本文主要是介绍14.(ECMAScript)es8完全解读,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1. 重点提炼
- 2. 异步编程解决方案Async Await
- 3. 对象扩展:Object.values(),Object.entries()
- 3.1 Object.values()
- 3.2 Object.entries()
- 4. 对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()
- 5. 字符串扩展:String.prototype.padStart(),String.prototype.padEnd()
- 5.1 String.prototype.padStart()
- 5.2 String.prototype.padEnd()
- 5.3 应用场景
- 5.3.1 日期格式化
- 5.3.2 数字替换
- 5.3.3 时间戳统一长度
- 6. 尾逗号Trailing commas
1. 重点提炼
async/await- 对象扩展和对象属性描述
- 字符串扩展
- 尾都会
2. 异步编程解决方案Async Await
async和 await是一种更加优雅的异步编程解决方案,是Promise的拓展,如果对 Promise还不了解的话,看一下小迪的 Promise 小结进行学习。
虽然promise可以更好的处理异步的状态,但是有很多请求和异步操作,每个异步操作互相的依赖关系很强的话,其实写起来也非常地繁琐。Async / Await写起来更加语义化并且更加优雅,实际它们是Generator函数的语法糖。
async function foo(){return 'hello' // Promise.resolve('hello')
}
console.log(foo())
async函数返回了一个promise对象,状态是resolveed。
return 'hello' 类似执行 => Promise.resolve('hello')

参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.47
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.47(异步编程解决方案Async Await——async 函数返回值)
tag:a3.47
await后面需要跟异步操作,不然就没有意义,而且await后面的Promise对象不必写then,因为await的作用之一就是获取后面Promise对象成功状态传递出来的参数。
async function foo() {let result = await 'hello'console.log(result)
}
foo()
正常情况下,await后加异步操作,这里的这种写法是不可取的。
hello
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.48
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.48(异步编程解决方案Async Await——await后跟字符串)
tag:a3.48
经典面试题 =>
function timeout() {return new Promise(resolve => {setTimeout(()=>{console.log(1)resolve()}, 1000)})
}async function foo(){timeout()console.log(2)
}
foo()
timeout里是异步操作,因此先去执行主线程的内容。
2
1
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.49
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.49(异步编程解决方案Async Await——经典面试题)
tag:a3.49
需求:等异步操作执行完成后再执行同步操作 =>
function timeout() {return new Promise(resolve => {setTimeout(()=>{console.log(1)resolve()}, 1000)})
}async function foo(){await timeout()console.log(2)
}
foo()
await=> 等待后面的异步操作代码执行完毕,再执行其下面的代码。
虽然Async Await是异步操作,但写法是同步的。
1
2
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.50
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.50(异步编程解决方案Async Await——等异步操作执行完成后再执行同步操作)
tag:a3.50
Promise操作,可以利用resolve传递成功的返回值给await前的变量。
await执行的时候,下面两行代码都不会执行,必须等到其异步代码执行完毕才行。
function timeout() {return new Promise(resolve => {setTimeout(()=>{resolve(1)}, 1000)})
}async function foo(){const res = await timeout()console.log(res)console.log(2)
}
foo()
1
2
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.51
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.51(异步编程解决方案Async Await——Promise操作,可以利用resolve传递成功的返回值给await前的变量)
tag:a3.51
异步操作失败的情况下,如何通过Async Await去处理?
timeout返回的是promise对象,因此可以直接利用then,如果是错误则用catch捕获。
在async函数中使用await,那么await这里的代码就会变成同步的了,意思就是说只有等await后面的Promise执行完成得到结果才会继续下去,await就是等待。
function timeout() {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {reject('fail')}, 1000)})
}
async function foo() {return await timeout()
}
foo().then(res => {console.log(res);
}).catch(err => {console.log(err)
})
fail
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.52
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.52(异步编程解决方案Async Await——利用then和catch获取结果)
tag:a3.52
发送ajax请求,使用async和await更为优雅!
es-demo\src\ajax.js
function ajax(url, callback) {// 1、创建XMLHttpRequest对象var xmlhttpif (window.XMLHttpRequest) {xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest()} else { // 兼容早期浏览器xmlhttp = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP')}// 2、发送请求xmlhttp.open('GET', url, true)xmlhttp.send()// 3、服务端响应xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {if (xmlhttp.readyState === 4 && xmlhttp.status === 200) {var obj = JSON.parse(xmlhttp.responseText)// console.log(obj)callback(obj)}}
}
export default ajax
es-demo\src\3-1.js
import ajax from './ajax'function request(url) {return new Promise(resolve => {ajax(url, res => {resolve(res)})})
}
async function getData(){const res1 = await request('static/a.json')console.log(res1)const res2 = await request('static/b.json')console.log(res2)const res3 = await request('static/c.json')console.log(res3)
}
getData()
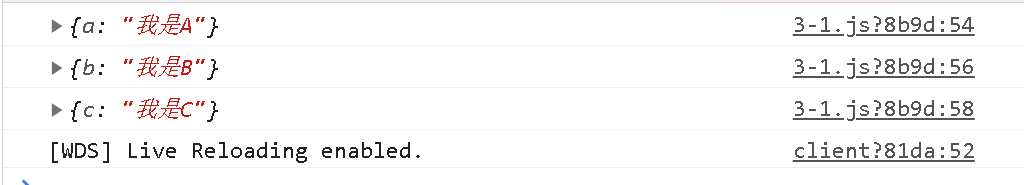
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.53
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.53(异步编程解决方案Async Await——发送ajax请求,使用async和await)
tag:a3.53
注意
await只能在async标记的函数内部使用,单独使用会触发Syntax error。
3. 对象扩展:Object.values(),Object.entries()
Object.values()Object.entries()
之前的语法如何获取对象的每一个属性值
获取对象中的value,Object.keys获取所有的key(数组类型),利用map遍历,map返回一个新的数组。
const obj = {name: 'baidu',web: 'www.baidu.com',target: 'es'
}
console.log(Object.keys(obj))
const res = Object.keys(obj).map(key => obj[key])
console.log(res)

