本文主要是介绍Gate学习2续——Defining a geometry(定义几何体),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
上一部分已经介绍了构建世界world、创建一个几何体对象volume,接下来的内容有:重复这个新建的volume、放置这个volume、移动这个volume以及最后更新创建的几何对象。
三、重复新建的Volume——Repeating a Volume
要创建x个相同的volume,不需要逐个去创建x个volume。只需要先创建一个volume,然后重复这个volume x次。有四种不同的重复体积的方法:线性重复、环形重复、立方阵列重复和象限重复。
列出为 volume( Name_Volume)定义的重复器:
/gate/Name_Volume/repeaters/info1、线性重复——linear
线性重复适合沿一个方向(X、Y或Z轴)重复一个Volume,步骤
• 首先选择合适的重复方式
• 然后确定重复数量N
• 再确定重复方向
/gate/Name_Volume/repeaters/insert linear #选用线性重复方式
/gate/Name_Volume/linear/setRepeatNumber N #Name_Volume重复的次数N
/gate/Name_Volume/linear/setRepeatVector 0. 0. dZ. mm #定义了沿Z方向步长为dZ mm进行重复
/gate/Name_Volume/linear/autoCenter true or false“true”选项将一组重复的volume集中在已重复的初始卷的位置。
“false”选项将第一个重复volume围绕初始volume位置。其他重复体补偿创建。默认选项为true。
示例:
/gate/hole/repeaters/insert linear
/gate/hole/linear/setRepeatNumber 12
/gate/hole/linear/setRepeatVector 0. 4. 0. cm#将volume沿Y轴每4cm重复1次,共12次。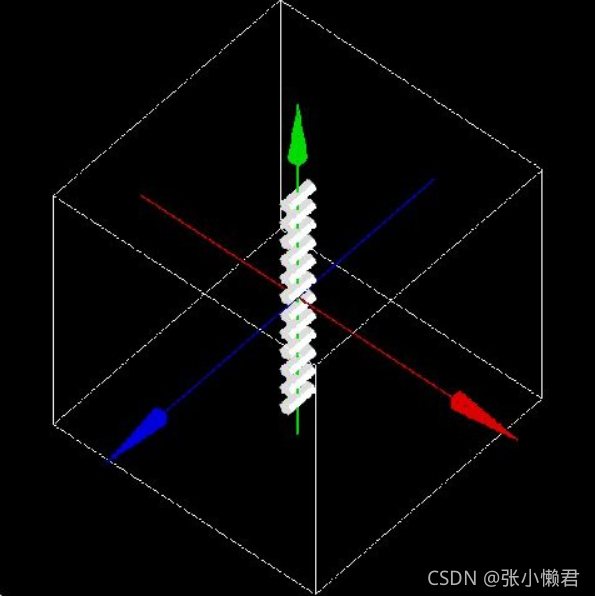
2、环形重复——ring
环形重复方法使沿环形重复volume成为可能,在PET中建立环形探测器是很有用的。
/gate/Name_Volume/repeaters/insert ring #选择环状重复方式
/gate/Name_Volume/ring/setRepeatNumber N #定义卷Name_Volume的重复次数/gate/Name_Volume/ring/setPoint1 0. 1. 0. mm #指定两点来确定环形重复的轴
/gate/Name_Volume/ring/setPoint2 0. 0. 0. mm #默认的重复轴是Z轴,默认的环形重复是逆时针的#以上四行命令足以实现沿环形旋转360度。我们可以使用下面的一个或多个命令进一步定制repeat操作。/gate/Name_Volume/ring/setFirstAngle x deg #设置第一个副本的旋转角度,默认角度为0/gate/Name_Volume/ring/setAngularSpan x deg #设置第一个副本和最后一个副本之间的旋转角度差#异,默认是360度
/gate/Name_Volume/ring/setModuloNumber M #周期结构中的volume数量???/gate/Name_Volume/ring/enableAutoRotation #启用自动旋转
