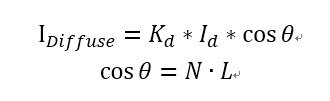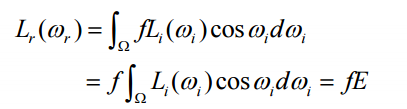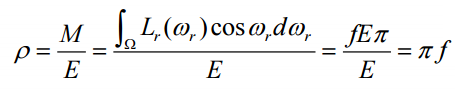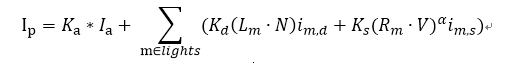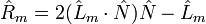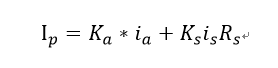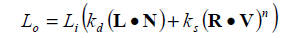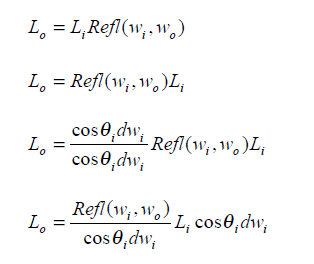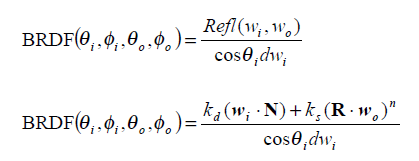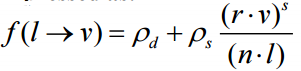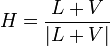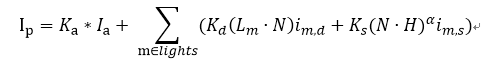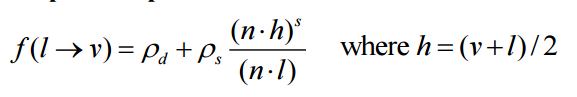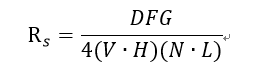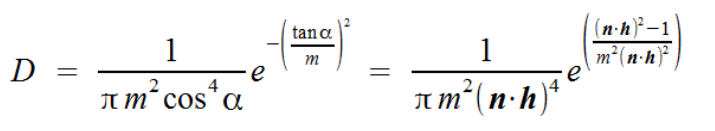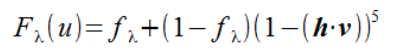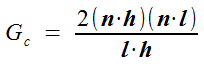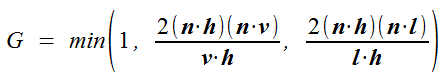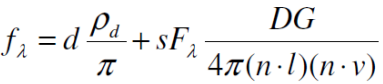本文主要是介绍局部光照模型及其BRDF,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
提要
常见的光照模型一般包括四个部分ambient, diffuse, specular, 和emitted light. 即:
vertex color = ambient + diffuse + specular + emitted light
当有多个光源的时候,最后的颜色就是多个结果的叠加。
对BRDF不熟悉的移步 基于BRDF的光照模型。
Ambient light:环境光,通常定义在光源的中,注意每个光源的衰减量。
Diffuse:漫反射部分,光照找到物体的表面,由于物体的表面凹凸不平而反射到各个方向的光。
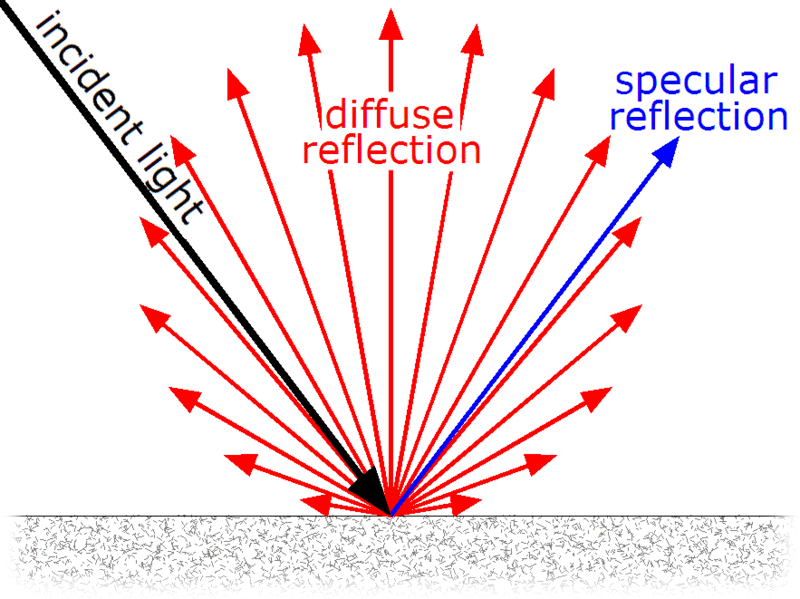
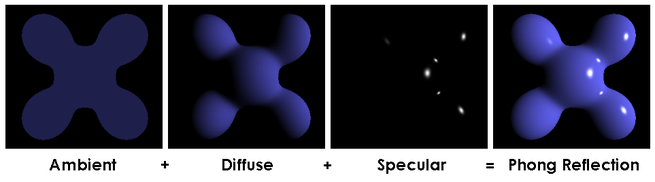
Specular :相比于漫反射,一道入射光通过镜面反射只产生一个方向的Specular,遵循反射法则,即入射角和出射角相同。Diffuse和Specular的区别可以参考下面的图。
Emittion:物体的自发光。
Lambert光照模型
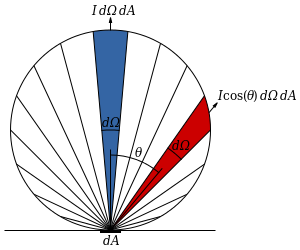
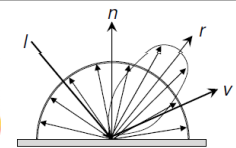
Lambert光照模型用于纯粹的漫反射表面的物体,比如磨砂的玻璃表面,观察者的所看到的反射光和观察的角度无关,这样的表面称为Lambertian。高端一点的说法就是他表面的亮度是各向同性的,亮度的计算遵循 Lambert's cosine 法则,何为 Lambert's cosine 法则, 看下图:
具体描述如下:一束光照在理想漫反射的物体表面,光照强度的变化由入射光线和物体表面法线的夹角决定。
在具体计算的时候,用到的公式是
Kd表示物体表面漫反射属性,Id表时入射光强。N表示入射点单位法向量,L表示从入射点指向光源的单位向量(注意是入射点指向光源,表示了入射光的方向),单位化之后相乘就得到了夹角的余弦值。在Unity中用Shader实现一下。
Shader "Custom/Lambert" {Properties {_MainTex ("Base (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}}SubShader {Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }LOD 200CGPROGRAM#pragma surface surf Lambsampler2D _MainTex;inline fixed4 LightingLamb (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, fixed atten){float diff = dot(s.Normal, lightDir);fixed4 c;c.rgb = (s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * diff) ;c.a = 1.0;return c;}struct Input {float2 uv_MainTex;};void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {half4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex);o.Albedo = c.rgb;o.Alpha = c.a;}ENDCG} FallBack "Diffuse"