参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.54
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.54(对象扩展:Object.values(),Object.entries()——之前获取对象中的value的方式)
tag:a3.54
ES8中对象扩展补充了两个静态方法,用于遍历对象:Object.values(),Object.entries()
3.1 Object.values()
Object.values() 返回一个数组,其元素是在对象上找到的可枚举属性值。属性的顺序与通过手动循环对象的属性值所给出的顺序相同(for...in,但是for...in还会遍历原型上的属性值)。
Object.values => 返回对象对应的value数组
const obj = {name: 'ls',web: 'www.ls.com',course: 'es'
}console.log(Object.values(obj))
// ["ls", "www.ls.com", "es"]
note
Object.values是在对象上找到可枚举的属性的值,所以只要这个对象是可枚举的就可以,不只是{}这种形式。
3.2 Object.entries()
Object.entries()方法返回一个给定对象自身可枚举属性的键值对数组,其排列与使用 for...in循环遍历该对象时返回的顺序一致。(区别在于 for-in循环也枚举原型链中的属性)
let grade = {'lilei': 98,'hanmei': 87
}for (let [key, value] of grade) {console.log(key, value) // Uncaught TypeError: grade is not iterable
}
我们知道 Object 是不可直接遍历的,上述代码足以说明直接遍历触发了错误。如果使用 Object.entries()则可以完成遍历任务。
let grade = {'lilei': 98,'hanmei': 87
}for (let [k, v] of Object.entries(grade)) {console.log(k, v)// lilei 98// hanmei 87
}