/gate/Name_Volume/ring/disableAutoRotation #禁用自动旋转/gate/Name_Volume/ring/setModuloNumber 1
/gate/Name_Volume/ring/setZShift1 Z mm #沿Z轴移位,最多有8个不同的shift可选, (setZShift1 to setZShift8).???AngularSpan、FirstAngle和RepeatNumber三者组合可以定义两个相邻副本之间的旋转角度差异(AngularPitch)。

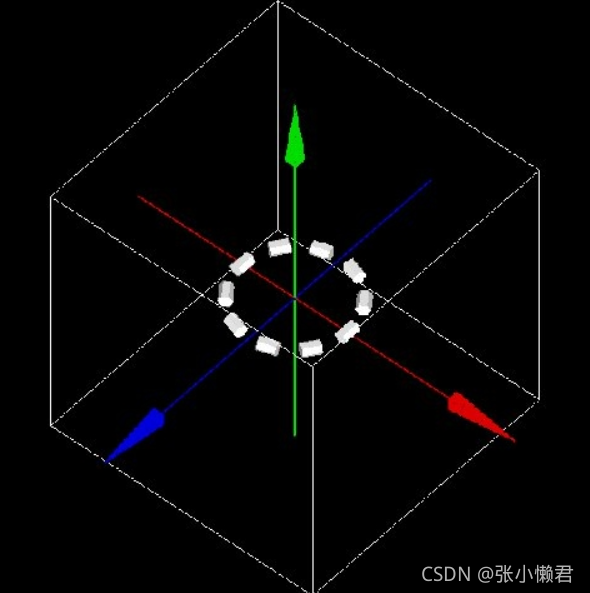
当Volume的自动旋转AutoRotation选项被启用时,Volume本身被旋转,如果禁用此选项,所有重复的volume保持相同的方向。如下图所示:


启用自动旋转选项 禁用自动旋转选项
示例1:
/gate/hole/repeaters/insert ring
/gate/hole/ring/setRepeatNumber 10
/gate/hole/ring/setPoint1 0. 1. 0. mm
/gate/hole/ring/setPoint2 0. 0. 0. mm重复结果如下图:

示例2:
/gate/rsector/repeaters/insert ring
/gate/rsector/ring/setRepeatNumber 20
/gate/rsector/ring/setModuloNumber 2
/gate/rsector/ring/setZShift1 -3500 mum
/gate/rsector/ring/setZShift2 +3500 mum
/gate/rsector/ring/enableAutoRotationrsector体积沿一个环重复20次。序列长度为2,第一和第二副本分别移动了-3500µm和3500µm。
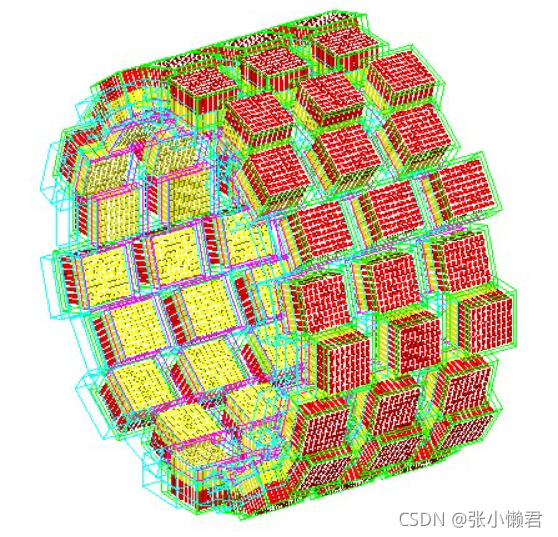
3、立方阵列重复——cubicArray
立方阵列重复适合沿一个、两个或三个轴重复一个体积。在SPECT仿真中建立准直器是很有用的。
/gate/Name_Volume/repeaters/insert cubicArray #选择立方阵列重复/gate/Name_Volume/cubicArray/setRepeatNumberX Nx
/gate/Name_Volume/cubicArray/setRepeatNumberY Ny
/gate/Name_Volume/cubicArray/setRepeatNumberZ Nz #定义volume在立方阵列中X Y Z三个方向的重复数/gate/Name_Volume/cubicArray/setRepeatVector X Y Z mm #定义沿三个方向的步长立方阵列重复有一个自动集中autocentering选项,一个volume最初位于位置P,如果autoCenter为True(默认),则重复后的volume集以P为中心。如果autoCenter为false,该组的第一个副本以P为中心。
示例:
/gate/hole/repeaters/insert cubicArray #选择立方阵列重复方式
/gate/hole/cubicArray/setRepeatNumberX 1 #X 轴方向1次
/gate/hole/cubicArray/setRepeatNumberY 5 #Y轴方向5次