}
BRDF
反射光在各个方向的量都是一样的,所以光照方程如下
反射量的求法如下
Phong光照模型
对于漫反射的物体表面,使用Lambert就足够,但是实际生活中并不存在这种理想的漫反射材质,所有Bui Tuong Phong这个家伙就提出了Phong模型。如下图
最终的光照结果由Ambient环境光,Diffuse漫反射,Specular高光组成,下面来看下详细的计算过程,首先定义下面几个变量。
is表示光源的高光强度,id表示光源的漫反射强度。
Ks 材质的高光反射系数,Kd 材质的漫反射系数,Ka 环境光反射系数,α 材质反射常数,表示物体表面镜面的程度。
光照的场景如下图
对于一个灯光m
Lm 表示从表面射向光源的向量;
N 表示表面的法线方向;
Rm 表示光线的按照反射定律得出的出射光线;
V 表示从表面射向人眼的向量。
有了这些量,就可以对光照进行求解了,
其中反射光线的方向需要进行求解
还是用shader实现一遍
Shader "Custom/Phong" {Properties {_MainTint ("Diffuse Tint", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_MainTex ("Base (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}_SpecularColor ("Specular Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_SpecularPower ("Specular Power", Range(0, 30)) = 1}SubShader {Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }LOD 200CGPROGRAM#pragma surface surf Phongfloat4 _MainTint;sampler2D _MainTex;float4 _SpecularColor;float _SpecularPower;inline fixed4 LightingPhong (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, half3 viewDir, fixed atten){float diff = dot(s.Normal, lightDir);float3 reflectionVector = normalize(2.0 * s.Normal * diff - lightDir);float spec = pow(max(0, dot(reflectionVector, viewDir)), _SpecularPower);float3 finalSpec = _SpecularColor * spec;fixed4 c;c.rgb = (s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * diff) + (_LightColor0.rgb * finalSpec);c.a = 1.0;return c;}struct Input { float2 uv_MainTex; }; void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {half4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex);o.Albedo = c.rgb;o.Alpha = c.a;}ENDCG} FallBack "Diffuse"
}
基本上不算太复杂(只有diffuse 和 specular ,ambient是常数,先忽略)的光照模型的Render Equation(单个点光源)都可以写为
其中 Rs 称为Specular term,不同的光照模型对应于不同的Rs.
BRDF
Phong模型的BRDF示意图如下
在单个光源的情况下,光照方程可以改写为
接下来进行推导
最后得出BRDF
或者写成
Blin-Phong光照模型
