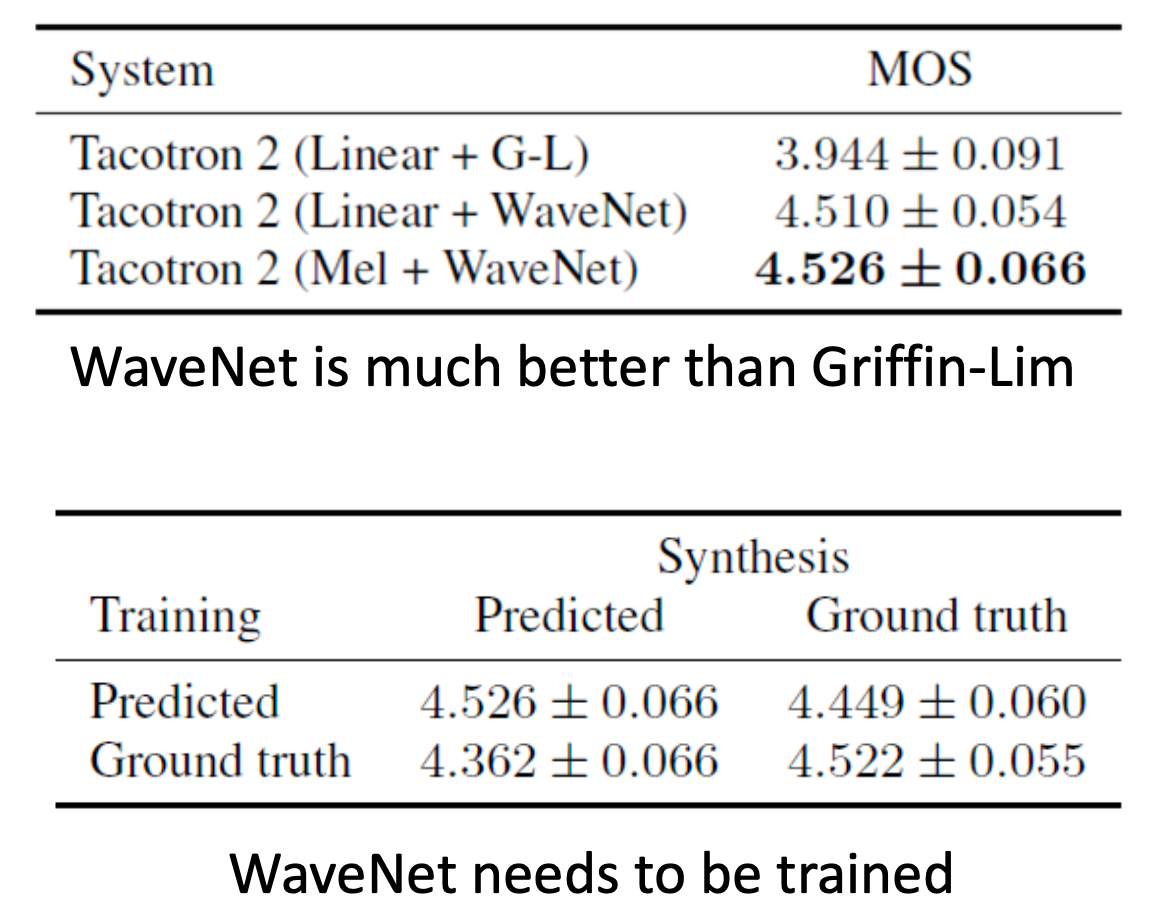
我们知道当boss线程监控到绑定端口上有accept事件,此时会为该socket连接实例化Pipeline,并将InboundHandler和OutboundHandler按序加载到Pipeline中,然后将该socket连接(也就是Channel对象)挂载到selector上。
一个selector对应一个线程,该线程会轮询所有挂载在他身上的socket连接有没有read或write事件,然后通过线程池去执行Pipeline的业务流。
selector如何查询哪些socket连接有read或write事件,主要取决于调用操作系统的哪种IO多路复用内核,
- 如果是
select(注意,此处的select是指操作系统内核的select IO多路复用,不是netty的seletor对象),那么将会遍历所有socket连接,依次询问是否有read或write事件,最终操作系统内核将所有IO事件的socket连接返回给netty进程,当有很多socket连接时,这种方式将会大大降低性能,因为存在大量socket连接的遍历和内核内存的拷贝。 - 如果是
epoll,性能将会大幅提升,因为它基于完成端口事件,已经维护好有IO事件的socket连接列表,selector直接取走,无需遍历,也少掉内核内存拷贝带来的性能损耗
在Netty中,Inbound和Outbound是两个重要的概念,用于描述数据在ChannelPipeline中的流动方向。
Inbound(入站)指的是数据从网络传输到应用程序,即数据从远程主机进入本地主机。在ChannelPipeline中,Inbound数据会依次经过Pipeline中的每个ChannelHandler进行处理,直到到达Pipeline的末尾。
Outbound(出站)指的是数据从应用程序传输到网络,即数据从本地主机发送到远程主机。在ChannelPipeline中,Outbound数据会从Pipeline的末尾开始,逆序经过Pipeline中的每个ChannelHandler进行处理,直到到达Pipeline的起始位置。
Inbound和Outbound的区别在于数据的流动方向。Inbound数据是从网络进入应用程序,而Outbound数据是从应用程序发送到网络。这意味着Inbound数据是应用程序接收和处理外部数据的入口,而Outbound数据是应用程序发送数据到外部的出口。
虽然Inbound和Outbound描述了数据的不同流动方向,但它们之间也存在联系。在ChannelPipeline中,Inbound和Outbound数据可以相互影响和交互。例如,一个ChannelHandler可以在处理Inbound数据时生成Outbound数据作为响应,或者在处理Outbound数据时修改Inbound数据的内容。
总结起来,Inbound和Outbound是描述数据在ChannelPipeline中流动方向的概念。Inbound数据是从网络进入应用程序,Outbound数据是从应用程序发送到网络。它们在ChannelPipeline中相互影响和交互,共同实现网络数据的处理和传输。
Pipeline的责任链是通过ChannelHandlerContext对象串联的,ChannelHandlerContext对象里封装了ChannelHandler对象,通过prev和next节点实现双向链表。Pipeline的首尾节点分别是head和tail,当selector轮询到socket有read事件时,将会触发Pipeline责任链,从head开始调起第一个InboundHandler的ChannelRead事件,接着通过fire方法依次触发Pipeline上的下一个ChannelHandler .