/gate/hole/cubicArray/setRepeatNumberZ 2 #Z轴方向2次
/gate/hole/cubicArray/setRepeatVector 0. 5. 15. cm #沿Y轴每5cm重复1次,沿Z轴每15cm重复1次结果如下图所示:

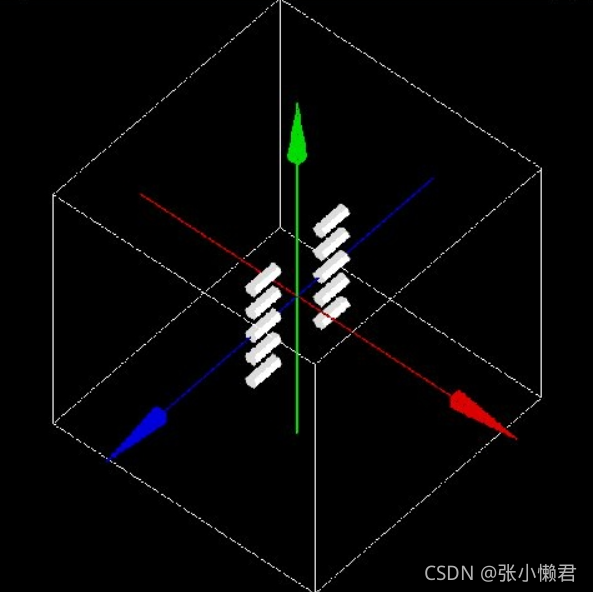
4、象限重复——quadrant
象限重复适合以类似于Derenzo分辨率幻像的三角形模式重复volume。
/gate/Name_Volume/repeaters/insert quadrant #确定使用quadrant重复
/gate/hole/quadrant/setLineNumber X #确定重复个数
/gate/hole/quadrant/setOrientation N deg #定义象限的方向(重复线的方向)
/gate/hole/quadrant/setCopySpacing xx cm #定义相邻副本之间的距离
/gate/hole/quadrant/setMaxRange xx cm #定义重复的最大范围,即副本与原始volume之间#最大距离,此命令可用于删除位于模体之外的角副本示例:
/gate/hole/repeaters/insert quadrant
/gate/hole/quadrant/setLineNumber 5
/gate/hole/quadrant/setOrientation 90 deg
/gate/hole/quadrant/setCopySpacing 6 cm
/gate/hole/quadrant/setMaxRange 30 cm应用于Name_Volume的重复方式可以通过以下方式列出
/gate/Name_Volume/repeaters/list5、球状排列重复——sphere
球面重复方式使沿着球面重复一个volume成为可能,对具有球形机架的PET扫描仪建立探测器环是有用的(e.g. SIEMENS Ecat Accel, Hi-Rez, ….)
/gate/Name_Volume/repeaters/insert sphere #选择球状重复方式/gate/Name_Volume /sphere/setRadius X cm #设置球面半径/gate/Name_Volume/sphere/setRepeatNumberWithTheta N1
/gate/Name_Volume/sphere/setRepeatNumberWithPhi N2 #不同轴面的重复次数/gate/Name_Volume/sphere/setThetaAngle x deg #设置相邻副本在横轴方向上的旋转角度差/gate/Name_Volume/sphere/setPhiAngle y deg #设置两个相邻副本在轴向上的旋转角度差示例:
/gate/block/repeaters/insert sphere
/gate/block/sphere/setRadius 25. cm
/gate/block/sphere/setRepeatNumberWithTheta 10
/gate/block/sphere/setRepeatNumberWithPhi 3
/gate/block/setThetaAngle 36 deg
/gate/block/setPhiAngle 20 deg沿着transaxial 重复10次,两个相邻块之间相差36度,在axial direction 重复3次和两个相邻块之间相差20度,半径25cm.
