本文主要是介绍图论11-欧拉回路与欧拉路径+Hierholzer算法实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1 欧拉回路的概念
- 2 欧拉回路的算法实现
- 3 Hierholzer算法详解
- 4 Hierholzer算法实现
- 4.1 修改Graph,增加API
- 4.2 Graph.java
- 4.3 联通分量类
- 4.4 欧拉回路类
1 欧拉回路的概念

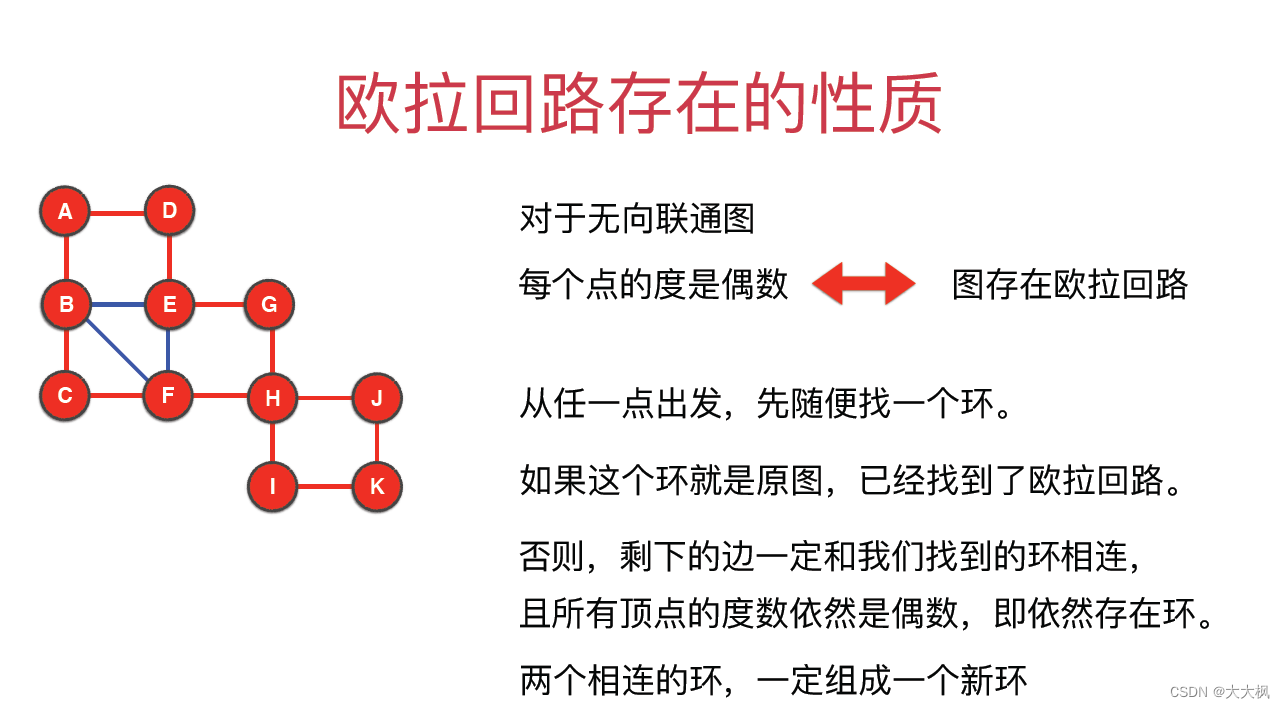
2 欧拉回路的算法实现
private boolean hasEulerLoop(){CC cc = new CC(G);if(cc.count() > 1) return false;for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)if(G.degree(v) % 2 == 1) return false;return true;
}
3 Hierholzer算法详解
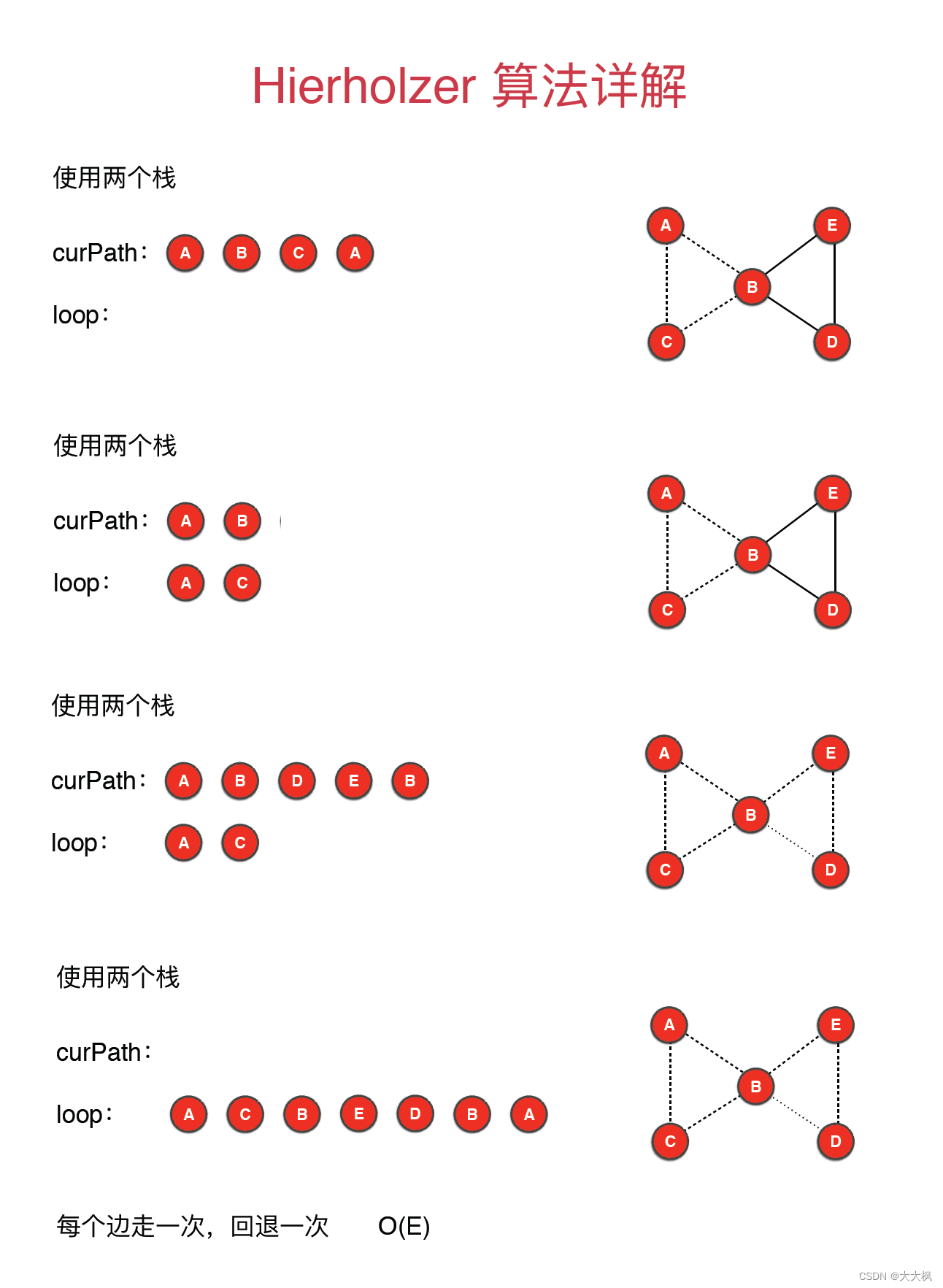
public ArrayList<Integer> result(){ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();if(!hasEulerLoop()) return res;//根据小g进行删边Graph g = (Graph)G.clone();Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();int curv = 0; //出发点stack.push(curv);while(!stack.isEmpty()){if(g.degree(curv) != 0){stack.push(curv);int w = g.adj(curv).iterator().next();g.removeEdge(curv, w);curv = w;}else{res.add(curv);curv = stack.pop();}}return res;
}
4 Hierholzer算法实现
4.1 修改Graph,增加API
//移除边
public void removeEdge(int v, int w){validateVertex(v);validateVertex(w);if(adj[v].contains(w)) E --;adj[v].remove(w);adj[w].remove(v);
}//深拷贝
@Override
public Object clone(){try{Graph cloned = (Graph) super.clone();cloned.adj = new TreeSet[V];for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){cloned.adj[v] = new TreeSet<Integer>();for(int w: adj[v])cloned.adj[v].add(w);}return cloned;}catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){e.printStackTrace();}return null;
}
4.2 Graph.java
package Chapter08_EulerLoop_And_EulerPath;import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Scanner;/// 暂时只支持无向无权图
public class Graph implements Cloneable{private int V;private int E;private TreeSet<Integer>[] adj;public Graph(String filename){File file = new File(filename);try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){V = scanner.nextInt();if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");adj = new TreeSet[V];for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++)adj[i] = new