本文主要是介绍文献阅读 - Edge-Preserving Decompositions for Multi-Scale Tone and Detail Manipulation (ACM TOG 2008),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Edge-Preserving Decompositions for Multi-Scale Tone and Detail Manipulation
Z. Farbman, R. Fattal, D. Lischinski, R Szeliski, Edge-Preserving Decompositions for Multi-Scale Tone and Detail Manipulation, ACM TOG (2008)
摘要
计算摄影技术通常将图像分层处理:分段平滑基础层、大尺度亮度变化层、小尺度细节残差层(computational photography techniques decompose an image into a piecewise smooth base layer, containing large scale variations in intensity, and a residual detail layer capturing the smaller scale details in the image)。因此,对提取细节空间尺度的控制至关重要,同时在处理多尺度细节时需避免产生视觉伪影(it is important to control the spatial scale of the extracted details, and it is often desirable to manipulate details at multiple scales, while avoiding visual artifacts)。
基于双边滤波器(bilateral filter)的细节分解技术(base-detail decomposition techniques)难以在任意尺度上提取细节(extract detail at arbitrary scales)。
本文提出一种基于加权最小二乘(WLS)框架的保边平滑算子,该算子适于图像粗尺度渐近平滑及多尺度细节提取(an alternative edge-preserving smoothing operator, based on the weighted least squares (WLS) optimization frame-work, which is particularly well suited for progressive coarsening of images and for multi-scale detail extraction)。
1 引言
计算摄影学(computational photography)通常将图像分解为基础平滑层和细节层(decompose an image into a piecewise smooth base layer and a detail layer)。
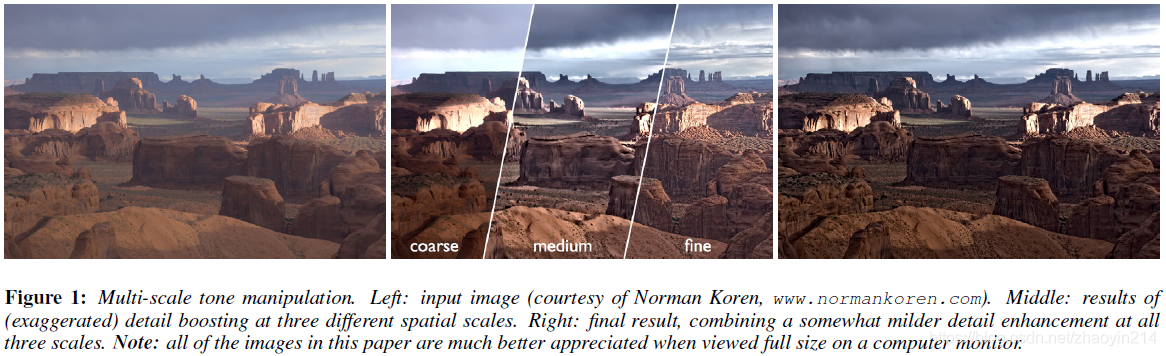
多尺度图像处理需要对图像进行多尺度分解,如拉普拉斯金字塔(Laplacian pyramid);多尺度分解也常用于色调映射(tone mapping)。然而,用线性滤波器(linear filters)构造的金字塔会在图像边缘附近产生光晕(halo artifacts near edges)。
双边滤波器(bilateral filter,BLF):适于去噪(noise removal)和提取小尺度细节(extraction of detail at a fine spatial scale),但不适于提取任意尺度细节(less appropriate for extraction of detail at arbitrary scales)。
2 背景
在计算摄影中,通常将图像分解成一个分段平滑基础层和一个(多个)细节层(In computational photography, images are often decomposed into a piecewise smooth base layer and one or more detail layers):
-
基础层用于提取大尺度亮度变化,一般通过保边平滑算子实现(the base layer captures the larger scale variations in intensity, and is typically computed by applying an edge-preserving smoothing operator to the image (sometimes applied to the logarithm of the luminance or to the lightness channel of the CIELAB color space))。
-
细节层为原始图像与基础层间的差值(或商)(the detail layer is then defined as the difference (or the quotient) between the original image and the base layer)。
-
对各层分别处理,然后合并即为最终输出(each of the resultant layers may be manipulated separately in various ways, depending on the application, and possibly recombined to yield the final result)。