6、一般排列重复——genericRepeater
我们还可以根据一系列的转换(旋转和平移)来重复一个volume。
下面的宏命令将读入一个简单的文本文件:
/gate/myvolume/repeaters/insert genericRepeater
/gate/myvolume/genericRepeater/setPlacementsFilename data/myvolume.placements
/gate/myvolume/genericRepeater/useRelativeTranslation 1myvolume.placements文件的内容:
###### List of placement (translation and rotation)
###### Column 1 is time in seconds 第一列必须是时间,单位为s
###### Column 2 is rotationAngle in degree 第二列是旋转角度
###### Columns 3,4,5 are rotation axis 第3,4,5是X Y Z的旋转轴
###### Columns 6,7,8 are translation in mm 第6,7,8是平移距离,单位mm
Time s
Rotation deg
Translation mm
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 10
0 10 0 1 0 0 0 10
0 15 0 1 0 0 0 20使用“useRelativeTranslation 1”(默认)允许根据初始volume平移组合转换。
四、放置新建的volume——Placing a volume
有三种类型的放置是可用的:平移,旋转和对齐
1、平移——Translation
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/setTranslation x. 0. 0. cm #将Name_Volume沿X方向平移X cm#位置总是相对于母体中心给出的。
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/setPhiOfTranslation N deg #设置平移向量的角度(在XY平面上)
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/setThetaOfTranslation N deg #设置平移向量的角度(相对于Z轴)
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/setMagOfTranslation xx cm #要设置平移向量的大小示例:
/gate/Phantom/placement/setTranslation 1. 0. 0. cm
/gate/Phantom/placement/setMagOfTranslation 10. cm
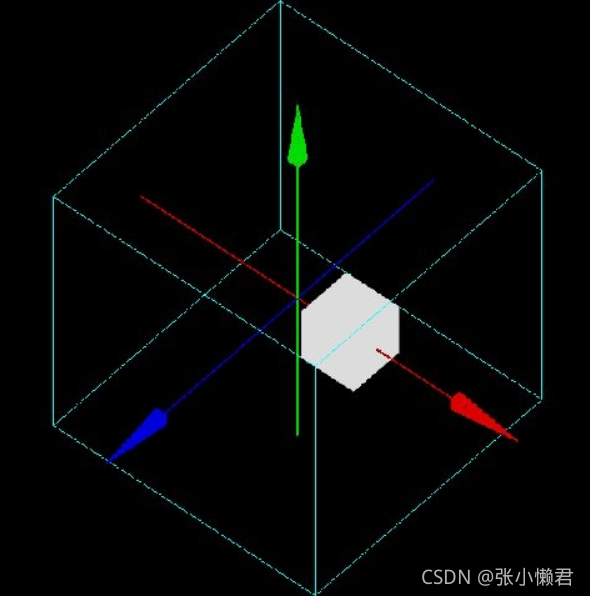
2、旋转——Rotation
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/setRotationAxis 1 0 0
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/setRotationAngle N deg #将Name_Volume绕X轴旋转N度
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/setAxis 0 1 0 默认旋转轴是Z轴。
示例:
/gate/Phantom/placement/setRotationAxis 0 1 0
/gate/Phantom/placement/setRotationAngle 90 deg #模体绕Y轴旋转90度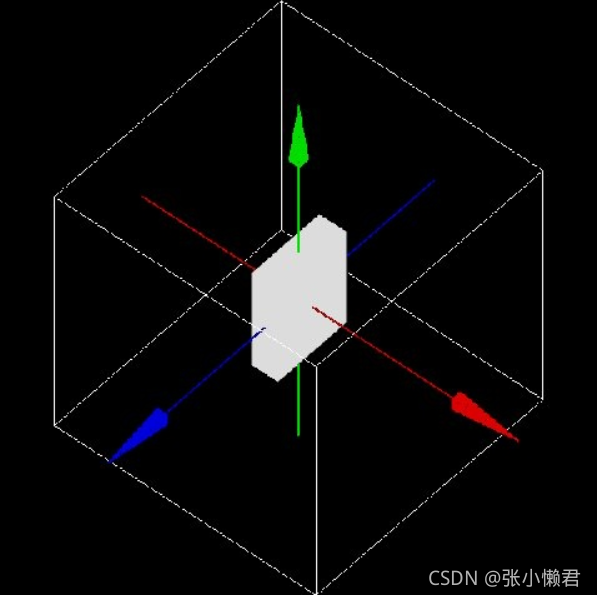
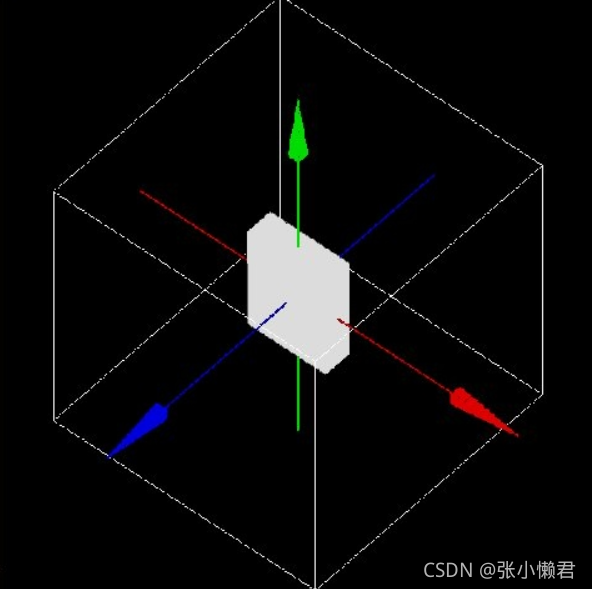
3、对齐——Alignment
对齐命令,具有对称轴(圆柱、椭圆、圆锥和六角)的volume可以与平行于轴系统的三个轴中的一个对齐。
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/alignToX #使Name_Volume沿X轴对齐,然后设置+90°围绕Y轴旋转