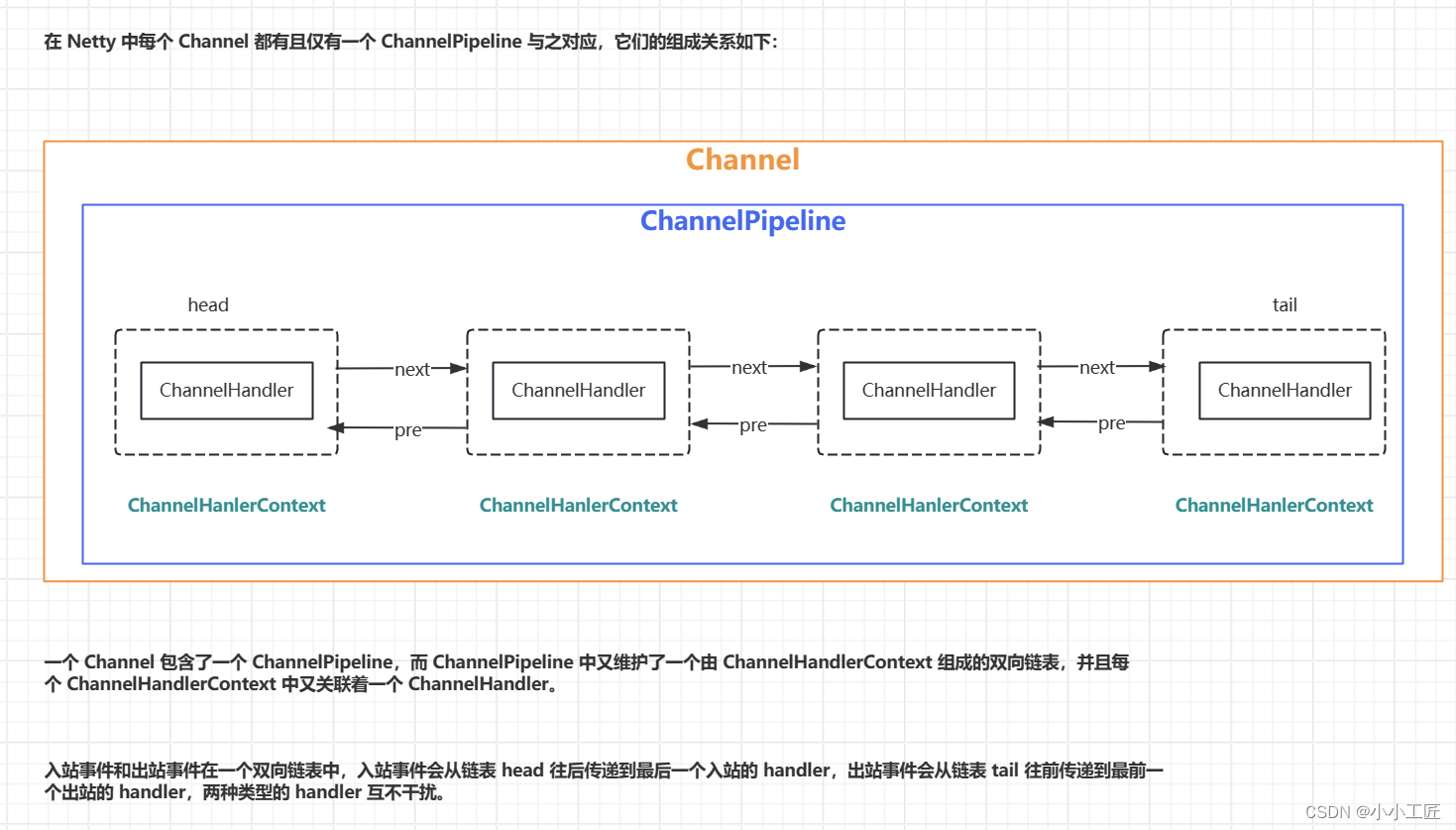
ChannelHandler分为InbounHandler和OutboundHandler
InboundHandler用来处理接收消息OutboundHandler用来处理发送消息。
head的ChannelHandler既是InboundHandler又是OutboundHandler,无论是read还是write都会经过head,所以head封装了unsafe方法,用来操作socket的read和write。tail的ChannelHandler只是InboundHandler,read的Pipleline处理将会最终到达tail
演示之前,我们先附一下代码
Server Code
package com.artisan.pipeline.inout;import com.artisan.pipeline.inout.handler.*;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
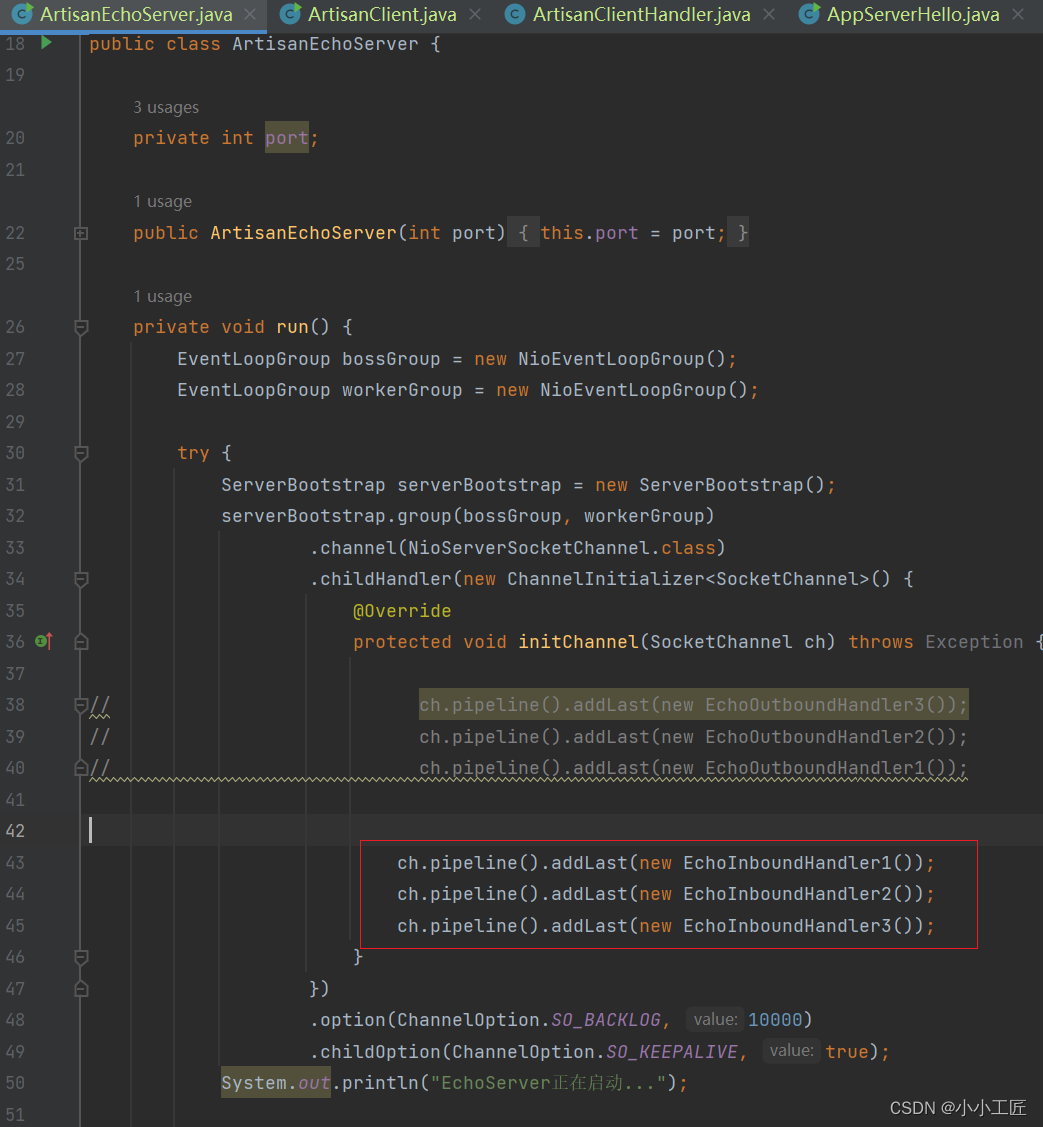
public class ArtisanEchoServer {private int port;public ArtisanEchoServer(int port) {this.port = port;}private void run() {EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoOutboundHandler3());ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoOutboundHandler2());ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoOutboundHandler1());ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoInboundHandler1());ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoInboundHandler2());ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoInboundHandler3());}}).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 10000).childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);System.out.println("EchoServer正在启动...");ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();System.out.println("EchoServer绑定端口:" + port);channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();System.out.println("EchoServer已关闭.");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}public