例如,调整HDR图像动态范围(reduce the dynamic range of an HDR image):对基础层非线性压缩映射,然后与细节层合并(the base layer is typically subjected to a non-linear compressive mapping, and then recombined with the (possibly attenuated or boosted) detail layers);图像风格化与抽象化(image and video stylization and abstraction):抛弃细节,只对基础层处理(details are discarded, while the base layer is further processed to achieve a stylized look),抛弃不同空间尺度上的细节能使所关注区域的细节获得视觉上的加强,并且使背景更抽象(discarding details at different spatial scales makes it possible to retain more detail inside intended regions of interest, while achieving more abstraction in the background)。
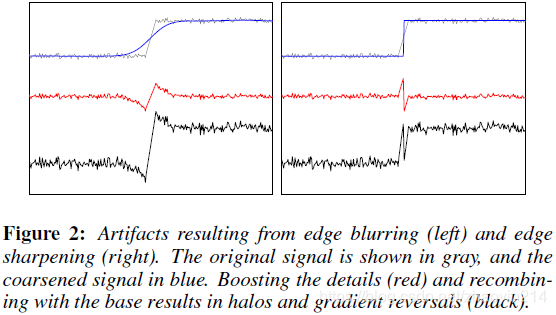
提取基础层是对图像进行粗化(computing the base layer is an image coarsening process)。对粗化图像进行边缘模糊或锐化都会导致细节层出现毛刺(both blurring and sharpening of edges in the coarsened image cause ringing in the detail layer),并在最终输出上为光晕和梯度反转(halos and gradient reversals)(Fig. 2)。因此,线性滤波和硬分割都不适于图像多尺度分解(neither linear filtering nor hard segmentation is well-suited for computing base-detail decompositions)。
双边滤波器(bilateral filter,BLF):非线性滤波器(non-linear filter),输出图像每个像素都是其邻域各像素的加权平均(a weighted mean of its neighbors),权值随空间距离和数值差异的增加而减小(the weights decreasing both with spatial distance and with difference in value)。
BLF ( g ) p = 1 k p ∑ q G σ s ( ∥ p − q ∥ ) G σ r ( ∥ g p − g q ∥ ) (1) \text{BLF} (g)_{p} = \frac{1}{k_{p}} \sum_{q} \text{G}_{\sigma_{s}} (\|p - q\|) \text{G}_{\sigma_{r}} (\|g_{p} - g_{q}\|) \tag {1} BLF(g)p=kp1q∑Gσs(∥p−q∥)Gσr(∥gp−gq∥)(1)
k p = ∑ q G σ s ( ∥ p − q ∥ ) G σ r ( ∥ g p − g q ∥ ) (2) k_{p} = \sum_{q} \text{G}_{\sigma_{s}} (\|p - q\|) \text{G}_{\sigma_{r}} (\|g_{p} - g_{q}\|) \tag {2} kp=q∑Gσs(∥p−q∥)Gσr(∥gp−gq∥)(2)
基中, g \mathbf{g} g为输入图像; p p p和 q q q表示像素的空间位置(spatial locations of pixels);核函数(kernel function) G σ s \text{G}_{\sigma_{s}} Gσs、 G σ r \text{G}_{\sigma_{r}} Gσr通常为高斯核(Gaussian), σ s \sigma_{s} σs决定空间支撑(spatial support)、 σ r \sigma_{r} σr决定值域支撑(range support)调节边缘敏感度(sensitivity to edges)。
双边滤波器性能定性分析:
-
给定像素 p p p,其原始像素值为 g p g_{p} gp(a particular pixel p p p, whose unfiltered value is g p g_{p} gp)。随 σ s \sigma_{s} σs的增大,更多的邻域像素 q q q参与像素 p p p的平滑,其中与 g p g_{p} gp相近的 g q g_{q} gq贡献最大,导致平滑后 p p p点像素值与 g p g_{p} gp差值很小(as σ s \sigma_{s} σs is increased, more and more distant pixels q q q, whose value g q g_{q} gq is close to g p g_{p} gp are being averaged together, and as a result the filtered value does not stray too far from g p g_{p} gp)。当 σ s → ∞ \sigma_{s} \rightarrow \infin σs→∞时,双边滤波器等同于值域滤波器(in the limit ( σ s → ∞ \sigma_{s} \rightarrow \infin σs→∞), the bilateral filter becomes a range filter)。因此,为实现大尺度平滑,不仅需要增大 σ s \sigma_{s} σs,
这篇关于文献阅读 - Edge-Preserving Decompositions for Multi-Scale Tone and Detail Manipulation (ACM TOG 2008)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!