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/alignToY #使Name_Volume沿Y轴对齐,然后设置-90°围绕X轴旋转
/gate/Name_Volume/placement/alignToZ #使Name_Volume沿Z轴对齐,旋转参数设置为0°4、例子——楔形volume和OPET扫描仪
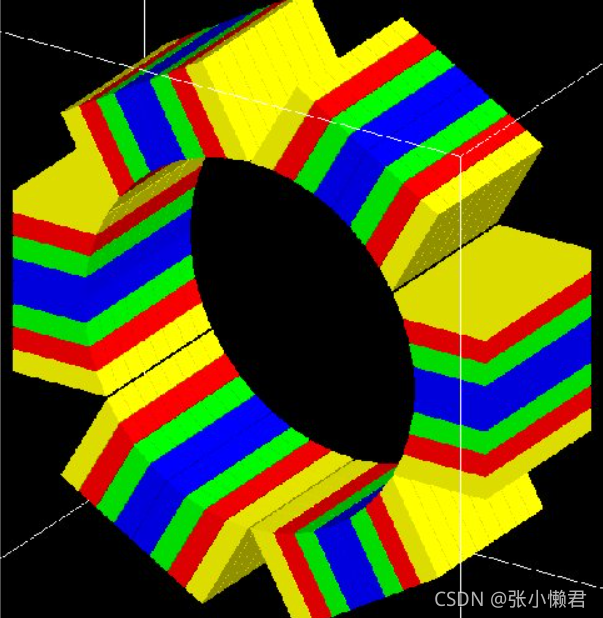
非完整程序,在这个例子中,应用了旋转放置,比如:使用的楔形模块,创建出来,斜面往往面向X轴正方向,如果要得到上图的效果,需要沿Y轴旋转楔形volume。
/gate/wedge0/placement/setRotationAxis 0 1 0
/gate/wedge0/placement/setRotationAngle 180 deg
#1、首先需要手工制作第一排晶体,创建一个足够容纳一排楔形晶体的模块:
/gate/rsector/daughters/name module
/gate/rsector/daughters/insert box
/gate/module/geometry/setXLength 10 mm
/gate/module/geometry/setYLength 17.765 mm
/gate/module/geometry/setZLength 2.162 mm
/gate/module/setMaterial Air#2、然后,将包含第一个楔形晶体的box位于模块内部:
/gate/module/daughters/name crystal0
/gate/module/daughters/insert box
/gate/crystal0/geometry/setXLength 10 mm
/gate/crystal0/geometry/setYLength 2.1620 mm
/gate/crystal0/geometry/setZLength 2.1620 mm
/gate/crystal0/placement/setTranslation 0. -7.8015 0. mm
/gate/crystal0/setMaterial Air
/gate/crystal0/vis/setColor black
/gate/crystal0/vis/setVisible false#3、最后,晶体被放置在它的box里
/gate/crystal0/daughters/name LSO0
/gate/crystal0/daughters/insert wedge
/gate/LSO0/geometry/setXLength 10 mm
/gate/LSO0/geometry/setNarrowerXLength 8.921 mm
/gate/LSO0/geometry/setYLength 2.1620 mm
/gate/LSO0/geometry/setZLength 2.1620 mm
/gate/LSO0/placement/setRotationAxis 0 1 0
/gate/LSO0/placement/setRotationAngle 180 deg
/gate/LSO0/placement/setTranslation 0.2698 0. 0. mm
/gate/LSO0/setMaterial BGO对模块内的每层晶体重复最后两步。然后沿Z轴线形重复该模块,并围绕扫描器中心环形重复6次。
五、移动新建volume——Moving a volume
GEANT4要求在模拟过程中几何结构是静态的。然而,典型的单个事件持续时间(例如粒子运输ps , 闪烁µs,或反应电子ms) 与大部分的几何体位置等的变化时间相比很短,(如几何体的运动或探测器 移动等)。因此,几何体被认为在每个时间步是静止的。在每个时间步之间,子volume集的位置和方向可以被改变,以模拟运动(如旋转或平移)。这些位移由它们的速度参数化,因此,体积位移的幅值由时间步长与位移速度的乘积得到。
给定几何组件的速度,用户需要将时间步长设置得足够短,以产生平滑的变化。
在模拟过程中,可以使用五种类型的运动来移动体积:旋转、平移、轨道、摆动和偏心旋转,如下所述。
1、平移——Translation
/gate/Name_Volume/moves/insert translation #设置移动方式是平移
/gate/Name_Volume/translation/setSpeed x 0 0 cm/s #x是平移的速度,沿x轴平移。示例:
/gate/Table/moves/insert translation
/gate/Table/translation/setSpeed 0 0 1 cm/s #Table以每秒1厘米的速度沿Z轴平移。2、旋转——Rotation
/gate/Name_Volume/moves/insert rotation #设置移动方式是旋转
/gate/Name_Volume/rotation/setSpeed N deg/s #设置旋转速度是N°每秒
/gate/Name_Volume/rotation/setAxis 0 1 0 #设置旋转轴是Y轴示例:
/gate/Phantom/moves/insert rotation
/gate/Phantom/rotation/setSpeed 1 deg/s
/gate/Phantom/rotation/setAxis 0 1 03、绕轨移动——Orbiting
在模拟过程中,可以使用轨道运动来绕任何轴旋转体积。该运动是在SPECT中建立相机头部旋转模型所必需的。
/gate/SPECThead/moves/insert orbiting #设置移动方式为绕轨方式
/gate/SPECThead/orbiting/setSpeed N. deg/s #设置旋转速度
/gate/SPECThead/orbiting/setPoint1 0 0 0 cm #设置两点上的一条直线做旋转轴
/gate/SPECThead/orbiting/setPoint2 1 0 0 cm /gate/Name_Volume/orbiting/enableAutoRotation #启用自动旋转/gate/Name_Volume/orbiting/disableAutoRotation #禁用自动旋转示例:
/gate/camera_head/moves/insert orbiting
/gate/camera_head/orbiting/setSpeed 1. deg/s
/gate/camera_head/orbiting/setPoint1 0 0 0 cm
/gate/camera_head/orbiting/setPoint2 0 0 1 cm4、摆动、摇动——Wobbling
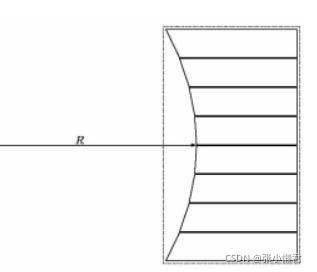
摆动运动是使volume产生摆动的平移运动,这种运动需要模拟某些PET扫描仪的行为,在采集期间摆动以增加数据的空间采样。模型中的运动定义为其中dM(t)是t时刻的平移矢量,A是最大位移矢量,f是运动频率,phi是t=0时刻的相位,t是时间。
/gate/Name_Volume/moves/insert osc-trans #设置移动方式
/gate/Name_Volume/osc-trans/setAmplitude x. 0. 0. cm #设置振荡平移的振幅矢量
/gate/Name_Volume/osc-trans/setFrequency N Hz #设置振荡平移的频率
/gate/Name_Volume/osc-trans/setPeriod N s #设置振荡平移的周期
/gate/Name_Volume/osc-trans/setPhase N deg #将振荡平移的相位设为t=0示例:
/gate/crystal/moves/insert osc-trans
/gate/crystal/osc-trans/setAmplitude 10. 0. 0. cm
/gate/crystal/osc-trans/setFrequency 50 Hz
/gate/crystal/osc-trans/setPeriod 1 s
/gate/crystal/osc-trans/setPhase 90 deg 上述设置的结果:
5、偏心旋转——Eccentric Rotation
偏心旋转运动使得volume能够偏心旋转运动。这是轨道运动的一个特殊情况。
/gate/Name_Volume/moves/insert eccent-rot #设置移动方法
/gate/Name_Volume/eccent-rot/setShiftXYZ x y z cm #把volume移动到偏心位置(X-Y-Z),围绕OZ轴旋转
/gate/Name_Volume/eccent-rot/setSpeed N deg/s #设置旋转速度示例:
/gate/crystal/moves/insert eccent-rot
/gate/crystal/eccent-rot/setShiftXYZ 5. 0. 0. cm