Object.entries => 返回二维数组,它的每一项又是一个数组,数组的第一项代表key,第二项代表value
for…of 搭配 Object.entries => 遍历key与 value
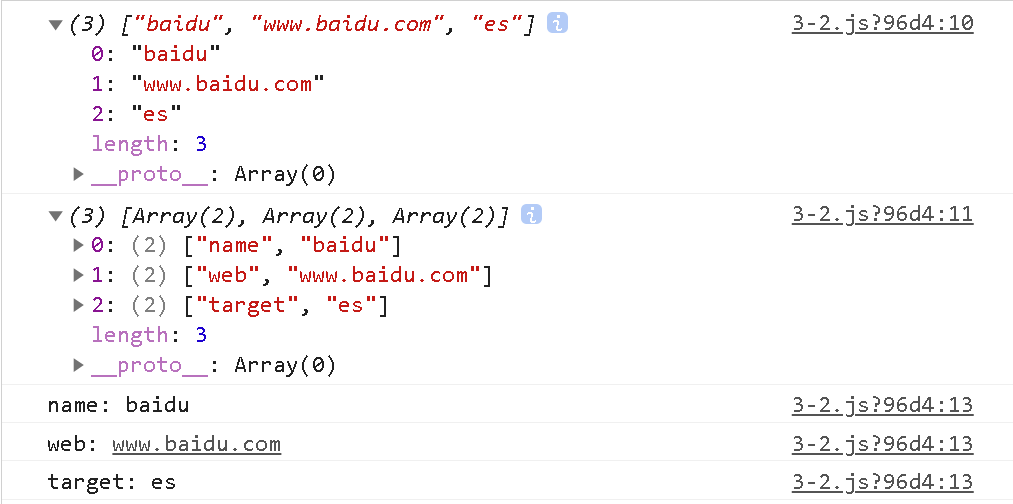
const obj = {name: 'baidu',web: 'www.baidu.com',target: 'es'
}console.log(Object.values(obj))
console.log(Object.entries(obj))
for(let [key, val] of Object.entries(obj)){console.log(`${key}: ${val}`)
}
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.55
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.55(对象扩展:Object.values(),Object.entries()——基本使用)
tag:a3.55
Object.entries参数是数组,也返回一个二维数组,第一个对应索引,第二个对应value。但一般都是传对象,没必要传数组。
console.log(Object.entries(['a', 'b', 'c']))

参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.56
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.56(对象扩展:Object.values(),Object.entries()——Object.entries传数组)
tag:a3.56
4. 对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()=> 获取对象自身所有的描述符valuewritableconfigurableenumerable
const data = {Portland: '78/50',Dublin: '88/52',Lima: '58/40'
}
这里有 key和 value,上边的代码把所有的 key、value遍历出来,如果我们不想让 Lima这个属性和值被枚举怎么办?
Object.defineProperty(data, 'Lima', {enumerable: false
})Object.entries(data).map(([city, temp]) => {console.log( `City: ${city.padEnd(16)} Weather: ${temp}` )// City: Portland Weather: 78/50// City: Dublin Weather: 88/52
})
补充 => String.prototype.padEnd()
方法会用一个字符串填充当前字符串(如果需要的话则重复填充),返回填充后达到指定长度的字符串。从当前字符串的末尾(右侧)开始填充。
const str1 = 'Breaded Mushrooms';console.log(str1.padEnd(25, '.'));
// expected output: "Breaded Mushrooms........"const str2 = '200';console.log(str2.padEnd(5));
// expected output: "200 "
很成功,Lima没有被遍历出来,那么 defineProperty 的第三个参数就是描述符(descriptor)。这个描述符包括几个属性:
value[属性的值(默认值)]writable[属性的值是否可被改变]enumerable[属性的值是否可被枚举,是否能通过for…in进行遍历]configurable[描述符本身是否可被修改,属性是否可被删除,能否用delete运算符删除该属性]
这个是获取对象指定属性的描述符,如果想获取对象的所有属性的描述符: => Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors
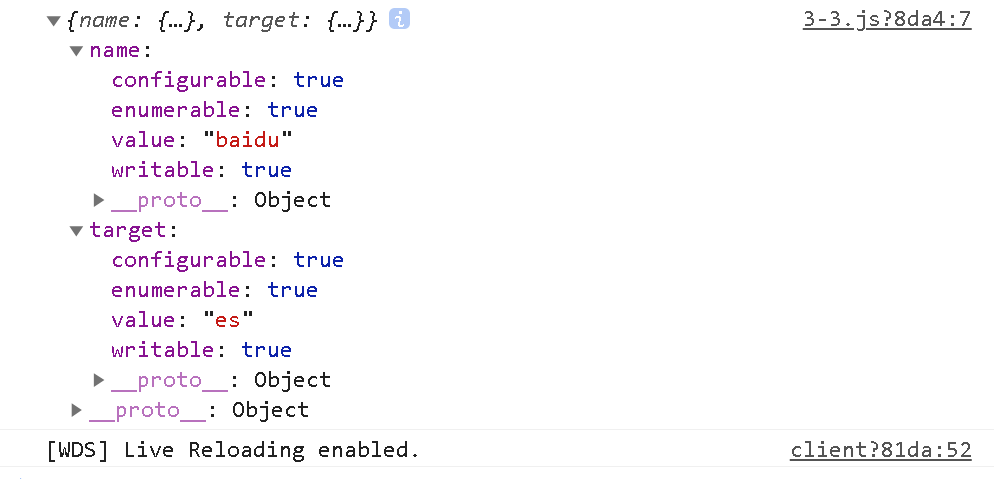
const obj = {name: 'baidu',target: 'es'
}const desc = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj)
console.log(desc)
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.57
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.57(对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()——基本使用)
tag:a3.57
这四个属性如何设置上去,可通过defineProperty。
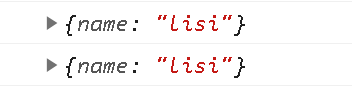
const obj = {}
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'name', {value: 'lisi',writable: false,configurable: false,enumerable: false
})console.log(obj)
obj.name = 'zhangsan'
console.log(obj)
writable为false,则不可写。
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.58
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.58(对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()——writable 为false,则不可写。)
tag:a3.58
const obj = {}
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'name', {value: 'lisi',writable: true,configurable: false,enumerable: false
})console.log(obj)
obj.name = 'zhangsan'
console.log(obj)writable为true,则可写。