static void main(String[] args) {int port = 1234;if (args != null && args.length > 0) {try {port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}ArtisanEchoServer server = new ArtisanEchoServer(port);server.run();}
}6个handler演示如下
package com.artisan.pipeline.inout.handler;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
public class EchoInboundHandler1 extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {System.out.println();System.out.println("进入 EchoInboundHandler1.channelRead");String data = ((ByteBuf) msg).toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);System.out.println("EchoInboundHandler1.channelRead 收到数据:" + data);ctx.fireChannelRead(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[EchoInboundHandler1] " + data, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));System.out.println("退出 EchoInboundHandler1 channelRead");System.out.println();}@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {System.out.println("[EchoInboundHandler1.channelReadComplete]");}@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {System.out.println("[EchoInboundHandler1.exceptionCaught]" + cause.toString());}
}package com.artisan.pipeline.inout.handler;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
public class EchoInboundHandler2 extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {System.out.println();System.out.println("进入 EchoInboundHandler2.channelRead");String data = ((ByteBuf) msg).toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);System.out.println("EchoInboundHandler2.channelRead 接收到数据:" + data);//ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[第一次write] [EchoInboundHandler2] " + data, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("测试一下channel().writeAndFlush", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));ctx.fireChannelRead(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[ArtisanEchoOutboundHandler2] " + data, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));System.out.println("退出 EchoInboundHandler2 channelRead");System.out.println();}@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {System.out.println("[EchoInboundHandler2.channelReadComplete]读取数据完成");}@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {System.out.println("[EchoInboundHandler2.exceptionCaught]");}
}package com.artisan.pipeline.inout.handler;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
public class EchoInboundHandler3 extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {System.out.println();System.out.println("进入 EchoInboundHandler3.channelRead");String data = ((ByteBuf)msg).toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);System.out.println("EchoInboundHandler3.channelRead 