这个模型就座位Phong光照模型的改进,在表现上基本与Phong模型一致,但是性能上却优化了很多。主要是在计算specular分项的时候将 Rm•V 换成了 N•H 。H也需要计算,但简单了非常多。
则光照的计算公式就变成了
在shader中只要在上面的基础上稍微修改一下就可以了
inline fixed4 LightingPhong (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, half3 viewDir, fixed atten)
{float diff = dot(s.Normal, lightDir);float3 halfVector = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);float spec = pow(max(0, dot(halfVector, s.Normal)), _SpecularPower);float3 finalSpec = _SpecularColor * spec;fixed4 c;c.rgb = (s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * diff) + (_LightColor0.rgb * finalSpec);c.a = 1.0;return c;
}BRDF
只是在Phong上做了一点修改
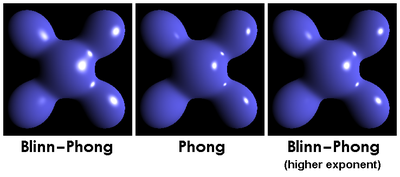
结果对比
Wiki上的对比结果
(所谓Higher exponent是将材质的反光系数乘以了4倍,这样看起来更加接近原始的phong计算出来的结果)
Unity中的对比结果
Cook Torrance
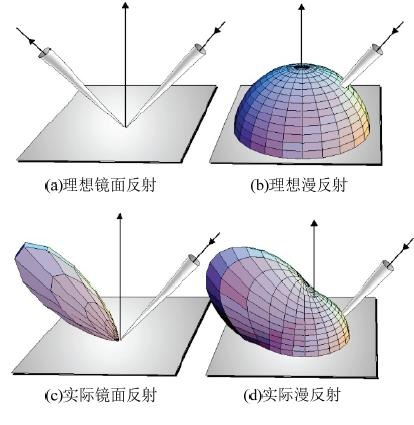
上面说说的三种模型都只能运用在理想的材质下,要么理想漫反射,要么理想镜面反射,这样渲染出来的物体就很假,真实的情况是漫反射和镜面反射都需要依据材质特征和物体表面微平面特征。 下图 是实际漫反射、镜面反射与理想漫反射、镜面反射的示意图。
Cook-Torrance 光照模型将物体粗糙表面( rough surface )看作由很多微小平面(微平面)组成,每一个微平面都被看作一个理想的镜面反射体,物体表面的粗糙度由微平面斜率的变化来衡量。一个粗糙表面由一系列斜率变化很大的微平面组成,而在相对平滑的表面上微平面斜率变化较小。
对于Cook-Torrance 光照模型,其Rs的计算公式为
V,H,L和上面介绍的一致,这里主要说一下DFG
D - microfacet distribution ,微平面分布系数,计算公式如下
F - fresnel factor,菲涅尔系数,主要用于定义菲涅尔反射,计算公式如下
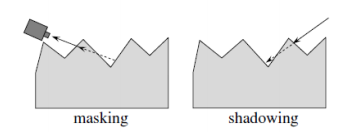
G - Geometrical attenuation ,几何衰减系数,衡量微平面自身遮蔽光强的影响,介于0到1之间。
光射到物体微表面上,会出现三种情况,
a.光被完全反射
G=1
b.一些光在反射后被阻挡
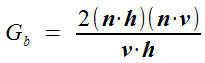
c.一些光在到达其它微面前被阻挡
则最终G的取值为
在Unity里实践一下,
Shader "CookbookShaders/Chapter03/MetallicSoft"
{Properties {_MainTint ("Diffuse Tint", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_MainTex ("Base (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}_RoughnessTex ("Roughness texture", 2D) = "" {}_Roughness ("Roughness", Range(0,1)) = 0.5_SpecularColor ("Specular Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)_SpecPower ("Specular Power", Range(0,30)) = 2_Fresnel ("Fresnel Value", Range(0,1.0)) = 0.05}SubShader {Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }LOD 200CGPROGRAM#pragma surface surf MetallicSoft#pragma target 3.0sampler2D _MainTex;sampler2D _RoughnessTex;float _Roughness;float _Fresnel;float _SpecPower;float4 _MainTint;float4 _SpecularColor;inline fixed4 LightingMetallicSoft (SurfaceOutput s, fixed3 lightDir, half3 viewDir, fixed atten){//Compute simple diffuse and view direction valuesfloat3 halfVector = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);float NdotL = saturate(dot(s.Normal, normalize(lightDir)));float NdotH_raw = dot(s.Normal, halfVector);float NdotH = saturate(dot(s.Normal, halfVector));float NdotV = saturate(dot(s.Normal, normalize(viewDir)));float VdotH = saturate(dot(halfVector, normalize(viewDir)));//Micro facets distributionfloat geoEnum = 2.0*NdotH;float3 G1 = (geoEnum * NdotV)/NdotH;float3 G2 = (geoEnum * NdotL)/NdotH;float3 G = min(1.0f, min(G1, G2));//Sample our Spceular look up BRDFfloat roughness = tex2D(_RoughnessTex, float2(NdotH_raw * 0.5 + 0.5, _Roughness)).r;//Create our custom fresnel valuefloat fresnel = pow(1.0-VdotH, 5.0);fresnel *= (1.0 - _Fresnel);fresnel += _Fresnel;//Create the final specfloat3 spec = float3(fresnel * G * roughness * roughness) * _SpecPower;float4 c;c.rgb = (s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * NdotL)+ (spec * _SpecularColor.rgb) * (atten * 2.0f);c.a = s.Alpha;return c;}struct Input {float2 uv_MainTex;};void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {half4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex) * _MainTint;o.Albedo = c.rgb;o.Alpha = c.a;}ENDCG} FallBack "Diffuse"
}
代码里面用纹理来代替D的计算,结果如下
BRDF
参考
Lambertian reflectance wiki - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lambertian_reflectance
Lambert's cosine law wiki - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lambert%27s_cosine_law
Phong reflection model wiki - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phong_reflection_model
Blinn–Phong shading model wiki - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blinn%E2%80%93Phong_shading_model
基于CPU实现的Cook-Torrance光照模型(Cg语言实现)- http://blog.csdn.net/liu_lin_xm/article/details/4845977
清华大学图形学公开课-http://cg.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/course/resource.htm
这篇关于局部光照模型及其BRDF的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!