参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.59
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.59(对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()——writable 为true,则可写。)
tag:a3.59
const obj = {}
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'name', {value: 'lisi',writable: true,configurable: false,enumerable: false
})console.log(obj)
obj.name = 'zhangsan'
console.log(obj)
delete obj.name
console.log(obj)
configurable为false,则属性不可被delete。

参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.60
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.60(对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()——configurable为false,则属性不可被delete。)
tag:a3.60
const obj = {}
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'name', {value: 'lisi',writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: false
})console.log(obj)
obj.name = 'zhangsan'
console.log(obj)
delete obj.name
console.log(obj)
configurable为true,则属性可被delete。

参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.61
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.61(对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()——configurable为true,则属性可被delete。)
tag:a3.61
const obj = {}
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'name', {value: 'lisi',writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: false
})
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'age', {value: 34,writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: true
})
for(let key in obj){console.log(key)
}
enumerable为true才可遍历。
age
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.62
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.62(对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()——enumerable为true才可遍历。)
tag:a3.62
const obj = {}
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'name', {value: 'lisi',writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: false
})
Reflect.defineProperty(obj, 'age', {value: 34,writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: true
})
for(let key in obj){console.log(key)
}
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj))
console.log(getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, 'age'))
getOwnPropertyDescriptor=> 获取单个属性的描述。