接收到数据:" + data);//ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[第二次write] [EchoInboundHandler3] " + data, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);System.out.println("退出 EchoInboundHandler3 channelRead");System.out.println();}@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {System.out.println("[EchoInboundHandler3.channelReadComplete]读取数据完成");}@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {System.out.println("[EchoInboundHandler3.exceptionCaught]");}}package com.artisan.pipeline.inout.handler;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
public class EchoOutboundHandler1 extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {System.out.println("进入 EchoOutboundHandler1.write");//ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[第一次write中的write]", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("在OutboundHandler里测试一下channel().writeAndFlush", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));ctx.write(msg);System.out.println("退出 EchoOutboundHandler1.write");}}package com.artisan.pipeline.inout.handler;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
public class EchoOutboundHandler2 extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {System.out.println("进入 EchoOutboundHandler2.write");//ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[第二次write中的write]", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));ctx.write(msg);System.out.println("退出 EchoOutboundHandler2.write");}
}package com.artisan.pipeline.inout.handler;import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
public class EchoOutboundHandler3 extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {System.out.println("进入 EchoOutboundHandler3.write");ctx.write(msg);System.out.println("退出 EchoOutboundHandler3.write");}}Client Code
package com.artisan.netty4.client;import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @description: 客户端启动程序* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
public class ArtisanClient {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {NioEventLoopGroup eventExecutors = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {//创建bootstrap对象,配置参数Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();//设置线程组bootstrap.group(eventExecutors)//设置客户端的通道实现类型.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//使用匿名内部类初始化通道.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//添加客户端通道的处理器ch.pipeline().addLast(new ArtisanClientHandler());}});System.out.println("客户端准备就绪");//连接服务端ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 1234).sync();//对通道关闭进行监听channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {//关闭线程组eventExecutors.shutdownGracefully();}}