TreeSet<Integer>();E = scanner.nextInt();if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){int a = scanner.nextInt();validateVertex(a);int b = scanner.nextInt();validateVertex(b);if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");if(adj[a].contains(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");adj[a].add(b);adj[b].add(a);}}catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}}public void validateVertex(int v){if(v < 0 || v >= V)throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + "is invalid");}public int V(){return V;}public int E(){return E;}public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){validateVertex(v);validateVertex(w);return adj[v].contains(w);}public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){validateVertex(v);return adj[v];}public int degree(int v){validateVertex(v);return adj[v].size();}public void removeEdge(int v, int w){validateVertex(v);validateVertex(w);if(adj[v].contains(w)) E --;adj[v].remove(w);adj[w].remove(v);}@Overridepublic Object clone(){try{Graph cloned = (Graph) super.clone();cloned.adj = new TreeSet[V];for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){cloned.adj[v] = new TreeSet<Integer>();for(int w: adj[v])cloned.adj[v].add(w);}return cloned;}catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){e.printStackTrace();}return null;}@Overridepublic String toString(){StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){sb.append(String.format("%d : ", v));for(int w : adj[v])sb.append(String.format("%d ", w));sb.append('\n');}return sb.toString();}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");System.out.print(g);}
}
4.3 联通分量类
package Chapter08_EulerLoop_And_EulerPath;import java.util.ArrayList;public class CC {private Graph G;private int[] visited;private int cccount = 0;public CC(Graph G){this.G = G;visited = new int[G.V()];for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i ++)visited[i] = -1;for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)if(visited[v] == -1){dfs(v, cccount);cccount ++;}}private void dfs(int v, int ccid){visited[v] = ccid;for(int w: G.adj(v))if(visited[w] == -1)dfs(w, ccid);}public int count(){return cccount;}public boolean isConnected(int v, int w){G.validateVertex(v);G.validateVertex(w);return visited[v] == visited[w];}public ArrayList<Integer>[] components(){ArrayList<Integer>[] res = new ArrayList[cccount];for(int i = 0; i < cccount; i ++)res[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)res[visited[v]].add(v);return res;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");CC cc = new CC(g);System.out.println(cc.count());System.out.println(cc.isConnected(0, 6));System.out.println(cc.isConnected(5, 6));ArrayList<Integer>[] comp = cc.components();for(int ccid = 0; ccid < comp.length; ccid ++){System.out.print(ccid + " : ");for(int w: comp[ccid])System.out.print(w + " ");System.out.println();}}
}4.4 欧拉回路类
package Chapter08_EulerLoop_And_EulerPath;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;public class EulerLoop {private Graph G;public EulerLoop(Graph G){this.G = G;}private boolean hasEulerLoop(){CC cc = new CC(G);if(cc.count() > 1) return false;for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)if(G.degree(v) % 2 == 1) return false;return true;}public ArrayList<Integer> result(){ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();if(!hasEulerLoop()) return res;Graph g = (Graph)G.clone();Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();int curv = 0;stack.push(curv);while(!stack.isEmpty()){if(g.degree(curv) != 0){stack.push(curv);int w = g.adj(curv).iterator().next();g.removeEdge(curv, w);curv = w;}else{res.add(curv);curv = stack.pop();}}return res;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g8.txt");EulerLoop el = new EulerLoop(g);System.out.println(el.result());Graph g2 = new Graph("g2.txt");EulerLoop el2 = new EulerLoop(g2);System.out.println(el2.result());}
}
这篇关于图论11-欧拉回路与欧拉路径+Hierholzer算法实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