/gate/crystal/eccent-rot/setSpeed 10 deg/scrystal晶体volume放置在距离母体中心(10 ,0 ,0 )cm处,在模拟过程中以每秒10度的速度绕Z轴旋转。
注:这个特殊的移动与LMF定义密切相关,因为移动参数(三个方向的移动和角速度)是在.cch头文件传递的。
6、一般性移动——Generic move
/gate/myvolume/moves/insert genericMove
/gate/myvolume/genericMove/setPlacementsFilename data/myvolume.placements与Generic repeater的思想相似,placement文件包含转换(旋转,平移)和应用此转换的时间:
###### List of placement (translation and rotation) according to time
###### Column 1 is Time in s (second)
###### Column 2 is rotationAngle in degree
###### Columns 3,4,5 are rotation axis
###### Columns 6,7,8 are translation in mm
Time s
Rotation deg
Translation mm
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 100
250.7 3 0 1 0 0 10 100
492.9 4 0 1 0 0 20 100
742.9 8 0 1 0 30 0 100警告:这里给出的时间值不一定与模拟的运行相对应。实际运行是用时间片定义的(例如,请参阅 Eighth step: Starting an acquisition )。在每次新运行时,GATE会查看时间安排列表,并选择与运行的开始时间相对应的时间。这将导致某些布局不能应用(如果一次运行在布局时间之前开始,而下一次运行在下一次布局时间之后开始)。如果运行时间在列表中的最后放置时间之后,则应用最后放置时间。
7、一般性重复移动——Generic repeater move
我们可以结合一般重复方式和一般移动方式,以允许不同的重复配置。这是一个有用的例子来描述多叶准直器将单个叶片重复在不同的位置,并根据每个光束移动:
/gate/myvolume/moves/insert genericRepeaterMove
/gate/myvolume/genericRepeaterMove/setPlacementsFilename data/myvolume.placements
/gate/myvolume/genericRepeaterMove/useRelativeTranslation 1###### List of placement (translation and rotation)
###### Column 1 is rotationAngle in degree
###### Columns 2,3,4 are rotation axis
###### Columns 5,6,7 are translation in mm
Time s
NumberOfPlacements 3
Rotation deg
Translation mm
#Time # Placement 1 # Placement 2 # Placement 3
0 10 0 1 0 20 0 0 10 0 1 0 80 0 0 10 0 1 0 -60 0 0
1 20 0 1 0 20 10 0 20 0 1 0 80 10 0 20 0 1 0 -60 10 0
2 30 1 1 0 20 0 0 30 1 1 0 80 0 0 30 1 1 0 -60 0 0
4 40 0 1 1 20 0 40 40 0 1 1 80 0 40 40 0 1 1 -60 0 40NumberOfPlacements是用来表示每个动作有多少不同的重复动作。
六、更新几何体——Updating the geometry
更新几何体需要考虑几何体中的任何变化,它还会刷新显示窗口。可以使用以下命令更新几何图形:
/gate/geometry/rebuild这篇关于Gate学习2续——Defining a geometry(定义几何体)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!