}package com.artisan.netty4.client;import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;/*** @author 小工匠* @version 1.0* @description: 通用handler,处理I/O事件* @mark: show me the code , change the world*/
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class ArtisanClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {//发送消息到服务端ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("msg send from client 2 server ", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));System.out.println("客户端发消息给服务端结束");System.out.println();}@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {//接收服务端发送过来的消息ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;System.out.println("收到服务端" + ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + "的消息:" + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));}}InboundHandler和OutboundHandler的执行顺序
在InboundHandler中不触发fire方法
ArtisanEchoServer#run 中我们先进存在InboundHandler
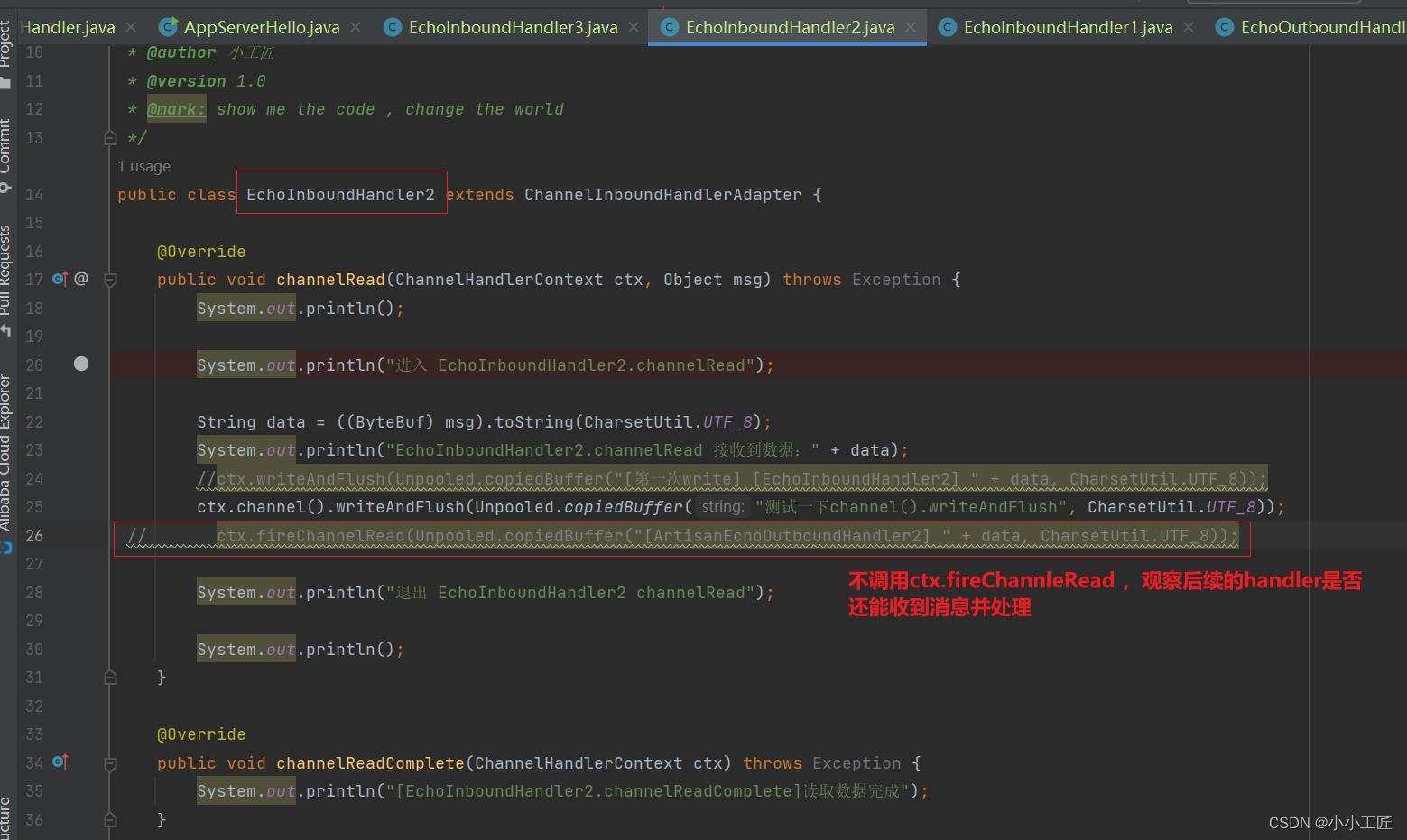
先启动server, 在启动Client,我们测试一下
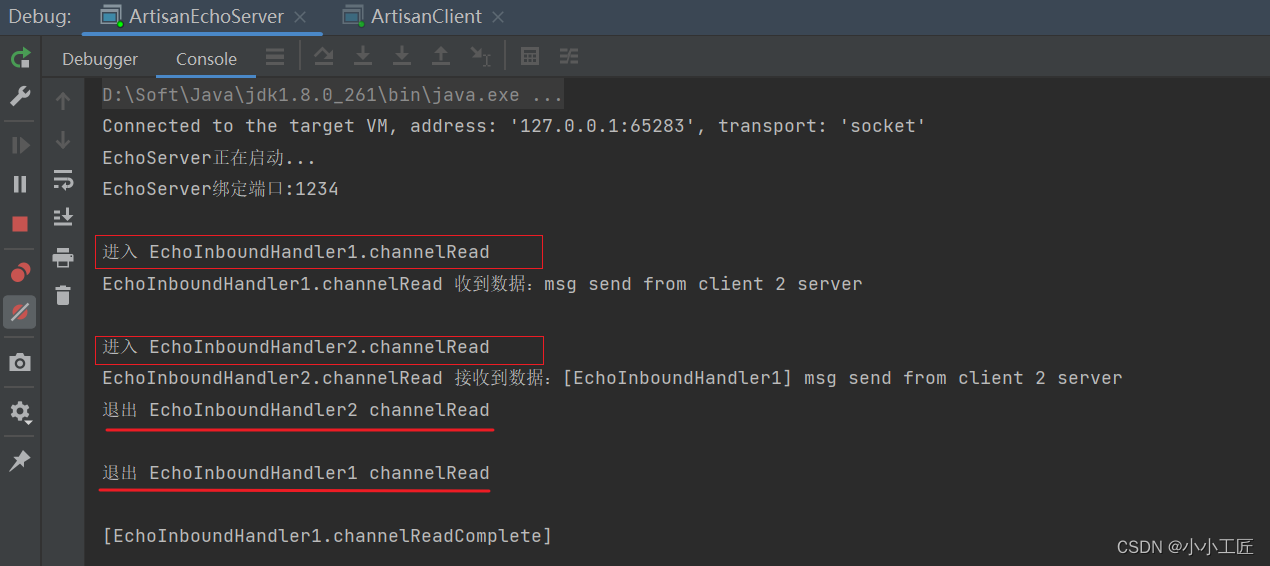
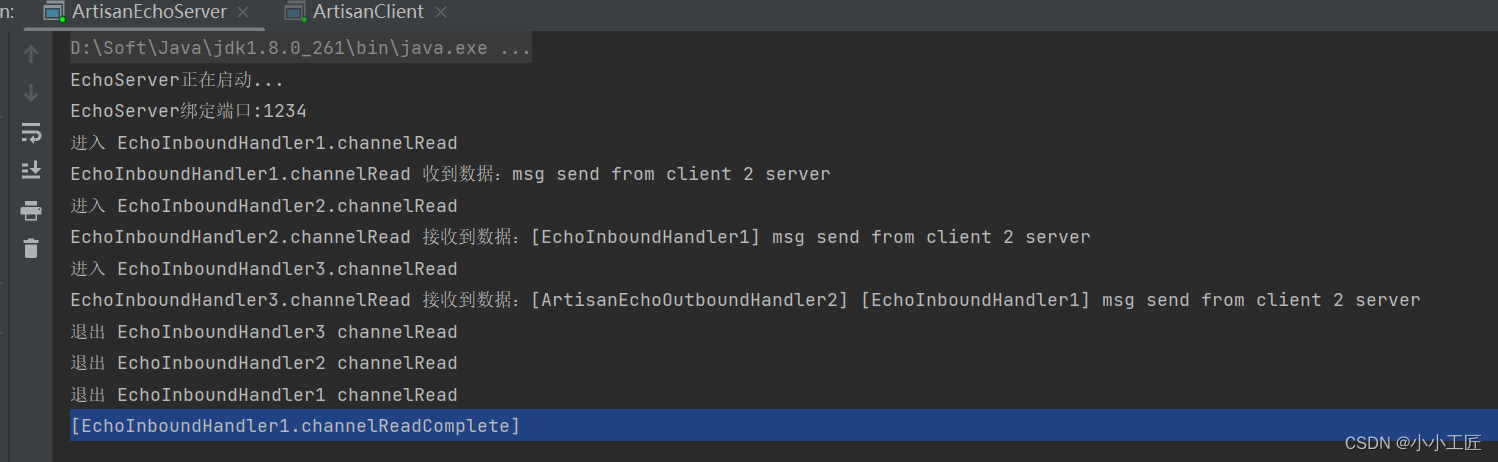
我们可以看到: InboundHandler2没有调用fire事件,InboundHandler3没有被执行
InboundHandler是通过fire事件决定是否要执行下一个InboundHandler,如果InboundHandler没有调用fire事件,那么后续的Pipeline中的Handler将不会执行。
我们来看下源码
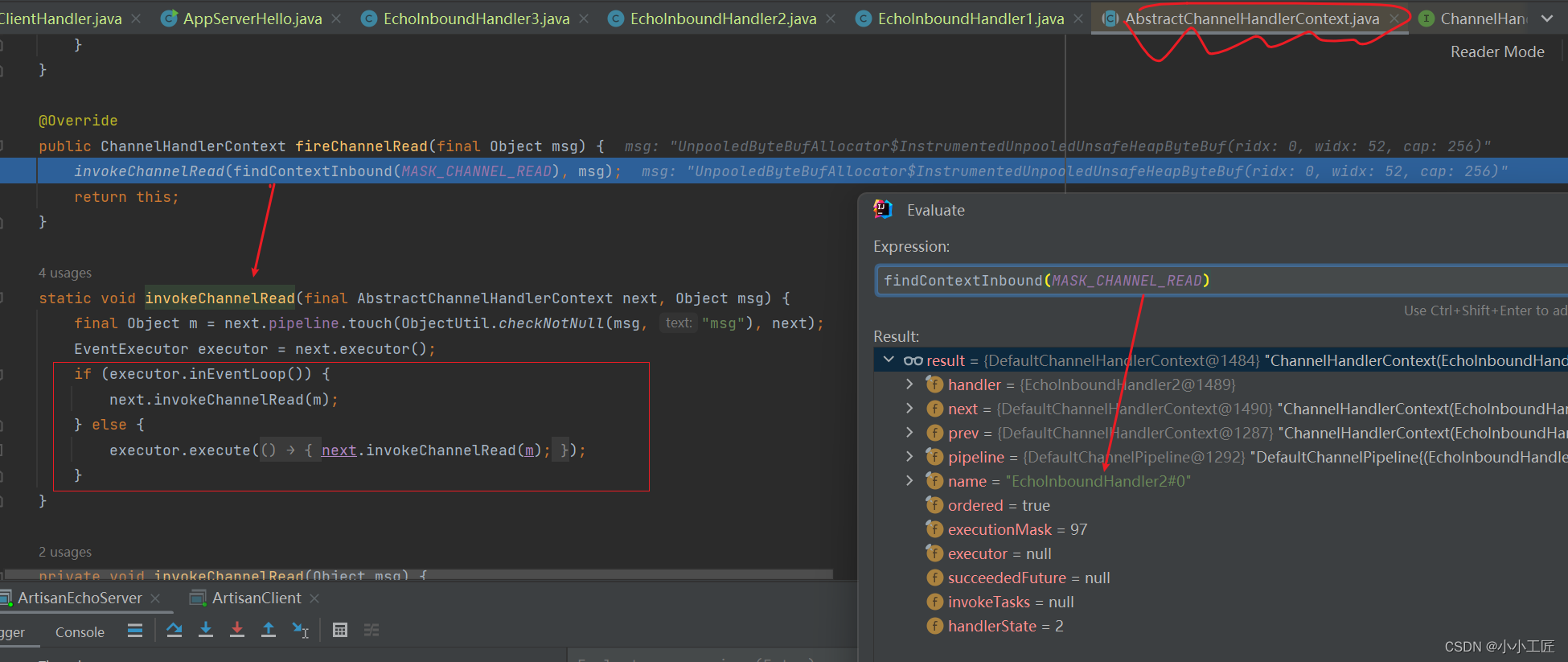
InboundHandler和OutboundHandler的执行顺序
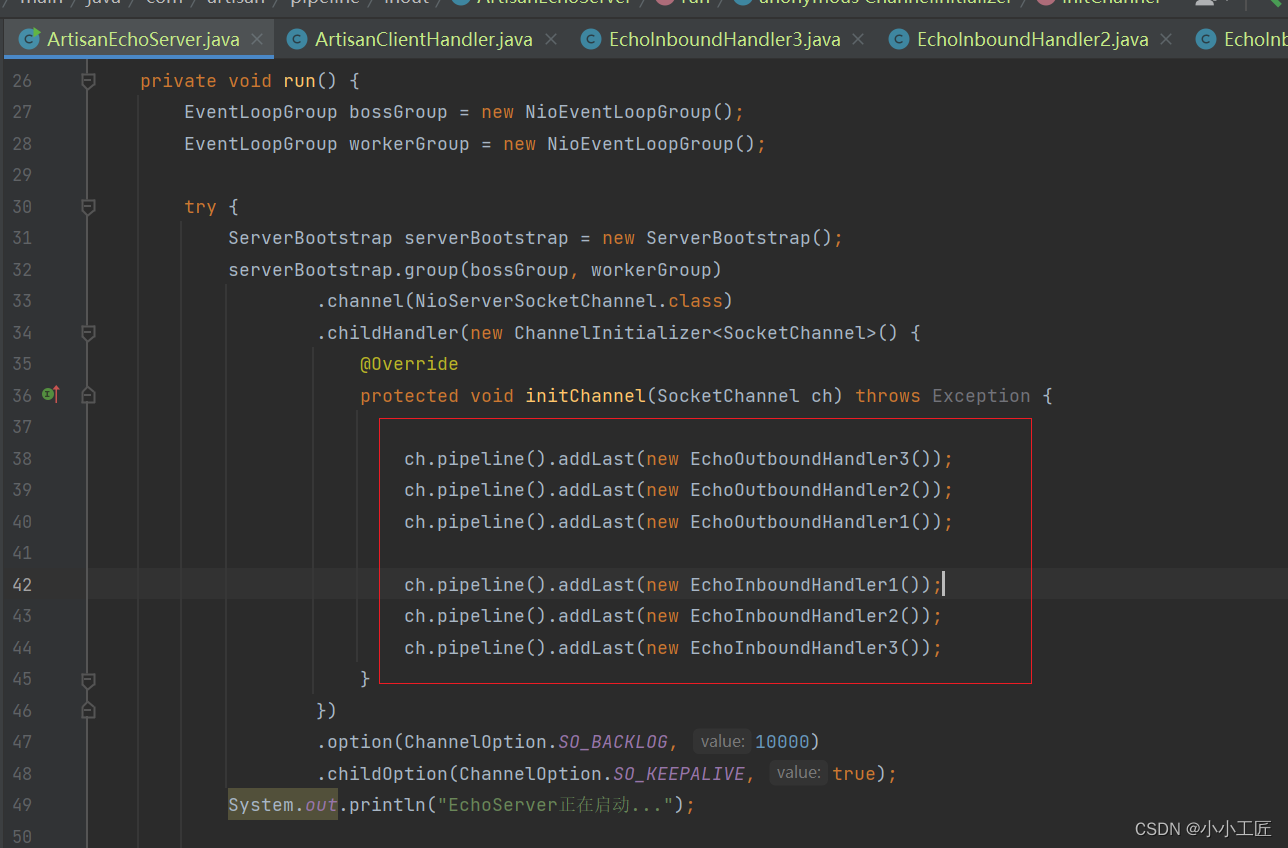
加入Pipeline的ChannelHandler的顺序如上。
别忘了放开EchoInboundHandler2