参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.63
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.63(对象属性描述: Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()——getOwnPropertyDescriptor => 获取单个属性的描述。)
tag:a3.63
5. 字符串扩展:String.prototype.padStart(),String.prototype.padEnd()
在 ES8中 String新增了两个实例函数 String.prototype.padStart 和 String.prototype.padEnd,允许将空字符串或其他字符串添加到原始字符串的开头或结尾。
- String.prototype.padStart()
- String.prototype.padEnd()
5.1 String.prototype.padStart()
把指定字符串填充到字符串头部,返回新字符串。
str.padStart(targetLength [, padString])
| 参数 | 含义 | 必选 |
|---|---|---|
| targetLength | 目标字符要保持的长度值 | Y |
| padString | 如果目标字符的长度不够需要的补白字符,默认为空 | N |
str.padStart 对应两个参数 => 在开始的位置填充字符串
第1个参数是需要填充的目标长度,即填充之后字符串的长度
第2个参数是可选的,即填充的字符串,如果省略,则用空格填充。
padEnd 则与之相反,是末尾填充
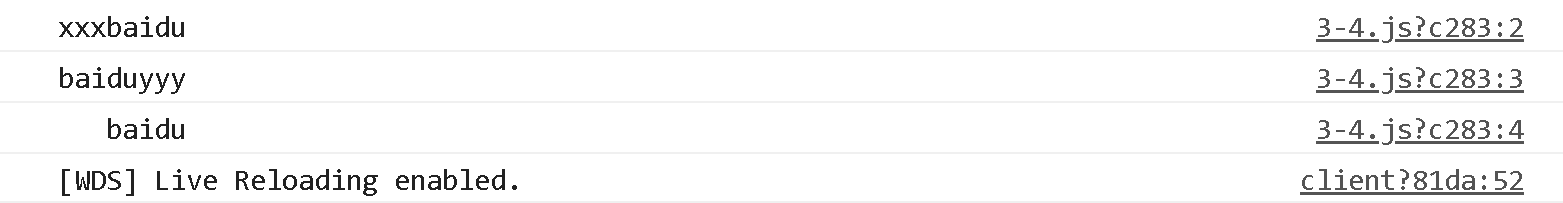
const str = 'baidu'
console.log(str.padStart(8, 'x'))
console.log(str.padEnd(8, 'y'))
console.log(str.padStart(8))
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.64
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.64(字符串扩展:String.prototype.padStart(),String.prototype.padEnd()——基本使用)
tag:a3.64
5.2 String.prototype.padEnd()
方法会用一个字符串填充当前字符串(如果需要的话则重复填充),返回填充后达到指定长度的字符串。从当前字符串的末尾(右侧)开始填充。
str.padEnd(targetLength [, padString])
| 参数 | 含义 | 必选 |
|---|---|---|
| targetLength | 目标字符要保持的长度值 | Y |
| padString | 如果目标字符的长度不够需要的补白字符,默认为空 | N |
const str1 = 'I am learning es in csdn'
console.log(str1.padEnd(30, '.'))
// I am learning es in csdn.....const str2 = '200'
console.log(str2.padEnd(5))
// "200 "
5.3 应用场景
5.3.1 日期格式化
输出日期 => yyyy-mm-dd 2020-04-01
Date.getMonth 返回的是月份,0~11,因此需要加1,并且个位数需要补0
Date.getDate
const now = new Date()
const year = now.getFullYear()
const month = (now.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2, '0') // 0~11
const day = (now.getDate()).toString().padStart(2, '0')
console.log(`${year}-${month}-${day}`)
2020-11-01
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.65
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.65(字符串扩展:String.prototype.padStart(),String.prototype.padEnd()——应用场景-拼接日期)
tag:a3.65
5.3.2 数字替换
如平时经常需要仅显示手机号或者身份证号的后四位,前面全部用星号代替。
const tel = '13012345678'
const newTel = tel.slice(-4).padStart(tel.length, '*')
console.log(newTel)

参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.66
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.66(字符串扩展:String.prototype.padStart(),String.prototype.padEnd()——应用场景-仅显示手机号或者身份证号的后四位,前面全部用星号代替)
tag:a3.66
5.3.3 时间戳统一长度
时间戳是13位的,固定单位是毫秒ms
有的时候时间戳是后端生成的,后端把时间戳返回过来,它返回的是以秒为单位的,即10位,这个时候需要补000。
console.log(new Date().getTime()) // 13位 ms
timestamp.padEnd(13, '0') // 伪代码
6. 尾逗号Trailing commas
ES8 允许函数的最后一个参数有尾逗号(Trailing comma)。
此前,函数定义和调用时,都不允许最后一个参数后面出现逗号。
- 允许函数参数列表使用尾逗号
定义函数时候,但最后一个参数定义完以后,再最后多写一个逗号。
开发时可能使用代码格式化工具格式化如下,实际作用就是多人开发使用git代码管理工具,追加一个参数,只需要修改一行即可,否则得添加逗号改两行。
function foo(a,b,c,
) {console.log(a, b, c)
}foo(4, 5, 6, )
4 5 6
这样的规定也使得,函数参数与数组和对象的尾逗号规则,保持一致了。
参考:https://github.com/6xiaoDi/blog-ECMScript-Series/tree/a3.67
Branch: branch02commit description:a3.67(尾逗号Trailing commas)
tag:a3.67
(后续待补充)
这篇关于14.(ECMAScript)es8完全解读的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