ctx.fireChannelRead(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[ArtisanEchoOutboundHandler2] " + data, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
我们来验证下
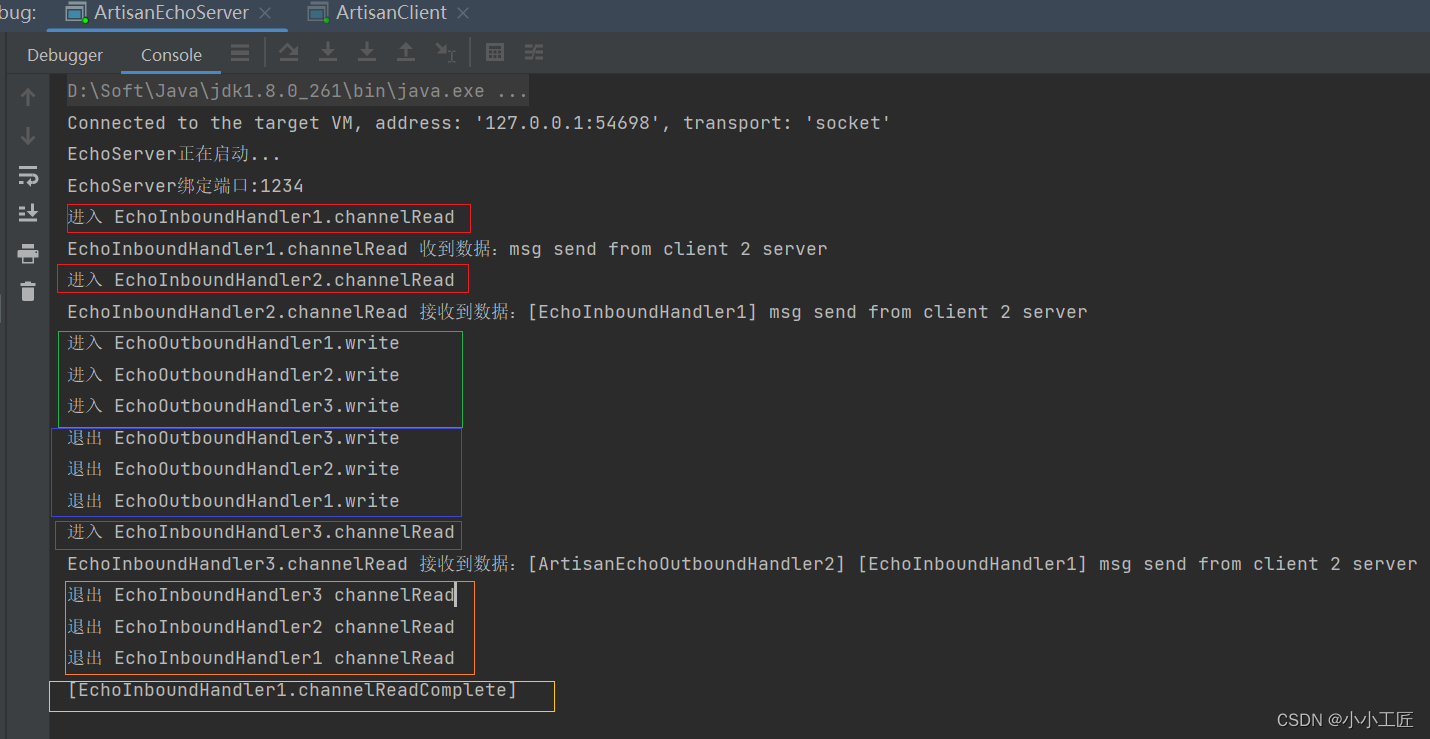
执行顺序如上。
InboundHandler1 => InboundHandler2 => OutboundHandler1 => OutboundHander2 => OutboundHandler3 => InboundHandler3
1、InboundHandler是按照Pipleline的加载顺序,顺序执行。
2、OutboundHandler是按照Pipeline的加载顺序,逆序执行。
如果把OutboundHandler放在InboundHandler的后面,OutboundHandler会执行吗
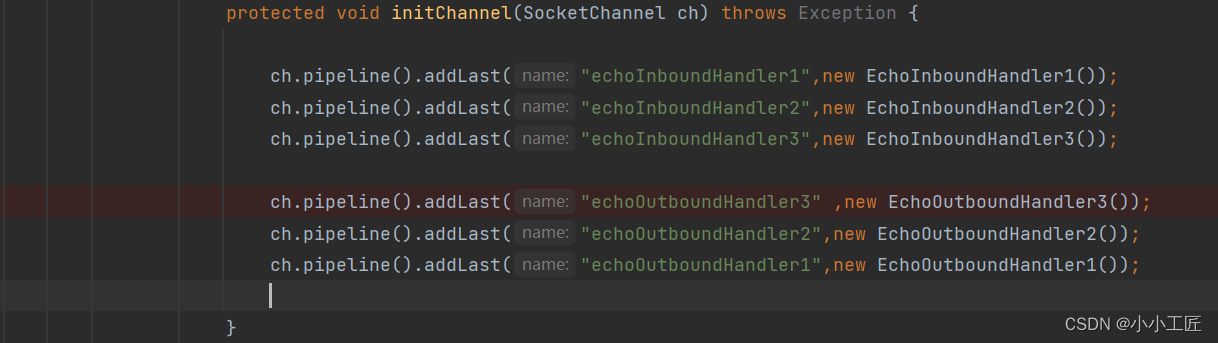
其中EchoInboundHandler2 先不要给客户端发送数据,先屏蔽掉。
public class EchoInboundHandler2 extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {System.out.println("进入 EchoInboundHandler2.channelRead");String data = ((ByteBuf) msg).toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8);System.out.println("EchoInboundHandler2.channelRead 接收到数据:" + data);
// ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[第一次write] [EchoInboundHandler2] " + data, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
// ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("测试一下channel().writeAndFlush", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));ctx.fireChannelRead(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("[ArtisanEchoOutboundHandler2] " + data, CharsetUtil.UTF_8));System.out.println("退出 EchoInboundHandler2 channelRead");}
.......
.......
.......
这篇关于Netty Review - 探索Pipeline的Inbound和Outbound的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!